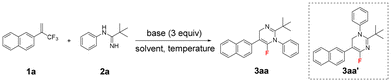Chemoselective defluorinative amination of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with amidines: synthesis of 6-fluoro-1,4-dihydropyrimidines
Han
Li
a,
Xujing
Long
a and
Chuanle
Zhu
 *abc
*abc
aSchool of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Engineering of Guangdong Province, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China. E-mail: cechlzhu@scut.edu.cn
bState Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Subtropical Agro-bioresources, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510642, China
cGuangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Technique and Equipment for Macromolecular Advanced Manufacturing, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
First published on 14th November 2025
Abstract
The chemoselective defluorinative amination of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with amidines is reported. This transition-metal-free method is operationally simple and gram-scalable, tolerates diverse useful functional groups, and gives a variety of synthetically valuable 6-fluoro-1,4-dihydropyrimidines in high yields under mild conditions.
Introduction
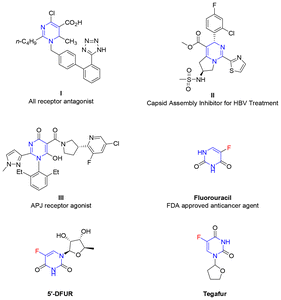
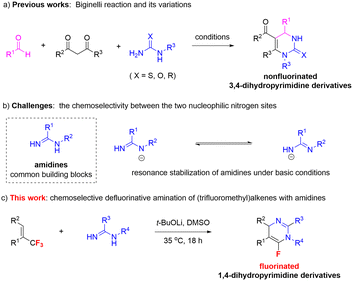
The nitrogen heterocycle dihydropyrimidine is not only a component of the most important nucleic acids, including cytosine, uracil in RNA, and thymine in DNA units, but also has proven to be a privileged skeleton of bioactive molecules in the field of drug discovery.1,2 For example, compound I is an angiotensin II (AII) receptor antagonist,2a compound II is a capsid assembly inhibitor for hepatitis B virus (HBV) treatment,2b and compound III is a potent apelin (APJ, gene symbol APLNR) receptor agonist for the potential treatment of heart failure (Fig. 1).2c Therefore, considerable efforts have been devoted to developing new and efficient methods for the synthesis of dihydropyrimidine derivatives, such as the famous Biginelli reaction and its variations.3 Generally, these protocols have led to the construction of nonfluorinated 3,4-dihydropyrimidine derivatives (Scheme 1a). Fluorine decoration of potential medicines could enhance the lipophilicity, catabolic stability, and transport rate of the parent molecules.4 The monofluoroalkene group is also recognized as a nonisomerizable and nonhydrolyzable bioisostere of the amide.5 Thus, the synthesis and application of novel fluorinated heterocycles have attracted considerable attention.6 In particular, fluorouracil, which features the dihydropyrimidine skeleton, is an FDA-approved anticancer agent (Fig. 1).2d Doxifluridine (5′-DFUR) is an important antitumor agent and a non-toxic prodrug of 5-fluorouracil.7 It is primarily used in the treatment of solid tumors such as breast cancer and gastrointestinal malignancies.8 Tegafur is a nucleoside analogue chemotherapy drug with excellent clinical efficacy. It not only exerts therapeutic effects on tumor-related disorders but is also indicated for treating gastric, rectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers.9 However, the attractive fluorinated dihydropyrimidines have still rarely been synthesized.Amidines are readily available building blocks to construct nitrogen heterocycles.10 Defluorinative amination11 represents a straightforward and efficient method to synthesize nitrogen compounds with fluorine decoration, although basic conditions are usually necessary to ensure the reaction reactivity. However, owing to the resonance stabilization of amidines under basic conditions, the defluorinative amination of amidines intrinsically suffers from issues of chemoselectivity between the two nucleophilic nitrogen sites (Scheme 1b).12 In our previous study, we reported a bond energy-enabled amine-distinguishing strategy via defluorinative amination with readily available (trifluoromethyl)alkenes.13 Inspired by this, as well as our continuous interest in the synthesis of fluorinated heterocycles via defluorinative amination of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with indoles and sulfonamides,13,14 we herein report the chemoselective defluorinative amination of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with amidines under mild conditions, delivering diverse attractive 6-fluoro-1,4-dihydropyrimidines in high yields (Scheme 1c).
Results and discussion
The initial experiment was carried out with (trifluoromethyl)alkene 1a and N-phenylpivalimidamide 2a in the presence of Li2CO3 in DMSO at 35 °C for 18 h (Table 1, entry 1). However, owing to the weak basicity and poor solubility of Li2CO3, the defluorinative amination reaction between (trifluoromethyl)alkene 1a and N-phenylpivalimidamide 2a did not occur, and the desired 6-fluoro-1,4-dihydropyrimidine 3aa was not detected. To our delight, the use of the strong base Cs2CO3 afforded product 3aa in 19% yield (entry 2). Thus, the influence of diverse inorganic and organic bases was examined (entries 3–11). Organic bases such as DBU, DABCO, and Et3N could not deliver 3aa (entries 9–11). Therefore, the different interactions between the C–F bonds and alkali–metal ions (Li+, Na+, and K+),15 as well as the different basicity and solubility of LiOH, NaOH, KOH, t-BuOLi, t-BuONa, and t-BuOK, had a significant impact on the yield of the product 3aa. The strong base t-BuOLi furnished the desired product 3aa in 70% yield (entry 6). Predictably, in the absence of a base, no reaction occurred (entry 12). Furthermore, the impact of different solvents was also investigated (entries 13–19). Strong polar aprotic solvents were beneficial to this reaction, and the solvent DMF produced 3aa in 63% yield. However, less-polar solvents such as MeCN, 1,4-dioxane, THF, toluene, DCE, and the protic solvent EtOH could not give 3aa. Increasing or decreasing the reaction temperature slightly eroded the yield of 3aa (entries 20 and 21). Additionally, performing this reaction under an N2 atmosphere did not further enhance the yield of 3aa, indicating that this reaction was not sensitive to air and moisture (entry 22). Significantly, the isomer 3aa′ was not detected under any of these conditions.| Entry | Base | Solvent | Temperature (°C) | Yield of 3aa![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) b (%) b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a The reaction conditions were: 1a (0.3 mmol, 1.5 equiv.), 2a (0.2 mmol, 1 equiv.), base (0.6 mmol, 3 equiv.) in the solvent (2 mL) for 18 h under air. b Yields were determined via1H NMR spectroscopy of the crude product with 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene as an internal standard. c Isolated yield. d Under N2 atmosphere. DCE = 1,2-dichloroethane. | ||||
| 1 | Li2CO3 | DMSO | 35 | 0 |
| 2 | Cs2CO3 | DMSO | 35 | 19 |
| 3 | LiOH | DMSO | 35 | 0 |
| 4 | NaOH | DMSO | 35 | 37 |
| 5 | KOH | DMSO | 35 | 33 |
| 6c | t-BuOLi | DMSO | 35 | 70 |
| 7 | t-BuONa | DMSO | 35 | 49 |
| 8 | t-BuOK | DMSO | 35 | 12 |
| 9 | DBU | DMSO | 35 | 0 |
| 10 | DABCO | DMSO | 35 | 0 |
| 11 | Et3N | DMSO | 35 | 0 |
| 12 | — | DMSO | 35 | 0 |
| 13 | t-BuOLi | DMF | 35 | 63 |
| 14 | t-BuOLi | MeCN | 35 | 0 |
| 15 | t-BuOLi | 1,4-Dioxane | 35 | 0 |
| 16 | t-BuOLi | THF | 35 | 0 |
| 17 | t-BuOLi | toluene | 35 | 0 |
| 18 | t-BuOLi | DCE | 35 | 0 |
| 19 | t-BuOLi | EtOH | 35 | 0 |
| 20 | t-BuOLi | DMSO | 25 | 65 |
| 21 | t-BuOLi | DMSO | 50 | 56 |
| 22d | t-BuOLi | DMSO | 35 | 69 |
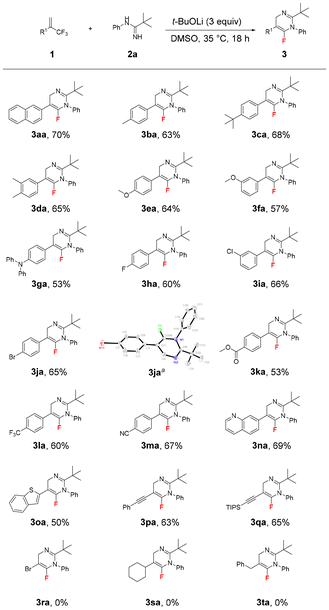
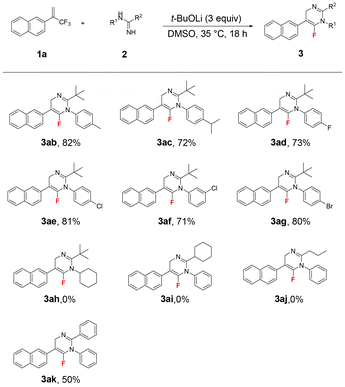
Under the optimized reaction conditions (Table 1, entry 6), we examined the scope of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes 1 in this chemoselective reaction with N-phenylpivalimidamide 2a as the reaction partner. The obtained results are shown in Scheme 2. This electron-neutral 2-naphthyl-substituted (trifluoromethyl)alkene delivered 3aa in 70% yield. 2-Aryl (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with electron-donating substituents such as methyl, tert-butyl, alkoxy, and amino groups and electron-withdrawing substituents such as fluoro, chloro, bromo, ester, trifluoromethyl, and cyano groups at different positions of the phenyl ring all delivered the desired products 3ba–3ma in 53–68% yields. Significantly, 3ja proved to be crystalline, and its structure was determined by means of X-ray crystallographic analysis.16 Despite the strong basic conditions, 2-aryl (trifluoromethyl)alkenes bearing an ester group or a cyano group smoothly delivered the desired products 3ka (53% yield) and 3ma (67% yield). Product 3la was obtained in 60% yield, clearly demonstrating the excellent chemoselectivity between the two different CF3 groups in this defluorinative amination reaction. It also indicates that the alkene moiety plays a crucial role in this reaction. Heteroaromatic quinolinyl and benzo[b]thiophen-3-yl substituted (trifluoromethyl)alkenes smoothly gave 3na (69% yield) and 3oa (50% yield). 2-Alkynyl (trifluoromethyl)alkenes also seemed to be good substrates, providing products 3pa and 3qa in high yields under the standard conditions. Interestingly, in the presence of the in situ-generated fluoride, the TIPS group of 3qa was maintained. Importantly, the high unsaturation of the alkynes in the obtained products of 3pa and 3qa provides a powerful platform for structural diversification.17 However, 2-bromo-3,3,3-trifluoroprop-1-ene, 2-cyclohexyl (trifluoromethyl)alkene and (2-(trifluoromethyl)allyl)benzene could not afford the corresponding products 3ra–3ta. These three substituents are unable to satisfy the core mechanistic prerequisites of this reaction, which was primarily attributed to steric hindrance impeding nucleophilic attack and electronic effects that attenuate reaction activity.
Furthermore, the scope of amidines was investigated (Scheme 3). As expected, N-arylpivalimidamides with electron-donating substituents such as methyl and iso-propyl groups and electron-withdrawing substituents such as fluoro, chloro, and bromo at different positions of the phenyl ring provided the corresponding products 3ab–3ag in 71–82% yields. However, the reaction between N-cyclohexylpivalimidamide 2h and (trifluoromethyl)alkene 1a did not proceed, even at 80 °C and using the different bases Cs2CO3, t-BuONa, and t-BuOK, which might be related to the poor reactivity of N-cyclohexylpivalimidamide 2h. Interestingly, when N-phenylcyclohexanecarboximidamide 2i and N-phenylbutyrimidamide 2j were used as the reactants, their reactions with (trifluoromethyl)alkene 1a proceeded smoothly under the standard reaction conditions. However, the corresponding products 3ai and 3aj decomposed completely during column chromatography on silica gel or aluminum oxide. In addition, N-phenylbenzimidamide 2k provided 3ak in 50% yield.
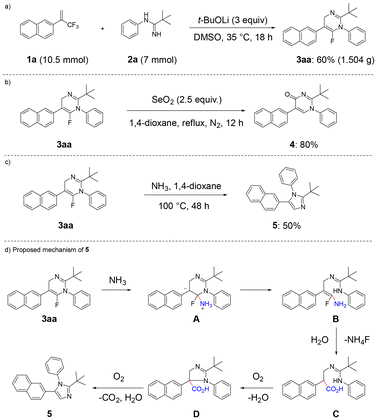
The reaction was scaled up to 7 mmol (Scheme 4a) and provided 3aa in 60% yield (1.504 g). Defluorinative oxidation of 3aa with SeO2 afforded compound 4 in 80% yield (Scheme 4b). Finally, editing the dihydropyrimidine skeleton of 3aavia treatment with NH3 delivered product 5, featuring a 1H-imidazole core building block in 50% yield (Scheme 4c). We proposed a possible pathway for the formation of 5 based on control experiments (see SI for details). Nucleophilic attack of ammonia on the fluorinated pyrimidine derivative 3aa generates intermediate A with a positively charged amino group. Subsequently, a rearrangement occurs, converting the pyrimidine ring into the amidine compound B. Then, upon hydrolysis and elimination of ammonium fluoride, the carboxylic acid derivative C is formed. This carboxylic acid undergoes oxidation in the presence of oxygen and water to yield the five-membered ring D. Finally, further oxidation, accompanied by the release of carbon dioxide and water, affords the product 5 (Scheme 4d).
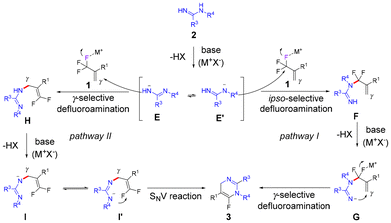
Based on the obtained results in previous literature,13,14,18 two possible pathways were proposed and are shown in Scheme 5. Deprotonation of amidine 2 with an alkali–metal base gives the nitrogen anion E, which also exists in its resonance form as the nitrogen anion E′. In pathway I,13,14 the ipso-selective defluorinative amination of (trifluoromethyl)alkene 1 with nitrogen anion E′ provides the gem-difluoroalkylated intermediate F. In the presence of an alkali–metal base, deprotonation of F delivers the nitrogen anion G, which is then converted to the product 3via the intramolecular γ-selective defluorinative amination. In pathway II,18 the nitrogen anion E undergoes γ-selective defluorinative amination with (trifluoromethyl)alkene 1 to afford intermediate H. Deprotonation of H with an alkali–metal base affords nitrogen anion I, which subsequently isomerizes to nitrogen anion I′via resonance. The following intramolecular SNV reaction of intermediate I′ gives the product 3.
Conclusions
In summary, we demonstrated the chemoselective defluorinative amination of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with amidines, affording various attractive 6-fluoro-1,4-dihydropyrimidines in high yields under mild conditions. This transition-metal-free method is operationally simple and gram-scalable, and tolerates diverse useful functional groups. The utilization of this defluorinative amination reaction in polymerization is currently ongoing in our laboratory.Experimental
General information
Chemical shifts are reported in ppm using the solvent resonance as the internal standard (CDCl3δH = 7.26 ppm, δC = 77.16 ppm). Multiplicity is indicated as follows: s (singlet), d (doublet), t (triplet), q (quartet), m (multiplet), dd (doublet of doublets), dt (doublet of triplets). Coupling constants are reported in hertz (Hz). 1H, 13C and 19F NMR data were recorded using a Bruker Avance III 500 MHz. IR spectra were obtained with an infrared spectrometer from either potassium bromide pellets or liquid films between two potassium bromide pellets. HRMS was carried out using a high-resolution mass spectrometer (Agilent 6210 ACPI/TOF MS). TLC was performed using commercially available 100–400 mesh silica gel plates (GF 254). Visualization was typically performed using UV light. X-ray structural analyses were conducted using a Bruker APEX-II CCD Diffractometer. Commercially available reagents and solvents were purchased and used without further purification. Analytical thin-layer chromatography was performed on 0.20 mm silica gel plates (GF254) using UV light as a visualizing agent. Flash column chromatography was carried out using silica gel (200–300 mesh) with the indicated solvent system. All reactions were conducted in oven-dried Schlenk tubes. All the reaction temperatures reported are oil bath temperatures. For optimization of the reaction conditions, the yield of 3aa was determined via1H NMR spectroscopy of the crude product with 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene as the internal standard. Isolated yields are presented for the newly synthesized products in this manuscript. In the substrate scope experiments, (trifluoromethyl)alkene 1r was purchased directly, and (trifluoromethyl)alkenes 1a–1q and 1s–1t were synthesized according to reports in the literature.19aN-Arylamidine 2k was purchased directly, and N-arylamidines 2a–2j were synthesized according to reports in the literature.19bGeneral procedure for defluorinative cyclization of (trifluoromethyl)alkenes with N-arylamidines
In a 25 mL oven-dried Schlenk tube equipped with a magnetic stirring bar, (trifluoromethyl)alkenes 1 (0.6 mmol, 1.5 equiv.), N-arylamidines 2 (0.4 mmol, 1 equiv.), t-BuOLi (96 mg, 1.2 mmol, 3 equiv.), and DMSO (4 mL) were vigorously stirred at 35 °C for 18 h. Stirring was then stopped, water was added (15 mL), and the mixture was extracted with diethyl ether (10 mL × 3). The combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. Further purification by flash column chromatography on silica gel (eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate) provided the product 3.Procedure for the gram-scale synthesis
In a 50 mL oven-dried round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar, 1a (2.331 g, 10.5 mmol, 1.5 equiv.), 2a (1.232 g, 7 mmol, 1 equiv.), t-BuOLi (1.680 g, 21 mmol, 3 equiv.), and DMSO (15 mL) were vigorously stirred at 35 °C for 18 h. Stirring was stopped, water was added (100 mL), and the mixture was extracted with diethyl ether (50 mL × 3). The combined organic phases were dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. Further purification by flash column chromatography on silica gel (eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate) provided the product 3aa (1.504 g, 60% yield).2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3aa)
100.2 mg, 70% yield; yellow solid; mp: 72–73 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.74–7.86 (m, 4H), 7.61–7.68 (m, 1H), 7.33–7.51 (m, 7H), 4.74 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.15 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.6 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 148.4 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 140.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.5, 132.0, 131.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.7, 129.3, 128.1, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 126.1, 125.8, 125.5 (d, J = 7.5 Hz), 125.3 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.6 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.6, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.5. IR (KBr): 2994, 1770, 1702, 1245, 1056, 816, 748.3 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H24FN2+, 359.1918; found, 359.1914.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.74–7.86 (m, 4H), 7.61–7.68 (m, 1H), 7.33–7.51 (m, 7H), 4.74 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.15 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.6 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 148.4 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 140.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.5, 132.0, 131.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.7, 129.3, 128.1, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 126.1, 125.8, 125.5 (d, J = 7.5 Hz), 125.3 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.6 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.6, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.5. IR (KBr): 2994, 1770, 1702, 1245, 1056, 816, 748.3 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H24FN2+, 359.1918; found, 359.1914.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-5-(p-tolyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ba)
81.8 mg, 63% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.31–7.44 (m, 5H), 7.25–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.09–7.17 (m, 2H), 4.57 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 1.09 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.7 (d, J = 260.0 Hz), 140.6 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 136.2, 131.3 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.6, 129.2, 129.1, 128.0, 126.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.7 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.6, 39.6, 30.4, 21.2; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.7. IR (KBr): 2955, 1704, 1285, 1219, 1153, 814, 699 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H24FN2+, 323.1918; found, 323.1914.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.31–7.44 (m, 5H), 7.25–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.09–7.17 (m, 2H), 4.57 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.33 (s, 3H), 1.09 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.7 (d, J = 260.0 Hz), 140.6 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 136.2, 131.3 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.6, 129.2, 129.1, 128.0, 126.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.7 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.6, 39.6, 30.4, 21.2; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.7. IR (KBr): 2955, 1704, 1285, 1219, 1153, 814, 699 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H24FN2+, 323.1918; found, 323.1914.
2-(tert-Butyl)-5-(4-(tert-butyl)phenyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ca)
99.1 mg, 68% yield; yellow solid; mp: 85–86 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.28–7.44 (m, 9H), 4.60 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.32 (s, 9H), 1.10 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.9 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 149.4, 147.9 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 131.2 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.5, 129.2, 128.0, 126.6 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 125.3, 92.7 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.6, 34.6, 31.4, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.3. IR (KBr): 2962, 2869, 1706, 1491, 1286, 838, 699 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H30FN2+, 365.2388; found, 365.2371.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.28–7.44 (m, 9H), 4.60 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.32 (s, 9H), 1.10 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.9 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 149.4, 147.9 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 131.2 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.5, 129.2, 128.0, 126.6 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 125.3, 92.7 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.6, 34.6, 31.4, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.3. IR (KBr): 2962, 2869, 1706, 1491, 1286, 838, 699 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H30FN2+, 365.2388; found, 365.2371.
2-(tert-Butyl)-5-(3,4-dimethylphenyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3da)
88.3 mg, 65% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.44–7.30 (m, 5H), 7.19 (s, 1H), 7.15–7.07 (m, 2H), 4.56 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 1.10 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 147.6 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 136.5, 134.9, 131.7 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.7, 129.5, 129.2, 128.2 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 128.0, 124.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.9 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.7, 39.6, 30.4, 20.0, 19.6; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.8. IR (KBr): 2957, 1706, 1491, 1259, 1152, 885, 759 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H26FN2+, 337.2075; found, 337.2074.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.44–7.30 (m, 5H), 7.19 (s, 1H), 7.15–7.07 (m, 2H), 4.56 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.25 (s, 3H), 2.24 (s, 3H), 1.10 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 147.6 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 136.5, 134.9, 131.7 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.7, 129.5, 129.2, 128.2 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 128.0, 124.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.9 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.7, 39.6, 30.4, 20.0, 19.6; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.8. IR (KBr): 2957, 1706, 1491, 1259, 1152, 885, 759 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H26FN2+, 337.2075; found, 337.2074.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ea)
87.4 mg, 64% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.28–7.43 (m, 7H), 6.83–6.92 (m, 2H), 4.55 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 1.09 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.9 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 158.1, 147.3 (d, J = 258.8 Hz), 140.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 129.5, 129.2, 128.1 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 128.0, 126.6 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 113.9, 92.5 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 55.3, 49.6, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −105.6. IR (KBr): 2957, 2930, 1707, 1249, 1034, 830, 700 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H24FN2O+, 339.1867; found, 339.1858.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.28–7.43 (m, 7H), 6.83–6.92 (m, 2H), 4.55 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 3.79 (s, 3H), 1.09 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.9 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 158.1, 147.3 (d, J = 258.8 Hz), 140.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 129.5, 129.2, 128.1 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 128.0, 126.6 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 113.9, 92.5 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 55.3, 49.6, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −105.6. IR (KBr): 2957, 2930, 1707, 1249, 1034, 830, 700 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H24FN2O+, 339.1867; found, 339.1858.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-5-(3-methoxyphenyl)-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3fa)
76.5 mg, 57% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.3 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.27 (m, 5H), 7.16–7.22 (m, 1H), 6.86–6.96 (m, 2H), 6.66–6.76 (m, 1H), 4.52 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 3.74 (s, 3H), 1.04 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 159.6, 148.2 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 135.6 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.6, 129.3, 129.3, 128.1, 119.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 112.6 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 112.2, 92.57, 92.46(d, J = 13.8 Hz), 55.3, 49.5, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.4. IR (KBr): 2956, 2833, 1704, 1365, 1151, 776, 697 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H24FN2O+, 339.1867; found, 339.1866.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.27 (m, 5H), 7.16–7.22 (m, 1H), 6.86–6.96 (m, 2H), 6.66–6.76 (m, 1H), 4.52 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 3.74 (s, 3H), 1.04 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 159.6, 148.2 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 135.6 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.6, 129.3, 129.3, 128.1, 119.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 112.6 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 112.2, 92.57, 92.46(d, J = 13.8 Hz), 55.3, 49.5, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.4. IR (KBr): 2956, 2833, 1704, 1365, 1151, 776, 697 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H24FN2O+, 339.1867; found, 339.1866.
4-(2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidin-5-yl)-N,N-diphenylaniline (3ga)
100.8 mg, 53% yield; yellow solid; mp: 92–93 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37–7.41 (m, 2H), 7.32–7.36 (m, 3H), 7.26–7.30 (m, 2H), 7.21–7.25 (m, 4H), 7.07–7.10 (m, 4H), 7.03–7.06 (m, 2H), 6.98–7.02 (m, 2H), 4.57 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.10 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 147.7, 147.7(d, J = 260.0 Hz), 146.1, 140.6 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 129.5, 129.3, 129.2, 128.3 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 128.0, 127.8 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 124.3, 123.8, 122.9, 92.46 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.2. IR (KBr): 2967, 1704, 1511, 1492, 1279, 732, 697 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C32H31FN3+, 476.2497; found, 476.2487.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37–7.41 (m, 2H), 7.32–7.36 (m, 3H), 7.26–7.30 (m, 2H), 7.21–7.25 (m, 4H), 7.07–7.10 (m, 4H), 7.03–7.06 (m, 2H), 6.98–7.02 (m, 2H), 4.57 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.10 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 147.7, 147.7(d, J = 260.0 Hz), 146.1, 140.6 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 129.5, 129.3, 129.2, 128.3 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 128.0, 127.8 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 124.3, 123.8, 122.9, 92.46 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.2. IR (KBr): 2967, 1704, 1511, 1492, 1279, 732, 697 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C32H31FN3+, 476.2497; found, 476.2487.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ha)
78.2 mg, 60% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.51–7.27 (m, 7H), 7.06–6.95 (m, 2H), 4.54 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.7 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 161.3 (dd, J = 243.8, 2.5 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 130.3 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.8 Hz), 129.6, 129.3, 128.5 (dd, J = 8.8, 6.3 Hz), 128.2, 115.3 (d, J = 21.3 Hz), 91.8 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.6, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.6, −115.5. IR (KBr): 2967, 1707, 1512, 1260, 1234, 834, 700 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C20H21F2N2+, 327.1667; found, 327.1674.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.51–7.27 (m, 7H), 7.06–6.95 (m, 2H), 4.54 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.7 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 161.3 (dd, J = 243.8, 2.5 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 140.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 130.3 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.8 Hz), 129.6, 129.3, 128.5 (dd, J = 8.8, 6.3 Hz), 128.2, 115.3 (d, J = 21.3 Hz), 91.8 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.6, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.6, −115.5. IR (KBr): 2967, 1707, 1512, 1260, 1234, 834, 700 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C20H21F2N2+, 327.1667; found, 327.1674.
2-(tert-Butyl)-5-(3-chlorophenyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ia)
90.2 mg, 66% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.46–7.29 (m, 6H), 7.26–7.09 (m, 3H), 4.53 (t, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.13–1.03 (m, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.4, 148.6 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 134.0, 136.1 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 134.3, 129.7, 129.6, 129.3, 128.3, 127.0 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 126.4, 124.9 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 91.3 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.2, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −102.5. IR (KBr): 2958, 2927, 1703, 1257, 1151, 730, 699 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C20H21ClFN2+, 343.1372; found, 343.1374.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.46–7.29 (m, 6H), 7.26–7.09 (m, 3H), 4.53 (t, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.13–1.03 (m, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.4, 148.6 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 134.0, 136.1 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 134.3, 129.7, 129.6, 129.3, 128.3, 127.0 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 126.4, 124.9 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 91.3 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.2, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −102.5. IR (KBr): 2958, 2927, 1703, 1257, 1151, 730, 699 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C20H21ClFN2+, 343.1372; found, 343.1374.
5-(4-Bromophenyl)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ja)
100.4 mg, 65% yield; yellow solid; mp: 89–90 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.30–7.46 (m, 7H), 7.20–7.26 (m, 2H), 4.54 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.5 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 148.3 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 140.0 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.2 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 131.5, 129.7, 129.3, 128.5 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 128.3, 120.0 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 91.4 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.2, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.1. IR (KBr): 2953, 2833, 1701, 1365, 1256, 763, 698 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C20H21BrFN2+, 387.0867; found, 387.0856.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.30–7.46 (m, 7H), 7.20–7.26 (m, 2H), 4.54 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.5 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 148.3 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 140.0 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.2 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 131.5, 129.7, 129.3, 128.5 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 128.3, 120.0 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 91.4 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.2, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.1. IR (KBr): 2953, 2833, 1701, 1365, 1256, 763, 698 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C20H21BrFN2+, 387.0867; found, 387.0856.
Methyl 4-(2-(tert-butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidin-5-yl)benzoate (3ka)
77.6 mg, 53% yield; yellow solid; mp: 105–106 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 7
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.91–7.99 (m, 2H), 7.35–7.44 (m, 4H), 7.27–7.34 (m, 3H), 4.55 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 1.04 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 167.0, 164.1 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 149.1 (d, J = 263.8 Hz), 139.7, 139.1(d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.6, 129.3, 128.4, 127.6, 126.5 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 91.4 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 52.1, 49.0, 39.6, 30.3; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −101.0. IR (KBr): 2954, 1721, 1699, 1279, 1151, 762, 701 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H24FN2O2+, 367.1816; found, 367.1813.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.91–7.99 (m, 2H), 7.35–7.44 (m, 4H), 7.27–7.34 (m, 3H), 4.55 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 1.04 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 167.0, 164.1 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 149.1 (d, J = 263.8 Hz), 139.7, 139.1(d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.6, 129.3, 128.4, 127.6, 126.5 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 91.4 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 52.1, 49.0, 39.6, 30.3; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −101.0. IR (KBr): 2954, 1721, 1699, 1279, 1151, 762, 701 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H24FN2O2+, 367.1816; found, 367.1813.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-5-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3la)
90.2 mg, 60% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.53–7.59 (m, 2H), 7.44–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.44–7.33 (m, 5H), 4.58 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 149.1 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 139.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 138.0 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.4, 128.5, 128.2, 126.9 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 125.3 (q, J = 3.8 Hz), 123.3, 91.1 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.1, 39.7, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −62.5, −101.8. IR (KBr): 2976, 2931, 1700, 1499, 1400, 1102, 690 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H21F4N2+, 377.1635; found, 377.1640.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.53–7.59 (m, 2H), 7.44–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.44–7.33 (m, 5H), 4.58 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 149.1 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 139.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 138.0 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.4, 128.5, 128.2, 126.9 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 125.3 (q, J = 3.8 Hz), 123.3, 91.1 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.1, 39.7, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −62.5, −101.8. IR (KBr): 2976, 2931, 1700, 1499, 1400, 1102, 690 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H21F4N2+, 377.1635; found, 377.1640.
4-(2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidin-5-yl)benzonitrile (3ma)
89.2 mg, 67% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.60–7.51 (m, 2H), 7.47–7.28 (m, 7H), 4.55 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.06 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.9 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 149.6 (d, J = 265.0 Hz), 139.3 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 139.2 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 132.1, 129.9, 129.3, 128.6, 127.1 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 119.2, 109.2 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 90.4 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 48.6, 39.6, 30.3; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −99.9. IR (KBr): 2954, 1697, 1262, 1151, 837, 722, 701 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H21FN3+, 334.1714; found, 334.1725.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.60–7.51 (m, 2H), 7.47–7.28 (m, 7H), 4.55 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.06 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.9 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 149.6 (d, J = 265.0 Hz), 139.3 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 139.2 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 132.1, 129.9, 129.3, 128.6, 127.1 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 119.2, 109.2 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 90.4 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 48.6, 39.6, 30.3; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −99.9. IR (KBr): 2954, 1697, 1262, 1151, 837, 722, 701 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C21H21FN3+, 334.1714; found, 334.1725.
7-(2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidin-5-yl)quinoline (3na)
99.2 mg, 69% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.82 (dd, J = 4.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.99–8.08 (m, 2H), 7.79–7.89 (m, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.29–7.43 (m, 6H), 4.67 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.09 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 150.1, 148.8 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 146.9, 140.0 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 135.9, 132.7 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 129.7, 129.3, 129.2, 129.1, 129.0, 128.3, 124.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 121.4, 91.7 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −102.7. IR (KBr): 2967, 2928, 1700, 1494, 1264, 837, 700 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C23H23FN3+, 360.1871; found, 360.1857.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.82 (dd, J = 4.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.99–8.08 (m, 2H), 7.79–7.89 (m, 1H), 7.66 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.29–7.43 (m, 6H), 4.67 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.09 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 150.1, 148.8 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 146.9, 140.0 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 135.9, 132.7 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 129.7, 129.3, 129.2, 129.1, 129.0, 128.3, 124.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 121.4, 91.7 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −102.7. IR (KBr): 2967, 2928, 1700, 1494, 1264, 837, 700 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C23H23FN3+, 360.1871; found, 360.1857.
5-(Benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3oa)
72.8 mg, 50% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.85 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.32–7.46 (m, 7H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 4.59 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.14 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 148.1 (d, J = 260.0 Hz), 140.5 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 140.0, 137.7, 130.0 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 129.4, 129.4, 128.1, 124.4, 124.2, 124.2, 123.3(d, J = 3.8 Hz), 122.9, 88.9 (d, J = 17.5 Hz), 50.9, 39.8, 30.5; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −99.9. IR (KBr): 2957, 2927, 1713, 1253, 1151, 760, 732 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H22FN2S+, 365.1482; found, 365.1481.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.85 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.32–7.46 (m, 7H), 7.30 (s, 1H), 4.59 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.14 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 165.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 148.1 (d, J = 260.0 Hz), 140.5 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 140.0, 137.7, 130.0 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 129.4, 129.4, 128.1, 124.4, 124.2, 124.2, 123.3(d, J = 3.8 Hz), 122.9, 88.9 (d, J = 17.5 Hz), 50.9, 39.8, 30.5; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −99.9. IR (KBr): 2957, 2927, 1713, 1253, 1151, 760, 732 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H22FN2S+, 365.1482; found, 365.1481.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-5-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3pa)
83.6 mg, 63% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.33–7.44 (m, 5H), 7.24–7.33 (m, 5H), 4.38 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.04 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.2 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 153.8 (d, J = 265.0 Hz), 139.5 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 131.4, 129.8, 129.3, 128.5, 128.4, 128.1, 123.5, 92.7 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 82.2 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 77.1, 49.6, 39.8, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −92.8. IR (KBr): 2961, 1702, 1491, 1293, 1149, 755, 691 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H22FN2+, 333.1762; found, 333.1769.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.33–7.44 (m, 5H), 7.24–7.33 (m, 5H), 4.38 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.04 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.2 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 153.8 (d, J = 265.0 Hz), 139.5 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 131.4, 129.8, 129.3, 128.5, 128.4, 128.1, 123.5, 92.7 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 82.2 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 77.1, 49.6, 39.8, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −92.8. IR (KBr): 2961, 1702, 1491, 1293, 1149, 755, 691 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C22H22FN2+, 333.1762; found, 333.1769.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-phenyl-5-((triisopropylsilyl)ethynyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3qa)
107.2 mg, 65% yield, yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37–7.45 (m, 3H), 7.29–7.34 (m, 2H), 4.33 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08–1.11 (m, 21H), 1.06 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.0, 154.5 (d, J = 265.0 Hz), 139.4, 129.9, 129.3, 128.5, 119.9, 99.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 94.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 49.6, 39.8, 30.4, 18.7, 11.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −92.7. IR (KBr): 2944, 2866, 1701, 1365, 883, 762, 676 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C25H38FN2Si+, 413.2783; found, 413.2770.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.37–7.45 (m, 3H), 7.29–7.34 (m, 2H), 4.33 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.08–1.11 (m, 21H), 1.06 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.0, 154.5 (d, J = 265.0 Hz), 139.4, 129.9, 129.3, 128.5, 119.9, 99.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 94.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 49.6, 39.8, 30.4, 18.7, 11.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −92.7. IR (KBr): 2944, 2866, 1701, 1365, 883, 762, 676 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C25H38FN2Si+, 413.2783; found, 413.2770.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1-(p-tolyl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ab)
122.0 mg, 82% yield; yellow solid; mp: 88–89 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.46–7.56 (m, 4H), 7.38 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.12–7.21 (m, 2H), 7.02 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 6.93 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 4.47 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.10 (s, 3H), 0.88 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 148.4 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 138.1, 137.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.4, 131.9, 131.9 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.6, 127.9, 127.7, 127.5, 126.1, 125.6, 125.5 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 125.1 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 91.9 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.5, 30.4, 21.1; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.9. IR (KBr): 3055, 2967, 1700, 1508, 1227, 815, 748 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C25H26FN2+, 373.2075; found, 373.2068.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.46–7.56 (m, 4H), 7.38 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.12–7.21 (m, 2H), 7.02 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 6.93 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 4.47 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.10 (s, 3H), 0.88 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 148.4 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 138.1, 137.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.4, 131.9, 131.9 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.6, 127.9, 127.7, 127.5, 126.1, 125.6, 125.5 (d, J = 6.3 Hz), 125.1 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 91.9 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.5, 30.4, 21.1; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.9. IR (KBr): 3055, 2967, 1700, 1508, 1227, 815, 748 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C25H26FN2+, 373.2075; found, 373.2068.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-(4-isopropylphenyl)-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ac)
115.2 mg, 72% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75–7.86 (m, 4H), 7.64–7.69 (m, 1H), 7.43–7.52 (m, 2H), 7.27–7.36 (m, 4H), 4.74 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.94–3.02 (m, 1H), 1.31 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 6H), 1.16 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8, 149.2, 148.4 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 137.6, 133.5, 132.0, 131.9 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.6, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 127.2, 126.2, 125.7, 125.5 (d, J = 7.5 Hz), 125.2 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.1 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 33.9, 30.4, 24.1; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.8. IR (KBr): 2961, 2870, 1700, 1507, 1265, 1150, 746 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C27H30FN2+, 401.2388; found, 401.2385.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75–7.86 (m, 4H), 7.64–7.69 (m, 1H), 7.43–7.52 (m, 2H), 7.27–7.36 (m, 4H), 4.74 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 2.94–3.02 (m, 1H), 1.31 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 6H), 1.16 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.8, 149.2, 148.4 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 137.6, 133.5, 132.0, 131.9 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.6, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 127.2, 126.2, 125.7, 125.5 (d, J = 7.5 Hz), 125.2 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 92.1 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 33.9, 30.4, 24.1; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.8. IR (KBr): 2961, 2870, 1700, 1507, 1265, 1150, 746 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C27H30FN2+, 401.2388; found, 401.2385.
2-(tert-Butyl)-6-fluoro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ad)
109.8 mg, 73% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.65–7.70 (m, 3H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.50 (dt, J = 8.7, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.28–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.20–7.27 (m, 2H), 6.99 (t, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 4.60 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.01 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 162.2 (d, J = 247.5 Hz), 148.0 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 136.0, 133.4, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 8.8 Hz), 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 126.2, 125.8, 125.4, 125.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 125.3, 116.2 (d, J = 22.5 Hz), 92.6 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.5, −112.8. IR (KBr): 2966, 2928, 1703, 1505, 1217, 838 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23F2N2+, 377.1824; found, 377.1807.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.65–7.70 (m, 3H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.50 (dt, J = 8.7, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.28–7.37 (m, 2H), 7.20–7.27 (m, 2H), 6.99 (t, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 4.60 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 1.01 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 162.2 (d, J = 247.5 Hz), 148.0 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 136.0, 133.4, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 8.8 Hz), 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 126.2, 125.8, 125.4, 125.4 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 125.3, 116.2 (d, J = 22.5 Hz), 92.6 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.4, 39.6, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.5, −112.8. IR (KBr): 2966, 2928, 1703, 1505, 1217, 838 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23F2N2+, 377.1824; found, 377.1807.
2-(tert-Butyl)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-fluoro-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ae)
127.0 mg, 81% yield; yellow solid; mp: 81–80 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75–7.81 (m, 3H), 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.60 (dt, J = 8.8, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.40–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.35–7.39 (m, 2H), 7.27–7.32 (m, 2H), 4.69 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.12 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 138.9 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 133.9, 133.4, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 130.8, 129.5, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 126.2, 125.9, 125.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 125.4, 93.2 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.5, 39.7, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.0. IR (KBr): 2967, 2870, 1677, 1490, 1092, 816 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23ClFN2+, 393.1528; found, 393.1517.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.75–7.81 (m, 3H), 7.73 (s, 1H), 7.60 (dt, J = 8.8, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.40–7.47 (m, 2H), 7.35–7.39 (m, 2H), 7.27–7.32 (m, 2H), 4.69 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.12 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 138.9 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 133.9, 133.4, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 130.8, 129.5, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 126.2, 125.9, 125.4 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 125.4, 93.2 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 49.5, 39.7, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −104.0. IR (KBr): 2967, 2870, 1677, 1490, 1092, 816 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23ClFN2+, 393.1528; found, 393.1517.
2-(tert-Butyl)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-6-fluoro-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3af)
111.2 mg, 71% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63–7.70 (m, 3H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.45–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.27–7.36 (m, 3H), 7.17–7.23 (m, 2H), 7.12–7.17 (m, 1H), 4.58 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.02 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 141.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 134.7, 133.4, 132.1, 131.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 130.2, 129.4, 128.3, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 127.5, 126.2, 125.9, 125.4, 125.4, 125.4, 93.9 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.7, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.3. IR (KBr): 2966, 2928, 1703, 1588, 1270, 746, 475 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23ClFN2+, 393.1528; found, 393.1528.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63–7.70 (m, 3H), 7.63 (s, 1H), 7.45–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.27–7.36 (m, 3H), 7.17–7.23 (m, 2H), 7.12–7.17 (m, 1H), 4.58 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.02 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 261.3 Hz), 141.7 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 134.7, 133.4, 132.1, 131.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 130.2, 129.4, 128.3, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 127.5, 126.2, 125.9, 125.4, 125.4, 125.4, 93.9 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.7, 30.4; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.3. IR (KBr): 2966, 2928, 1703, 1588, 1270, 746, 475 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23ClFN2+, 393.1528; found, 393.1528.
1-(4-Bromophenyl)-2-(tert-butyl)-6-fluoro-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ag)
139.6 mg, 80% yield; yellow solid; mp: 99–100 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63–7.69 (m, 3H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.44–7.49 (m, 1H), 7.40 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.27–7.35 (m, 2H), 7.11 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 4.56 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 0.99 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 139.5 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.4, 132.5, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 131.1, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 126.3, 125.9, 125.5 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 125.4, 122.0, 93.3 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.7, 30.5; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.9. IR (KBr): 3055, 2967, 1702, 1485, 1268, 855, 747 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23BrFN2+, 437.1023; found, 437.1010.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.63–7.69 (m, 3H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 7.44–7.49 (m, 1H), 7.40 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.27–7.35 (m, 2H), 7.11 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.4 Hz, 2H), 4.56 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 2H), 0.99 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.3 (d, J = 3.8 Hz), 147.9 (d, J = 262.5 Hz), 139.5 (d, J = 2.5 Hz), 133.4, 132.5, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 131.1, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 126.3, 125.9, 125.5 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 125.4, 122.0, 93.3 (d, J = 13.8 Hz), 49.5, 39.7, 30.5; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −103.9. IR (KBr): 3055, 2967, 1702, 1485, 1268, 855, 747 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C24H23BrFN2+, 437.1023; found, 437.1010.
6-Fluoro-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1,2-diphenyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine (3ak)
75.6 mg, 50% yield; yellow oil; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 4
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.70–7.78 (m, 4H), 7.59–7.64 (m, 1H), 7.46–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.35–7.43 (m, 2H), 7.12–7.19 (m, 7H), 7.06–7.11 (m, 1H), 4.92 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 155.4 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 150.5, 147.3 (d, J = 260.0 Hz), 138.9, 134.5 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 133.4, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.1 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 128.6 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 128.1, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 127.4, 126.3, 125.9, 125.5 (d, J = 7.5 Hz), 125.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 89.9 (d, J = 11.3 Hz), 50.5; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −106.1. IR (KBr): 3057, 1702, 1492, 1271, 912, 749, 696 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C26H20FN2+, 379.1605; found, 379.1592.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.70–7.78 (m, 4H), 7.59–7.64 (m, 1H), 7.46–7.50 (m, 2H), 7.35–7.43 (m, 2H), 7.12–7.19 (m, 7H), 7.06–7.11 (m, 1H), 4.92 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 155.4 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 150.5, 147.3 (d, J = 260.0 Hz), 138.9, 134.5 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 133.4, 132.1, 131.5 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 129.8, 129.1 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 128.6 (d, J = 1.3 Hz), 128.1, 128.0, 127.9, 127.6, 127.4, 126.3, 125.9, 125.5 (d, J = 7.5 Hz), 125.4 (d, J = 5.0 Hz), 89.9 (d, J = 11.3 Hz), 50.5; 19F NMR (376 MHz, CDCl3) δ −106.1. IR (KBr): 3057, 1702, 1492, 1271, 912, 749, 696 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd for C26H20FN2+, 379.1605; found, 379.1592.
2-(tert-Butyl)-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1-phenylpyrimidin-4(1H)-one (4)
To a 25 mL oven-dried Schlenk tube equipped with a magnetic stirring bar, 3aa (179.0 mg, 0.5 mmol, 1 equiv.), SeO2 (138.8 mg, 1.25 mmol, 2.5 equiv.) were added. The tube was evacuated and filled with N2, and 1,4-dioxane (3 mL) was added. The mixture was sealed and vigorously stirred at 100 °C for 12 h. After completion of the reaction (monitored by TLC analysis), the reaction mixture was quenched with H2O (15 mL) and extracted with EtOAc (10 mL × 3). The combined organic layers were then dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. Further purification by flash column chromatography on silica gel (eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate) provided the product 4 in 80% isolated yield.283.2 mg, 80% yield; white solid; mp: 237–238 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.37 (s, 1H), 8.33 (s, 1H), 7.78–7.89 (m, 4H), 7.44–7.58 (m, 5H), 7.32 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.22 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.4, 163.4, 149.9, 138.2, 133.4, 133.1, 130.8, 130.1, 129.5, 129.1, 128.5, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 126.3, 126.2, 125.9, 124.2, 40.7, 30.8. IR (KBr): 2969, 1679, 1510, 1351, 822, 764, 704 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd For C24H23N2O+, 355.1805; found, 355.1794.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.37 (s, 1H), 8.33 (s, 1H), 7.78–7.89 (m, 4H), 7.44–7.58 (m, 5H), 7.32 (d, J = 10.0 Hz, 2H), 1.22 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 166.4, 163.4, 149.9, 138.2, 133.4, 133.1, 130.8, 130.1, 129.5, 129.1, 128.5, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 126.3, 126.2, 125.9, 124.2, 40.7, 30.8. IR (KBr): 2969, 1679, 1510, 1351, 822, 764, 704 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd For C24H23N2O+, 355.1805; found, 355.1794.
2-(tert-Butyl)-5-(naphthalen-2-yl)-1-phenyl-1H-imidazole (5)
To a 25 mL oven-dried Schlenk tube equipped with a magnetic stirring bar, 3aa (107.4 mg, 0.3 mmol, 1 equiv.) and NH3 (0.4 M) solution in 1,4-dioxane (3 mL) was added. The mixture was vigorously stirred at 100 °C for 48 h under air. After completion of the reaction (monitored by TLC analysis), the reaction mixture was quenched with H2O (15 mL), extracted with EtOAc (10 mL × 3). The combined organic layers then were dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. Further purification by flash column chromatography on silica gel (eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate) provided the product 5 in 50% isolated yield.163.1 mg, 50% yield; white solid; mp: 222–223 °C; Rf = 0.4 (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5
1); eluted with petroleum ether/ethyl acetate = 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.67–7.73 (m, 1H), 7.57–7.62 (m, 2H), 7.46 (s, 1H), 7.41–7.31 (m, 7H), 7.25 (s, 1H), 7.18 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 1.30 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.6, 138.7, 135.7, 133.1, 132.2, 130.1, 129.1, 128.9, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 127.5, 127.1, 126.4, 126.2, 126.1, 125.9, 34.8, 30.6. IR (KBr): 2963, 2926, 1489, 1378, 1277, 814, 751 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd For C23H23N2+, 327.1856; found, 327.1843.
1; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.67–7.73 (m, 1H), 7.57–7.62 (m, 2H), 7.46 (s, 1H), 7.41–7.31 (m, 7H), 7.25 (s, 1H), 7.18 (dd, J = 8.6, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 1.30 (s, 9H); 13C{1H} NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 156.6, 138.7, 135.7, 133.1, 132.2, 130.1, 129.1, 128.9, 128.0, 127.8, 127.6, 127.5, 127.1, 126.4, 126.2, 126.1, 125.9, 34.8, 30.6. IR (KBr): 2963, 2926, 1489, 1378, 1277, 814, 751 cm−1; HRMS (ESI, m/z): [M + H]+ Calcd For C23H23N2+, 327.1856; found, 327.1843.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
Supplementary information (SI): experimental section and characterization of all products, are presented in the manuscript and SI. Copies of the 1H, 13C, and 19F spectra for all products. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5ob01554e.CCDC 2475106 (3ja) contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper.16
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22271097), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515240017), the Sinopec Seed Program, the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, South China Agricultural University (gplscau202409), and the Open Fund of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Technique and Equipment for Macromolecular Advanced Manufacturing, South China University of Technology (2024kfkt01) for financial support of our programs.References
- (a) H. Cho, Heterocycles, 2013, 87, 1441 CrossRef CAS; (b) L. H. S. Matos, F. T. Masson, L. A. Simeoni and M. Homem-de-Mello, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, 143, 1779–1789 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) A. C. Dudhe, R. Dudhe, O. Porwal and G. Katole, Mini-Rev. Med. Chem., 2022, 22, 701–728 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) K. S. Atwal, S. Z. Ahmed, J. E. Bird, C. L. Delaney, K. E. J. Dickinson, F. N. Ferrara, A. Hedberg, A. V. Miller, S. Moreland, B. C. O'Reilly, T. R. Schaeffer, T. L. Waldron and H. N. Weller, J. Med. Chem., 1992, 35, 4751–4763 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X. Li, K. Zhou, H. He, Q. Zhou, Y. Sun, L. Hou, L. Shen, X. Wang, Y. Zhou, Z. Gong, S. He, H. Jin, Z. Gu, S. Zhao, L. Zhang, C. Sun, S. Zheng, Z. Cheng, Y. Zhu, M. Zhang, J. Li and S. Chen, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8, 969–974 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) W. Meng, Z. Pi, R. Brigance, K. A. Rossi, W. A. Schumacher, J. S. Bostwick, P. S. Gargalovic, J. M. Onorato, C. E. Luk, C. N. Generaux, T. Wang, R. R. Wexler and H. J. Finlay, J. Med. Chem., 2021, 64, 18102–18113 CrossRef CAS; (d) S. Vodenkova, T. Buchler, K. Cervena, V. Veskrnova, P. Vodicka and V. Vymetalkova, Pharmacol. Ther., 2020, 206, 107447 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) C. O. Kappe, Acc. Chem. Res., 2000, 33, 879–888 CrossRef CAS; (b) L. V. Chopda and P. N. Dave, ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5, 5552–5572 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Chandravarkar, T. Aneeja and G. Anilkumar, J. Heterocycl. Chem., 2024, 61, 5–28 CrossRef CAS; (d) H. Zhang, Q. Hu, J. Liu, P. Zhang, S. Fu and S. Wu, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2022, 5, 16987–16995 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) K. Mgller, C. Faeh and F. Diederich, Science, 2007, 317, 1881–1886 CrossRef PubMed; (b) S. Purser, P. R. Moore, S. Swallow and V. Gouverneur, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 320–330 RSC; (c) W. K. Hagmann, J. Med. Chem., 2008, 51, 4359–4369 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. Landelle, M. Bergeron, M.-O. Turcotte-Savard and J.-F. Paquin, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 2867–2908 RSC; (b) H. Yanai and T. Taguchi, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2011, 5939–5954 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) V. Gouverneur and K. Müller, Fluorine in Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Chemistry: From Biophysical Aspects to Clinical Applications, ICP, Oxford, 2012 CrossRef; (b) N. A. Meanwell, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 2529–2591 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Hitt, A. Jimeno, M. Rodríguez-Pinilla, J. L. Rodríguez-Peralto, J. M. Millán, A. López-Martín, A. Brandariz, C. Peña and H. Cortés-Funes, Br. J. Cancer, 2004, 91(12), 2005–2011 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) I. Baek, B. Lee, W. Kang and K. Kwon, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 2010, 39(1–3), 175–180 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Hazama, A. Nagashima, H. Kondo, S. Yoshida, R. Shimizu, A. Araki, S. Yoshino, N. Okayama, Y. Hinoda and M. Oka, Cancer Sci., 2010, 101(3), 722–727 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) D. K. Pan, H. Zhang, T. Zhang and X. Duan, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2010, 65(12), 3762–3771 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) N. Zhang, Y. Yin, S.-J. Xu and W.-S. Chen, Molecules, 2008, 13, 1551–1569 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. J. Kajanti, S. O. Pyrhönen and A. G. Maiche, Eur. J. Cancer, 1993, 29, 863–866 CrossRef PubMed; (c) Y. Yue, Q. Zhang, X. Wang and Z. Sun, Cancer Sci., 2023, 114, 2293–2305 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. Y. Quek, T. P. Davis and A. B. Lowe, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 7326–7334 RSC; (b) T. R. M. Rauws and B. U. W. Maes, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 2463–2497 RSC; (c) J. Ren, Y. Xiong, Q. Li, B. Wang, G. Wang, B. Wang, H. Liu and X. Yang, RSC Adv., 2025, 15, 16921–16938 RSC.
- (a) H. Amii and K. Uneyama, Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 2119–2183 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) T. Ahrens, J. Kohlmann, M. Ahrens and T. Braun, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 931–972 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) A. Das and N. Chatani, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 12915–12930 CrossRef CAS; (d) T. T. Simur, T. Ye, Y. J. Yu, F. L. Zhang and Y. F. Wang, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2022, 33, 1193–1198 CrossRef CAS; (e) T. Stahl, H. F. T. Klare and M. Oestreich, ACS Catal., 2013, 3, 1578–1587 CrossRef CAS; (f) T. Fujita, K. Fuchibe and J. Ichikawa, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 390–402 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) H.-J. Ai, X. Ma, Q. Song and X.-F. Wu, Sci. China: Chem., 2021, 64, 1630–1659 CrossRef CAS; (h) L. V. Hooker and J. S. Bandar, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202308880 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) J. Ling and L. Zhou, Chem. Rec., 2024, 24, e202300332 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) A. Saha, M. Roy, S. Maji, G. Rana, D. Maiti and D. Adhikari, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 20735–20747 CrossRef PubMed; (k) Y. Aoki, H. M. O'Brien, H. Kawasaki, H. Takaya and M. Nakamura, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 461–464 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) J. Zhou, Z. Zhao and N. Shibata, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 1847 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. A. Aly and A. M. Nour-El-Din, Functionality of Amidines and Amidrazones, ARKIVOC, 2008, 2008, 153–194 Search PubMed.
- H. Zeng, H. Li, C. Li, H. Jiang and C. Zhu, Org. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 1383–1388 RSC.
- (a) H. Zeng, Y. Cai, H. Jiang and C. Zhu, Org. Lett., 2021, 23, 66–70 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Zeng, H. Li, H. Jiang and C. Zhu, Sci. China: Chem., 2022, 65, 554–562 CrossRef CAS.
- D. O'Hagan, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 308–319 RSC.
- CCDC 2475106: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination, 2025, DOI:10.5517/ccdc.csd.cc2p2k4h.
- B. M. Trost and C.-J. Li, Modern Alkyne Chemistry: Catalytic and Atom-Economic Transformations, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2015 Search PubMed.
- (a) J.-P. Bégué, D. Bonnet-Delpon and M. H. Rock, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1996, 1409–1413 RSC; (b) J. He, C. Liu, Y. Deng, Q. Zeng, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, P. Zheng and S. Cao, Org. Lett., 2022, 24, 2299–2304 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. Fuchibe, M. Takahashi and J. Ichikawa, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 12059 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. Nie, H. F. Jiang and C. L. Zhu, Chem. Commun., 2023, 59, 8238–8241 RSC; (b) Y. L. Li, C. Q. Jia, H. Li, L. H. Xu, L. H. Wang and X. L. Cui, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 4930–4933 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |