Electron affinities with GPU-accelerated density-fitting EOM-CCSD, approximate EOM-CCSD methods and EOM-CCSD with frozen natural orbitals
Yanmei
Hu
 a,
Zhifan
Wang
a,
Zhifan
Wang
 b and
Fan
Wang
b and
Fan
Wang
 *a
*a
aInstitute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Key Laboratory of High Energy Density Physics and Technology, Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, People's Republic of China. E-mail: wangf44@gmail.com
bCollege of Chemistry and Life Science, Chengdu Normal University, Chengdu 611130, People's Republic of China
First published on 25th November 2025
Abstract
This work employs multiple strategies to reduce computational cost or increase computational efficiency in calculating electron affinities (EAs) based on the equation-of-motion coupled-cluster singles and doubles (EOMEA-CCSD) method. To reduce storage requirements and computational time, an EOMEA-CCSD program is developed with terms involving 〈vv‖vv〉 treated with density-fitting and GPU-acceleration using single-precision data. EAs of 24 medium-sized organic molecules related to organic photovoltaics materials are calculated with this program using the aug-cc-pVXZ (X = D, T and Q) basis sets. Results indicate that the basis set incomplete error on the EAs is significant with the DZ basis set, while the EAs obtained with the TZ and QZ basis sets agree well with each other in the EOMEA-CCSD calculations. The approximate EOM-CCSD method, namely, the corr-CIS(D∞) method with a scaling of N5 and storage of OV3, achieves EAs with a mean absolute deviation (MAD) of about 0.18 eV using the QZ basis. EOMEA-CCSD with frozen natural orbitals (FNO) is also employed to reduce computational cost. Results show that the error of the FNO on EAs is the smallest with NOs from the wavefunction of the electron-attached state (eaNO) with CIS(D∞). The MAD of the EAs is 0.03 eV with eaNO compared with results without FNO when ∼30% virtual orbitals are kept with the QZ basis set. The error of the FNO on the EAs with NOs from the mean density matrix of the electron-attached state with CIS(D∞) and the MP2 density matrix for the reference is larger than that with eaNO. However, its error on the EAs can be estimated reliably from that of CIS(D∞), especially with the TZ and QZ basis sets.
1. Introduction
Electron affinities (EAs) refer to the change in energy when attaching a free electron to an atom or a molecule. In addition, EA is a key metric for evaluating the performance of organic photovoltaic (OPV) materials,1,2 which are extensively utilized in organic solar cells.3 These cells consist of a light-absorption layer and a charge-transport layer and are designed to convert sunlight into electrical energy.4 Organic acceptor molecules are responsible for light absorption, while organic donor molecules facilitate the transfer of electrons and holes, affecting the efficiency of charge transfer and energy conversion.5 The EAs of acceptor molecules are key indicators for evaluating the performance of organic materials and determining optimal material combinations for high-efficiency energy conversion.1 EAs can be obtained experimentally by determining the minimum photon energy required to strip off an electron from an anion.6,7 However, the reliability of experimentally obtained EAs is often not high,8,9 and theoretical calculations are thus important in determining EAs. This necessitates the use of accurate electronic structure methods to ensure the reliability of the obtained EAs.Many methods have been developed to directly compute EAs, such as the extended Koopmans’ theorem based on orbital optimization,10 Green's function and its approximate methods,11,12 and the equation-of-motion coupled-cluster theory for EAs (EOMEA-CC).13–17 Sherrill et al. calculated the first vertical EAs of 24 medium-sized organic molecules related to OPV using the “gold standard” of quantum chemistry, i.e. the coupled-cluster theory at the single and doubles level augmented with perturbative triples (CCSD(T))18 with extensive basis sets.19 These CCSD(T) results serve as references to evaluate the performance of other methods with lower computational cost on EAs.20–22 According to ref. 23, the GW method,11,24 based on Green's function, has an average absolute error exceeding 0.4 eV on EAs, while methods such as NR2,25 ADC(3),26 and P327 can yield EAs with a mean absolute error (MAE) of less than 0.2 eV,22 but their computational scaling is OV4, where O represents the number of occupied orbitals and V represents the number of virtual orbitals. Additionally, the storage requirements for these electron propagator methods are V4, making them challenging to apply to larger systems. For EOMEA-CCSD,28 its computational cost is N6, where N represents the system size, and its storage requirement is V4. It is thus applicable only to relatively small systems or to calculations with a small basis set. VEAs for the 24 molecules with EOMEA-CCSD were calculated with the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set29 recently.30 However, the effects of the basis set on EAs with EOMEA-CCSD deserve further study.
Density-fitting (DF)31,32 has been widely adopted in electronic structure calculations to reduce the storage requirement.33–39 With the DF approximation, only three-index two-electron integrals are needed instead of four-index two-electron integrals. The storage requirement of two-electron integrals with DF scales as N3, thus significantly reducing the time consumed by I/O operations. Previous results show that the error introduced by DF is typically less than 0.03 kJ mol−1 for some reaction energies compared to conventional CCSD(T) results.34 Currently, graphics-processing units (GPUs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in the field of numerical computation and have begun to be widely utilized in various quantum chemistry calculations,40–43 such as density functional theory (DFT),44 the Hartree–Fock (HF) method, and the second-order Møller–Plesset perturbation theory (MP2).45 DF-CCSD codes that make use of GPUs have also been developed.36 Highly efficient CCSD calculations were reported for molecules with about 1300 basis functions.46 By making use of DF and GPUs in EOM-CCSD calculations, EAs for larger systems, or systems with large basis sets, can be obtained.
Introducing certain approximations in the EOMEA-CCSD method can reduce the computational cost of calculating EAs. The most expensive step in the EOMEA-CCSD calculations is solving the CCSD amplitude equations. Approximating the cluster amplitudes with MP2 yields the EOM-CCSD(2) method.47,48 Its computational scaling is N5, and its storage requirement is the same as that of EOMEA-CCSD. One can further approximate the 1h2p–1h2p block in the effective Hamiltonian of the EOM-CCSD(2) method by orbital energy differences, which gives the P-EOM-MBPT2 method.49 Its computational scaling is N5 and storage requirement is OV3, as shown in ref. 50. Neglecting the term involving the cluster amplitudes in the 2p1h–1p block of the effective Hamiltonian leads to CIS(D∞).51 Its computational scaling is N4, and its storage requirement is the same as that of P-EOM-MBPT2.50 Previous work has demonstrated that P-EOM-MBPT2 can provide reasonable electron affinities for light-element systems.52 In our previous work, we introduced a corr-CIS(D∞) method where EAs are obtained from the left and right eigenvectors of CIS(D∞) and the effective Hamiltonian of P-EOM-MBPT2.50 Our results show that EAs from corr-CIS(D∞) closely resemble those of P-EOM-MBPT2, but its computational cost is only about half that of P-EOM-MBPT2.50
A potentially simpler yet equally effective method for reducing computational cost is the frozen natural orbital (FNO) approximation.53–58 Natural orbitals (NOs) and their occupation numbers are eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the one-particle density matrix.54–58 In FNOs, NOs with an occupation number smaller than a threshold are frozen in the calculations. The virtual orbital part of the MP2 density matrix is usually employed to determine NOs and their occupation numbers, and higher-level calculations are carried out with the FNOs from MP2.53,59–62 In EOM-CCSD calculations63,64 for IPs, reliable results can be achieved with the FNOs from the virtual MP2 density matrix.61,62 However, this is not the case for EAs and EEs with EOM-CCSD, since important virtual orbitals for electron-attached states or excited states may be quite different from those for the ground state.62 A previous work shows that at least 85% of the natural orbitals generated by MP2 need to be retained to achieve EAs with an error of 0.1 eV compared with full EOMEA-CCSD results.62 Alternatively, NOs obtained from density matrices with approximate methods, such as CIS(D∞), may be employed in the EOMEA-CCSD calculations. A similar method has been proposed in EOM-CCSD* calculations for IPs with FNOs where the NOs are obtained from ADC(2),65 which is a symmetrized CIS(D∞) method. In addition to the FNO approach, there have been attempts to reduce the computational cost of EOM-CC using localized pair natural orbitals by Dutta et al.66,67
In this study, EOMEA-CCSD using DF on a GPU with different basis sets is applied to 24 medium-sized organic molecules related to OPV, and the obtained EAs are compared to the reference values. Basis set effects on the EAs with the EOMEA-CCSD will be illustrated. In addition, the performance of corr-CIS(D∞) on these EAs will also be investigated. Furthermore, FNO is applied to EOMEA-CCSD calculations with the NOs obtained from CIS(D∞). The error due to the FNOs is estimated with lower-level methods, and the performance of the method is also evaluated. This paper is organized in the following manner: basic theory and implementation details are presented in Section 2, EAs with EOMEA-CCSD and corr-CIS(D∞), as well as those with FNO, are presented in Section 3. Conclusions are drawn in Section 4.
2. Theory
2.1 EOM-CCSD and its approximations
The methods employed for calculating the EAs in this work will be briefly introduced. In EOMEA-CCSD, the EAs are determined from the eigenvalues of the non-symmetric effective Hamiltonian![[H with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0048_0304.gif) = e−THeT in the space spanned by {Φa, Φabi}, where T is the cluster operator, Φa = â†aΦ0, Φabi = âiâ†aâ†bΦ0, âi is an annihilation operator which removes an electron from the occupied orbital i, â†a and â†b are creation operators, which add an electron to virtual orbitals a and b, respectively. The effective Hamiltonian matrix in this space is given by:
= e−THeT in the space spanned by {Φa, Φabi}, where T is the cluster operator, Φa = â†aΦ0, Φabi = âiâ†aâ†bΦ0, âi is an annihilation operator which removes an electron from the occupied orbital i, â†a and â†b are creation operators, which add an electron to virtual orbitals a and b, respectively. The effective Hamiltonian matrix in this space is given by: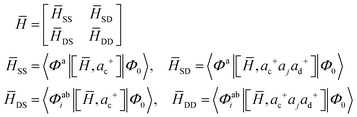 | (1) |
![[H with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0048_0304.gif) SS,
SS, ![[H with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0048_0304.gif) SD,
SD, ![[H with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0048_0304.gif) DS, and
DS, and ![[H with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0048_0304.gif) DD represent the 1p–1p, 1p–2p1h, 2p1h–1p, and 2p1h–2p1h blocks of the effective Hamiltonian matrix, respectively. a, b, … (i, j, …) in eqn (1) and the following are indices for virtual (occupied) orbitals. EOMEA-CCSD can provide reliable EAs, but it is quite expensive for large molecules, as the computational cost for solving the cluster amplitude equations scales as N6. On the other hand, the computational scaling for determining EAs with EOMEA-CCSD is N5, although it is still N6 when calculating some intermediates. In addition, the 〈vv‖vv〉 type two-electron integrals are needed both for solving the amplitude equations and for calculating the EAs with EOMEA-CCSD, where v represents virtual orbitals. Therefore, its storage requirement is V4.
DD represent the 1p–1p, 1p–2p1h, 2p1h–1p, and 2p1h–2p1h blocks of the effective Hamiltonian matrix, respectively. a, b, … (i, j, …) in eqn (1) and the following are indices for virtual (occupied) orbitals. EOMEA-CCSD can provide reliable EAs, but it is quite expensive for large molecules, as the computational cost for solving the cluster amplitude equations scales as N6. On the other hand, the computational scaling for determining EAs with EOMEA-CCSD is N5, although it is still N6 when calculating some intermediates. In addition, the 〈vv‖vv〉 type two-electron integrals are needed both for solving the amplitude equations and for calculating the EAs with EOMEA-CCSD, where v represents virtual orbitals. Therefore, its storage requirement is V4.
P-EOM-MBPT2 can be obtained by approximating the cluster amplitudes with MP2 and replacing the 1h2p–1h2p block of the effective Hamiltonian matrix with orbital energy difference. The effective Hamiltonian matrix in this method thus reads:
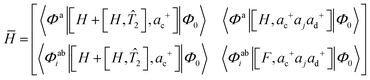 | (2) |
Computational scaling for calculating the eigenvalues of the effective Hamiltonian in eqn (2) is N5, and steps with a computational cost of N6 can be avoided. Furthermore, 〈vv‖vv〉 type two-electron integrals are not required in P-EOM-MBPT2, and its storage requirement is reduced significantly compared with EOMEA-CCSD. One can further reduce computation cost by ignoring the [[H, T2], ac+] term in the 1h2p–1p block of the effective Hamiltonian in P-EOM-MBPT2. This leads to the CIS(D∞) method. The computational effort for determining EAs with CIS(D∞) scales as N4, but there are still non-iterative steps with a scaling of N5, such as integral transformations. Previous works indicated that P-EOM-MBPT2 can provide reasonable EAs, while the error of the EAs with CIS(D∞) is rather pronounced.50 To improve the EAs with CIS(D∞), the corr-CIS(D∞) method is proposed. In this method, the contribution of the [[H, T2], ac+] term in the 1h2p–1p block is treated with the perturbation theory, and the EAs are calculated with the following equation:
EcorrEA = 〈LCIS(D∞)|![[H with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0048_0304.gif) P-EOM-MBPT2|RCIS(D∞)〉 P-EOM-MBPT2|RCIS(D∞)〉 | (3) |
2.2 GPU-based DF-EOM-CCSD method
Two-electron integrals can be obtained from the following equation in DF via the resolution of the identity (RI) approximation31 in PySCF: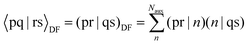 | (4) |
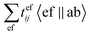 term in the CCSD calculations will be taken as an example in the following discussions, where tefij is the cluster amplitude. It is the term with the highest computational cost in the CCSD calculations and a computational scaling of Nv4No2, where Nv and No are the number of virtual and occupied orbits, respectively. Since 〈ef‖ab〉 = 〈ef|ab〉 − 〈fe|ab〉 = 〈ea|fb) − (fa|eb), this term can be rewritten as the following when DF is introduced:
term in the CCSD calculations will be taken as an example in the following discussions, where tefij is the cluster amplitude. It is the term with the highest computational cost in the CCSD calculations and a computational scaling of Nv4No2, where Nv and No are the number of virtual and occupied orbits, respectively. Since 〈ef‖ab〉 = 〈ef|ab〉 − 〈fe|ab〉 = 〈ea|fb) − (fa|eb), this term can be rewritten as the following when DF is introduced: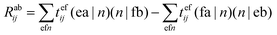 | (5) |
The DF-CCSD and DF-EOMEA-CCSD programs in this work were developed with Fortran 95. All codes were compiled using PGI-20 in combination with Intel MKL and cuBLAS. In the DF-CCSD and DF-EOMEA-CCSD calculations, the terms involving 〈vv‖vv〉 are also among the most expensive steps, especially when the number of virtual orbitals is much larger than the number of occupied orbitals. The programs for CCSD and EOMEA-CCSD calculations are optimized to take advantage of GPU acceleration and single-precision arithmetic for terms involving 〈vv||vv〉, where matrix transposition and compression operations are parallelized on the GPU using OpenACC directives, and matrix contractions are implemented using sgemm from cuBLAS. Other terms in the DF-CCSD and DF-EOMEA-CCSD calculations are computed using the CPU with double-precision arithmetic. Using a node with an Intel I9-10900k CPU and an RTX 3090 GPU, the computation speed for the 〈vv‖vv〉 terms in CCSD and EOMEA-CCSD is increased by about 50-fold, and the CCSD calculation is about 5 times faster when using single-precision data with the GPU for benzoquinone with 20 occupied orbitals and 796 virtual orbitals, compared to calculations with double-precision data on the CPU. We note that computational speed depends on a lot of factors, such as the memory size and I/O speed. In addition, test calculations show that the error introduced by using single-precision data is less than 0.0003 eV for EAs with EOMEA-CCSD compared with results from calculations using double-precision data.
2.3 Natural orbitals for EA in EOMEA-CCSD
The computational cost of coupled-cluster and EOM-CC methods can be significantly reduced by excluding unimportant virtual orbitals from relevant calculations. Directly freezing high-energy canonical virtual orbitals can lead to significant errors, since dynamic correlation effects converge slowly with the size of the virtual orbital space.59–62,65 However, correlation energy has been proven to converge rapidly with the size of the natural orbitals (NO) space, which are eigenfunctions of the correlated one-particle reduced density matrix.53–59 Reliable results can usually be achieved with frozen natural orbitals (FNOs), i.e. those NOs with an occupation number smaller than a predefined threshold.60 In practical calculations, NOs are always determined using the one-particle density matrix obtained from the wave function of a lower-level method. In CC calculations, NOs are typically obtained from MP2 calculations. The virtual–virtual block of the density matrix in MP2 is calculated with: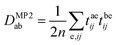 | (6) |
The wavefunction for the electron-attached state with EOMEA-CCSD reads:
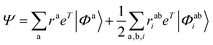 | (7) |
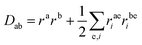 | (8) |
3. Computational details and results
3.1 Computational details
CIS(D∞), corr-CIS(D∞) and EOMEA-CCSD were applied to calculate the EAs of the Koopman-type states, i.e. those dominated by the attachment of one electron without additional excitation, for the 24 selected organic acceptor molecules with the aug-cc-pVXZ (X = D, T and Q) basis sets.71–73 The frozen-core approximation was employed in all the calculations. The geometries of these molecules, which were optimized at the B3LYP75/6-311G**76 level, were taken from ref. 19 and are provided in the SI. The corresponding jkfit auxiliary basis sets77 were employed for the DF in these calculations. Test calculations show that the error of the DF on the EAs is less than 0.002 eV. The convergence criteria for the self-consistent field (SCF) step, CCSD, and EOMEA were set to 10−9, 10−7, and 10−6, respectively. Due to the high computational cost of the EOMEA-CCSD calculations with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set, those calculations are carried out with GPU acceleration and single-precision data. Even with these techniques, we were not able to obtain EAs from EOMEA-CCSD with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set for Cl4-isobenzofurandione, due to the larger number of occupied orbitals, boron-dipyrromethene, due to a lower symmetry, and NDCA and acridine, due to the large number of virtual orbitals. EOMEA-CCSD calculations with frozen NOs using eaNOs, meaNOs and mp2NOs were performed for these molecules with these basis sets. Besides these FNOs, EOMEA-CCSD calculations with the highest virtual HF orbitals frozen were also performed. The errors introduced in the FNOs in the EOMEA-CCSD calculations are discussed below. All these calculations were carried out using locally developed CCSD and EOMEA-CCSD programs using libraries in the CFOUR78,79 program package on the Hefei advanced computing center, while the Hartree–Fock results and three-index integrals in density fitting (DF) were obtained using PySCF.80,813.2 Results
| AVTZ-AVDZ | AVQZ-AVTZ | AVQZ-AVDZ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAD | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.23 |
| MAX | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.27 |
| MIN | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.15 |
The mean deviation (MD), mean absolute deviation (MAD), maximum (MAX) and minimum (MIN) deviation of the EAs calculated with EOM-CCSD using these basis sets compared with reference values19 are presented in Table 2. It can be seen from this table that EAs with the DZ basis set are underestimated to some extent, and their MAD is about 0.21 eV. On the other hand, the MADs of the EAs with the TZ and QZ basis sets are 0.05 eV, and their maximum absolute error is about 0.12 eV. In addition, the MD of the EAs with the QZ basis set is only 0.01 eV, while the EAs with the TZ basis set are somewhat underestimated in most cases. These results show that reliable EAs can be achieved with EOMEA-CCSD using the TZ and QZ basis sets for most of the molecules. It should be noted that the EA of benzonitrile is calculated to be negative with EOMEA-CCSD and CCSD(T), although its experimental EA is positive.19 Special techniques, such as complex absorption potential (CAP), are required to deal with negative EAs, and basis set effects are also pronounced on such EAs, even with CAP.82
| aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Ref. 19. | ||||
| Corr-CIS(D∞) | ||||
| EOMEA-CCSD | MD | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.16 |
| MAD | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.16 | |
| MAX | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.27 | |
| MIN | −0.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Ref.a | MD | −0.2 | 0.07 | 0.18 |
| MAD | 0.2 | 0.10 | 0.18 | |
| MAX | 0.003 | 0.30 | 0.40 | |
| MIN | −0.35 | −0.10 | −0.04 | |
| CIS(D∞) | ||||
| EOMEA-CCSD | MD | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.62 |
| MAD | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.62 | |
| MAX | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.83 | |
| MIN | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.07 | |
| Ref.a | MD | 0.27 | 0.55 | 0.64 |
| MAD | 0.29 | 0.55 | 0.64 | |
| MAX | 0.56 | 0.85 | 0.95 | |
| MIN | −0.13 | −0.03 | 0.02 | |
It can be seen from Table 3 that the EAs obtained using CIS(D∞) are overestimated by about 0.5–0.6 eV compared with the EOM-CCSD results. In contrast, corr-CIS(D∞) significantly improves the accuracy of the EAs.
According to results in Table 3, EAs obtained with corr-CIS(D∞) agree rather well with those of EOM-CCSD using the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set, with a MAD of about 0.05 eV and MAX of 0.15 eV. However, their difference becomes larger with larger basis sets. Corr-CIS(D∞) overestimates the EAs compared with the EOM-CCSD results, and the MADs of the EAs obtained with corr-CIS(D∞) become 0.12 eV and 0.16 eV with the aug-cc-pVTZ and aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets, respectively. EAs obtained with corr-CIS(D∞) agree the best with reference values when the aug-cc-pVTZ basis set is adopted, with a MAD of 0.1 eV and a MAX of about 0.3 eV due to fortuitous error cancellation. On the other hand, the MAD of the EAs is around 0.2 eV, and the maximum error is about 0.4 eV with the aug-cc-pVDZ or aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets. These results indicate that corr-CIS(D∞) can provide reasonable EAs for these molecules, and its mean absolute errors for the EAs of these molecules are similar to those of more expensive methods, such as ADC(3) and P3,22 although its errors remain notable in certain cases.
According to Fig. 1, the error for the FNO on the CCSD reference energy with mp2NO is rather close to that with meanNO. On the other hand, it is significantly larger with eaNO when the same number of NOs are frozen. This is what one would expect since mp2NO is the best for the reference among these Nos. For the energy of the electron-attached state, the error for the FNO is smallest with the meanNO, and that with the mp2NO is slightly larger. The error for the FNO is again the largest with the eaNO. This may be because eaNOs are obtained from the eigenvector of the density matrix in eqn (8) and it does not contain information on the reference state. The situation is completely different when it comes to EAs. The error for the FNO is the smallest with eaNO, and that with meanNO is slightly larger. In fact, the error for FNO with mp2NO is even larger than that with the HF orbitals. To achieve EAs with an error of 0.1 eV, about 20% orbitals are needed with eaNO, and 35% orbitals are required with meanNO for this molecule with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set. On the other hand, about 65% and 78% orbitals are required with HF orbitals and with mp2NO, respectively. This is understandable since the occupation number of mp2NO only provides information on the importance of the virtual orbitals related to the ground state. Virtual orbitals that are important for the electron-attached state may be unimportant for the ground state. The truncation errors of EAs with CIS(D∞) follow the same trend as in EOM-CCSD: eaNO gives the smallest error, followed by meanNO. Interestingly, for an equal number of truncated orbitals, HF orbitals lead to larger errors than MP2 orbitals, opposite to the case for EOM-CCSD. In the following, we only report EOMEA-CCSD results with FNO using eaNOs and meanNOs.
We are discussing vertical EAs in this work. Adiabatic EAs are defined as the sum of the vertical EAs evaluated at the equilibrium geometry of the electron-attached state and the ground-state energy difference between this geometry and that of the neutral species. When the geometries of the neutral and anionic states are similar, and their energy difference is small, both eaNO and meanNO provide reliable adiabatic EAs. However, when the structural relaxation is significant, meanNO gives more accurate ground-state energies and is thus preferred for adiabatic EA calculations.
Errors for the FNOs on EAs obtained with EOMEA-CCSD and CIS(D∞) using meanNOs and eaNOs with these three basis sets are listed in Table SII of the SI. In calculations with meanNOs, a cumulative threshold of 0.005 is adopted, where the summation of the occupation numbers for the frozen NOs is 0.005. On the other hand, a cumulative threshold of 0.00015 is employed with eaNOs. With these thresholds, the number of retained virtual orbitals for the same molecule with these two NOs are close to each other. On the other hand, the percentage of retained orbitals for these molecules varies slightly. The percentages of retained virtual orbitals are roughly 50%, 40%, and 30% with the aug-cc-pVDZ, aug-cc-pVTZ, and aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets, respectively. The mean error (ME), maximum error (MAX) and minimum error (MIN) of the EAs with FNO are presented in Table 4.
| aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| meanNO | ||||
| EOMEA-CCSD | ME | 0.132 | 0.118 | 0.121 |
| MAX | 0.152 | 0.145 | 0.140 | |
| MIN | 0.77 | 0.041 | 0.044 | |
| CIS(D∞) | ME | 0.088 | 0.108 | 0.131 |
| MAX | 0.100 | 0.124 | 0.152 | |
| MIN | 0.074 | 0.042 | 0.046 | |
| eaNO | ||||
| EOMEA-CCSD | ME | 0.029 | 0.028 | 0.033 |
| MAX | 0.051 | 0.058 | 0.066 | |
| MIN | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.009 | |
| CIS(D∞) | ME | 0.022 | 0.040 | 0.057 |
| MAX | 0.024 | 0.047 | 0.067 | |
| MIN | 0.016 | 0.021 | 0.023 | |
One can see from Table 4 that the EAs are always overestimated with FNOs. Our results show that the error for the FNO on EAs with CIS(D∞) is smaller than that for EOMEA-CCSD with the aug-cc-pVDZ and aug-cc-pVTZ basis sets when meanNOs are employed. However, the FNO error for EAs with EOMEA-CCSD is even smaller with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets, although the NOs are obtained from CIS(D∞). For results with eaNOs, the error of the FNOs with EOMEA-CCSD is larger than that of CIS(D∞) only with the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set. With these thresholds, the mean errors of the FNOs on the EAs with EOMEA-CCSD using these basis sets are about 0.12 eV with meanNOs, while they are about 0.03 eV with eaNOs. This again confirms that the error of the FNOs on the EAs with eaNOs is smaller than that with meanNOs.
The maximum FNO errors for the EAs reach 0.15 eV with meanNOs, but they are only 0.05–0.06 eV with eaNOs. This means the error of the FNOs on EAs is non-negligible for some molecules, even with eaNOs. To achieve an even smaller error on the EAs with the FNOs, a smaller threshold is required, which will increase the computational cost. In addition, EOMEA-CCSD calculations with FNOs using a smaller threshold will be expensive for even larger systems. Alternatively, one may estimate the error of the FNOs on the EAs with EOMEA-CCSD from that with CIS(D∞). The EAs can thus be calculated with the following equation:
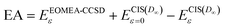 | (9) |
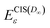 denote EAs obtained with EOMEA-CCSD and CIS(D∞), respectively, using FNO with a cumulative threshold ε. The ME, MAE, MAX and MIN of EAs with eqn (9) compared to the EOMEA-CCSD results without FNO using aug-cc-pVXZ basis sets (X = D, T and Q) with meanNO and eaNO are listed in Table 5. One can see from this table that the MAE of the EAs obtained with eqn (9) using the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set and meanNO is 0.044 eV with a maximum absolute error of about 0.06 eV. The error of EAs obtained with eqn (9) is indeed reduced to a large extent compared with those using FNO, but the error of the EAs with eqn (9) using the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set and meanNO is still non-negligible. On the other hand, the MAE and the maximum absolute error of the EAs using the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set are only about 0.01 eV and 0.027 eV, respectively, when eaNOs are employed.
denote EAs obtained with EOMEA-CCSD and CIS(D∞), respectively, using FNO with a cumulative threshold ε. The ME, MAE, MAX and MIN of EAs with eqn (9) compared to the EOMEA-CCSD results without FNO using aug-cc-pVXZ basis sets (X = D, T and Q) with meanNO and eaNO are listed in Table 5. One can see from this table that the MAE of the EAs obtained with eqn (9) using the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set and meanNO is 0.044 eV with a maximum absolute error of about 0.06 eV. The error of EAs obtained with eqn (9) is indeed reduced to a large extent compared with those using FNO, but the error of the EAs with eqn (9) using the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set and meanNO is still non-negligible. On the other hand, the MAE and the maximum absolute error of the EAs using the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set are only about 0.01 eV and 0.027 eV, respectively, when eaNOs are employed.
| aug-cc-pVDZ | aug-cc-pVTZ | aug-cc-pVQZ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| meanNO | eaNO | meanNO | eaNO | meanNO | eaNO | |
| Fumaronitrile | −0.046 | 0.001 | −0.013 | 0.024 | 0.007 | 0.034 |
| Maleic anhydride | −0.052 | −0.005 | −0.023 | 0.016 | 0.000 | 0.025 |
| TCNE | −0.054 | 0.013 | −0.002 | 0.031 | 0.011 | 0.035 |
| Benzoquinone | −0.047 | −0.008 | −0.022 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.028 |
| F4-benzoquinone | −0.043 | −0.002 | −0.002 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.025 |
| Cl4-benzoquinone | −0.059 | −0.027 | −0.018 | −0.011 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Benzonitrile | −0.003 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.014 |
| F4-benzenedicarbonitrile | −0.047 | −0.018 | −0.005 | −0.001 | 0.007 | 0.01 |
| mDCNB | −0.043 | −0.001 | −0.005 | 0.02 | 0.014 | 0.03 |
| Nitrobenzene | −0.052 | −0.005 | −0.019 | 0.015 | 0.009 | 0.031 |
| Nitrobenzonitrile | −0.052 | −0.003 | −0.013 | 0.019 | 0.009 | 0.034 |
| Phthalic anhydride | −0.048 | −0.006 | −0.016 | 0.014 | 0.009 | 0.029 |
| Cl4-isobenzofurandione | −0.045 | −0.015 | −0.003 | 0.002 | ||
| Phthalimide | −0.046 | −0.008 | −0.018 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.029 |
| Dinitrobenzonitrile | −0.054 | −0.026 | −0.009 | −0.01 | 0.009 | 0.001 |
| Naphthalenedione | −0.043 | −0.011 | −0.015 | 0.011 | 0.010 | 0.029 |
| Azulene | −0.036 | −0.018 | −0.006 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 0.019 |
| Dichlone | −0.043 | −0.009 | −0.010 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.025 |
| TCNQ | −0.043 | 0.000 | −0.002 | 0.021 | 0.013 | 0.03 |
| Boron-dipyrromethene | −0.036 | −0.015 | −0.006 | 0.006 | ||
| NDCA | −0.041 | 0.000 | −0.009 | 0.022 | ||
| Phenazine | −0.041 | −0.011 | −0.011 | 0.011 | 0.016 | 0.029 |
| Acridine | −0.038 | −0.009 | −0.008 | 0.015 | ||
| Anthracene | −0.038 | −0.008 | −0.006 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.033 |
| ME | −0.044 | −0.008 | −0.010 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.025 |
| MAE | 0.044 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.025 |
| MAX | −0.003 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.019 | 0.035 |
| MIN | −0.059 | −0.027 | −0.023 | −0.011 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
However, we note that errors of the EAs obtained with eqn (9) reduce when the basis set increases with meanNOs, while they increase with the basis set using eaNOs. The MAE and maximum absolute error of the EAs obtained from eqn (9) with the aug-cc-pVTZ and aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets are 0.01 eV and about 0.02 eV, respectively, when meanNOs are employed; they are about 0.02 eV and 0.031–0.035 eV with eaNOs. This result means that the errors of the EAs with FNOs using EOMEA-CCSD are rather close to those with CIS(D∞) with the aug-cc-pVTZ and aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets when meanNOs are adopted. To further confirm the accuracy of the EAs obtained with eqn (9) using meanNOs, calculations were also performed with thresholds of 0.003 and 0.007, and the errors on the EAs in these two cases were 0.005–0.02 eV and 0.005–0.025 eV, respectively. These results indicate that the errors of the EAs using the FNOs with EOMEA-CCSD are rather close to those with CIS(D∞), and eqn (9) can provide reliable estimates for the EAs with the aug-cc-pVTZ and aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets when meanNOs are employed. On the other hand, the errors of the EAs obtained with eqn (9) and the aug-cc-pVTZ and aug-cc-pVQZ basis sets are slightly larger using eaNOs compared with the EOMEA-CCSD results without FNOs. Compared with reference values, the MAEs of the EAs obtained from eqn (9) using the aug-cc-pVTZ basis set with eaNO and meanNO are 0.06 eV and 0.07 eV, respectively, and they are 0.05 eV and 0.04 eV, respectively, with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set.
4. Conclusion
In this work, density-fitting for 〈vv‖vv〉 type two-electron integrals is employed to reduce the storage requirement in CCSD and EOMEA-CCSD calculations for EAs of larger molecules or molecules with a larger basis set. In addition, GPU acceleration with single-precision data is also adopted in EOMEA-CCSD calculations for terms involving 〈vv‖vv〉. This GPU-accelerated DF-EOMEA-CCSD program can be applied to systems with up to 1600 virtual orbitals with D2h symmetry. EAs of 24 medium-sized organic molecules related to OPV are obtained using the aug-cc-pVXZ (X = D, T and Q) basis sets with this program. Our results show that EAs with EOMEA-CCSD using the aug-cc-pVTZ basis set are about 0.17 eV higher than those with the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set on average. On the other hand, EAs increase by about 0.06 eV using the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set compared with those with aug-cc-pVTZ. Compared with the reference values, the MAE of EAs with EOMEA-CCSD is about 0.05 eV with the aug-cc-pVTZ or aug-cc-pVQZ basis set, whereas it rises to 0.21 eV with the aug-cc-pVDZ basis set. These results indicate that using a large basis set, such as aug-cc-pVQZ, is important for calculating EAs with EOMEA-CCSD.To reduce the computational cost, the approximate method, i.e., corr-CIS(D∞), is adopted. EAs obtained with corr-CIS(D∞) closely resemble those with P-EOM-MBPT2. Our results show that the MADs of the EAs with corr-CIS(D∞) compared with EOMEA-CCSD results increase with the basis set. Reasonable EAs can still be achieved using corr-CIS(D∞) at a low computational cost, with a MAD of about 0.16 eV compared to EOMEA-CCSD results with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set. Compared with the reference values, the MAD of EAs with corr-CIS(D∞) is 0.18 eV with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set. Furthermore, FNO is also adopted in EOMEA-CCSD calculations to reduce the computational cost. Our results show that the error for FNO is smaller with eaNO than with meanNO. When about 30% virtual orbitals are kept with the aug-cc-pVQZ basis set, the MAEs of the EAs for eaNO and meanNO are 0.03 eV and 0.12 eV, respectively. In addition, our results show that the error for FNO with meanNO in EOMEA-CCSD can be reliably estimated with that of CIS(D∞), especially when a large basis set is chosen. The mean absolute errors of the EAs obtained in this way are about 0.01 eV compared with EOMEA-CCSD results without FNO. On the other hand, the error of the EAs obtained in this way with eaNO is slightly larger. These methods can be employed to obtain reliable EAs for larger systems with a large basis set. Furthermore, it is also possible to estimate EAs with EOMEA-CCSD at the complete basis set (CBS) limit using this approach from EOMEA-CCSD with FNOs and the truncation error obtained from CIS(D∞) at CBS limit or from large basis sets that approximate the CBS limit.
Author contributions
Yanmei Hu: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, writing – original draft. Zhifan Wang: software. Fan Wang: writing – review & editing.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Data availability
The data supporting this study are available with the article.The data supporting this article have been included as part of the supplementary information (SI). Supplementary information: Electron affinities obtained from EOMEA-CCSD and approximate EOM-CCSD methods (Table SI); errors of FNOs on EAs with EOMEA-CCSD and CIS(D∞) using meanNOs and eaNOs (Table SII). See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5cp03020j.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22373070).References
- B. Kippelen and J. L. Brédas, Organic photovoltaics, Energy Environ. Sci., 2009, 2, 251–261 RSC.
- J. L. Delgado, P. A. Bouit, S. Filippone, M. Á. Herranz and N. Martín, Organic photovoltaics: A chemical approach, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 4853–4865 RSC.
- M. Grätzel, Photoelectrochemical cells, Nature, 2001, 414, 338–344 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Li, R. Zhu and Y. Yang, Polymer solar cells, Nat. Photonics, 2012, 6, 153–161 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Yan, S. Barlow, Z. Wang, H. Yan, A. K.-Y. Jen, S. R. Marder and X. Zhan, Non-fullerene acceptors for organic solar cells, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2018, 3, 18003 CrossRef CAS.
- K. P. Huber and G. Herzberg, Molecular Spectra and Molecular Structure IV. Constants of Diatomic Molecules, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, 1979 Search PubMed.
- C. Blondel, C. Delsart, C. Valli and C. Drag, Electron affinities of 16O, 17O, 18O, the fine structure of 16O−, and the hyperfine structure of 17O−, Phys. Rev. A:At., Mol., Opt. Phys., 2001, 64, 052504 CrossRef.
- J. C. Rienstra-Kiracofe, G. S. Tschumper, H. F. Schaefer, S. Nandi and G. B. Ellison, Atomic and molecular electron affinities: Photoelectron experiments and theoretical computations, Chem. Rev., 2002, 102, 231–282 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. G. Lias and J. E. Bartmess, Gas-Phase Ion Thermochemistry, National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2012, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ion/ (accessed July 24, 2025) Search PubMed.
- U. Bozkaya, Accurate electron affinities from the extended Koopmans’ theorem based on orbital-optimized methods, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2014, 10, 2041–2048 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Hedin, New method for calculating the one-particle Green's function with application to the electron-gas problem, Phys. Rev., 1965, 139, A796–A823 CrossRef.
- J. Linderberg and Y. Öhrn, Propagators in Quantum Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, 2004 Search PubMed.
- R. J. Bartlett and M. Musiał, Coupled-cluster theory in quantum chemistry, Rev. Mod. Phys., 2007, 79, 291–352 CrossRef CAS.
- D. I. Lyakh, M. Musiał, V. F. Lotrich and R. J. Bartlett, Multireference nature of chemistry: The coupled-cluster view, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 182–243 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Bartlett, The coupled-cluster revolution, Mol. Phys., 2010, 108, 2905–2920 CrossRef CAS.
- A. I. Krylov, Equation-of-motion coupled-cluster methods for open-shell and electronically excited species: The hitchhiker's guide to Fock space, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2008, 59, 433–462 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Bartlett, Coupled-cluster theory and its equation-of-motion extensions, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.:Comput. Mol. Sci., 2012, 2, 126–138 CAS.
- K. Raghavachari, G. W. Trucks, J. A. Pople and M. Head-Gordon, A fifth-order perturbation comparison of electron correlation theories, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1989, 157, 479–483 CrossRef CAS.
- R. M. Richard, M. S. Marshall, O. Dolgounitcheva, J. V. Ortiz, J. L. Brédas, N. Marom and C. D. Sherrill, Accurate ionization potentials and electron affinities of acceptor molecules I. Reference data at the CCSD(T) complete basis set limit, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2016, 12, 595–604 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Gallandi, N. Marom, P. Rinke and T. Körzdörfer, Accurate ionization potentials and electron affinities of acceptor molecules II: Non-empirically tuned long-range corrected hybrid functionals, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2016, 12, 605–614 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Knight, X. Wang, L. Gallandi, O. Dolgounitcheva, X. Ren, J. V. Ortiz, P. Rinke, T. Körzdörfer and N. Marom, Accurate ionization potentials and electron affinities of acceptor molecules III: A benchmark of GW methods, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2016, 12, 615–626 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Dolgounitcheva, M. Díaz-Tinoco, V. G. Zakrzewski, R. M. Richard, N. Marom, C. D. Sherrill and J. V. Ortiz, Accurate ionization potentials and electron affinities of acceptor molecules IV: Electron-propagator methods, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2016, 12, 627–637 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. van Setten, F. Caruso, S. Sharifzadeh, X. Ren, M. Scheffler, F. Liu, J. Lischner, L. Lin, J. R. Deslippe, S. G. Louie, C. Yang, F. Weigend, J. B. Neaton, F. Evers and P. Rinke, GW100: Benchmarking G0W0 for molecular systems, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2015, 11, 5665–5687 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Golze, M. Dvorak and P. Rinke, The GW compendium: A practical guide to theoretical photoemission spectroscopy, Front. Chem., 2019, 7, 377 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Christiansen, P. Jørgensen and C. Hättig, Response functions from Fourier component perturbation theory applied to a time-averaged quasienergy, Int. J. Quantum Chem., 1998, 68, 1–52 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Hellweg, S. A. Grün and C. Hättig, Benchmarking the performance of spin-component scaled CC2 in ground and electronically excited states, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2008, 10, 4119–4127 RSC.
- J. V. Ortiz, Partial third-order quasiparticle theory: Comparisons for closed-shell ionization energies and an application to the borazine photoelectron spectrum, J. Chem. Phys., 1996, 104, 7599–7605 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Nooijen and R. J. Bartlett, Equation of motion coupled cluster method for electron attachment, J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 102, 3629–3647 CrossRef CAS.
- R. A. Kendall, T. H. Dunning and R. J. Harrison, Electron affinities of the first-row atoms revisited. Systematic basis sets and wave functions, J. Chem. Phys., 1992, 96, 6796–6806 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Shaalan Alag, D. P. Jelenfi, A. Tajti and P. G. Szalay, Accurate evaluation of coupled-cluster ionization potentials and electron affinities via excitation energy calculations, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2022, 18, 6794–6801 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Vahtras, J. Almlöf and M. W. Feyereisen, Integral approximations for LCAO-SCF calculations, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1993, 213, 514–518 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Van Alsenoy, Ab initio calculations on large molecules: The multiplicative integral approximation, J. Comput. Chem., 1988, 9, 620–626 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Kats, T. Korona and M. Schütz, Transition strengths and first-order properties of excited states from local coupled cluster CC2 response theory with density fitting, J. Chem. Phys., 2007, 127, 064107 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. E. DePrince and C. D. Sherrill, Accuracy and Efficiency of Coupled-Cluster Theory Using Density Fitting/Cholesky Decomposition, Frozen Natural Orbitals, and a t1-Transformed Hamiltonian, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2013, 9, 2687–2696 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Epifanovsky, D. Zuev, X. Feng, K. Khistyaev, Y. Shao and A. I. Krylov, General implementation of the resolution-of-the-identity and Cholesky representations of electron repulsion integrals within coupled-cluster and equation-of-motion methods, J. Chem. Phys., 2013, 139, 134105 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. E. DePrince, M. R. Kennedy, B. G. Sumpter and C. D. Sherrill, Density-fitted singles and doubles coupled cluster on graphics processing units, Mol. Phys., 2014, 112, 844–852 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Lesiuk, A straightforward a posteriori method for reduction of density-fitting error in coupled-cluster calculations, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, 044104 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Bozkaya and C. D. Sherrill, Analytic energy gradients for the coupled-cluster singles and doubles with perturbative triples method with the density-fitting approximation, J. Chem. Phys., 2017, 147, 044104 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Shen, Z. Zhu, I. Y. Zhang and M. Scheffler, Massive-parallel implementation of the resolution-of-identity coupled-cluster approaches in the numeric atom-centered orbital framework for molecular systems, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2019, 15, 4721–4734 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Harvey and G. De Fabritiis, A survey of computational molecular science using graphics processing units, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.:Comput. Mol. Sci., 2012, 2, 734–742 Search PubMed.
- R. C. Walker and A. W. Götz, Electronic Structure Calculations on Graphics Processing Units: From Quantum Chemistry to Condensed Matter Physics, John Wiley & Sons, 2016 Search PubMed.
- Z. Wang, B. Huang, Y. Lu and F. Wang, Single-precision CCSD and CCSD(T) calculations with density fitting approximations on graphics processing units, Acta Chim. Sin., 2022, 80, 1401–1410 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wang, M. Guo and F. Wang, Single-precision open-shell CCSD and CCSD(T) calculations on graphics processing units, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2020, 22, 25103–25111 RSC.
- R. G. Parr and W. Yang, Density-Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules (New York, 1995, online edn, Oxford Academic, 12 Nov. 2020), accessed 24 July 2025 DOI:10.1093/oso/9780195092769.001.0001.
- R. J. Bartlett and G. D. Purvis, Many-body perturbation theory, coupled-pair many-electron theory, and the importance of quadruple excitations for the correlation problem, Int. J. Quantum Chem., 1978, 14, 561–581 CrossRef CAS.
- B. S. Fales, E. R. Curtis, K. G. Johnson, D. Lahana, S. Seritan, Y. Wang, H. Weir, T. J. Martínez and E. G. Hohenstein, Performance of Coupled-Cluster Singles and Doubles on Modern Stream Processing Architectures, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2020, 16, 4021–4028 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. F. Stanton and J. Gauss, Perturbative treatment of the similarity transformed Hamiltonian in equation-of-motion coupled-cluster approximations, J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 103, 1064–1076 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Nooijen and J. G. Snijders, Second order many-body perturbation approximations to the coupled cluster Green's function, J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 102, 1681–1688 CrossRef CAS.
- S. R. Gwaltney, M. Nooijen and R. J. Bartlett, Simplified methods for equation-of-motion coupled-cluster excited state calculations, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1996, 248, 189–198 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Ma, Z. Wang, M. Guo and F. Wang, Approximate equation-of-motion coupled-cluster methods for electron affinities of closed-shell molecules, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, 124111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Head-Gordon, M. Oumi and D. Maurice, Quasidegenerate second-order perturbation corrections to single-excitation configuration interaction, Mol. Phys., 1999, 96, 593–602 CAS.
- A. K. Dutta, J. Gupta, H. Pathak, N. Vaval and S. Pal, Partitioned EOMEA-MBPT(2): An Efficient N5 Scaling Method for Calculation of Electron Affinities, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2014, 10, 1923–1933 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. R. Nagy, L. Gyevi-Nagy and M. Kállay, Basis set truncation corrections for improved frozen natural orbital CCSD(T) energies, Mol. Phys., 2021, 119, e1963495 CrossRef.
- P. O. Löwdin, Quantum theory of many-particle systems. I. Physical interpretations by means of density matrices, natural spin-orbitals, and convergence problems in the method of configurational interaction, Phys. Rev., 1955, 97, 1474–1489 CrossRef.
- T. R. Barr and E. R. Davidson, Nature of the Configuration-Interaction Method in Ab Initio Calculations. I. Ne Ground State, Phys. Rev. A:At., Mol., Opt. Phys., 1970, 1, 644–658 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Meyer, PNO–CI Studies of electron correlation effects. I. Configuration expansion by means of nonorthogonal orbitals, and application to the ground state and ionized states of methane, J. Chem. Phys., 1973, 58, 1017–1035 CrossRef CAS.
- P. J. Hay, On the calculation of natural orbitals by perturbation theory, J. Chem. Phys., 1973, 59, 2468–2475 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ahlrichs, H. Lischka, V. Staemmler and W. Kutzelnigg, PNO–CI (pair natural orbital configuration interaction) and CEPA–PNO (coupled electron pair approximation with pair natural orbitals) calculations of molecular systems. I. Outline of the method for closed-shell states, J. Chem. Phys., 1975, 62, 1225–1234 CrossRef CAS.
- A. G. Taube and R. J. Bartlett, Frozen natural orbitals for coupled-cluster calculations, Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun., 2005, 70, 837–850 CrossRef CAS.
- A. G. Taube and R. J. Bartlett, Frozen natural orbital coupled-cluster theory: Forces and application to decomposition of nitroethane, J. Chem. Phys., 2008, 128, 164101 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Landau, K. Khistyaev, S. Dolgikh and A. I. Krylov, Frozen natural orbitals for ionized states within equation-of-motion coupled-cluster formalism, J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132, 014109 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. W. Windom, A. V. Lam, A. Perera and R. J. Bartlett, An assessment of frozen natural orbitals and band gaps using equation of motion coupled cluster theory: A case study on polyacene and trans-polyacetylene, arXiv, 2024, preprint, arXiv:2402.08776 DOI:10.48550/arXiv.2402.08776.
- D. S. Ranasinghe, J. T. Margraf, A. Perera and R. J. Bartlett, Vertical valence ionization potential benchmarks from equation-of-motion coupled cluster theory and QTP functionals, J. Chem. Phys., 2019, 150, 074108 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Pavliček, Z. W. Windom, A. Perera, R. J. Bartlett and L. M. Mentel, A comparison of QTP functionals against coupled-cluster methods for EAs of small organic molecules, J. Chem. Phys., 2024, 160, 014106 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Manna, B. Jangid, R. Pant and A. K. Dutta, Efficient state-specific natural orbital based equation of motion coupled cluster method for core-ionization energies: Theory, implementation, and benchmark, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2024, 20, 6604–6620 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. K. Dutta, F. Neese and R. Izsák, Towards a pair natural orbital coupled cluster method for excited states, J. Chem. Phys., 2016, 145, 034102 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. K. Dutta, M. Saitow, B. Demoulin, F. Neese and R. Izsák, A domain-based local pair natural orbital implementation of the equation of motion coupled cluster method for electron attached states, J. Chem. Phys., 2019, 150, 164123 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. M. Parrish, C. D. Sherrill, E. G. Hohenstein, S. I. Kokkila and T. J. Martínez, Communication: Acceleration of coupled cluster singles and doubles via orbital-weighted least-squares tensor hypercontraction, J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 140, 181102 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. K. Dutta, F. Neese and R. Izsák, Speeding up equation of motion coupled cluster theory with the chain of spheres approximation, J. Chem. Phys., 2016, 144, 034102 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Datar and D. A. Matthews, Robust Tensor Hypercontraction of the Particle–Particle Ladder Term in Equation-of-Motion Coupled Cluster Theory, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2024, 20, 708–720 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. H. Dunning, Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. I. The atoms boron through neon and hydrogen, J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90, 1007–1023 CrossRef CAS.
- D. E. Woon and T. H. Dunning, Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. III. The atoms aluminum through argon, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 1358–1371 CrossRef CAS.
- D. E. Woon and T. H. Dunning, Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. IV. Calculation of static electrical response properties, J. Chem. Phys., 1994, 100, 2975–2988 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Sommerfeld, Dipole-Bound States as Doorways in (Dissociative) Electron Attachment, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2005, 4, 245–250 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D. Becke, Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 5648–5652 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Krishnan, J. S. Binkley, R. Seeger and J. A. Pople, Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. XX. A basis set for correlated wave functions, J. Chem. Phys., 1980, 72, 650–654 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Weigend, A fully direct RI-HF algorithm: Implementation, optimised auxiliary basis sets, demonstration of accuracy and efficiency, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2002, 4, 4285–4291 RSC.
- J. F. Stanton, J. Gauss, L. Cheng, M. E. Harding, D. A. Matthews, P. G. Szalay, et al., CFOUR, Coupled-Cluster Techniques for Computational Chemistry, Quantum-Chemical Program Package (with contributions from A. A. Auer, R. J. Bartlett, U. Benedikt, C. Berger, D. E. Bernholdt, Y. J. Bomble, O. Christiansen, F. Engel, R. Faber, M. Heckert, O. Heun, C. Huber, T.-C. Jagau, D. Jonsson, J. Jusélius, K. Klein, W. J. Lauderdale, F. Lipparini, T. Metzroth, L. A. Muck, D. P. O’Neill, D. R. Price, E. Prochnow, C. Puzzarini, K. Ruud, F. Schiffmann, W. Schwalbach, C. Simmons, S. Stopkowicz, A. Tajti, J. Vázquez, F. Wang, J. D. Watts, and the integral packages MOLECULE (J. Almlöf and P. R. Taylor), PROPS (P. R. Taylor), ABACUS (T. Helgaker, H. J. A. Jensen, P. Jørgensen, and J. Olsen), and ECP routines by A. V. Mitin and C. van Wüllen), https://www.cfour.de (accessed July 24, 2025).
- D. A. Matthews, L. Cheng, M. E. Harding, F. Lipparini, S. Stopkowicz, T.-C. Jagau, P. G. Szalay, J. Gauss and J. F. Stanton, Coupled-cluster techniques for computational chemistry: The CFOUR program package, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, 214108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Sun, X. Zhang, S. Banerjee, P. Bao, M. Barbry, N. S. Blunt, N. A. Bogdanov, G. H. Booth, J. Chen, Z.-H. Cui, J. J. Eriksen, Y. Gao, S. Guo, J. Hermann, M. R. Hermes, K. Koh, P. Koval, S. Lehtola, Z. Li, J. Liu, N. Mardirossian, J. D. McClain, M. Motta, B. Mussard, H. Q. Pham, A. Pulkin, W. Purwanto, P. J. Robinson, E. Ronca, E. R. Sayfutyarova, M. Scheurer, H. F. Schurkus, J. E. T. Smith, C. Sun, S.-N. Sun, S. Upadhyay, L. K. Wagner, X. Wang, A. White, J. D. Whitfield, M. J. Williamson, S. Wouters, J. Yang, J. M. Yu, T. Zhu, T. C. Berkelbach, S. Sharma, A. Y. Sokolov and G. K.-L. Chan, Recent developments in the PySCF program package, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 153, 024109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Sun, T. C. Berkelbach, N. S. Blunt, G. H. Booth, S. Guo, Z. Li, J. Liu, J. McClain, S. Sharma, S. Wouters and G. K.-L. Chan, PySCF: The Python-based simulations of chemistry framework, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.:Comput. Mol. Sci., 2018, 8, e1340 Search PubMed.
- D. Zuev, T.-C. Jagau, K. B. Bravaya, E. Epifanovsky, Y. Shao, E. Sundstrom, M. Head-Gordon and A. I. Krylov, Complex absorbing potentials within EOM-CC family of methods: Theory, implementation, and benchmarks, J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 141, 024102 CrossRef PubMed.
| This journal is © the Owner Societies 2026 |

