Diffusion of vaporous guests into a seemingly non-porous organic crystal†
Abstract
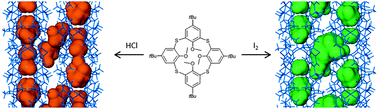
The tetragonal apohost phase of p-tert-butyltetramethoxythiacalix[4]arene absorbs hydrochloric acid and iodine. These guest molecules occupy different sites in the solid-state structure – either within the small intrinsic voids of the macrocycle or within the interstitial spaces between the host molecules. This study illustrates the dynamic deformation of the host, providing strong mechanistic insight into the diffusion of guests into this seemingly non-porous material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...