 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleMicrofluidic shape-based separation for cells and particles: recent progress and future perspective
Muhammad Soban
Khan
 a,
Raihan Hadi
Julio
a,
Raihan Hadi
Julio
 a,
Mushtaq
Ali
a,
Mushtaq
Ali
 a,
Sebastian
Sachs
a,
Sebastian
Sachs
 b,
Christian
Cierpka
b,
Christian
Cierpka
 b,
Jörg
König
b,
Jörg
König
 *b and
Jinsoo
Park
*b and
Jinsoo
Park
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, Chonnam National University, 77 Yongbong-ro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 61186, Republic of Korea. E-mail: jinsoopark@jnu.ac.kr
bInstitute of Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics, Technische Universität Ilmenau, Ehrenbergstraße 29, Ilmenau 98693, Germany. E-mail: Joerg.Koenig@tu-ilmenau.de
First published on 7th January 2026
Abstract
Shape-based separation of micro- and nanoparticles has emerged as a powerful yet underdeveloped strategy in microfluidics, offering distinct advantages over conventional size-based methods, particularly for biomedical and functional material applications. Unlike size-based separation, shape-based approaches enable discrimination between particles of identical volume but differing morphology, an essential capability for isolating pathological cells, engineered particles, or anisotropic biological entities whose function is inherently linked to shape. This review provides a comprehensive and critical overview of recent progress in both passive and active microfluidic platforms tailored for shape-selective separation. Passive systems such as deterministic lateral displacement, pinched flow fractionation, inertial, and viscoelastic microfluidics exploit hydrodynamic and flow–structure interactions, while active methods including dielectrophoresis, magnetophoresis, optophoresis, and acoustophoresis utilize external fields to modulate particle trajectories based on geometric anisotropy. For example, recent advancements demonstrate high purities often exceeding 95%, with throughput rates ranging from several microliters to milliliters per minute depending on the device configuration, achieving shape-based cell and particle sorting efficiencies above 90% under optimal conditions. For each technique, we highlight the underlying mechanisms enabling shape sensitivity, key technological advancements, and emerging trends in experimental and computational approaches. We also discuss the challenges in capturing complex particle behaviors such as rotation, alignment, and deformability and emphasize the need for integrated modeling, real-time control, and system-level optimization. Finally, we outline future directions and opportunities for advancing shape-based microfluidic separation toward scalable, high-precision applications in diagnostics, therapeutics, and materials science.
1. Introduction
Recent advancements in microfluidic device design have transformed traditional biochemical lab protocols by miniaturizing complex processes into efficient, cost-effective microchannel networks.1 These cutting-edge microdevices integrate micro- and nano-sized components, enabling precise particle manipulation and highly sensitive detection on a single, compact platform. By seamlessly combining physics, engineering, and biology, these devices have opened new frontiers in diagnostics, drug development, and personalized medicine. While different microfluidic devices serve overlapping biomedical functions, their mechanisms of operation set them apart. Passive systems, for example, rely on inherent natural forces such as diffusion and inertia to facilitate particle mixing2,3 and movement,2,4–7 whereas active systems harness external energy sources such as electric, magnetic, or acoustic fields – to exert precise control over particle trapping8–15 and sensing.16–19 The synergy between these two approaches has led to groundbreaking advancements in lab-on-a-chip technology, making biomedical research more accessible, scalable, and efficient. As microfluidics continues to evolve, it holds immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare, offering faster diagnostics, enhanced drug screening, innovative therapeutic solutions and localized drug delivery tailored to individual patient needs.Building on the advancements in microfluidic technology, one of its most transformative applications lies in cell sorting and separation, a fundamental process in biomedical research, clinical diagnostics and therapy. Cells, as the basic units of life, exist in complex, heterogeneous environments where multiple distinct cell types coexist and interact.20,21 For instance, human blood is composed primarily of red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets,22 yet it can also contain rare cell types such as circulating tumor cells (CTCs)23 and even bacteria,24 making precise isolation crucial for disease detection and treatment. Microfluidic sorting techniques have shown significant clinical promise; for example, inertial microfluidic devices have achieved up to 95% purity for WBC isolation from diluted whole blood, enhancing sample quality for downstream analysis.25,26 In cancer diagnostics, microfluidic systems for CTC sorting have demonstrated capture yields better than 90% and specificities above 97%, while maintaining cell viability, supporting their application in precision oncology.27,28 Similarly, label-free dielectrophoretic sorting has effectively separated live/dead cells with approximately 90% purity and 85% recovery rates, minimizing cell damage.29 Similarly, even unicellular organisms like Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae)30 can exhibit different phenotypes, with size variations corresponding to different cell cycle phases, further highlighting the importance of efficient cell separation techniques. Traditional separation methods, while effective, often rely on complex labeling procedures and may induce stress or damage to cells, limiting their applicability in sensitive experiments and therapeutic interventions. For example, centrifugation, which is often a mandatory step for sample preparation and bulk purification, subjects cells to high shear forces causing potential cell damage, particularly in the case of shear-sensitive cells.31 Similarly, fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) requires fluorescent labeling, expensive instrumentation, and expert knowledge.32 Microfluidic cell sorting, however, offers an innovative alternative by leveraging intrinsic and extrinsic forces to enable precise, label-free separation, on the condition that the appropriate physical principle is selected depending on the particle's properties.33 This approach not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes cell damage, reduces operational costs, and allows for high-throughput analysis.26
Expanding on the remarkable advancements in microfluidic cell sorting, shape-based separation is emerging as a powerful way for isolating particles and cells based solely on their morphology, offering unprecedented precision in biological, chemical, and industrial applications. In complex biological environments where multiple cell types of similar size/volume coexist, shape-based separation provides a critical tool for targeted isolation and analysis. Unlike conventional methods that rely on size or biochemical markers, shape-based separation exploits the distinct geometries of cells and particles to enable efficient and label-free sorting. Various pioneering studies have demonstrated potential across multiple domains, including particle confinement techniques for sorting RBCs,34 inertial focusing of differently shaped particles,35 capillary electrophoresis for nanoparticle separation,36 acoustofluidic separation of prolate and spherical shapes for Thalassiosira eccentrica,37 and the separation of micro-objects like sickle cells using magnetic fields.38 Shape-based separation is essential not only for advancing disease diagnostics and personalized medicine, but also for revolutionizing material synthesis and transforming industrial manufacturing processes.39 By integrating shape-based separation with microfluidic technologies, researchers are unlocking new possibilities in high-precision sorting, ensuring greater efficiency, scalability, and applicability across biomedical and engineering disciplines.34,40
In this paper, we aim to provide a comprehensive review of microfluidic shape-based separation, consolidating the wide array of existing methods, identifying their limitations, and exploring the latest advancements in the field through a physics-oriented perspective. By critically examining current research, we analyze how the intrinsic physical behaviors of non-spherical particles such as rotational motions (tumbling, kayaking, and log-rolling), hydrodynamic interactions, and lateral migration govern their trajectories within different microfluidic environments. Both passive techniques including deterministic lateral displacement (DLD), inertial microfluidics, viscoelastic flows, and pinched flow fractionation (PFF) and active methods such as acoustic, optical, electric, and magnetic actuation are discussed in terms of their ability to exploit these shape-dependent dynamics for effective separation. We seek to clarify the operational principles, advantages, and constraints of each technique, while highlighting innovations aimed at enhancing sorting precision and throughput. This review serves as an essential reference for advancing the use of shape-based separation in healthcare diagnostics, materials synthesis, and bioprocessing. Fig. 1 presents an overview of the various types of microfluidic platforms employed for shape-based separation of micro-organisms, illustrating the diversity of approaches guided by particle physics and microfluidic design.
This review is organized as follows. In section 2 we will discuss the dynamics of differently shaped bioparticles as it significantly differs from that of spherical particles. In section 3, platforms for passive (3.1) and active (3.2) separation will be presented in detail. Section 4 emphasizes current challenges and future applications while all findings are summarized in the conclusion in section 5.
2. Dynamics of differently shaped bioparticles
2.1 Importance of shape-specific classification
Shape-specific analysis is crucial for shape-based separation in microfluidics, as the particle shape significantly influences how objects interact with relevant forces within microchannels. Unlike size-based separation, which relies on differences in volume or mass, shape-based separation exploits variations in rotational and translational motion under relevant forces. Theoretical models, such as Jeffery's equations for particle motion in shear flow and Saffman's theory for oblate particles in shear, help explain these shape-dependent dynamics. This distinction is particularly relevant for biological applications, where the cell morphology plays a critical role in function and disease identification.40–42Fig. 2 presents various biological entities categorized as mammalian cells, viruses, bacteria, and plant cells, each exhibiting distinct shapes that critically influence their function and pathology. Mammalian cells, such as RBCs ranging from 6.5 μm to 8.5 μm in size, display morphological variations – normal biconcave disk shape,43 sickle-shaped cells (as in sickle cell anemia, leading to vascular blockages and cardiovascular disease),44 spherocytes (linked to hereditary spherocytosis),45,46 and elliptocytes (seen in elliptocytosis) – with each shape affecting deformability, circulation, and disease progression (Fig. 2(a)). Viruses ranging from 0.06 μm to 0.14 μm in size, come in shapes like icosahedral (e.g., adenovirus),47 helical (e.g., influenza),48 and complex (e.g., bacteriophages),49 with the geometry impacting infectivity, immune evasion, and separation by size and drag (Fig. 2(b)). Bacteria ranging from 0.1 μm to 10 μm in size exhibit rod (bacillus),50 spherical (coccus),51 and spiral (spirillum) shapes,52 which determine their mobility, adhesion, and resistance profiles, relevant in infection and treatment strategies (Fig. 2(c)). Plant cells ranging from 2 μm to 200 μm in size show diverse morphologies such as spherical, filamentous, or star-shaped forms, with the shape influencing light absorption, nutrient uptake, and bioreactor dynamics (Fig. 2(d)).53 Given the above information, shape-based separation is essential across these categories because biological function, pathology, and identity are often directly tied to their physical form. Cells deform and interact differently based on shape, viruses and bacteria may evade detection or clog systems without morphological sorting, and microalgae applications benefit from selective harvesting of specific species for example in process engineering. In microfluidics, extensive work has been done to exploit shape-dependent hydrodynamic behaviors (like tumbling, log-rolling, and margination) to develop precise, label-free separation techniques that are capable of handling heterogeneous biological mixtures for diagnostics, therapeutics, and environmental monitoring.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Diverse shapes of biological particles including (a) cells, (b) viruses, (c) bacteria, and (d) microalgae. The figure has been particularly generated by https://Biorender.com. | ||
Although sperm cells exhibit a distinct head–tail morphology, most microfluidic sperm separation techniques rely not on shape, but on motility-driven mechanisms such as rheotaxis, chemotaxis, and boundary-following behavior. These approaches aim to isolate morphologically normal, motile sperm with high DNA integrity for assisted reproductive technologies (ARTs). Recent developments include rheotaxis-based channels and microstructured designs that mimic the female reproductive tract, enabling passive yet selective isolation of high-quality sperm. Readers interested in this topic are referred to several comprehensive reviews and recent advances in microfluidic sperm separation and selection techniques.54–58
Viruses also exhibit a rich diversity in geometric architectures, ranging from icosahedral and spherical to filamentous and rod-like morphologies, each influencing their hydrodynamic behavior during flow-based separation. The geometric resistance model provides a framework to understand how the virus geometry affects translational and rotational drag forces under flow, which directly impact migration trajectories and trapping efficiency in microfluidic and filtration systems.59 For instance, elongated or filamentous viruses such as Ebola or influenza exhibit higher hydrodynamic drag and orientation-dependent resistance compared to spherical viruses like adenovirus, leading to distinct flow-alignment behaviors and separation responses. These biomechanical characteristics can be harnessed to optimize shape-based sorting or filtration by tuning parameters such as the flow rate, channel dimensions, and pore geometry. While most microfluidic approaches to virus manipulation focus on size, charge, or affinity-based mechanisms, incorporating shape-dependent hydrodynamic resistance can further enhance selectivity and throughput. Understanding how the virus morphology contributes to motion resistance and flow alignment not only aids in refining microfluidic separation design but also supports the broader goal of developing geometry-sensitive diagnostic and purification platforms.60,61
2.2 Rotational behavior of non-spherical particles
Various particle geometries have been investigated in the context of flow dynamics. They can be classified into two main categories: ellipsoids and spheroids. Ellipsoidal particles are further classified as prolate or oblate, depending on their aspect ratio (λ = radial diameter/equatorial diameter). A prolate ellipsoid has λ > 1, indicating an elongated shape, while an oblate ellipsoid has λ < 1, indicating a flattened form. In 1922, Jeffery theoretically described how a rigid, isolated, neutrally buoyant ellipsoidal particle behaves in a simple shear flow within a Newtonian fluid.41 He discovered that such a particle undergoes continuous rotation around the vorticity axis (perpendicular to the flow-gradient plane), tracing one of an infinite number of closed paths known as Jeffery orbits. These orbits are uniquely determined by the particle's initial orientation, aspect ratio, and the shear rate of the flow. Among the possible modes of rotation, Jeffery identified three characteristic behaviors: kayaking, where the particle's motion mimics a kayak paddle (Fig. 3ai and bi), tumbling, in which the particle's axis of revolution rotates within the flow-gradient plane (Fig. 3aii and bii), and log-rolling, where the particle spins around its symmetry axis aligned with the vorticity direction (Fig. 3aiii and biii). Importantly, Jeffery (1922) showed that the angular velocity of the particle is periodic, reaching its maximum when the particle is oriented perpendicular to the flow and its minimum when aligned with it. The rotation period T, which defines the time required to complete a full rotation, depends on both the shear rate![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) and the particle's aspect ratio λ, and is given by the expression:
and the particle's aspect ratio λ, and is given by the expression:T = (λ + 1/λ) × 2π/![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) . . | (1) |
 | ||
| Fig. 3 Rotational motion of a) prolate and b) oblate spheroids in shear or laminar microfluidic flow: i) kayaking, ii) tumbling and iii) log-rolling motions. | ||
The aspect ratio of an ellipsoidal particle significantly influences its rotational dynamics in shear flow. In the absence of fluid inertia, an increase in the aspect ratio leads to a longer rotation period, as described by eqn (1). This trend remains valid even when weak fluid inertia is present. Additionally, as the aspect ratio increases, the variation in the rotational rate increases; particles exhibit higher maximum angular velocities when oriented perpendicular to the flow and lower minimum velocities when aligned with it. The initial orientation of the particle also plays a critical role in determining its rotational trajectory. Jeffery's theory assumes that, without inertia, the initial orientation fully dictates the particle's orbit.41 However, under inertial conditions, this dependency becomes more controversial. Some studies, such as those by Yu et al.,62 suggest that the initial orientation continues to govern the trajectory at moderate shear Reynolds numbers (Res ≈ 300). The shear Reynolds number incorporates the shear rate and particle diameter as components, replacing the channel properties and flow velocity found in the conventional Reynolds number equation, wherein the rotation motion of the particles is induced by shear gradients present in the flow profile.63 In contrast, others, including Huang et al.64 and Rosén et al.,65 report that this influence is only significant within certain Re ranges, indicating that the effect of initial orientation diminishes as inertial forces become dominant.
3. Microfluidic platforms for shape-based separation
Microfluidic devices are broadly categorized into passive and active systems, each with distinct operational principles and limitations. Passive devices rely on intrinsic hydrodynamic forces, diffusion, inertial effects, and secondary flows to manipulate particles, but their performance is heavily constrained by the channel geometry and flow conditions. Passive methods offer significant advantages, including simple design, low cost, ease of fabrication, and operation without external power sources or the need for control strategies, making them highly suitable for point-of-care and portable diagnostic applications. In contrast, active devices utilize external energy sources such as electric, magnetic, optical, and acoustic fields to achieve precise particle control. However, some external forces, like magnetic fields, are limited to act on specific particle properties, such as magnetically responsive materials. In particular, acoustic driven methods overcome many of these constraints, enabling broader applicability across diverse biomedical applications, including cell sorting, targeted drug delivery, and biofabrication. While recent reviews have addressed particle manipulation under external force fields66 and design innovations in pinched flow fractionation,67 a comprehensive perspective specifically centered on shape-based separation mechanisms across both passive and active microfluidic techniques is still lacking, underscoring the need for our review. This section explores recent advancements in shape-based particle separation and manipulation in microfluidics, highlighting the underlying physics and the development of both passive and active device technologies.To facilitate an overall comparison of the major microfluidic strategies employed for shape-based separation, Table 1 summarizes the key performance indicators across both passive and active platforms. The table lists the primary governing forces, throughput range, target cell or particle type, and separation marker, as well as reported efficiency, purity, and recovery data, together with each technique's main merits and limitations. This comparative overview highlights recent technological improvements and establishes a foundation for the detailed analysis presented in the following subsections.
| PASSIVE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Principle | Throughput | Cell type | Separation marker | Merits | Demerits |
| Deterministic lateral displacement34,80,81,85–87,89,90,91,93,94 | Lateral displacement of cells by periodically arranged micropillars or other objects | 0.1–10 μL min−1 (∼103–106 cells per min) | T. cyclops from RBCs, RBC discocytes, echinocytes, stomatocytes, malaria RBCs, glutaraldehyde-treated RBCs, CTCs, skeletal stem cells, nonspherical micro-objects | Size, shape, motility, morphology, deformability, stiffness | Label-free, continuous, precise, high purity, robust | Pillar clogging, sensitivity to deformability, fabrication complexity |
| Inertial microfluidics2,25,100,103–105,108 | Focusing of cells at the equilibrium position in the channel cross-section by hydrodynamic forces, e.g. shear-gradient induced lift force, wall-induced lift force, rotation-induced force | 0.1–10 mL min−1 (∼105–107 cells per min) | Cylindrical and disk-shaped particles, sphere and ellipsoid particles, yeast cells, non-spherical capsules, chromosomes from cell debris, RBCs and WBCs, erythrocytes and leukocytes from diluted blood sample, Euglena gracilis | Size, shape, stiffness | Label-free, continuous, very high throughput, robust, simple design | Needs rather high Re, shape/stiffness interplay, channel optimization needed, scalability |
| Viscoelastic microfluidics30,110–118 | Varying focus time of cells to equilibrium positions by inertial lift forces and elastic forces | 1.7–500 μL min−1 | E. coli from RBCs, MCF-7 cancer cells from WBCs, rigid RBCs from softer RBCs, WBCs from blood, platelets from blood, sphere E. coli for rod-like E. coli, C. anabaena cells (5–1000 μm) | Size, shape, stiffness, deformability | Label-free, continuous, low to high Re, simple design, handling of irregular shaped samples | Needs viscoelastic fluid, sensitive to polymer concentration and temperature, possible bio-compatibility issues |
| Pinched flow fractionation119–121 | Separation of cells by hydrodynamic forces utilizing the position and rotation in a sudden expansion of the microchannel | ∼0.06–60 μL min−1 | Spherical from peanut-shaped, spherical and disc-shaped from blood components (RBC and platelets), clustered disc-shaped particles, ovoid and filamentous E. coli | Size, shape, deformability | Label-free, continuous, low shear stress, simple design | Limited throughput, sensitive to cell orientation, sensitive to concentration, scalability |
| ACTIVE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrophoresis32,131–134 | Migration of cells through a medium under the influence of an electric field | 0.1–100 μL min−1 | Polymer-coated spherical, rod, triangular gold and silver nanoparticles, long nanorods, nanoplates, nanoclusters, nonspherical polyelectrolyte, prolate polystyrene spheroids | Size, shape, electric charge, relative permittivity, conductivity | Label-free, scalable, integrable, applicable to many cell types | Joule heating, medium constraints, fouling, sensitive to cell orientation, semi-continuous if used as in a filter |
| Optophroresis145,146 | Migration of cells by mechanical, thermal, or electrical driving forces induced by optical energy | Single cell to small ensembles (<1 μL min−1) | Oblate ellipsoidal particles with various aspect ratios, oblate elastic capsule | Size, shape, refractive index, surface properties, elastic properties | Label-free, high spatial precision, low mechanical stress, dynamic control, integrable | Limited scalability, low throughput, heating, photothermal damage, complex optics |
| Magnetophoresis38,155–159 | Migration of cells by magnetic forces, particularly in the presence of a magnetic field gradient and/or gradient in the magnetization of the surrounding medium | 0.1–80 μL min−1 | Spherical particles, peanut-shaped particles, ellipsoidal particles, drug-treated yeast cells of different shapes | Size, shape, magnetic susceptibility, morphology | Scalable, gentle, integrable, contactless, highly controllable, continuous | Magnetic labels often required, ferrofluid complexity, cell clustering, fouling |
| Acoustophoresis37,162,172,173,176,177 | Migration of cells by acoustic forces utilizing surface acoustic waves or bulk acoustic waves | 0.1–125 μL min−1 | Prolate spheroids, polystyrene microspheres, polystyrene prolate particles, polystyrene peanut-shaped particles, T. eccentrica microalgae, RBCs, CTCs | Size, shape, acoustic contrast factor | Label-free, biocompatible, orientation control, scalable, integrable, continuous | Heating at high power, acoustic streaming can complicate trapping, sensitive to cell orientation, medium throughput |
3.1 Passive microfluidic techniques
Passive microfluidic devices play a crucial role in various applications, including fluid mixing, particle focusing, separation, sorting, and isolation, by leveraging intrinsic hydrodynamic forces and carefully designed channel geometries. Although their reliance on geometric constraints can limit flexibility and adaptability, continuous innovations in microchannel design, surface modifications, and biomimetic architectures have significantly expanded their capabilities.68 One notable advancement is the development of organ-on-a-chip systems, which integrate passive microfluidic principles to mimic physiological microenvironments, enabling more precise control over cellular behavior for biomedical applications like drug testing and disease modeling.69 Additionally, shape-based separation techniques exploit the particle geometry to efficiently sort or isolate, enhancing the performance of passive devices in fields like personalized medicine and high-throughput screening.In microcirculatory blood flow and microfluidic channels, RBCs exhibit a well-known margination phenomenon, a hydrodynamic segregation effect driven by differences in cell deformability, size, and shape. Due to their high deformability and biconcave geometry, RBCs tend to migrate away from the channel walls toward the central streamlines, while stiffer or less deformable particles such as leukocytes, platelets, or synthetic microspheres are displaced toward the periphery. This spatial redistribution occurs as a result of lift forces generated by hydrodynamic interactions between deformable cells and the channel walls, as well as shear-induced diffusion in dense suspensions. The margination behavior of RBCs plays an important role in physiological blood flow and can be exploited in microfluidic systems for passive cell separation and enrichment. For instance, by tuning the flow rate, channel geometry, and hematocrit, microfluidic designs can leverage this natural segregation to isolate stiffer cells (e.g., leukocytes or circulating tumor cells) or synthetic particles from whole blood without requiring external fields or labeling. Such margination-assisted separation relies on the interplay between inertial migration, cell deformability, and hydrodynamic lift, providing a simple, label-free mechanism that complements size- and shape-based sorting strategies.70
Several studies have analyzed this phenomenon both experimentally and computationally to understand the role of deformability and flow conditions in determining migration trajectories. For example, Kumar and Graham71 demonstrated that deformability contrast is the key determinant of margination in confined flows, while Fedosov et al.72 used numerical simulations to quantify the balance between inertial and viscous forces influencing RBC distribution. These insights have contributed to the development of microfluidic designs that exploit RBC margination to improve separation efficiency in blood-on-a-chip and diagnostic platforms.
| Dc = 1.4Gε0.48 | (2) |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) θ, with θ representing the pillar array's tilt angle. In addition to size, particle properties such as shape,80 deformability,81 and density82 can also influence separation. In a recent numerical study, Reinecke et al. (2023)83 introduced corrections to eqn (2) to account for Re up to 60 and particle density. While DLD pillars are often circular, they may also adopt alternative cross-sectional geometries. For instance, shapes such as I, L, diamond, triangular, and asymmetric pillars have been employed to tailor local flow fields, promote differential particle rotation or alignment, and enhance separation based on shape, deformability, or orientation.84
θ, with θ representing the pillar array's tilt angle. In addition to size, particle properties such as shape,80 deformability,81 and density82 can also influence separation. In a recent numerical study, Reinecke et al. (2023)83 introduced corrections to eqn (2) to account for Re up to 60 and particle density. While DLD pillars are often circular, they may also adopt alternative cross-sectional geometries. For instance, shapes such as I, L, diamond, triangular, and asymmetric pillars have been employed to tailor local flow fields, promote differential particle rotation or alignment, and enhance separation based on shape, deformability, or orientation.84
Zeming et al.85 introduced advanced pillar geometries to enhance size-based separation of non-spherical micro-objects. Their experiments showed that I-shaped pillars outperform conventional square or circular designs in separating RBCs due to their ability to induce rotation in non-spherical particles (Fig. 4a). As illustrated in Fig. 4b, I-shaped pillars feature two protrusions that initiate rotation in disc-shaped cells and a semicircular groove that accommodates this motion. This rotation shifts the basis of separation from a particle's narrowest width to its maximum rotational diameter, effectively mimicking a spherical profile, directing RBCs an oblique path to the left outlet (Fig. 4c). As a result, the design improves the separation of diverse bioparticles by accounting for their shape and orientation, not just size. Further, Ranjan et al.80 investigated into other asymmetric pillar shapes such as anvil, T-, I- and L-shaped revealing that specific features like protrusions and grooves can either induce or restrict particle rotation, thereby influencing orientation and separation behavior. While I-shaped pillars effectively separated both spherical and non-spherical particles, in addition, the L-shaped ones were found to have significant effectiveness in separating the different-shaped particles (Fig. 4d). For comparison, the separation index (Is) used for general comparison between the efficiency and separation quality between the pillar shapes showed that I-shaped and L-shaped pillars have the highest value among the other pillar shapes (I-shaped Is = 95.3 and L-shaped Is = 92.3). High Is indicates their effectiveness. These findings underscore the potential of specially designed pillars for targeted separation of diverse cell types, including spherical particles, blood cells, and rod-shaped bacteria, with experimental results confirming the superior performance of I-shaped pillars over round and square configurations in DLD systems.86
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Particle focusing in DLD: pillar shapes and non-spherical particle focusing: (a) comparing RBC separation efficiency using round, square, and I-shaped pillars. Reproduced from Zeming et al., with permission from Nature, copyright 2013.85 (b) Observing how particle rotation differs with round vs. I-shaped pillars. Reproduced from Zeming et al., with permission from Nature, copyright 2013.85 (c) Visualizing RBC trajectories through various pillar geometries. Reproduced from Zeming et al., with permission from Nature, copyright 2013.85 (d) Tracking movement of RBCs and beads in I- and L-shaped pillar arrays. Reproduced from Ranjan et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2014.80 (e) Isolating parasites from human blood. Reproduced from Holm et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2011.87 (f) Sorting based on size, shape, and deformability. Reproduced from Beech et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2012.34 | ||
Holm et al.87 utilized DLD to separate parasites from RBCs by exploiting their distinct physical characteristics. RBCs, being biconcave and highly deformable, align with the flow streamlines and follow a zigzag trajectory through the DLD array. In contrast, T. cyclops parasites are typically larger, more rigid, and often elongated with tapered bodies and a single flagellum, interacting differently with the flow field and pillar geometry. An important factor influencing this behavior is the channel height. In shallow microchannels, RBCs are confined and tend to align flat (horizontally), which enhances their ability to deform and follow streamlines. However, elongated parasites may not orient as easily due to their shape and stiffness, and thus experience more frequent interactions with the pillars, leading to displacement. Therefore, the height of the channel plays a key role by controlling the orientation and deformation of the cells, further improving the efficiency of separating parasites from deformable RBCs (Fig. 4e). The purified fraction of the parasites achieved 99.5%. As outlined above, besides size and shape, cell deformability plays a critical role in DLD-based separation, particularly for biological particles like RBCs. Unlike rigid spheres, deformable cells undergo shape changes under flow shear, reducing their effective size and making their critical diameter unpredictable by standard DLD models (Fig. 4f).34 Parameters such as the flow rate (Re number), fluid viscosity, and capillary number significantly influence this behavior.88–90 For instance, diseases like malaria increase stiffness of RBCs, making them deform less and thus more likely to be laterally displaced in the array. Krüger et al.91 demonstrated via simulations that stiffer RBCs show greater displacement, while experiments using glutaraldehyde-treated RBCs confirmed that increased stiffness leads to higher migration angles. Sharp-edged pillar designs such as triangular and diamond shapes further enhance deformability-based separation.92 This strategy has also proven effective in isolating circulating tumor cells and stem cells, with studies showing improved separation efficiency and purity under optimized flow conditions and using multi-stage DLD designs.93,94
| FIL = CilρU2d4/Dh2 | (3) |
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Manipulation of non-spherical particles in inertial microfluidic channels: (a) a schematic representation of particle focusing of different shapes within a Poiseuille flow profile. (b) Focusing behavior of ellipsoidal particles with varying aspect ratios. Reproduced from Hur et al., with permission from AIP, copyright 2011.100 (c) Various shaped microparticles aligning within a straight microchannel. Reproduced from Masaeli et al., with permission from APS, copyright 2012.103 (d) Demonstration of chromosome front and side projection areas, illustrating their alignment behavior under inertial and Dean flow in microfluidic channels. Reproduced from Feng et al., with permission from AIP, copyright 2020.105 (e) Ellipsoidal Euglena gracilis cells with different aspect ratios focused in a stepped microchannel. Reproduced from Li et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2016.107 (f) Shape-based separation of E. gracilis driven by lateral inertial focusing, where equilibrium positions depend on the particle shape and aspect ratio. Reproduced from Li et al. with permission from Nature, copyright 2017.108 | ||
For non-spherical particles, rotational dynamics add complexity to inertial focusing. Their migration depends on the rotation perpendicular to the wall given by the expression:99
| FΩ = (1/8)πd3ρΩV | (4) |
Feng et al.105 investigated chromosome separation based on size and shape in a low aspect ratio spiral channel and found that chromosomes have two equilibrium modes: aligned and focused. The aligned fibers stay at the center of the channel due to hydrodynamic interactions. Further downstream, the aligned particle is pushed and focused to the outer wall as it experiences the Dean forces to the outer wall and circulating Dean vortices at the near top and bottom edges, while the smaller particle is focused on the inner wall due to inertial lift force dominance (Fig. 5d). Spiral channel designs improved continuous separation of blood cells by enhancing the influence of inertial lift and Dean flows but still faced limitations in distinguishing overlapping shape/size distributions.25 To address these challenges, sheath-free separation in viscoelastic fluids introduced elasticity-driven focusing. This improved non-spherical particle sorting without requiring external sheath flow, although it was constrained by fluid viscosity effects.106 Stepped microchannel configurations addressed some of these challenges by coupling inertial focusing with secondary cross-sectional flows.107 Initially, ellipsoidal particles are focused on two positions in a low-aspect-ratio segment; the subsequent stepped section induces a transverse flow that merges these into a single equilibrium position.107 This design not only facilitates precise focusing of asymmetrical biological cells, such as Euglena gracilis used by Li et al.,108 but also simplifies 3D focusing in complex geometries (Fig. 5e).
Recent studies have extended inertial microfluidics to new frontiers, including subcellular bioparticles like chromosomes and paired-particle systems. These have revealed the profound influence of shape, softness, density, and inter-particle spacing on migration behavior, adding layers of complexity to separation processes. For example, while inertial sorting of Euglena gracilis achieved better control over asymmetric particles, it struggled with deformable cell types (Fig. 5f).108 Paired-particle studies further revealed how particle–particle interactions, governed by shape and deformability, significantly affect focusing accuracy.109 Altogether, these findings reinforce the need to carefully tailor the microchannel geometry, flow conditions, and fluid rheology to optimize shape-based separation performance. Future advancements will likely be possible on integrative designs that accommodate rotational dynamics, secondary flows, and elastic deformation to address the evolving demands of biomedical and analytical applications.
| FEL = Celd3∇N1 | (5) |
![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) 2 (λ and
2 (λ and ![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) are the relaxation time and average fluid shear rate, respectively). In a rectangular channel, FEL focuses the particles to 5 low shear gradients at low Reynolds number (Re ≪ 1) in the center and corner channel cross-section. The combined effect of FIL and FEL at moderate to high Reynolds numbers (Re ≫ 1) distinguished corner effects, generating a single focused particle position at the channel center, enhancing the lateral distance between a large range of particle sizes, and increasing the overall output.111 By harnessing the characteristic properties of viscoelastic fluids, such as fluid elasticity and potentially shear-thinning behavior, this method enables particle differentiation based on shape, size, and deformability, without the need for external sheath flow. Similar to the inertial microfluidics, the flow rate determines the lateral distribution of the non-spherical particles. However, a study by Langella et al.112 showed that an optimal flow rate is required to reduce the shear-thinning effect, which arises from the nature of the viscoelastic fluid. The non-spherical particles have a different lateral focusing mechanism, leaving a significant difference on particle focusing time to reach a stable position within the flow (Fig. 6a). Tai and Narsimhan113 implied in their work that a spherical particle migrates faster than a non-spherical particle. Non-spherical particles undergo rotation with a period of T, which generates a lift from the wall region, whereas spherical particles do not show this rotation. These findings suggest that a longer channel length is required for the non-spherical particle to be able to focus at the channel center optimally. Non-spherical particles are able to focus in the center of the channel, and do not show a clear particle orientation there due to weak shear gradients. These findings are supported by numerical simulation using the power-law model by Hu et al.114 They suggest that a spherical particle with an aspect ratio of one (this case is a sphere) travels faster to the channel center than an oblate one, followed by prolate particles in a shear-thinning fluid. The longest migration time occurs for prolate particles due to oscillatory migration due to rotation-induced lift force and becomes obvious as the aspect ratio increases (Fig. 6b).
are the relaxation time and average fluid shear rate, respectively). In a rectangular channel, FEL focuses the particles to 5 low shear gradients at low Reynolds number (Re ≪ 1) in the center and corner channel cross-section. The combined effect of FIL and FEL at moderate to high Reynolds numbers (Re ≫ 1) distinguished corner effects, generating a single focused particle position at the channel center, enhancing the lateral distance between a large range of particle sizes, and increasing the overall output.111 By harnessing the characteristic properties of viscoelastic fluids, such as fluid elasticity and potentially shear-thinning behavior, this method enables particle differentiation based on shape, size, and deformability, without the need for external sheath flow. Similar to the inertial microfluidics, the flow rate determines the lateral distribution of the non-spherical particles. However, a study by Langella et al.112 showed that an optimal flow rate is required to reduce the shear-thinning effect, which arises from the nature of the viscoelastic fluid. The non-spherical particles have a different lateral focusing mechanism, leaving a significant difference on particle focusing time to reach a stable position within the flow (Fig. 6a). Tai and Narsimhan113 implied in their work that a spherical particle migrates faster than a non-spherical particle. Non-spherical particles undergo rotation with a period of T, which generates a lift from the wall region, whereas spherical particles do not show this rotation. These findings suggest that a longer channel length is required for the non-spherical particle to be able to focus at the channel center optimally. Non-spherical particles are able to focus in the center of the channel, and do not show a clear particle orientation there due to weak shear gradients. These findings are supported by numerical simulation using the power-law model by Hu et al.114 They suggest that a spherical particle with an aspect ratio of one (this case is a sphere) travels faster to the channel center than an oblate one, followed by prolate particles in a shear-thinning fluid. The longest migration time occurs for prolate particles due to oscillatory migration due to rotation-induced lift force and becomes obvious as the aspect ratio increases (Fig. 6b).
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Manipulation of non-spherical particles in viscoelastic microfluidic channels: (a) typical image sequences showing a spheroid undergoing tumbling motion, aligning with the flow, and captured by superimposing successive frames. Reproduced from Langella et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2023.112 (b) Trajectories of prolate and oblate spheroids and the final rate-of-strain tensor in the (YOZ plane) cross-section of a square channel for shear-thinning, with the dotted line representing the channel diagonal. Reproduced from Hu et al. with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023.114 (c) Schematic of sheathless shape-based separation of Candida cells in a viscoelastic microfluidics. Reproduced from Nam et al. with permission from MDPI, copyright 2019.115 (d) Schematic of viscoelastic microfluidic sorting of S. cerevisiae based on shape-dependent lateral migration. Reproduced from Liu et al. with permission from ACS, copyright 2021.30 (e) Schematic top-view representation of length-based separation of cyanobacterial cells in a viscoelastic microchannel. Reproduced from Yuan et al. with permission from ACS, copyright 2021.116 (f) Design of a viscoelastic microfluidic device for shape-based separation of drug-treated E. coli. Reproduced from Zhang et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2022.117 | ||
Sheathless separation of different-shaped Candida albicans cells demonstrated the potential of viscoelastic fluids to sort elongated and spherical cells, but faced limitations in handling irregularly shaped microorganisms (Fig. 6c).115 Improved shaped-based separation and enrichment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae were achieved by optimizing viscoelastic effects using a co-flow configuration, utilizing the competing force of inertial and elastic lift force between two fluids at the fluid interface, able to achieve 81.2% and 90% purity of singlets and clusters. Further enhancements for the separation output can be made by optimizing the viscoelastic properties and channel geometries (Fig. 6d).30 Expanding the approach to filamentous microorganisms, sheathless separation of Anabaena enabled the sorting of cyanobacteria based on chain-like structures, though variations in filament length impacted sorting precision (Fig. 6e).116 This work concludes that an appropriate flow rate is required to enhance the separation performance of Anabaena. Moreover, as suggested before,30 the channel length plays a crucial role in enhancing the migration of Anabaena of different aspect ratios. Shape-based separation of drug-treated Escherichia coli demonstrated how co-flow inertial and viscoelastic microfluidics could be applied to distinguish bacteria undergoing morphological changes, though its performance was sensitive to the flow rate and bacterial density.117 Finally, bacteria separation and enrichment using viscoelastic flows in a straight microchannel further optimized the technique for high-throughput applications. However, its dependence on the fluid's properties introduced challenges in achieving consistent reproducibility across varying experimental conditions.118 This shows the difference in physical phenomena acting on the spherical and non-spherical particles, in which, by manipulating their equilibrium position, the separation between the two different particle shapes can be achieved. A parameter that needs to be emphasized for the separation operations is rotation for non-spherical particles. If the flow conditions cannot meet a rotation criterion, negative isolation occurs, and the targeted particle cannot migrate in the lateral direction. This statement is supported by the findings of Zhang et al.,117 where non-treated drug E. coli, which had a rod shape, cannot migrate from the channel wall due to flow conditions that prevent rotation of the prolate particles (Fig. 6f). Despite this, the integration of viscoelastic flows has shown significant promise in large-scale applications, yet further refinement is needed to mitigate the challenges and improve reliability. Advancements may focus on optimizing fluid compositions, designing microchannels for dynamic shape variations, enabling more efficient and reproducible shape-based separation.
 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) Schematic of the shape-based particle separation mechanism using elasto-inertial pinched flow fractionation (eiPFF). In a viscoelastic fluid, flow-induced elasto-inertial lift forces enhance the lateral displacement of sheath-focused spherical and peanut-shaped particles, enabling high-purity separation. Reproduced from Lu et al. with permission from ACS, copyright 2015.119 (b) Demonstration of red blood cell (RBC) separation from platelets. Reproduced from Nho et al. with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2017.120 (c) Depiction of tumbling behavior of two elongated, axisymmetric particles with differing aspect ratios within a PFF channel. Reproduced from de Timary et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2023.121 | ||
Building on such insights, Nho et al.120 advanced the PFF design by introducing structural modifications. They used tilted sidewalls and vertical focusing channels, termed t-PFF-v. These modifications significantly improved the alignment and separation efficiency of non-spherical particles. The t-PFF-v device successfully separated disc-shaped RBCs from spherical platelets by exploiting differences in particle orientation and interaction with the side wall. Time-lapse imaging revealed that both spherical platelets and disc-shaped RBCs are aligned along the lower corner of the pinched segment flow due to vertical focusing. Thereby, the RBCs likely adopt an orientation prescribed by the angle of the tilted sidewall. This shape-dependent positioning within the pinched segment leads to distinct lateral displacement compared to spherical platelets, enabling separation (Fig. 7b). This refinement illustrates how the control of rotational dynamics through geometric design can improve the resolution in shape-based separation. However, the device still faces challenges with flow-induced particle overlapping at higher concentrations, which can reduce separation accuracy. Nevertheless, this study emphasized how structural design and flow manipulation can be harnessed to optimize the orientation and rotational states of particles for shape-specific separation.
Fundamentally, PFF leverages the hydrodynamic forces generated by a narrowed flow path often resulting in a parabolic velocity profile to induce lateral migration based on shape, size, and deformability. Elongated or flexible particles respond differently to these forces compared to compact, rigid ones, enabling their spatial separation. De Timary et al.121 investigated the behavior of filamentous (prolate) and ovoid (spherical) E. coli cells in a low aspect ratio PFF device for varying flow rates. At low Re = 0.25, the initial particle distribution distance to the wall determines whether it will migrate away from the wall or not. The interaction between the filamentous cells, wall, and high-shear region near the wall induced pole vaulting, inclined pole vaulting, vertical bending, kayaking, sliding, kiting, and wiggling rotational behaviors, shifting their geometric centers toward the channel centerline, effectively increasing their separation distance and enabling their separation from ovoid cells, which remained near the walls due to either minimal rotation or no rotation. As flow rates increased, the rotational modes were suppressed by stronger shear forces, aligning cells vertically and reducing lateral migration, which in turn compromised separation resolution (Fig. 7c). These results highlight how the interplay between the flow-induced rotation and particle geometry governs separation efficiency in PFF. When combined with optimized flow conditions and tailored channel geometries, PFF proves to be a powerful platform for isolating complex cell populations based on intrinsic physical properties, though challenges remain in separating highly similar or dynamically deformable particles.
3.2 Active microfluidic techniques
Active microfluidic devices utilize external forces such as acoustic, electric, magnetic, and optical forces to precisely manipulate fluid flow, droplets, or particles for a wide range of applications. In comparison with passive methods, they allow adjusting control parameters so that the separation can be fine-tuned to different tasks. The effectiveness of these techniques depends on the properties of the sample and the nature of the external field. Acoustic-based transducers generate longitudinal pressure waves within the fluid that influence particles in a large range of material compositions, making them highly versatile. In contrast, electric and magnetic fields selectively act on particles with specific electrical conductivity, permittivity, or magnetic susceptibility, limiting their application to compatible materials. Optical methods offer additional control, particularly for biological and temperature-sensitive samples because of their refractive index contrast, and optical force tuning. These active microfluidic systems are typically classified based on the type of energy applied, with the choice of transducer carefully matched to the electrical, magnetic, acoustic, or optical characteristics of the target particles. As advancements continue, active microfluidics plays an increasingly vital role in areas such as biomedical diagnostics, cell sorting, and high-precision material processing, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and efficiency compared to passive methods.Since the advent of gel electrophoresis, a variety of advanced techniques have emerged to improve particle separation, including capillary electrophoresis,125 microfluidic arrays,126 and nanopore-based platforms.127 When a charged particle or macromolecule is suspended in an electrolyte solution, it attracts counter-ions to its surface, forming a structured region called the electric double layer. This consists of a tightly bound inner layer of ions, known as the Stern layer, and a more diffuse outer region of mobile ions (diffuse layer). The characteristic thickness of this double layer is described by the Debye length. Upon application of an external electric field, the particle and its associated Stern layer are pulled in the direction of the field, while the mobile ions in the diffuse layer experience a force in the opposite direction. The net motion of the particle, or its electrophoretic mobility, depends critically on the ratio between the Debye length and the particle radius a. When the Debye length is relatively large, the electric and viscous forces acting on the particle are effectively decoupled and reach a balance. Under these conditions, the particle's electrophoretic mobility μ can be approximated by the ratio of its net charge Q to the hydrodynamic drag it experiences.128
| μ = Q/6πηa | (6) |
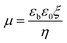 | (7) |
Hanauer et al.131 demonstrated that gel electrophoresis can be used to separate gold and silver nanoparticles based on both shape and size. By coating the nanoparticles with polyethylene glycol to impart surface charge, they enabled electrophoretic mobility through the gel. The analysis of different gel regions revealed distinct shape distributions: the initial mixture consisted of 13% rods, 34% spheres, 44% triangles, and 9% others (Fig. 8a). Rod-shaped particles exhibited the slowest mobility and became enriched to 60% in the first gel region, while triangular particles showed the fastest migration, and spheres appeared across both moderate and fast regions (Fig. 8a(i and ii)). Further analysis in Fig. 8a(iii) indicated that longer rods migrated more slowly, and larger spheres tended to move faster, though no clear trend was found for triangles, possibly due to thickness variations undetectable by TEM. A separate experiment with a 35![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 65 mixture of spheres and rods confirmed the effectiveness of gel electrophoresis in achieving shape-based separation. Xu et al.132 similarly demonstrated shape- and size-based separation of gold nanoparticles using gel electrophoresis with 100 nm pores, showing that nanospheres migrated fastest, nanorods slowest, and triangular plates exhibited intermediate mobility, consistent with Hanauer et al.'s findings. Later, Hsu et al.133 investigated how different parameters influence the electrophoretic behavior of non-spherical polyelectrolyte particles with equal volume but varying aspect ratios.
65 mixture of spheres and rods confirmed the effectiveness of gel electrophoresis in achieving shape-based separation. Xu et al.132 similarly demonstrated shape- and size-based separation of gold nanoparticles using gel electrophoresis with 100 nm pores, showing that nanospheres migrated fastest, nanorods slowest, and triangular plates exhibited intermediate mobility, consistent with Hanauer et al.'s findings. Later, Hsu et al.133 investigated how different parameters influence the electrophoretic behavior of non-spherical polyelectrolyte particles with equal volume but varying aspect ratios.
 | ||
| Fig. 8 a) Gel electrophoresis enabled shape- and size-dependent separation of gold and silver nanoparticles, as evidenced by TEM images and particle distribution analysis across different gel regions. Reproduced from Hanauer et al. with permission from ACS, copyright 2007.131 b) In the FACS-based procedure, particles are analyzed by laser-induced scattered light detected at forward and side angles, then encapsulated into droplets and sorted based on defined scattering intensity gates. Reproduced from Mage et al. with permission from Nature, copyright 2019.32 c) Mesh-based DEP filter using a porous insulating mesh between ITO electrodes to enhance trapping selectivity at low voltages with a mixed shaped sample for shape-based separation. Reproduced from Weirauch et al. with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022.134 | ||
In 2018, Mage et al.32 presented a label-free, high-throughput strategy for separating microparticles based purely on shape using a standard fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) instrument as shown in Fig. 8b. Based on elastic scattering, they developed a four-dimensional gating strategy that analyzes four independent light scattering signals to generate unique “scattering signatures” for individual and non-fluorescently labeled particles. This approach enables classification and separation of microparticles ranging from spheres to ellipsoids and discs, and spanning sizes from 0.5 to 20 μm, while eliminating errors caused by random particle orientation. The method achieves high purity and throughput (∼107 particles per hour) and is compatible with diverse materials without requiring labels or complex sample preparation. In 2022, Weirauch et al.134 presented an improved dielectrophoresis (DEP)-based separation method that uses a mesh material as an insulating structure between two indium tin oxide-coated electrodes (Fig. 8c). This mesh-based DEP filter enables enhanced selectivity by creating a structured porous environment that better distinguishes particles based on shape. The small electrode gap (0.6–0.8 mm) allows for effective electric field generation at relatively low voltages. Unlike traditional DEP setups using sponges or packed beds, the mesh structure provides more precise control over particle trapping and remobilization. Separation in this system occurs through DEP-induced trapping: when an alternating electric field is applied, particles experience dielectrophoretic forces that either attract them to high-field regions (positive DEP) or repel them (negative DEP), depending on their dielectric properties and geometry. The mesh structure amplifies these effects by generating localized field gradients, allowing particles with different shapes to interact differently with the field and become selectively trapped. Once separated, particles can be remobilized by adjusting field or flow conditions, enabling efficient, high-throughput shape-based sorting without the need for complex sample preparation.
For a prolate ellipsoidal particle with volume 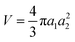 , the DEP force along axes i is
, the DEP force along axes i is
![[F with combining right harpoon above (vector)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0046_20d1.gif) DEP,pr = 2πa1a22εmRe(CMi)∇( DEP,pr = 2πa1a22εmRe(CMi)∇(![[E with combining right harpoon above (vector)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0045_20d1.gif) RMS)2 RMS)2 | (8) |
![[E with combining right harpoon above (vector)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0045_20d1.gif) RMS) is the gradient of the squared electric field (
RMS) is the gradient of the squared electric field (![[E with combining right harpoon above (vector)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0045_20d1.gif) RMS in VRMS m−1), and εm is the dielectric constant of the surrounding medium of the particle. The effective polarizability of the particle is captured by the real part of the Clausius–Mossotti factor Re(CMi), which is axis-specific and depends on the complex permittivities of the particles
RMS in VRMS m−1), and εm is the dielectric constant of the surrounding medium of the particle. The effective polarizability of the particle is captured by the real part of the Clausius–Mossotti factor Re(CMi), which is axis-specific and depends on the complex permittivities of the particles ![[small epsilon, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0de.gif) p and the medium
p and the medium ![[small epsilon, Greek, tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0de.gif) m, as well as the depolarization factor Lai.135,136
m, as well as the depolarization factor Lai.135,136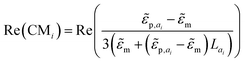 | (9) |
In a ray optics model, an incoming light ray is characterized by its direction of propagation and associated momentum. When the ray encounters a surface, momentum is transferred to that surface through reflection and refraction interactions. The resulting optical force can be described as the rate at which momentum is transferred from the photons to the surface, that is the momentum imparted per unit time.
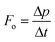 | (10) |
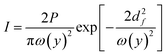 | (11) |
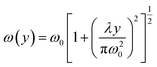 | (12) |
 | ||
| Fig. 9 a) An oblate spheroidal particle with major and minor semi-axes a and b, respectively, and the trajectory of an incident ray interacting with the particle at an inclination angle θ3 in the x–y plane (rotated about the z-axis). Reproduced from Chang et al. with permission from AIP, copyright 2014.145 b) Inclination angle evolution of an ellipsoidal particle with initial θ3 = π/2 along the streamwise direction, along with instantaneous positions and surface optical force distributions near the laser beam axis for aspect ratios: b/a = 0.9, 0.5, and 0.3. Reproduced from Chang et al. with permission from AIP, copyright 2014.145 c) Instantaneous shapes and optical force distributions of an oblate capsule with varying inclination angle θ1 and Es (surface Young's modulus) = 4000 near the laser beam axis: side views and top views, respectively, with the dotted line marking z = 0. Reproduced from Chang et al. with permission from AIP, copyright 2015.146 | ||
Despite the versatility of optophoresis, its potential for shape-based particle separation remains largely unexplored. Most existing studies focus on size, refractive index, or surface properties, with very limited attention to particle shape as a key separation parameter. Notably, there is a lack of experimental demonstrations validating shape-selective optophoretic manipulation. Early investigations, such as those by Chang et al.,145 showed that shape influences optical trapping efficiency, as elongated particles experience different optical forces compared to spherical ones (Fig. 9b). However, this method was limited to well-defined ellipsoidal particles and struggled with biological samples that exhibit irregular morphologies. With this, Chang et al.146 introduced a more advanced optical trapping configuration, allowing the selective separation of soft, shape-dependent capsules under uniform flow (Fig. 9c). While this improved the handling of deformable particles, it still faced challenges in efficiently separating highly complex or heterogeneous shapes. Both of these studies relied on optical radiation pressure and gradient forces, where particle shape affects light scattering and absorption, leading to distinct migration behaviors. Despite these advances, optical shape-based separation remains largely unexplored compared to acoustic, inertial, or viscoelastic methods, mainly due to limitations in scalability and throughput. Improvements could focus on integrating tunable optical landscapes to provide more precise control over particle manipulation, as well as combining optical forces with fluidic mechanisms for enhanced separation efficiency. By addressing these challenges, optical shape-based separation has the potential to expand its application across a wider range of biological and synthetic particles, offering a non-invasive and highly versatile sorting method.
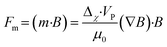 | (13) |
| Tm = m × B | (14) |
In conventional magnetic separation, non-uniform magnetic fields generate magnetic forces that drive particle movement, a process referred to as magnetophoresis. When Δχ > 0, particles are attracted toward the magnetic field source, this is known as positive magnetophoresis. Conversely, when Δχ < 0, particles are repelled from the magnetic field source, referred to as negative magnetophoresis. Typically, positive magnetophoresis is used to manipulate paramagnetic or ferromagnetic particles, or magnetically labeled cells, in a diamagnetic medium like water.149–151 In contrast, negative magnetophoresis is employed to separate diamagnetic particles or cells within a magnetized medium such as ferrofluids.152–154 Most studies have focused on size-based separation,147 where particles experience different forces based on size (eqn (7)). Shape-based separation in microchannels using magnetic fields is more recent and achieved mainly by (1) shape-dependent forces in non-uniform magnetic fields or (2) shape-dependent torques in uniform fields without net magnetic force.
Kose et al.38 demonstrated separation of sickle cells from healthy red blood cells using a periodic, non-uniform magnetic field in a ferrofluid-filled microchannel. Electrodes beneath the channel generated time-varying magnetic forces and torques, pushing cells upward by negative magnetophoresis as shown in Fig. 10a. Once at the top, cell rotation caused linear movement along the channel. Key factors like excitation frequency, current amplitude, and electrode position influenced cell velocity. Above a critical frequency dependent on cell size, shape, and elasticity, magnetic torque-driven translation overcame magnetic forces, enabling selective trapping of sickle cells at 300 Hz, while healthy cells continued flowing. Zhou et al.155 demonstrated shape-based separation of same volume spherical and peanut-shaped diamagnetic particles using a T-shaped microfluidic device with a perpendicular permanent magnet to create non-uniform magnetic fields (Fig. 10b). They explored how the flow rate and sheath-to-sample flow ratio influenced separation efficiency. This technique was later extended by Chen et al.156 to separate drug-treated yeast cells with varying sizes and shapes in ferrofluids (Fig. 10c).
 | ||
| Fig. 10 a) The ferromicrofluidic device uses phase-shifted sinusoidal currents through patterned electrodes to generate traveling magnetic fields that levitate and propel nonmagnetic particles via magnetic force and torque. Simulations confirm frequency-dependent control of particle motion, enabling continuous transport along the channel ceiling. Reproduced from Kose et al. with permission from PNAS, copyright 2009.38 b) The PDMS-based microfluidic chip features observation windows and defined flow directions for monitoring particle separation. Shape-based separation of spherical and peanut-shaped diamagnetic particles is demonstrated in a ferrofluid-filled T-shaped microchannel using sequential imaging along key channel regions. Reproduced from Zhou et al. with permission from AIP, copyright 2016.155 c) Magnetic fractionation of yeast cells in ferrofluid is demonstrated using a T-shaped microchannel. Experimental images and PDF plots show distinct separation of four yeast cell groups based on their spatial distribution at key channel locations. Reproduced from Chen et al. with permission from AIP, copyright 2017.156 d) Magnetic separation of microparticles by shape (prolate and sphere). Reproduced from Zhou et al. with permission from RSC, copyright 2017.157 | ||
Zhou et al.157 introduced a straightforward and effective method to separate equal-volume prolate paramagnetic ellipsoidal and spherical particles based solely on shape-dependent magnetic torque in a uniform static magnetic field, under low Re conditions (Fig. 10d). In the absence of a magnetic field, ellipsoidal particles rotate symmetrically in shear flow without any net lateral movement, preventing separation. However, applying a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the flow (α = 0°) generates a magnetic torque:
| Tm = μ0∫Vp[(MP − Mf) × H0]dV | (15) |
| Fac = ∫S0[〈σ〉 − ρ0〈v1v1〉]·n dS |
While the acoustofluidic separation of spherical particles is well understood and widely used, recent studies found dependencies of the acoustic force also on the shape and orientation of non-spherical particles due to scattering effects and gradients in the acoustic fields.37,172,173 Moreover, non-spherical particles not only experience translational forces but also an acoustic torque Tac according to:163,164
| Tac = ∫S0r × [〈σ〉 − ρ0〈v1v1〉]·n dS |
Analytical predictions of the acoustic force and torque that govern the behavior of non-spherical particles in an acoustic wave field are typically limited to inviscid fluids,178–180 predefined incident waves,181,182 and specific particle geometries.183–186 To overcome these limitations, Hahn et al. (2015) set up a three-dimensional numerical model that allows the migration of arbitrarily shaped particles in a standing acoustic wave field to be predicted.187 Based on this model, Hoque et al. (2022) revealed only a slight influence of the aspect ratio of an oblate shaped particle on the resulting acoustic force.188 However, the acoustically induced fluid velocity field was assumed constant across the particle surface, and thermoviscous boundary layers surrounding the particle were neglected. These thermoviscous effects can cause localized microstreaming, which was included in the axisymmetric numerical model derived by Pavlic et al. (2022).189 The axisymmetric setup of the numerical model significantly reduced the numerical effort, but restricted investigations on the effect of the orientation of the particle relative to the incident acoustic wave on the acoustic force. With a three-dimensional numerical model, Wijaya and Lim (2015) confirmed the direct influence of the particle orientation and shape on the acoustic force, although less significant than on the acoustic torque.172 These dependencies result in a shape-dependent migration of the particles in microfluidic devices, which laid the foundation for separation.
Focusing on prolate polystyrene spheroids in an acoustic field induced by SSAWs, Sachs et al. (2023) were among the first to show that the shape-dependent acoustic force can be used to separate elongated from spherical particles by tailoring the design of the microfluidic device (Fig. 11a).173 In a subsequent study,162 they further found that the electric field accompanying the SSAWs causes a dielectrophoretic force and torque on the particles, which influence the orientation and 3D position of the particles in the microchannel. Relying on the combined effect of the acoustic and electric fields, the particle separation could be improved as shown by Collins et al. (2014) for spherical particles.190 However, the work of Sachs et al. (2023, 2024) primarily focused on theoretical analysis and lacked practical separation demonstrations. To address this, Khan et al. (2024) applied TSAWs to successfully separate spheroids from spheres, demonstrating a functional, shape-based acoustic sorting system (Fig. 11b).37 While effective, this method still faced challenges in handling highly irregular or deformable particles. Compared to passive methods like DLD and viscoelastic microfluidics, acoustofluidic shape-based separation provides tunable, non-contact manipulation without relying on sheath flow. Unlike active magnetic and optical techniques, which are often material- or refractive index-dependent, acoustics can separate a broader range of materials of particles without external labeling. Furthermore, acoustofluidic manipulation is biocompatible, which allows for handling of complex biological samples and particle shapes. Despite its advancements, the method is less sensitive to shape than to particle size (Fac ∼ d3p), which poses challenges when separating industrial particles, which may vary both in volume and shape. While the technique has demonstrated significant potential, further research is needed to explore its full capabilities. By refining acoustic parameters and improving the design of microfluidic devices, selectivity and throughput can be greatly enhanced.
 | ||
Fig. 11 a) Schematic representation of an acoustofluidic device with prolate spheroids inside a microchannel sealed with a PDMS cover, which was omitted for visualization. In the middle, the numerically calculated acoustic force component ![[F with combining tilde]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0046_0303.gif) x, normalized by its maximum, is shown for a prolate spheroid and sphere with identical volume in a region between two pressure nodes (PN). Reproduced from Sachs et al. with permission from Springer, copyright 2023.173 b) The schematic and top-view show an acoustofluidic device used to separate 6 μm spheres and similarly sized peanut-shaped particles under a 117 MHz acoustic field. Images at the midstream, downstream, and collection outlets demonstrate effective shape-based separation across three outlets. Reproduced from Khan et al. with permission from Nature, copyright 2024.37 x, normalized by its maximum, is shown for a prolate spheroid and sphere with identical volume in a region between two pressure nodes (PN). Reproduced from Sachs et al. with permission from Springer, copyright 2023.173 b) The schematic and top-view show an acoustofluidic device used to separate 6 μm spheres and similarly sized peanut-shaped particles under a 117 MHz acoustic field. Images at the midstream, downstream, and collection outlets demonstrate effective shape-based separation across three outlets. Reproduced from Khan et al. with permission from Nature, copyright 2024.37 | ||
4. Challenges and future perspectives
This review has comprehensively analyzed the current state of shape-based microfluidic separation techniques, categorizing them into passive and active approaches. While microfluidics has already proven its efficacy for size-based particle manipulation, the extension toward shape-based separation reveals a promising yet underexplored frontier. The shape of a particle or cell is often a more sensitive and informative marker than size, especially in biological and medical contexts. For instance, abnormally shaped cells such as the crescent-shaped erythrocytes in sickle cell anemia, or the irregular morphologies seen in various cancers and infections, can serve as valuable diagnostic or prognostic indicators.191,192 Therefore, separating particles and cells based on their shape can enhance detection sensitivity and specificity in clinical and research applications. Below, we discuss current challenges, emerging trends, and future directions to advance the field.Underlying mechanisms
Despite considerable advancements across microfluidic platforms utilizing hydrodynamic forces, viscoelastic stresses, and external fields such as acoustic, electric, magnetic, and optical forces, many current techniques still fall short in fully exploiting the complex shape-dependent behaviors of particles and cells. A fundamental limitation lies in the lack of generalized models such as lift force equations for non-spherical particles suspended in Newtonian or viscoelastic fluids, which hinders predictive control in passive systems like inertial, viscoelastic, or pinched flow devices. Existing theoretical models are largely based on idealized spherical assumptions, making them inadequate for accurately describing the migration of elongated, asymmetric, or deformable particles. Additionally, particle–particle interactions involving non-spherical geometries remain poorly understood, particularly in how they influence rotational behaviors and trajectory stability. In the case of active methods, rotational modes such as tumbling, kayaking, and log-rolling induced by torque under electric, acoustic, or magnetic fields are known to occur but are rarely harnessed in device design. To bridge this gap, future research must focus on the integration of the comprehensive particle dynamics – from rotation and deformation to material compliance – into theoretical models and experimental platforms. A better understanding of how shape interacts with flow regimes, local shear gradients, and field distributions will enable the development of more robust, high-resolution, and versatile shape-based separation systems across both passive and active modalities.Separation efficiency
One of the primary challenges in shape-based microfluidic separation is achieving high separation efficiency and resolution, as shape differences often induce subtler hydrodynamic effects compared to size-based distinctions. This becomes particularly problematic when dealing with particles that differ only slightly in aspect ratio, making it difficult to establish a clear separation threshold. Moreover, many biological samples are inherently heterogeneous, exhibiting variability in both size and shape, often within polydisperse populations. This complexity makes it challenging to isolate shape as the sole parameter governing migration behavior. To improve performance, future efforts should therefore focus on developing strategies that can effectively decouple shape from size influences through both device design and integrated sensing, adapting to the presence of mixed populations. Advancements in simulation-guided design and adaptive control mechanisms will be essential for tailoring microfluidic platforms to address these multifactorial challenges with greater precision and robustness.Enhancing throughput and multiplexing
Many shape-based microfluidic systems are still constrained by relatively low throughput, which hinders their utility in large-scale biological screening or industrial processing. Furthermore, multiplexed separation, i.e., distinguishing and isolating multiple distinct shapes simultaneously, remains a challenge. Future systems need to integrate intelligent flow control, real-time feedback, and potentially AI-assisted image recognition to enhance decision-making during sorting processes.Sensor–actuator integration and intelligent control
An important future direction for shape-based microfluidic separation is the integration of intelligent feedback-driven control systems using sensors and actuators. While many current platforms rely on passive hydrodynamic effects or externally applied fields, these mechanisms often offer limited resolution when shape-induced forces are weak or ambiguous. In such cases, a promising alternative is to actively detect particle shape – for example, through optical imaging or real-time shape recognition – and precisely trigger an actuation event (e.g. via fluidic, acoustic, and electric forces) only when a target particle enters a specific region. This sensor–actuator framework offers maximum flexibility, allowing programmable, shape-specific sorting even within complex, heterogeneous samples. However, implementing such systems introduces new challenges, including device complexity, real-time data processing, and the development of robust control algorithms capable of synchronizing sensing and actuation. Addressing these issues will require interdisciplinary collaboration across microfluidics, optics, control engineering, computer vision, and computational analysis, ultimately paving the way for adaptive, high-precision separation systems.Scalability and sustainability
As microfluidic technologies transition from laboratory to industrial applications, scalability and sustainability emerge as critical considerations. High-throughput shape-based separation is essential for several applications such as bioprocessing and materials synthesis. However, most current platforms are designed for low-volume, high-precision tasks, limiting their scalability. Innovations in parallelized microfluidic architectures could address this scalability gap by increasing processing capacity without compromising resolution. Furthermore, sustainable fabrication methods, such as recyclable materials or energy-efficient actuation, will align shape-based separation with global efforts to reduce environmental impact. These advancements will broaden the applicability of microfluidic systems in large-scale industrial processes, fostering their adoption through enhanced sustainability.Interdisciplinary opportunities
The advancement of shape-based separation requires interdisciplinary collaboration between physicists, engineers, chemists, and biologists. Machine learning techniques could be employed for predictive modeling of particle trajectories based on shape and flow characteristics. Similarly, 3D printing and hybrid soft-lithography methods could aid in designing more sophisticated channel geometries that magnify shape sensitivity.Microfluidic-based imaging cytometers
Recent developments in microfluidic imaging cytometry have introduced systems that combine real-time imaging with cell sorting capabilities. These systems utilize algorithms to classify and sort cells based on their morphological features, offering label-free and high-throughput solutions for cell analysis. For instance, advancements in deep learning have enabled real-time cell sorting with high precision and speed, utilizing brightfield and fluorescence microscopy data. Such integration allows for the sorting of cells with specific shapes or morphologies, which is crucial for applications in disease diagnostics and personalized medicine. Incorporating these emerging technologies into microfluidic platforms could significantly enhance the sensitivity and specificity of cell separation techniques. Future research should focus on developing hybrid systems that combine the advantages of microfluidic shape-based separation with advanced imaging and machine learning algorithms. This integration holds the potential to revolutionize cell sorting processes, making them more efficient and applicable to a broader range of biomedical applications.5. Conclusion
Shape-based separation in microfluidics has advanced significantly, enabling the selective manipulation of particles and cells based on morphology rather than size. This capability is crucial for applications in biomedicine, diagnostics, and materials science. This review has outlined key developments across both passive (e.g., DLD, pinched flow, inertial, and viscoelastic systems) and active (e.g., dielectrophoresis, magnetophoresis, optophoresis, and acoustophoresis) approaches, each leveraging distinct physical principles to exploit shape-induced behaviors such as orientation, rotation, and deformability. Importantly, combining numerical modeling and experimental validation has been essential for designing and optimizing these platforms, especially in three-dimensional systems with complex or unknown boundary conditions. As the field advances, continued research is needed to address challenges such as limited throughput, sensitivity to particle shape, and integration with real-time control systems. We encourage stronger interdisciplinary collaboration to develop robust, predictive, and adaptable shape-based separation technologies capable of meeting the demands of real-world biological and engineering applications.Author contributions
M. S. K.: writing – original draft (lead); investigation (lead). R. H. J.: writing – original draft (supporting). M. A.: investigation (supporting). S. S.: investigation (supporting); writing – review & editing (supporting). C. C.: writing – review & editing (supporting). J. K.: conceptualization (supporting); writing – review & editing (supporting). J. P.: conceptualization (lead); funding acquisition (lead); writing – review & editing (lead).Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included, and no new data were generated or analyzed as part of this review.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. RS-2023-00210891 and RS-2020-NR049568), and by the German Research Foundation within the priority programme PP2045 “MehrDimPart” under grant number 444806275. The microfluidic devices were fabricated using a mask aligner (MDA-400S, MIDAS) at the Energy Convergence Core Facility at Chonnam National University.References
- G. Gharib, İ. Bütün, Z. Muganlı, G. Kozalak, İ. Namlı and S. S. Sarraf, et al., Biomedical Applications of Microfluidic Devices: A Review, Biosensors, 2022, 12(11), 1023, DOI:10.3390/bios12111023.
- H. Alijani, A. Özbey, M. Karimzadehkhouei and A. Koşar, Inertial Micromixing in Curved Serpentine Micromixers with Different Curve Angles, Fluids, 2019, 4(4), 204, DOI:10.3390/fluids4040204.
- V. E. Ahmadi, I. Butun, R. Altay, S. R. Bazaz, H. Alijani and S. Celik, et al., The effects of baffle configuration and number on inertial mixing in a curved serpentine micromixer: Experimental and numerical study, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2021, 168, 490–498, DOI:10.1016/j.cherd.2021.02.028.
- A. Özbey, M. Karimzadehkhouei, S. Akgönül, D. Gozuacik and A. Koşar, Inertial Focusing of Microparticles in Curvilinear Microchannels, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6(1), 38809, DOI:10.1038/srep38809.
- K. Erdem, V. E. Ahmadi, A. Kosar and L. Kuddusi, Differential Sorting of Microparticles Using Spiral Microchannels with Elliptic Configurations, Micromachines, 2020, 11(4), 412, DOI:10.3390/mi11040412.
- D. Jiang, C. Ni, W. Tang, D. Huang and N. Xiang, Inertial microfluidics in contraction-expansion microchannels: A review, Biomicrofluidics, 2021, 15(4), 041501, DOI:10.1063/5.0058732.
- Q. Zhao, D. Yuan, J. Zhang and W. Li, A Review of Secondary Flow in Inertial Microfluidics, Micromachines, 2020, 11(5), 461, DOI:10.3390/mi11050461.
- A. Kotnala, Y. Zheng, J. Fu and W. Cheng, Microfluidic-based high-throughput optical trapping of nanoparticles, Lab Chip, 2017, 17(12), 2125–2134, 10.1039/C7LC00286F.
- Z. Zhang, T. E. P. Kimkes and M. Heinemann, Manipulating rod-shaped bacteria with optical tweezers, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 19086, DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-55657-y.
- H. Sun, Y. Ren, L. Hou, Y. Tao, W. Liu and T. Jiang, et al., Continuous Particle Trapping, Switching, and Sorting Utilizing a Combination of Dielectrophoresis and Alternating Current Electrothermal Flow, Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(9), 5729–5738, DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05861.
- G. R. Pesch, M. Lorenz, S. Sachdev, S. Salameh, F. Du and M. Baune, et al., Bridging the scales in high-throughput dielectrophoretic (bio-)particle separation in porous media, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8(1), 10480, DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-28735-w.
- H. Cong, J. Chen and H.-P. Ho, Trapping, sorting and transferring of micro-particles and live cells using electric current-induced thermal tweezers, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 264, 224–233, DOI:10.1016/j.snb.2018.02.016.
- J. Chen, H. Cong, J. Loo, Z. Kang, M. Tang and H. Zhang, et al., Thermal gradient induced tweezers for the manipulation of particles and cells, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6(1), 35814, DOI:10.1038/srep35814.
- L. Malik, A. Nath, S. Nandy, T. Laurell and A. K. Sen, Acoustic particle trapping driven by axial primary radiation force in shaped traps, Phys. Rev. E, 2022, 105(3), 035103, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.105.035103.
- L. Shen, Z. Tian, J. Zhang, H. Zhu, K. Yang and T. Li, et al., Acousto-dielectric tweezers for size-insensitive manipulation and biophysical characterization of single cells, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2023, 224, 115061, DOI:10.1016/j.bios.2023.115061.
- D. Mandal and S. Banerjee, Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Sensors: Physics, Materials, and Applications, Sensors, 2022, 22(3), 820, DOI:10.3390/s22030820.
- N. Nesakumar, S. Kesavan, C.-Z. Li and S. Alwarappan, Microfluidic Electrochemical Devices for Biosensing, J. Anal. Test., 2019, 3(1), 3–18, DOI:10.1007/s41664-019-0083-y.
- G. Luka, A. Ahmadi, H. Najjaran, E. Alocilja, M. DeRosa and K. Wolthers, et al., Microfluidics Integrated Biosensors: A Leading Technology towards Lab-on-a-Chip and Sensing Applications, Sensors, 2015, 15(12), 30011–30031, DOI:10.3390/s151229783.
- C. Zhao, C. Li, M. Li, L. Qian, L. Wang and H. Li, Surface acoustic wave immunosensor based on Au-nanoparticles-decorated graphene fluidic channel for CA125 detection, Sens. Actuators, B, 2022, 367, 132063, DOI:10.1016/j.snb.2022.132063.
- P. E. Kolenbrander, R. N. Andersen, D. S. Blehert, P. G. Egland, J. S. Foster and R. J. Palmer Jr., Communication among oral bacteria, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2002, 66(3), 486–505, DOI:10.1128/mmbr.66.3.486-505.2002.
- T. Pereira-Veiga, S. Schneegans, K. Pantel and H. Wikman, Circulating tumor cell-blood cell crosstalk: Biology and clinical relevance, Cell Rep., 2022, 40(9), 111298, DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111298.
- B. J. Bain, Blood cells a practical guide, Malden, 4th edn, 2006 Search PubMed.
- S. C. P. Williams, Circulating tumor cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, 110(13), 4861, DOI:10.1073/pnas.1304186110.
- W. V. Kern and S. Rieg, Burden of bacterial bloodstream infection-a brief update on epidemiology and significance of multidrug-resistant pathogens, Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2020, 26(2), 151–157, DOI:10.1016/j.cmi.2019.10.031.
- N. Nivedita and I. Papautsky, Continuous separation of blood cells in spiral microfluidic devices, Biomicrofluidics, 2013, 7(5), 54101, DOI:10.1063/1.4819275.
- N. Lu, H. M. Tay, C. Petchakup, L. He, L. Gong and K. K. Maw, et al., Label-free microfluidic cell sorting and detection for rapid blood analysis, Lab Chip, 2023, 23(5), 1226–1257, 10.1039/D2LC00904H.
- A. Saliba, L. Saias, F. Bidard, C. Mathiot, V. Saada and F. Farace, et al., Microfluidic device for circulating tumor cell sorting, characterization, and culture, J. Clin. Oncol., 2009, 27(15_suppl), 11068, DOI:10.1200/jco.2009.27.15_suppl.11068.
- V. Omrani, M. Z. Targhi, F. Rahbarizadeh and R. Nosrati, High-throughput isolation of cancer cells in spiral microchannel by changing the direction, magnitude and location of the maximum velocity, Sci. Rep., 2023, 13(1), 3213, DOI:10.1038/s41598-023-30275-x.
- M. Aghaamoo, B. Cardenas-Benitez and A. P. Lee, A High-Throughput Microfluidic Cell Sorter Using a Three-Dimensional Coupled Hydrodynamic-Dielectrophoretic Pre-Focusing Module, Micromachines, 2023, 14(10), 1813, DOI:10.3390/mi14101813.
- P. Liu, H. Liu, D. Yuan, D. Jang, S. Yan and M. Li, Separation and Enrichment of Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by Shape Using Viscoelastic Microfluidics, Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(3), 1586–1595, DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03990.
- A. Molina-Miras, L. López-Rosales, M. C. Cerón-García, A. Sánchez-Mirón, F. García-Camacho and A. Contreras-Gómez, et al., A new approach to finding optimal centrifugation conditions for shear-sensitive microalgae, Algal Res., 2019, 44, 101677, DOI:10.1016/j.algal.2019.101677.
- P. L. Mage, A. T. Csordas, T. Brown, D. Klinger, M. Eisenstein and S. Mitragotri, et al., Shape-based separation of synthetic microparticles, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18(1), 82–89, DOI:10.1038/s41563-018-0244-9.
- R. Nasiri, A. Shamloo, S. Ahadian, L. Amirifar, J. Akbari and M. J. Goudie, et al., Microfluidic-Based Approaches in Targeted Cell/Particle Separation Based on Physical Properties: Fundamentals and Applications, Small, 2020, 16(29), 2000171, DOI:10.1002/smll.202000171.
- J. P. Beech, S. H. Holm, K. Adolfsson and J. O. Tegenfeldt, Sorting cells by size, shape and deformability, Lab Chip, 2012, 12(6), 1048–1051, 10.1039/C2LC21083E.
- A. Reece, B. Xia, Z. Jiang, B. Noren, R. McBride and J. Oakey, Microfluidic techniques for high throughput single cell analysis, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2016, 40, 90–96, DOI:10.1016/j.copbio.2016.02.015.
- F. K. Liu, F. H. Ko, P. W. Huang, C. H. Wu and T. C. Chu, Studying the size/shape separation and optical properties of silver nanoparticles by capillary electrophoresis, J. Chromatogr. A, 2005, 1062(1), 139–145, DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.11.010.
- M. S. Khan, M. Ali, S. H. Lee, K. Y. Jang, S. J. Lee and J. Park, Acoustofluidic separation of prolate and spherical micro-objects, Microsyst. Nanoeng., 2024, 10(1), 6, DOI:10.1038/s41378-023-00636-7.
- A. R. Kose, B. Fischer, L. Mao and H. Koser, Label-free cellular manipulation and sorting via biocompatible ferrofluids, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2009, 106(51), 21478–21483, DOI:10.1073/pnas.0912138106.
- Z. Lan, R. Chen, D. Zou and C. X. Zhao, Microfluidic Nanoparticle Separation for Precision Medicine, Adv Sci, 2025, 12(4), e2411278, DOI:10.1002/advs.202411278.
- B. Behdani, S. Monjezi, M. J. Carey, C. G. Weldon, J. Zhang and C. Wang, et al., Shape-based separation of micro−/nanoparticles in liquid phases, Biomicrofluidics, 2018, 12(5), 051503, DOI:10.1063/1.5052171.
- G. B. Jeffery, The Motion of Ellipsoidal Particles Immersed in a Viscous Fluid, Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1922, 102, 161–179, DOI:10.1098/rspa.1922.0078.
- P. G. Saffman, On the motion of small spheroidal particles in a viscous liquid, J. Fluid Mech., 1956, 1(5), 540–553, DOI:10.1017/S0022112056000354.
- J. Ford, Red blood cell morphology, Int. J. Lab. Hematol., 2013, 35(3), 351–357, DOI:10.1111/ijlh.12082.
- D. C. Rees, T. N. Williams and M. T. Gladwin, Sickle-cell disease, Lancet, 2010, 376(9757), 2018–2031, DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)61029-x.
- A. K. Dasanna, S. Hillringhaus, G. Gompper and D. A. Fedosov, Effect of malaria parasite shape on its alignment at erythrocyte membrane, Elife, 2021, 10, e68818, DOI:10.7554/eLife.68818.
- S. Perrotta, P. G. Gallagher and N. Mohandas, Hereditary spherocytosis, Lancet, 2008, 372(9647), 1411–1426, DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(08)61588-3.
- J. P. Lynch 3rd, M. Fishbein and M. Echavarria, Adenovirus, Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 2011, 32(4), 494–511, DOI:10.1055/s-0031-1283287.
- G. Stubbs and A. Kendall, in Viral Molecular Machines, ed. M. G. Rossmann and V. B. Rao, Boston, MA, Springer US, 2012, pp. 631–658 Search PubMed.
- M. Adams, Bacteriophages, Inter-science Publishers, New York (London), 1959, xviii +, p. 592 Search PubMed.
- P. C. Turnbull, J. Kramer and J. Melling, Bacillus, Med. Microbiol., 1996, 4, 233 Search PubMed.
- A. Zapun, T. Vernet and M. G. Pinho, The different shapes of cocci, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2008, 32(2), 345–360, DOI:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00098.x.
- P. B. Hylemon, J. S. Wells, N. R. Krieg and H. W. Jannasch, The Genus Spirillum: a Taxonomic Study1, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 1973, 23(4), 340–380, DOI:10.1099/00207713-23-4-340.
- P. Spolaore, C. Joannis-Cassan, E. Duran and A. Isambert, Commercial applications of microalgae, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2006, 101(2), 87–96, DOI:10.1263/jbb.101.87.
- O. Smirnova, D. Golubchikov, A. Murashko, N. Kosheleva, M. Saadatmand and P. Timashev, et al., Design clues for motility and rheotaxis-based microfluidic chips for sperm sorting, Prog. Biomed. Eng., 2025, 7(4), 042004, DOI:10.1088/2516-1091/adf92f.
- S. Fleming, D. Morroll and M. Nijs, Sperm Separation and Selection Techniques to Mitigate Sperm DNA Damage, Life, 2025, 15(2), 302, DOI:10.3390/life15020302.
- G. R. Bhat, F. A. Lone and J. Dalal, Microfluidics-A novel technique for high-quality sperm selection for greater ART outcomes, FASEB BioAdv., 2024, 6(10), 406–423, DOI:10.1096/fba.2024-00041.
- M. Bouloorchi Tabalvandani, Z. Saeidpour, Z. Habibi, S. Javadizadeh, S. A. Firoozabadi and M. Badieirostami, Microfluidics as an emerging paradigm for assisted reproductive technology: A sperm separation perspective, Biomed. Microdevices, 2024, 26(2), 23, DOI:10.1007/s10544-024-00705-2.
- N. Ahmadkhani, M. Hosseini, M. Saadatmand and A. Abbaspourrad, The influence of the female reproductive tract and sperm features on the design of microfluidic sperm-sorting devices, J. Assist. Reprod. Genet., 2022, 39(1), 19–36, DOI:10.1007/s10815-021-02377-w.
- C. Chen, R. Saxena and G. W. Wei, A multiscale model for virus capsid dynamics, Int. J. Biomed. Imaging, 2010, 2010, 308627, DOI:10.1155/2010/308627.
- T. T. Nguyen, R. F. Bruinsma and W. M. Gelbart, Elasticity theory and shape transitions of viral shells, Phys. Rev. E, 2005, 72(5), 051923, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.72.051923.
- R. Zandi and D. Reguera, Mechanical properties of viral capsids, Phys. Rev. E, 2005, 72(2), 021917, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.72.021917.
- Z. Yu, N. Phan-Thien and R. I. Tanner, Rotation of a spheroid in a Couette flow at moderate Reynolds numbers, Phys. Rev. E, 2007, 76(2), 026310, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.76.026310.
- C. M. Zettner and M. Yoda, Moderate-aspect-ratio elliptical cylinders in simple shear with inertia, J. Fluid Mech., 2001, 442, 241–266, DOI:10.1017/S0022112001005006.
- H. Huang, X. Yang, M. Krafczyk and X.-Y. Lu, Rotation of spheroidal particles in Couette flows, J. Fluid Mech., 2012, 692, 369–394, DOI:10.1017/jfm.2011.519.
- T. Rosén, M. Do-Quang, C. K. Aidun and F. Lundell, The dynamical states of a prolate spheroidal particle suspended in shear flow as a consequence of particle and fluid inertia, J. Fluid Mech., 2015, 771, 115–158, DOI:10.1017/jfm.2015.127.
- C. Xue, Y. Yin, X. Xu, K. Tian, J. Su and G. Hu, Particle manipulation under X-force fields, Lab Chip, 2025, 25(5), 956–978, 10.1039/D4LC00794H.
- Q. Cui, G. Tian, T. Zhou, Y. Shen, S. Feng and M. Li, et al., Design advances in pinched flow fractionation for enhanced particle separation in microfluidics, Lab Chip, 2025, 25(17), 4290–4308, 10.1039/D5LC00497G.
- V. Narayanamurthy, Z. E. Jeroish, K. S. Bhuvaneshwari, P. Bayat, R. Premkumar and F. Samsuri, et al., Advances in passively driven microfluidics and lab-on-chip devices: a comprehensive literature review and patent analysis, RSC Adv., 2020, 10(20), 11652–11680, 10.1039/D0RA00263A.
- S. N. Bhatia and D. E. Ingber, Microfluidic organs-on-chips, Nat. Biotechnol., 2014, 32(8), 760–772, DOI:10.1038/nbt.2989.
- Y. Chen, D. Li, Y. Li, J. Wan, J. Li and H. Chen, Margination of Stiffened Red Blood Cells Regulated By Vessel Geometry, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), 15253, DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-15524-0.
- A. Kumar and M. D. Graham, Mechanism of Margination in Confined Flows of Blood and Other Multicomponent Suspensions, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2012, 109(10), 108102, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.108102.
- D. A. Fedosov, J. Fornleitner and G. Gompper, Margination of White Blood Cells in Microcapillary Flow, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2012, 108(2), 028104, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.028104.
- L. R. Huang, E. C. Cox, R. H. Austin and J. C. Sturm, Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement, Science, 2004, 304(5673), 987–990, DOI:10.1126/science.1094567.
- J. A. Davis, D. W. Inglis, K. J. Morton, D. A. Lawrence, L. R. Huang and S. Y. Chou, et al., Deterministic hydrodynamics: Taking blood apart, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006, 103(40), 14779–14784, DOI:10.1073/pnas.0605967103.
- S. C. Kim, B. H. Wunsch, H. Hu, J. T. Smith, R. H. Austin and G. Stolovitzky, Broken flow symmetry explains the dynamics of small particles in deterministic lateral displacement arrays, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2017, 114(26), E5034–E5041, DOI:10.1073/pnas.1706645114.
- D. W. Inglis, J. A. Davis, R. H. Austin and J. C. Sturm, Critical particle size for fractionation by deterministic lateral displacement, Lab Chip, 2006, 6(5), 655–658, 10.1039/B515371A.
- K. K. Zeming, T. Salafi, C. H. Chen and Y. Zhang, Asymmetrical Deterministic Lateral Displacement Gaps for Dual Functions of Enhanced Separation and Throughput of Red Blood Cells, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 22934, DOI:10.1038/srep22934.
- K. K. Zeming, T. Salafi, S. Shikha and Y. Zhang, Fluorescent label-free quantitative detection of nano-sized bioparticles using a pillar array. Nature, Communications, 2018, 9(1), 1254, DOI:10.1038/s41467-018-03596-z.
- K. K. Zeming, N. V. Thakor, Y. Zhang and C. H. Chen, Real-time modulated nanoparticle separation with an ultra-large dynamic range, Lab Chip, 2016, 16(1), 75–85, 10.1039/c5lc01051a.
- S. Ranjan, K. K. Zeming, R. Jureen, D. Fisher and Y. Zhang, DLD pillar shape design for efficient separation of spherical and non-spherical bioparticles, Lab Chip, 2014, 14(21), 4250–4262, 10.1039/c4lc00578c.
- Z. Zhang, E. Henry, G. Gompper and D. A. Fedosov, Behavior of rigid and deformable particles in deterministic lateral displacement devices with different post shapes, J. Chem. Phys., 2015, 143(24), 243145, DOI:10.1063/1.4937171.
- S. R. Reinecke, S. Blahout, T. Rosemann, B. Kravets, M. Wullenweber and A. Kwade, et al., DEM-LBM simulation of multidimensional fractionation by size and density through deterministic lateral displacement at various Reynolds numbers, Powder Technol., 2021, 385, 418–433, DOI:10.1016/j.powtec.2021.02.062.
- S. R. Reinecke, S. Blahout, Z. Zhang, T. Rosemann, J. Hussong and H. Kruggel-Emden, Effects of particle size, particle density and Reynolds number on equilibrium streaks forming in a square wave serpentine microchannel: A DEM-LBM simulation study including experimental validation of the numerical framework, Powder Technol., 2023, 427, 118688, DOI:10.1016/j.powtec.2023.118688.
- T. Salafi, Y. Zhang and Y. Zhang, A Review on Deterministic Lateral Displacement for Particle Separation and Detection, Nano-Micro Lett., 2019, 11(1), 77, DOI:10.1007/s40820-019-0308-7.
- K. K. Zeming, S. Ranjan and Y. Zhang, Rotational separation of non-spherical bioparticles using I-shaped pillar arrays in a microfluidic device, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4(1), 1625, DOI:10.1038/ncomms2653.
- D. Fan, Y. Liu and Y. Liu, The Latest Advances in Microfluidic DLD Cell Sorting Technology: The Optimization of Channel Design, Biosensors, 2025, 15(2), 126, DOI:10.3390/bios15020126.
- S. H. Holm, J. P. Beech, M. P. Barrett and J. O. Tegenfeldt, Separation of parasites from human blood using deterministic lateral displacement, Lab Chip, 2011, 11(7), 1326–1332, 10.1039/C0LC00560F.
- Z. Zhang, E. Henry, G. Gompper and D. A. Fedosov, Behavior of rigid and deformable particles in deterministic lateral displacement devices with different post shapes, J. Chem. Phys., 2015, 143(24), 243145, DOI:10.1063/1.4937171.
- S. Ye, X. Shao, Z. Yu and W. Yu, Effects of the particle deformability on the critical separation diameter in the deterministic lateral displacement device, J. Fluid Mech., 2014, 743, 60–74, DOI:10.1017/jfm.2014.22.
- G. Kabacaoğlu and G. Biros, Optimal design of deterministic lateral displacement device for viscosity-contrast-based cell sorting, Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2018, 3(12), 124201, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevFluids.3.124201.
- T. Krüger, D. Holmes and P. V. Coveney, Deformability-based red blood cell separation in deterministic lateral displacement devices-A simulation study, Biomicrofluidics, 2014, 8(5), 054114, DOI:10.1063/1.4897913.
- Z. Zhang, W. Chien, E. Henry, D. A. Fedosov and G. Gompper, Sharp-edged geometric obstacles in microfluidics promote deformability-based sorting of cells, Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2019, 4(2), 024201, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.024201.
- M. Xavier, S. H. Holm, J. P. Beech, D. Spencer, J. O. Tegenfeldt and R. O. C. Oreffo, et al., Label-free enrichment of primary human skeletal progenitor cells using deterministic lateral displacement, Lab Chip, 2019, 19(3), 513–523, 10.1039/C8LC01154K.
- Z. Liu, R. Chen, Y. Li, J. Liu, P. Wang and X. Xia, et al., Integrated Microfluidic Chip for Efficient Isolation and Deformability Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells, Adv. Biosyst., 2018, 2(10), 1800200, DOI:10.1002/adbi.201800200.
- W. Tang, S. Zhu, D. Jiang, L. Zhu, J. Yang and N. Xiang, Channel innovations for inertial microfluidics, Lab Chip, 2020, 20(19), 3485–3502, 10.1039/D0LC00714E.
- D. Di Carlo, Inertial microfluidics, Lab Chip, 2009, 9(21), 3038–3046, 10.1039/B912547G.
- D.-K. Sun, D. Jiang, N. Xiang, K. Chen and Z.-H. Ni, An Immersed Boundary-Lattice Boltzmann Simulation of Particle Hydrodynamic Focusing in a Straight Microchannel, Chin. Phys. Lett., 2013, 30(7), 074702, DOI:10.1088/0256-307X/30/7/074702.
- H. Amini, W. Lee and D. Di Carlo, Inertial microfluidic physics, Lab Chip, 2014, 14(15), 2739–2761, 10.1039/C4LC00128A.
- S. I. Rubinow and J. B. Keller, The transverse force on a spinning sphere moving in a viscous fluid, J. Fluid Mech., 1961, 11(3), 447–459, DOI:10.1017/S0022112061000640.
- S. C. Hur, S.-E. Choi, S. Kwon and D. D. Carlo, Inertial focusing of non-spherical microparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 99(4), 044101, DOI:10.1063/1.3608115.
- J. Su, X. Chen and G. Hu, Inertial migrations of cylindrical particles in rectangular microchannels: Variations of equilibrium positions and equivalent diameters, Phys. Fluids, 2018, 30(3), 032007, DOI:10.1063/1.5018714.
- S. R. Reinecke, Z. Zhang, T. Rosemann, J. Hussong and H. Kruggel-Emden, DEM-LBM study on the behavior of non-spherical particles in a square wave serpentine microchannel, Powder Technol., 2024, 436, 119474, DOI:10.1016/j.powtec.2024.119474.
- M. Masaeli, E. Sollier, H. Amini, W. Mao, K. Camacho and N. Doshi, et al., Continuous Inertial Focusing and Separation of Particles by Shape, Phys. Rev. X, 2012, 2(3), 031017, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevX.2.031017.
- A. Unverfehrt and H. Rehage, Deformation, Orientation and Bursting of Microcapsules in Simple Shear Flow: Wrinkling Processes, Tumbling and Swinging Motions, Procedia IUTAM, 2015, 16, 12–21, DOI:10.1016/j.piutam.2015.03.003.
- H. Feng, M. Hockin, M. Capecchi, B. Gale and H. Sant, Size and shape based chromosome separation in the inertial focusing device, Biomicrofluidics, 2020, 14(6), 064109, DOI:10.1063/5.0026281.
- X. Lu, L. Zhu, R.-M. Hua and X. Xuan, Continuous sheath-free separation of particles by shape in viscoelastic fluids, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107(26), 264102, DOI:10.1063/1.4939267.
- M. Li, H. E. Muñoz, A. Schmidt, B. Guo, C. Lei and K. Goda, et al., Inertial focusing of ellipsoidal Euglena gracilis cells in a stepped microchannel, Lab Chip, 2016, 16(22), 4458–4465, 10.1039/C6LC01118G.
- M. Li, H. E. Muñoz, K. Goda and D. Di Carlo, Shape-based separation of microalga Euglena gracilis using inertial microfluidics, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), 10802, DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-10452-5.
- K. Patel and H. Stark, A pair of particles in inertial microfluidics: effect of shape, softness, and position, Soft Matter, 2021, 17(18), 4804–4817, 10.1039/D1SM00276G.
- H. Jeon, S. H. Lee, J. Shin, K. Song, N. Ahn and J. Park, Elasto-inertial microfluidic separation of microspheres with submicron resolution at high-throughput, Microsyst. Nanoeng., 2024, 10(1), 15, DOI:10.1038/s41378-023-00633-w.
- J. Zhou and I. Papautsky, Viscoelastic microfluidics: progress and challenges, Microsyst. Nanoeng., 2020, 6(1), 113, DOI:10.1038/s41378-020-00218-x.
- A. Langella, G. Franzino, P. L. Maffettone, D. Larobina and G. D'Avino, Dynamics of non-spherical particles in viscoelastic fluids flowing in a microchannel, Soft Matter, 2023, 19(48), 9541–9549, 10.1039/D3SM01399E.
- C.-W. Tai and V. Narsimhan, Experimental and theoretical studies of cross-stream migration of non-spherical particles in a quadratic flow of a viscoelastic fluid, Soft Matter, 2022, 18(24), 4613–4624, 10.1039/D2SM00011C.
- X. Hu, J. Lin, P. Lin and Z. Zhu, Rigid spheroid migration in square channel flow of power-law fluids, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2023, 247, 108194, DOI:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108194.
- J. Nam, H. Jee, W. S. Jang, J. Yoon, B. G. Park and S. J. Lee, et al., Sheathless Shape-Based Separation of Candida Albicans Using a Viscoelastic Non-Newtonian Fluid, Micromachines, 2019, 10(12), 817, DOI:10.3390/mi10120817.
- D. Yuan, S. Yan, J. Zhang, R. M. Guijt, Q. Zhao and W. Li, Sheathless Separation of Cyanobacterial Anabaena by Shape Using Viscoelastic Microfluidics, Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(37), 12648–12654, DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02389.
- T. Zhang, H. Liu, K. Okano, T. Tang, K. Inoue and Y. Yamazaki, et al., Shape-based separation of drug-treated Escherichia coli using viscoelastic microfluidics, Lab Chip, 2022, 22(15), 2801–2809, 10.1039/D2LC00339B.
- T. Zhang, A. K. Cain, L. Semenec, J. V. Pereira, Y. Hosokawa and Y. Yalikun, et al., Bacteria separation and enrichment using viscoelastic flows in a straight microchannel, Sens. Actuators, B, 2023, 390, 133918, DOI:10.1016/j.snb.2023.133918.
- X. Lu and X. Xuan, Elasto-Inertial Pinched Flow Fractionation for Continuous Shape-Based Particle Separation, Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(22), 11523–11530, DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03321.
- H. W. Nho, N. Yang, J. Song, J. S. Park and T. H. Yoon, Separations of spherical and disc-shaped polystyrene particles and blood components (red blood cells and platelets) using pinched flow fractionation device with a tilted sidewall and vertical focusing channels (t-PFF-v), Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 249, 131–141, DOI:10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.081.
- G. de Timary, C. J. Rousseau, L. Van Melderen and B. Scheid, Shear-enhanced sorting of ovoid and filamentous bacterial cells using pinch flow fractionation, Lab Chip, 2023, 23(4), 659–670, 10.1039/D2LC00969B.
- F. Strubbe, F. Beunis, T. Brans, M. Karvar, W. Woestenborghs and K. Neyts, Electrophoretic Retardation of Colloidal Particles in Nonpolar Liquids, Phys. Rev. X, 2013, 3(2), 021001, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevX.3.021001.
- D. A. Saville, Electrokinetic Effects with Small Particles, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech., 1977, 9, 321–337, DOI:10.1146/annurev.fl.09.010177.001541.
- J.-L. Viovy, Electrophoresis of DNA and other polyelectrolytes: Physical mechanisms, Rev. Mod. Phys., 2000, 72(3), 813–872, DOI:10.1103/RevModPhys.72.813.
- D. J. Harrison, K. Fluri, K. Seiler, Z. Fan, C. S. Effenhauser and A. Manz, Micromachining a Miniaturized Capillary Electrophoresis-Based Chemical Analysis System on a Chip, Science, 1993, 261(5123), 895–897, DOI:10.1126/science.261.5123.895.
- J. Han and H. G. Craighead, Separation of long DNA molecules in a microfabricated entropic trap array, Science, 2000, 288(5468), 1026–1029, DOI:10.1126/science.288.5468.1026.
- N. Laohakunakorn, S. Ghosal, O. Otto, K. Misiunas and U. F. Keyser, DNA Interactions in Crowded Nanopores, Nano Lett., 2013, 13(6), 2798–2802, DOI:10.1021/nl401050m.
- R. F. Stout and A. S. Khair, A continuum approach to predicting electrophoretic mobility reversals, J. Fluid Mech., 2014, 752, R1, DOI:10.1017/jfm.2014.354.
- M. V. Smoluchowski, Contribution à la théorie de l'endosmose électrique et de quelques phénomènes corrélatifs, Bull. Int. Acad. Sci. Cracovie, 1903, 8, 182–200 Search PubMed.
- C. Binns, Medical Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles, Frontiers of Nanoscience, ed. C. Binns, Elsevier, 2014, ch. 6, vol. 6, pp. 217–258 Search PubMed.
- M. Hanauer, S. Pierrat, I. Zins, A. Lotz and C. Sönnichsen, Separation of Nanoparticles by Gel Electrophoresis According to Size and Shape, Nano Lett., 2007, 7(9), 2881–2885, DOI:10.1021/nl071615y.
- X. Xu, K. K. Caswell, E. Tucker, S. Kabisatpathy, K. L. Brodhacker and W. A. Scrivens, Size and shape separation of gold nanoparticles with preparative gel electrophoresis, J. Chromatogr. A, 2007, 1167(1), 35–41, DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.07.056.
- J.-P. Hsu, C.-Y. Lin, L.-H. Yeh and S.-H. Lin, Influence of the shape of a polyelectrolyte on its electrophoretic behavior, Soft Matter, 2012, 8(36), 9469–9479, 10.1039/C2SM25741F.
- L. Weirauch, J. Giesler, M. Baune, G. R. Pesch and J. Thöming, Shape-selective remobilization of microparticles in a mesh-based DEP filter at high throughput, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2022, 300, 121792, DOI:10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121792.
- H. A. Pohl, K. Pollock and J. S. Crane, Dielectrophoretic force: A comparison of theory and experiment, J. Biol. Phys., 1978, 6(3–4), 133–160, DOI:10.1007/BF02328936.
- J. S. Kirby, M. Tehrani and M. D. Ioffreda, Patchy alopecia following chemotherapy, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 2010, 62(3), 536–538, DOI:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.04.043.
- N. Nitta, T. Sugimura, A. Isozaki, H. Mikami, K. Hiraki and S. Sakuma, et al., Intelligent Image-Activated Cell Sorting, Cell, 2018, 175(1), 266–276.e13, DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.028.
- S. Stavrakis, G. Holzner, J. Choo and A. deMello, High-throughput microfluidic imaging flow cytometry, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2019, 55, 36–43, DOI:10.1016/j.copbio.2018.08.002.
- S. Zhou, B. Chen, E. S. Fu and H. Yan, Computer vision meets microfluidics: a label-free method for high-throughput cell analysis, Microsyst. Nanoeng., 2023, 9(1), 116, DOI:10.1038/s41378-023-00562-8.
- J. Zhou, L. Mei, M. Yu, X. Ma, D. Hou and Z. Yin, et al., Imaging flow cytometry with a real-time throughput beyond 1,000,000 events per second, Light:Sci. Appl., 2025, 14(1), 76, DOI:10.1038/s41377-025-01754-9.
- M. Girault, H. Kim, H. Arakawa, K. Matsuura, M. Odaka and A. Hattori, et al., An on-chip imaging droplet-sorting system: a real-time shape recognition method to screen target cells in droplets with single cell resolution, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7(1), 40072, DOI:10.1038/srep40072.
- P. Y. Chiou, A. T. Ohta and M. C. Wu, Massively parallel manipulation of single cells and microparticles using optical images, Nature, 2005, 436(7049), 370–372, DOI:10.1038/nature03831.
- W. Wang, R. Xie, X.-J. Ju, T. Luo, L. Liu and D. A. Weitz, et al., Controllable microfluidic production of multicomponent multiple emulsions, Lab Chip, 2011, 11(9), 1587–1592, 10.1039/C1LC20065H.
- Y. Harada and T. Asakura, Radiation forces on a dielectric sphere in the Rayleigh scattering regime, Opt. Commun., 1996, 124(5), 529–541, DOI:10.1016/0030-4018(95)00753-9.
- C. B. Chang, W.-X. Huang, K. H. Lee and H. J. Sung, Optical separation of ellipsoidal particles in a uniform flow, Phys. Fluids, 2014, 26(6), 062001, DOI:10.1063/1.4880214.
- C. B. Chang, W.-X. Huang and H. J. Sung, Cross-type optical separation of elastic oblate capsules in a uniform flow, J. Appl. Phys., 2015, 117(3), 034701, DOI:10.1063/1.4906092.
- A. Munaz, M. J. A. Shiddiky and N. T. Nguyen, Recent advances and current challenges in magnetophoresis based micro magnetofluidics, Biomicrofluidics, 2018, 12(3), 031501, DOI:10.1063/1.5035388.
- M. Hejazian, W. Li and N.-T. Nguyen, Lab on a chip for continuous-flow magnetic cell separation, Lab Chip, 2015, 15(4), 959–970, 10.1039/C4LC01422G.
- J. D. Adams, P. Thévoz, H. Bruus and H. T. Soh, Integrated acoustic and magnetic separation in microfluidic channels, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 95(25), 254103, DOI:10.1063/1.3275577.
- K. Hoshino, Y.-Y. Huang, N. Lane, M. Huebschman, J. W. Uhr and E. P. Frenkel, et al., Microchip-based immunomagnetic detection of circulating tumor cells, Lab Chip, 2011, 11(20), 3449–3457, 10.1039/C1LC20270G.
- J. H. Kang, S. Krause, H. Tobin, A. Mammoto, M. Kanapathipillai and D. E. Ingber, A combined micromagnetic-microfluidic device for rapid capture and culture of rare circulating tumor cells, Lab Chip, 2012, 12(12), 2175–2181, 10.1039/C2LC40072C.
- M. Hejazian and N. T. Nguyen, Magnetofluidic concentration and separation of non-magnetic particles using two magnet arrays, Biomicrofluidics, 2016, 10(4), 044103, DOI:10.1063/1.4955421.
- L. Liang, C. Zhang and X. Xuan, Enhanced separation of magnetic and diamagnetic particles in a dilute ferrofluid, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 102(23), 234101, DOI:10.1063/1.4810874.
- R. Zhou and C. Wang, Multiphase ferrofluid flows for micro-particle focusing and separation, Biomicrofluidics, 2016, 10(3), 034101, DOI:10.1063/1.4948656.
- Y. Zhou and X. Xuan, Diamagnetic particle separation by shape in ferrofluids, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 109(10), 102405, DOI:10.1063/1.4962638.
- Q. Chen, D. Li, J. Zielinski, L. Kozubowski, J. Lin and M. Wang, et al., Yeast cell fractionation by morphology in dilute ferrofluids, Biomicrofluidics, 2017, 11(6), 064102, DOI:10.1063/1.5006445.
- R. Zhou, F. Bai and C. Wang, Magnetic separation of microparticles by shape, Lab Chip, 2017, 17(3), 401–406, 10.1039/C6LC01382A.
- Q. Cao, Z. Li, Z. Wang and X. Han, Rotational motion and lateral migration of an elliptical magnetic particle in a microchannel under a uniform magnetic field, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 2017, 22(1), 3, DOI:10.1007/s10404-017-2025-1.
- J. Zhang and C. Wang, Numerical Study of Lateral Migration of Elliptical Magnetic Microparticles in Microchannels in Uniform Magnetic Fields, Magnetochemistry, 2018, 4(1), 16, DOI:10.3390/magnetochemistry4010016.
- V. Haehnel, F. Z. Khan, G. Mutschke, C. Cierpka, M. Uhlemann and I. Fritsch, Combining magnetic forces for contactless manipulation of fluids in microelectrode-microfluidic systems, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9(1), 5103, DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-41284-0.
- P. Zhang, H. Bachman, A. Ozcelik and T. J. Huang, Acoustic Microfluidics, Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2020, 13(1), 17–43, DOI:10.1146/annurev-anchem-090919-102205.
- S. Sachs, D. Schreier, F. Brand, K. S. Drese, C. Cierpka and J. König, Interplay of acoustophoresis and dielectrophoresis in a standing surface acoustic wave field: from spherical to non-spherical particles, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 2024, 28(10), 67, DOI:10.1007/s10404-024-02762-8.
- J. Dual, P. Hahn, I. Leibacher, D. Möller, T. Schwarz and J. Wang, Acoustofluidics 19: Ultrasonic microrobotics in cavities: devices and numerical simulation, Lab Chip, 2012, 12(20), 4010–4021, 10.1039/C2LC40733G.
- A. A. Doinikov, Acoustic radiation force on a spherical particle in a viscous heat-conducting fluid. I. General formula, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 1997, 101(2), 713–721, DOI:10.1121/1.418035.
- G. Destgeer, B. H. Ha, J. Park, J. H. Jung, A. Alazzam and H. J. Sung, Microchannel anechoic corner for size-selective separation and medium exchange via traveling surface acoustic waves, Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(9), 4627–4632, DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00525.
- G. Destgeer, J. H. Jung, J. Park, H. Ahmed, K. Park and R. Ahmad, et al., Acoustic impedance-based manipulation of elastic microspheres using travelling surface acoustic waves, RSC Adv., 2017, 7(36), 22524–22530, 10.1039/C7RA01168G.
- R. Guldiken, M. C. Jo, N. D. Gallant, U. Demirci and J. Zhe, Sheathless Size-Based Acoustic Particle Separation, Sensors, 2012, 12(1), 905–922, DOI:10.3390/s120100905.
- P. Li, J. Zhong, N. Liu, X. Lu, M. Liang and Y. Ai, Physical properties-based microparticle sorting at submicron resolution using a tunable acoustofluidic device, Sens. Actuators, B, 2021, 344, 130203, DOI:10.1016/j.snb.2021.130203.
- S. Sachs, J. König and C. Cierpka, Multidimensional Particle Separation by Tilted-Angle Standing Surface Acoustic Waves—Physics, Control, and Design, Powders, 2025, 4(1), 2, DOI:10.3390/powders4010002.
- M. S. Khan, M. A. Sahin, G. Destgeer and J. Park, Residue-free acoustofluidic manipulation of microparticles via removal of microchannel anechoic corner, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2022, 89, 106161, DOI:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106161.
- M. Pessoa and A. Neves, Acoustic scattering and forces on an arbitrarily sized fluid sphere by a general acoustic field, J. Sound Vib., 2020, 479, 115373, DOI:10.1016/j.jsv.2020.115373.
- F. Wijaya and K.-M. Lim, Numerical Calculation of Acoustic Radiation Force and Torque Acting on Rigid Non-spherical Particles, Acta Acust. Acust., 2015, 101(3), 531–542, DOI:10.3813/AAA.918850.
- S. Sachs, H. Schmidt, C. Cierpka and J. König, On the behavior of prolate spheroids in a standing surface acoustic wave field, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 2023, 27(12), 81, DOI:10.1007/s10404-023-02690-z.
- O. Jakobsson, M. Antfolk and T. Laurell, Continuous flow two-dimensional acoustic orientation of nonspherical cells, Anal. Chem., 2014, 86(12), 6111–6114, DOI:10.1021/ac5012602.
- A. Garbin, I. Leibacher, P. Hahn, H. Le Ferrand, A. Studart and J. Dual, Acoustophoresis of disk-shaped microparticles: A numerical and experimental study of acoustic radiation forces and torques, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2015, 138(5), 2759–2769, DOI:10.1121/1.4932589.
- T. Schwarz, G. Petit-Pierre and J. Dual, Rotation of non-spherical micro-particles by amplitude modulation of superimposed orthogonal ultrasonic modes, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2013, 133(3), 1260–1268, DOI:10.1121/1.4776209.
- T. Schwarz, P. Hahn, G. Petit-Pierre and J. Dual, Rotation of fibers and other non-spherical particles by the acoustic radiation torque, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 2014, 18, 65–79, DOI:10.1007/s10404-014-1408-9.
- T. Tang and L. Huang, An efficient semi-analytical procedure to calculate acoustic radiation force and torque for axisymmetric irregular bodies, J. Sound Vib., 2022, 532, 117012, DOI:10.1016/j.jsv.2022.117012.
- G. T. Silva, Acoustic radiation force and torque on an absorbing compressible particle in an inviscid fluid, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2014, 136(5), 2405–2413, DOI:10.1121/1.4895691.
- J. P. Leão-Neto, M. Hoyos, J. L. Aider and G. T. Silva, Acoustic radiation force and torque on spheroidal particles in an ideal cylindrical chamber, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2021, 149(1), 285, DOI:10.1121/10.0003046.
- J. Wang and J. Dual, Theoretical and numerical calculations for the time-averaged acoustic force and torque acting on a rigid cylinder of arbitrary size in a low viscosity fluid, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2011, 129(6), 3490–3501, DOI:10.1121/1.3589247.
- Z. Gong, P. L. Marston and W. Li, $T$-matrix evaluation of three-dimensional acoustic radiation forces on nonspherical objects in Bessel beams with arbitrary order and location, Phys. Rev. E, 2019, 99(6), 063004, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.99.063004.
- J. Wang and J. Dual, Theoretical and numerical calculation of the acoustic radiation force acting on a circular rigid cylinder near a flat wall in a standing wave excitation in an ideal fluid, Ultrasonics, 2012, 52(2), 325–332, DOI:10.1016/j.ultras.2011.09.002.
- G. T. Silva and B. W. Drinkwater, Acoustic radiation force exerted on a small spheroidal rigid particle by a beam of arbitrary wavefront: Examples of traveling and standing plane waves, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2018, 144(5), EL453, DOI:10.1121/1.5080529.
- T. S. Jerome, Y. A. Ilinskii, E. A. Zabolotskaya and M. F. Hamilton, Acoustic radiation torque on a compressible spheroid, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2021, 149(3), 2081, DOI:10.1121/10.0003813.
- E. B. Lima and G. T. Silva, Mean acoustic fields exerted on a subwavelength axisymmetric particlea, J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 2021, 150(1), 376–384, DOI:10.1121/10.0005625.
- P. Hahn, I. Leibacher, T. Baasch and J. Dual, Numerical simulation of acoustofluidic manipulation by radiation forces and acoustic streaming for complex particles, Lab Chip, 2015, 15(22), 4302–4313, 10.1039/C5LC00866B.
- S. Z. Hoque, K. Bhattacharyya and A. K. Sen, Dynamical motion of an oblate shaped particle exposed to an acoustic standing wave in a microchannel, Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2022, 7(11), 114204, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevFluids.7.114204.
- A. Pavlic, P. Nagpure, L. Ermanni and J. Dual, Influence of particle shape and material on the acoustic radiation force and microstreaming in a standing wave, Phys. Rev. E, 2022, 106(1), 015105, DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.106.015105.
- D. J. Collins, T. Alan and A. Neild, Particle separation using virtual deterministic lateral displacement (vDLD), Lab Chip, 2014, 14(9), 1595–1603, 10.1039/C3LC51367J.
- E. Alizadeh, J. Castle, A. Quirk, C. D. L. Taylor, W. Xu and A. Prasad, Cellular morphological features are predictive markers of cancer cell state, Comput. Biol. Med., 2020, 126, 104044, DOI:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104044.
- Z. Mousavikhamene, D. J. Sykora, M. Mrksich and N. Bagheri, Morphological features of single cells enable accurate automated classification of cancer from non-cancer cell lines, Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1), 24375, DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-03813-8.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |








