Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleAdvances and future prospects of low-temperature electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries†
Mehdi
Shanbedi
 a,
Hossein
Shahali
a,
Hossein
Shahali
 b,
Andreas A.
Polycarpou
b,
Andreas A.
Polycarpou
 *a and
Ahmad
Amiri
*a and
Ahmad
Amiri
 *ab
*ab
aDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK 74104, USA. E-mail: andreas-polycarpou@utulsa.edu
bRussell School of Chemical Engineering, The University of Tulsa, Tulsa, OK 74104, USA. E-mail: ahmad-amiri@utulsa.edu
First published on 7th May 2025
Abstract
Energy storage is a fundamental requirement in modern society. Among various options, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) stand out as a key solution for energy storage in electrical devices and transportation systems. However, their performance at sub-zero temperatures presents significant challenges, restricting their broader use. This review first outlines the structure and components of LIBs, followed by an exploration of the primary low-temperature limitations, such as reduced ionic conductivity in the bulk electrolyte, slower charge transfer rates, lithium dendrite formation, and decreased diffusion coefficients in the solid electrolyte interface and the cathode electrolyte interface layers. Furthermore, it examines various aqueous and non-aqueous electrolytes, including solvents, lithium salts, and additives, along with a comprehensive overview of advancements in the field. The review aims to provide readers with a thorough understanding of the mechanisms influencing electrolytes at low temperatures and offers guidance for enhancing the applicability of LIBs in cold environments.
Broader contextLithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have become the cornerstone of portable electronics, electric mobility, and stationary energy storage, anchoring the global transition toward low-carbon technologies. Yet, as our energy demands extend beyond conventional environments—into arctic regions, aerospace platforms, and high-altitude systems—the limitations of current battery chemistries become pronounced. In particular, sub-zero temperatures impose severe constraints on battery performance, manifesting as diminished ionic conductivity, suppressed electrochemical kinetics, and interfacial instabilities. These challenges compromise both safety and reliability, undermining mission-critical applications ranging from planetary exploration to cold-chain logistics. This review provides a comprehensive exploration of the material science and electrochemistry underpinning low-temperature LIB operation. It examines the multifaceted barriers—including lithium-ion desolvation, electrolyte viscosity, and interfacial ion transport—and highlights how recent innovations in solvent selection, salt pairing, and molecular additives are shifting the performance envelope. These breakthroughs not only enable operation at extreme temperatures but also open new design pathways for robust, climate-resilient batteries. By integrating insights from materials chemistry, thermal modeling, and device engineering, this work outlines a roadmap for advancing LIB technologies into uncharted operational domains and global sustainability frameworks. |
1. Introduction
In recent decades, humanity has faced a multitude of interconnected global challenges, including global warming, climate change, polar ice melting, environmental pollution, rapid population growth, and food supply shortages. International agreements such as the Kyoto Protocol (1992) and the Paris Agreement (2016), under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, aim to mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Despite ongoing efforts to transition to cleaner energy sources, the demand for energy continues to grow globally. Traditional vehicles powered by gasoline or diesel contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, presenting an environmental challenge. As global energy consumption increases to levels comparable to Europe and the US, fossil fuels are expected to remain a significant energy source for the foreseeable future until alternative solutions, such as advanced nuclear technologies or other innovations, become more widely adopted.1While developed nations have made strides in renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, wave, and nuclear power, these efforts alone are insufficient to meet the growing demand for clean energy. A pivotal solution lies in the development of advanced energy storage systems, which are integral to achieving carbon neutrality. Among these, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have emerged as a cornerstone technology. Introduced over half a century ago, LIBs operate on the principle of lithium-ion migration between the cathode and anode, with electrolytes playing a crucial role in preventing direct current and facilitating ion transport.2,3
Electrolytes, comprising inorganic and organic components, are essential for forming the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on the anode and the cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI) on the cathode. These interphases are vital for efficient lithium-ion transfer and the overall functionality of LIBs. Due to their high energy density, rapid charge–discharge rates, lightweight, and longevity, LIBs have garnered significant attention from researchers and become indispensable in portable electronic devices and energy storage systems.
However, despite substantial advancements, LIBs face notable limitations, particularly in sub-zero environments. At temperatures below 0 °C, the performance of LIBs deteriorates significantly. The key chemical reactions within the electrodes and electrolytes slow down, leading to reduced energy capacity and disrupted charge–discharge cycles. Additionally, the increased viscosity of conventional electrolytes, often based on ethylene carbonate (EC), decreases ionic conductivity and charge transfer rates. This not only heightens internal resistance but also promotes lithium dendrite formation, which can damage battery structures.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches. Current strategies include incorporating solvent additives into multicomponent electrolyte systems to lower freezing points and improve ionic conductivity. Moreover, research is increasingly focused on alternatives to traditional organic electrolytes, such as ionic liquids, ceramics, and liquefied gas solvents, to enhance the low-temperature performance of LIBs. The practical importance of improving LIBs performance in sub-zero conditions spans numerous critical applications. Fig. 1 shows some of the applications and their required lower limit operating temperature. However, these extreme conditions highlight the necessity for specialized battery designs capable of ensuring reliability and efficiency in harsh environments, specifically cold temperatures.
Improving the low-temperature performance of LIBs is critical for expanding their application potential and addressing humanity's energy storage needs, both on Earth and beyond. This review first examines the structure of LIBs, then explores the mechanisms and limitations that arise at sub-zero temperatures. Furthermore, it goes beyond the conventional analysis of electrolyte properties by investigating the characteristics of SEI/CEI layers at low temperatures and how to optimize these layers for enhanced cycle stability. The review also highlights recent advances in electrolyte formulations and additives designed to improve LIB performance under extreme conditions. Finally, it discusses the future outlook for high-energy cells at low temperatures and the specific challenges in this area, which have been less addressed in similar studies.
2. Structure and components of lithium-ion batteries
LIBs are widely recognized today, and it is important to understand what sets them apart from other types of batteries. Fig. 2 illustrates the functional components of a LIBs. The electric current flows through conductive surfaces that connect to the cells-aluminum on one side and copper on the other. Like all batteries, LIBs feature two electrodes: the cathode (positive) and the anode (negative). The cathode is composed of lithium-containing metal oxides, and its uniform chemical composition enhances performance and extends the battery's lifespan. Conversely, the anode consists of carbon-based materials, such as graphite or graphene.An electrolyte layer, serving as the medium for lithium-ion transport, fills the space between the electrodes. To ensure safe charging and discharging, this layer must be as free of water particles as possible. A separator layer is placed between the cathode and anode to prevent short circuits, allowing only lithium ions to pass through. During charging, lithium ions migrate across the separator into the carbon-based anode, where they are stored. This movement facilitates the charging process, while electrons flow in the opposite direction through an external circuit, generating electric current. The potential difference and resistance between the electrodes drive this current. When discharging, lithium ions return to the cathode through the separator, completing the cycle.
The performance of a LIB is directly linked to the quality of its materials. Using highly pure, specially formulated materials results in enhanced performance and longer battery life. Research in this field focuses on improving factors such as lifespan, energy density, thermal stability, cycle life, cost, weight, and charging speed. Cycle life depends on the stability of the SEI at the anode and the CEI at the cathode. Degradation of these layers can lead to capacity loss and reduced performance over time. Ensuring stable SEI and CEI under varying temperatures is critical for safety and longevity, as high temperatures accelerate degradation, and low temperatures hinder lithium-ion intercalation and deintercalation kinetics.
Safety concerns regarding the flammability and volatility of organic solvents in conventional electrolytes have spurred research into non-flammable alternatives, including both aqueous and non-aqueous electrolytes. Most LIBs use electrolytes made from lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents, which are specifically designed to prevent reactivity with water. The battery housing is also sealed to minimize moisture absorption.
Key processes in LIBs include solvation and desolvation. Solvation refers to the interaction of solvent molecules with lithium ions, forming a solvation shell. During desolvation, these shells are stripped away, allowing the lithium ions to intercalate into the electrode material. At low temperatures, solvation dynamics change, potentially forming more rigid solvation shells that hinder desolvation, increase energy requirements, and slow charge transfer kinetics. This leads to diminished battery performance and capacity in cold conditions. Tailored electrolytes and additives are employed to promote stable SEI and CEI layers, even at low temperatures, which is vital for maintaining performance in extreme environments. The overall electrochemical reactions in a LIBs including carbon-based anode can be summarized as follows:
| Charging reaction: LiCoO2 + C ↔ Li1−xCoO2 + LixC + e− |
| Discharging reaction: Li1−xCoO2 + LixC + e− ↔ LiCoO2 + C |
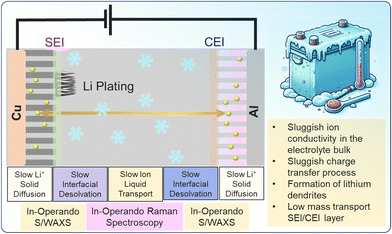
This family of LIBs faces significant challenges at low temperatures. As illustrated in the schematic of Fig. 2, the reduced mobility of lithium ions across the SEI and the CEI layers limits battery performance. At low temperatures, the energy barrier for lithium-ion desolvation increases due to the formation of a more rigid solvation shell, making the process slower and less efficient. Additionally, sluggish ion transport within the electrolyte and reduced ionic conductivity exacerbate these limitations. Low temperatures also heighten the risk of lithium plating on the anode, which can lead to capacity fade and safety risks. The image underscores the need for advanced materials and tailored electrolytes to mitigate these issues, ensuring stable SEI and CEI layers under extreme thermal conditions.
The relationship between electrode materials, electrolyte composition, and lithium-ion dynamics is central to improving LIBs at extreme temperatures. Optimized anode and cathode porosity, tailored electrolyte viscosity, and the use of novel separators with enhanced thermal stability are strategies being explored to mitigate the negative effects of low-temperature operation. Understanding these material interactions is key to achieving reliable battery performance in harsh environments. Furthermore, at low temperatures, the stability and conductivity of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI) become critical factors that dictate battery performance. The SEI, which forms on the anode surface due to electrolyte decomposition, functions as a passivation layer that regulates lithium-ion transport. However, at sub-zero temperatures, the SEI layer becomes more resistive and rigid, impeding lithium-ion diffusion and leading to an increase in interfacial resistance. Similarly, the CEI layer on the cathode may undergo structural instability, further deteriorating charge transfer kinetics. These factors contribute to sluggish charge/discharge rates, lower energy efficiency, and increased risk of lithium plating. Consequently, advanced electrolyte formulations with optimized solvation structures and additives designed to stabilize SEI/CEI at low temperatures have gained significant research interest.4,5
3. Mechanism and main limitations of low-temperature lithium-ion batteries
Four basic factors of the limitation of ionic conductivity in bulk electrolyte, namely, the reduction of charge transfer rate at electrolyte, the formation of lithium dendrites and sluggish diffusion coefficient in SEI and CEI layers and reduced desolvation kinetics have been investigated. Fig. 3 shows a schematic of the main limiting factors (resistances) on the performance of LIBs with low-temperature electrolyte.3.1. Limitation of ionic conductivity in bulk electrolyte
This section explores four fundamental factors limiting the performance of LIBs: the restricted ionic conductivity in the bulk electrolyte, the reduced charge transfer rate at the electrolyte interface, the formation of lithium dendrites, and the slow diffusion coefficients within the SEI and CEI layers.As the temperature decreases, the viscosity of the electrolyte increases, leading to reduced ion mobility and, consequently, a decrease in ionic conductivity. Ionic conductivity (σ), a critical parameter for evaluating an electrolyte's ability to facilitate ion transport, is defined by the following equations:6,7
| σ = ∑niμizie | (1) |
 | (2) |
While aqueous electrolytes generally exhibit higher ionic conductivity than non-aqueous alternatives at room temperature, their performance is hindered at low temperatures (lower 0 °C) due to the higher freezing point of water compared to organic solvent mixtures, such as cyclic and non-cyclic carbonates. This results in a steeper decline in ionic conductivity as temperature decreases.9,10 To address these challenges, an optimal electrolyte formulation requires a balance between low viscosity and high dielectric constant solvents. Such a combination ensures sufficient ion dissociation and mobility while minimizing the risk of electrolyte crystallization, which can severely degrade battery performance at low temperatures,11 less than ethylene carbonate-based electrolyte (EC-based).
3.2. Reduction of charge transfer rate at electrolyte
The efficiency of charge transfer at the electrolyte–electrode interfaces plays a critical role in determining the performance of LIBs, particularly at low temperatures where this process becomes a limiting factor. Charge transfer kinetics are characterized by the charge transfer resistance (Rct), which quantifies the difficulty of this process. Based on the Arrhenius equation and the Butler-Volmer equation, Rct is directly influenced by the activation energy (Ea) associated with the charge transfer process. Higher Ea results in greater Rct, thereby reducing the rate of charge transfer and adversely affecting battery performance at low temperatures.The Rct is described by the Arrhenius equation:
 | (3) |
The Li+ desolvation process, where Li+ loses its solvation sheath before migrating through the SEI,13 and the subsequent migration of the naked Li+ across the resistive SEI, are two critical steps in the diffusion of Li+ from the electrolyte to the anode. Among these, the Li+ desolvation process is generally considered the major contributor to Rct. It can be concluded from eqn (3) that the charge transfer impedance is determined by the temperature and Ea of the charge transfer process.14
The Ea of the charge transfer process depends on the desolvation process of Li+ and the binding energy of Li+ at the electrode surface sites.14,15 Xu et al.15 reported that Li+ desolvation in binary carbonate electrolytes has an Ea value of around 50 kJ mol−1, which is substantially higher than Ea for Li+ conduction through the SEI (20 kJ mol−1). Subsequent research corroborates these findings, showing that Li+ desolvation, rather than Li+ diffusion in solid electrodes or migration through the SEI, is the dominant kinetic barrier to Li+ transport at low temperatures.16 Therefore, enhancing the electrolyte's capability to facilitate Li+ desolvation at the electrode–electrolyte interface is essential for improving LIBs performance at low temperatures.
EIS is a powerful tool for investigating the electrochemical kinetics of LIBs. As shown in Fig. 4a, the Nyquist plot reveals the impedance response of LIB cells over multiple charge–discharge cycles. The impedance consists of three primary components: ohmic resistance (Rb), solid electrolyte interphase (RSEI) resistance, and Rct.17Rct is a crucial parameter that increases at lower temperatures due to hindered Li-ion kinetics.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 EIS analysis of LIBs at low temperatures, illustrating the impact of Rct and electrolyte composition on cell performance. (a) Nyquist plot comparing impedance spectra of LIB and BIF cells over multiple charge–discharge cycles. Reproduced with permission from ref. 17. (b) Temperature-dependent variations of Rb, RSEI, and Rct during cycling, emphasizing the increasing dominance of Rct at low temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 17. (c) Comparative analysis of solvated vs. desolvated lithium-ion transfer at graphite electrodes, highlighting activation energy differences. Reproduced with permission from ref. 18. (d) Arrhenius plot of charge transfer resistance for various electrolytes, illustrating the relationship between solvation structure and temperature-dependent impedance changes. Reproduced with permission from ref. 18. | ||
The influence of temperature on the overall impedance profile is highlighted in Fig. 4b, which presents the variation of Rct as a function of the cycle number.17 The data shows that at subzero temperatures, Rct dominates the total cell resistance, causing performance degradation. These findings align with recent studies emphasizing the critical role of Li+ desolvation and interfacial resistance in determining low-temperature performance.
Charge polarization during low-temperature cycling primarily originates from sluggish Li+ desolvation at the electrode/electrolyte interface, as illustrated in Fig. 4c.18 EIS analysis indicates that the solvation structure and activation energy of lithium-ion desolvation significantly impact charge transfer resistance at subzero temperatures. The transformation of Nyquist plots into distribution of relaxation times (DRT) plots enables better visualization of individual electrochemical processes, aiding in precise diagnosis of interfacial resistance behavior.
Finally, Fig. 4d presents an updated Arrhenius plot of charge transfer resistance for LIB cells with different electrolyte compositions.18 The results indicate that electrolyte formulations with optimized solvation structures exhibit lower activation energy barriers, thus reducing charge transfer resistance at low temperatures. These insights highlight the need for advanced electrolyte engineering to enhance the performance of LIBs under extreme conditions.
At temperatures below −20 °C, Rct becomes nearly equal to the total cell resistance, identifying lithium-ion (Li+) desolvation as the rate-limiting step in the charge transfer process. This finding strongly suggests that Li+ desolvation predominantly dictates the low-temperature performance of rechargeable lithium batteries, provided the effect of ion transport within bulk active materials is excluded. Xu et al. experimentally validated this conclusion.19 They assembled symmetric cells with graphite/graphite, LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 (NCA)/NCA, and Li4Ti5O12 (LTO)/LTO electrodes, all using the same carbonate-based electrolyte. This setup eliminated the influence of multiple electrode materials and solvation structures.
Despite the vastly different interfacial chemistries and material properties of these cells, their EIS spectra at −40 °C were strikingly similar. This similarity was attributed to their identical solvation structures, which created a similar desolvation energy barrier. The desolvation process accounted for most of the impedance at −40 °C. Furthermore, significant variations in low-temperature discharge capacities were observed in cells with the same interfacial chemistry but different electrolytes, confirming that low-temperature performance is more closely tied to the bulk solvation structure than to the SEI chemistry. However, there is ongoing debate about whether the desolvation process is exclusively influenced by the solvation structure in the bulk electrolyte. It is plausible that the SEI or CEI chemistry, as well as the nature of the electrode, could impact the desolvation process by interacting with the solvent molecules or ions in the solvation sheath. These interactions require further investigation using advanced modeling and characterization techniques to provide clarity.20
Low-temperature charging is inherently more challenging than low-temperature discharging. Consequently, many studies on low-temperature electrolytes for LIBs have focused on improving discharge performance after room-temperature charging. Paradoxically, the charge-transfer process at the cathode, which is critical for low-temperature discharge, has been largely overlooked. More in-depth research is needed to better understand and optimize the cathode-side charge-transfer process to enhance the performance of LIBs under low-temperature conditions.
3.3. The formation of lithium dendrites
As operating temperatures decrease, slow lithium-ion diffusion exacerbates non-uniform lithium plating and accelerates dendrite formation near the anode, leading to significant safety concerns and limited battery lifespan. This issue is particularly severe at low temperatures, where LIBs experience considerable capacity loss due to the abnormal growth of the SEI caused by lithium dendrites. These dendrites continuously consume lithium ions during cycling, reducing the available charge and degrading performance.Lithium plating, the direct deposition of lithium metal on the anode surface, occurs due to the mismatch between the rate of lithium-ion reduction and the rate of lithium-ion intercalation into bulk graphite. This phenomenon is largely driven by high overpotentials caused by anode polarization.21,22 Anode polarization includes three main types: ohmic polarization, electrochemical polarization, and concentration polarization. Ohmic polarization arises from the contact resistance between cell components, electrochemical polarization is related to charge transfer processes, and concentration polarization is caused by ion concentration gradients in the electrolyte and electrode.23,24 Together, these polarizations contribute significantly to lithium plating.
Lithium plating is closely tied to the electrolyte, as it affects lithium-ion transport, desolvation, and interfacial diffusion. The transport of Li+ within the bulk electrolyte, its segregation at the electrode/electrolyte interface, and its diffusion through the SEI all influence the plating process. A well-designed electrolyte system can significantly reduce the likelihood of lithium plating. However, at low temperatures, plated lithium reacts poorly during annealing, resulting in low Coulombic efficiency. Historically, research on lithium plating has focused on ambient conditions, particularly in the context of fast charging at room temperature (∼25 °C), a critical performance metric for electric vehicles.25 In such studies, lithium plating is often examined as a factor limiting fast-charging capabilities. However, lithium plating at low temperatures has received comparatively less attention due to the reliance on urban charging infrastructures with pre-heating or indoor facilities that maintain LIBs at moderate temperatures during charging. While these setups mitigate the effects of low-temperature charging, expanding applications in space exploration, military, and defense necessitate a deeper understanding of LIBs behavior under such extreme conditions.
At low temperatures, mass transport and charge transfer kinetics are severely hindered, resulting in large polarization even at low current densities.26,27 The increased polarization significantly lowers the critical current density required for lithium plating during charging, compared to room-temperature conditions. von Lüders et al. studied the characteristics of lithium plating in commercial 18650 LIBs at −2 °C using static voltage and neutron diffraction techniques. Their results revealed that when the charge rate exceeded 0.5C, visible lithium plating occurred on the graphite anode. At 1C charge rate, lithium plating accounted for approximately 10% of the total charging capacity.28
Lithium plating is associated with several challenges, including loss of lithium inventory, formation of dendritic lithium, dead lithium accumulation, additional SEI growth, and gas generation (Fig. 5a). These effects not only degrade battery performance but also pose significant safety risks. For example, at −29 °C, substantial lithium plating in a high-capacity (50 A h) battery caused violent reactions between plated lithium and the electrolyte, generating large quantities of gas. The resulting stress on the electrodes was identified as a key factor in battery failure.29
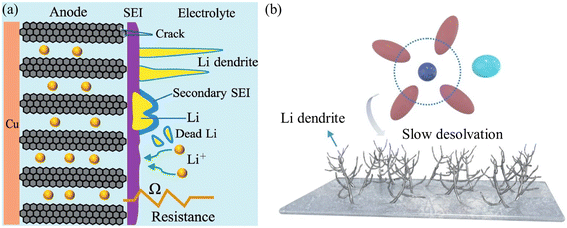 | ||
| Fig. 5 (a) Degradation mechanism caused by lithium plating on a graphite anode at low temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 32. (b) Schematic illustration showing the impact of low temperature on the morphology of lithium deposition. Reproduced with permission from ref. 31. | ||
In lithium–metal batteries (LMBs), the intrinsic electrode reaction involves lithium plating and stripping. However, during low-temperature cycling, issues related to dendrite formation are magnified. Holoubek et al.30 reported that sluggish desolvation at low temperatures exacerbates lithium deposition dynamics, leading to tip-driven dendrite growth. According to Tao Ma et al.,31 the deposition characteristics of lithium at low temperatures are significantly influenced by the solvation properties of the electrolyte. While electrolytes containing solvents with strong solvation abilities typically exhibit enhanced ionic conductivity, they also experience hindered desolvation kinetics. As a result, during lithium plating at low temperatures, the reduction of Li+ ions on the lithium metal surface becomes inefficient, leading to the formation of fewer initial lithium nuclei. Subsequent deposition tends to occur preferentially on these limited nucleation sites, promoting the growth of lithium dendritic structures (Fig. 5b). These rapidly growing dendrites eventually result in short-circuit failure of the cell.
To address these challenges, future research should prioritize the development of advanced electrolytes with improved low-temperature performance. Efforts should also focus on understanding the interaction between the electrolyte, SEI/CEI chemistry, and lithium-ion transport processes. By mitigating lithium plating and dendrite formation, the safety, efficiency, and lifespan of LIBs in extreme environments can be significantly enhanced.
3.4. Sluggish diffusion coefficient in SEI and CEI layers
The influence of the interphase films, including the SEI and CEI, on the charge transfer process in LIBs remains an area of ongoing investigation. While the exact role of these interphases in facilitating or hindering charge transfer is not fully understood, the mass transport of Li+ within the SEI and CEI layers has been identified as a significant contributor to overall cell impedance.Early studies using EIS suggested that the RSEI was consistently lower than the charge transfer resistance at room temperature under EC-based electrolyte conditions.30 However, recent research has questioned this understanding. On one hand, the reliability of EIS results obtained from two-electrode systems has been called into question due to interference from the counter electrode, which may distort impedance measurements.33 On the other hand, the similar time constants of charge transfer and Li+ transport within the SEI often result in their impedance signals overlapping into a single semicircle in EIS spectra (Fig. 6a and b), making it difficult to separate the contributions of RSEI and Rct.34,35
 | ||
Fig. 6 EIS spectra of delithiated Li/MCMB cells using 1 M LiPF6 in EC/PC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 v/v/v) with fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC, squares) and without FEC (circles) at (a) −20 °C and (b) −40 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 34. (c) DRT analysis of the Nyquist plots for graphite electrodes at various temperatures using 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (3 8 v/v/v) with fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC, squares) and without FEC (circles) at (a) −20 °C and (b) −40 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 34. (c) DRT analysis of the Nyquist plots for graphite electrodes at various temperatures using 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7 v/v) electrolyte. Reproduced with permission from ref. 27. (d) RSEI and Rct values of graphite electrodes obtained from EIS fitting at different temperatures using various electrolytes. Reproduced with permission from ref. 27. 7 v/v) electrolyte. Reproduced with permission from ref. 27. (d) RSEI and Rct values of graphite electrodes obtained from EIS fitting at different temperatures using various electrolytes. Reproduced with permission from ref. 27. | ||
To address these challenges, Yao et al. utilized a three-electrode system combined with DRT technology to decouple the intertwined electrochemical processes of charge transfer and interfacial Li+ transport while minimizing the influence of the counter electrode (Fig. 6c).27 Their findings revealed that RSEI was significantly larger than Rct in a Li/Li reference/graphite cell with EC-based electrolytes over a temperature range of −15 °C to 25 °C (Fig. 6d). These results suggest that the high resistance of the SEI, particularly in EC-based systems, makes RSEI the dominant rate-limiting step as temperatures approach sub-zero levels. The rate-limiting step in LIBs performance may also vary depending on the specific electrolyte and temperature range. For example, in low-temperature electrolytes that form high-resistance SEI layers, RSEI may dominate at moderately low temperatures (e.g., above −20 °C). However, as the temperature drops below −20 °C, Rct often becomes the limiting factor due to its steep increase in magnitude. This underscores the importance of tailoring electrolyte properties to balance SEI and charge transfer resistances across a range of operating conditions.
A critical challenge for low-temperature LIBs lies in the instability of many commonly used solvents when interacting with graphite anodes. Solvents capable of functioning well below 20 °C, such as linear carbonates and propylene carbonate (PC), exhibit poor stability on graphite surfaces. These solvents tend to co-intercalate into graphite, leading to structural exfoliation and damage to the anode.6 Furthermore, esters, another class of low-temperature solvents, undergo condensation reactions with lithiated graphite, generating significant amounts of gas. Even at low temperatures, such reactions contribute to extreme instability at the electrode/electrolyte interface.36 This instability manifests as rapid capacity fade, increased cell impedance, and reduced cycling life.
In addition to SEI-related issues, the CEI at the cathode also plays a critical role in determining low-temperature performance. The CEI's chemical composition, spatial structure, and stability significantly influence the interfacial properties and lithium-ion transport dynamics. These factors become even more critical when high-voltage cathodes are introduced to improve the baseline capacity of low-temperature LIBs.37,38 A poorly formed CEI can exacerbate interfacial resistance, lead to side reactions, and further degrade battery performance under extreme conditions. To enhance low-temperature performance, future research needs to prioritize the comprehensive optimization of both SEI and CEI layers. Specific strategies are discussed below:
1. Good SEI/CEI components: Incorporating functional additives that can form robust, low-resistance interphases under low-temperature conditions.41 These additives may include lithium salts with weakly coordinating anions or SEI/CEI-forming agents. A stable SEI and CEI at low temperatures typically consists of inorganic compounds such as LiF and Li2CO3, which provide high ionic conductivity and mechanical stability. Organic components, such as lithium alkyl carbonates, are less stable at low temperatures and can lead to increased impedance.
2. Degradation mechanisms: At low temperatures, the SEI/CEI layers are more prone to cracking due to the increased mechanical stress caused by lithium plating and volume changes in the electrodes. Additionally, the reduced ion mobility at low temperatures can lead to incomplete SEI/CEI formation, resulting in poor interfacial stability.42,43
3. Diagnostic methods: To diagnose the properties of SEI/CEI layers at low temperatures, advanced characterization techniques such as cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), in situ spectroscopy, and DRT analysis can be employed. Cryo-EM allows for high-resolution imaging of the SEI/CEI layers at cryogenic temperatures, while in situ spectroscopy provides real-time information on the chemical composition and evolution of the interphases. DRT analysis can decouple the contributions of SEI/CEI resistance and charge transfer resistance, providing valuable insights into the interfacial kinetics at low temperatures.
4. Modeling and simulation: Leveraging molecular dynamics and ab initio simulations to understand the mechanistic interplay between interphase chemistry, Li+ transport, and charge transfer processes at the atomic scale.
1. Electrolyte additives: The use of functional additives, such as fluorinated solvents or ether-based systems, to minimize interfacial resistance and enhance stability, can promote the formation of stable and conductive SEI/CEI layers. These additives can also suppress side reactions and reduce gas generation at low temperatures.44,45
2. Cathode coatings: Exploring alternative cathode materials and coatings that are less prone to degradation and side reactions under low-temperature conditions, thereby complementing SEI and electrolyte improvements. The application of protective coatings, such as Al2O3, LiCoO2, and Li3PO4, on the cathode surface can enhance the stability of the CEI layer and prevent the dissolution of transition metals at low temperatures.46–48
3. Advanced characterization techniques: The use of advanced characterization techniques, such as cryo-EM and in situ spectroscopy, can provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of SEI/CEI layers at low temperatures. These techniques can help identify the key factors influencing interfacial stability and guide the development of optimized electrolyte formulations.49,50
By addressing the fundamental challenges associated with SEI and CEI at low temperatures, it is possible to extend the operating range and longevity of LIBs, making them more reliable for applications in extreme environments such as aerospace, polar exploration, and military systems.
4. Current advances in low-temperature electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries
4.1. The role of electrolytes in low-temperature lithium-ion batteries
The electrolyte is a critical component of LIBs, comprising a mixture of solvents, lithium salts, and functional additives. However, LIBs often suffer from reduced discharge capacity or even failure to discharge at low temperatures. This performance degradation is primarily caused by significant increases in solvent viscosity and poor compatibility between the electrolyte and the electrodes.51,52 At low temperatures, the electrolyte's behavior is influenced by several key factors, including lithium salt dissociation efficiency, solvent viscosity, melting point, and the effectiveness of additives.To address these challenges, the design of low-temperature electrolytes requires solvents with low viscosity, high dielectric constant, and excellent electrochemical stability. These properties promote enhanced ionic conductivity and efficient dissociation of lithium salts, ensuring the smooth transport of Li+ ions even at sub-zero temperatures.53
Electrolytes typically incorporate lithium salts to facilitate Li+ dissociation, including options such as lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), lithium bis(oxalato)borate (LiBOB), lithium (oxalato)difluoroborate (LiDFOB), lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI), lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI), lithium hexafluoroarsenate monohydrate (LiAsF6), lithium perchlorate (LiClO4), lithium tetrafluoroborate (LiBF4), and lithium triflate (LiTf). These salts are often combined with various organic compounds designed to optimize ionic conductivity and control electrolyte viscosity.
Solvent selection plays an equally critical role in achieving low-temperature performance. Commonly used solvent families include acyclic and cyclic carbonates, such as EC, dimethyl carbonate (DMC), and PC, as well as linear and cyclic esters, ethers, liquefied gases, ionic liquids, and solid-state lithium-ion complexes. These solvents are tailored to balance viscosity, dielectric properties, and thermal stability, creating an electrolyte environment conducive to efficient Li+ transport. Functional additives are another vital component of low-temperature electrolytes. These additives are designed to form robust SEI films, which enhance electrode stability and minimize side reactions at the electrode–electrolyte interface. Additives can also improve electrolyte compatibility with both the anode and cathode, further boosting battery performance under extreme temperature conditions.
This section highlights recent advancements in the development of solvents, lithium salts, and additives for low-temperature LIBs, focusing on strategies to overcome the challenges posed by extreme thermal environments. By optimizing electrolyte formulations, researchers aim to enhance the safety, performance, and lifespan of LIBs in a broad range of applications, from electric vehicles to aerospace technologies.
4.2. Non-aqueous electrolytes
| Solvent type | Ionic conductivity (mS cm−1) | Oxidation stability (V) | Compatibility with graphite | Cyclic performance at −20 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonates | 1.5–2.0 | 4.5–5.0 | Good | 80% capacity retention |
| Ethers | 0.8–1.2 | 3.5–4.0 | Poor (co-intercalation) | 70% capacity retention |
| Esters | 1.0–1.5 | 4.0–4.5 | Moderate | 75% capacity retention |
One effective strategy is the incorporation of cosolvents with low freezing points and/or low viscosity. This approach significantly reduces the overall viscosity and freezing point of the electrolyte, thereby improving ionic conductivity in the bulk phase at low temperatures. Additionally, care must be taken to ensure that these solvents do not compromise the integrity of the SEI layer, as its degradation can lead to increased impedance and capacity loss.
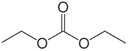
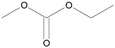
4.2.1.1. Carbonate family (acyclic and cyclic). The electrolytes used in LIBs are usually composed of a mixture of carbonate-based solvents. These carbonates are either linear carbonates with low viscosity, which provide higher ionic conductivity-such as diethyl carbonate (DEC), dimethyl carbonate (DMC), and ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC)-or cyclic carbonates with a high dielectric constant, which enhance salt dissociation-such as EC, PC, and vinyl carbonate (VC).54 Therefore, the main advantage of carbonates compared to other solvents lies in their higher conductivity and better ion separation. Additionally, there are significant differences in their surface properties, as well as their electrochemical, thermal, and chemical stabilities. Currently, the main limitation of cyclic ethyl carbonate is its high melting point (36 °C), which severely restricts its performance at low temperatures.55
On the other hand, PC exhibits a relatively low melting point (−48 °C), but incorporating PC molecules into graphite can lead to the reduction of the electrolyte and exfoliation of the graphite structure. However, linear carbonates such as methyl 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl carbonate (FEMC, −55 °C), EMC (−55 °C), and DEC (−43 °C) have lower melting points than cyclic carbonates. Although linear carbonates have higher dielectric constants and lower boiling points, their viscosity is higher than that of cyclic carbonates. Additionally, the unstable SEI layer formed by linear carbonates cannot prevent the continuous decomposition of the electrolyte and the intercalation of Li-ion shells.
Li et al.56 found that carbonate-based electrolytes (EC/DMC/LiPF6) exhibited good cyclability stability at low temperatures in lithium–sulfur batteries. This finding indicates that binary mixtures of linear and cyclic carbonates are favorable for improving the ionic conductivity of electrolytes at low temperatures. Therefore, multicomponent mixtures can be used to expand the liquid range of the electrolyte and increase its conductivity. Multicomponent systems are more tunable and usually have better conductivity than single-solvent systems due to the balance between ionic conductivity and dielectric constant provided by linear and cyclic carbonates. Mixed solvent systems can easily ameliorate the disordering influence on lithium's physicochemical characteristics and ion coordination.
As mentioned above, balancing the high dielectric constant and low viscosity of the electrolyte solvent is crucial for achieving excellent conductivity. Therefore, the amount of cyclic carbonates is very important. When the content of cyclic carbonates in electrolytes is low, the small proportion of cyclic carbonates provides a high dielectric constant for the electrolyte and reduces the degree of dissociation of the lithium salt, resulting in a lower concentration of free Li+ ions in the electrolyte. Conversely, when the cyclic carbonate content is high, the viscosity increases. To reduce the viscosity of cyclic carbonate-based solvent electrolytes and improve conductivity at low temperatures, the amount of cyclic carbonate should be reduced, and the proportion of linear carbonate in the mixed solvent system should be increased.
Xiao et al.57 discovered that organic solvents with insignificant EC (10% to 20% by weight) but rich in EMC may effectively extend the operating temperature range. Compared with binary mixtures, ternary solvent electrolytes have shown better discharge capacity at different temperatures. In a long-term cycling test, the LIBs with an EC/DEC/DMC electrolyte showed a high initial capacity of 0.41 A h and a low fading rate of 0.033% per cycle at 20 °C. Later studies used EMC to replace DEC in the ternary system due to EMC's better film-forming ability.58 Xiao et al.57 found that an EC/DMC/EMC (8.3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 25
25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 66.7 v/v/v) electrolyte delivered the best low-temperature performance, allowing LIBs to retain 90.3% of their nominal capacity when discharged to 2.0 V at −40 °C at 0.1C. Their experiments demonstrated that co-solvents with high dielectric constants and low viscosities improve ionic conductivity at room temperature, while low-melting-point co-solvents effectively expand the electrolyte's operating temperature range. In a separate study, Smart et al. found that EC-DMC-EA/EC-DMC-MB, used as an electrolyte, retained more than 80% of its ambient capacity at −40 °C. This formulation combined the low freezing temperature of DEC and the low viscosity of DMC, resulting in higher ionic conductivity compared to EC/DEC or EC/DMC binary mixtures below 20 °C (Fig. 7a). The ternary solvent electrolyte demonstrated superior discharge capacities at various temperatures (Fig. 7b). This allowed the battery to operate at low temperatures by adjusting the EC content in the electrolyte (15–33 wt%). At low temperatures, these electrolytes with low EC content showed increased capacitance and partial polarization.
66.7 v/v/v) electrolyte delivered the best low-temperature performance, allowing LIBs to retain 90.3% of their nominal capacity when discharged to 2.0 V at −40 °C at 0.1C. Their experiments demonstrated that co-solvents with high dielectric constants and low viscosities improve ionic conductivity at room temperature, while low-melting-point co-solvents effectively expand the electrolyte's operating temperature range. In a separate study, Smart et al. found that EC-DMC-EA/EC-DMC-MB, used as an electrolyte, retained more than 80% of its ambient capacity at −40 °C. This formulation combined the low freezing temperature of DEC and the low viscosity of DMC, resulting in higher ionic conductivity compared to EC/DEC or EC/DMC binary mixtures below 20 °C (Fig. 7a). The ternary solvent electrolyte demonstrated superior discharge capacities at various temperatures (Fig. 7b). This allowed the battery to operate at low temperatures by adjusting the EC content in the electrolyte (15–33 wt%). At low temperatures, these electrolytes with low EC content showed increased capacitance and partial polarization.
 | ||
Fig. 7 (a) Ionic conductivities of 1 M LiPF6 in (1) EC/DMC (30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 70 v/v), (2) EC/DEC (30 70 v/v), (2) EC/DEC (30![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 70 v/v), and (3) EC/DMC/DEC (1 70 v/v), and (3) EC/DMC/DEC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) mixtures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 59. (b) Low-temperature performance of graphite-based LIBs with various electrolytes at 0.05C and different temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 59. (c) Nyquist plots of Li/MCMB cells using various electrolytes at −20 °C after formation cycles.60 (d) Delithiation capacities of MCMB electrodes using different electrolytes at 20 °C following lithiation at 20 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 60. 1 v/v/v) mixtures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 59. (b) Low-temperature performance of graphite-based LIBs with various electrolytes at 0.05C and different temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 59. (c) Nyquist plots of Li/MCMB cells using various electrolytes at −20 °C after formation cycles.60 (d) Delithiation capacities of MCMB electrodes using different electrolytes at 20 °C following lithiation at 20 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 60. | ||
Electrolytes with a small proportion of EC combined with linear carbonates had higher conductivity at −40 °C compared to other studied electrolytes. Subsequently, Smart et al.59,60 found that an electrolyte made of EC, DEC, and DMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) performed better at low temperatures than EC/DMC and EC/DEC solvents. According to their experimental results, co-solvents with high dielectric constants and low viscosities can improve the ionic conductivity at room temperature, while only low-melting co-solvents can effectively extend the operating temperature range of the electrolyte. These electrolytes form superior SEI films with enhanced Li+ transport kinetics and protective properties (Fig. 7c), resulting in significantly improved low-temperature performance in the presence of MCMB electrodes (Fig. 7d).
1) performed better at low temperatures than EC/DMC and EC/DEC solvents. According to their experimental results, co-solvents with high dielectric constants and low viscosities can improve the ionic conductivity at room temperature, while only low-melting co-solvents can effectively extend the operating temperature range of the electrolyte. These electrolytes form superior SEI films with enhanced Li+ transport kinetics and protective properties (Fig. 7c), resulting in significantly improved low-temperature performance in the presence of MCMB electrodes (Fig. 7d).
PC is a well-known solvent (ε = 65) with a large liquid range (−49 to 242 °C), this feature has piqued interest since the beginning of LIBs research. Because PC has a lower viscosity and melting point than EC,61 partially or completely replacing EC with PC can increase conductivity at low temperatures and drastically reduce crystallization propensity—characteristics that many researchers have taken advantage of. Several of the studies discussed in this review used electrolytes that included some PC as a solvent. For example, Zhang et al.62 found that compared to the binary solvent system (EC/EMC = 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7 w/w), the SEI formed by the ternary solvent electrolyte (PC/EC/EMC = 1
7 w/w), the SEI formed by the ternary solvent electrolyte (PC/EC/EMC = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 w/w/w) has higher ion conduction at temperatures below zero. Although the introduction of PC reduced the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte, the formation of a low-impedance SEI significantly improved the LIBs performance at low temperatures (Fig. 8a and b). The beneficial impact of PC and EC on a wide range of operating temperatures was also demonstrated by Li et al.19 They tested many electrolytes and obtained the best results using 1.0 M LiPF6 and 0.05 M CsPF6 in PC/EC/EMC (1
3 w/w/w) has higher ion conduction at temperatures below zero. Although the introduction of PC reduced the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte, the formation of a low-impedance SEI significantly improved the LIBs performance at low temperatures (Fig. 8a and b). The beneficial impact of PC and EC on a wide range of operating temperatures was also demonstrated by Li et al.19 They tested many electrolytes and obtained the best results using 1.0 M LiPF6 and 0.05 M CsPF6 in PC/EC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 by weight). These investigations showed that the PC-containing solvent can exhibit 68% capacity retention at −40 °C and a C/5 rate. Although PC exhibits co-intercalation with graphite, it can reduce EC crystallization and is a useful component of low-temperature electrolytes.
8 by weight). These investigations showed that the PC-containing solvent can exhibit 68% capacity retention at −40 °C and a C/5 rate. Although PC exhibits co-intercalation with graphite, it can reduce EC crystallization and is a useful component of low-temperature electrolytes.
 | ||
Fig. 8 Capacity retention of LIBs containing (a) 1 m LiPF6 in EC/EMC (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7 v/v) and (b) 1 m LiPF6 in PC/EC/EMC (1 7 v/v) and (b) 1 m LiPF6 in PC/EC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v/v) at various temperatures when compared with 20 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 62. 3 v/v/v) at various temperatures when compared with 20 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 62. | ||
Ren et al.63 evaluated the performance of electrolytes composed of different ratios of solvents (EC/PC/EMC/FEC). At −40 °C, the battery charge capacity was able to reach 91% of the capacity obtained at room temperature. Fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) may work as a suitable co-solvent with PC to improve the unfavorable PC behavior in LIBs at low temperatures on the graphite anode. FEC is commonly used as an additive (5 vol/wt%) to enhance the low-temperature performance of LIBs.20,34 However, under the following conditions, a higher content of FEC is required to act as a co-solvent (10 vol/wt%) to maintain a stable electrode/electrolyte interface:
1. The main solvent is not able to form a film at the usual concentration of lithium salt (2 M).64,65
2. Anode materials undergo strong volume fluctuations, such as Si and Li metal.66–69
New electrolyte systems based on sulfone-, nitrile-, and fluorinated solvents have also been explored to enhance lithium salt solubility, increase operating voltage, extend temperature ranges, and improve battery safety. For instance, in a 1 M LiPF6 electrolyte with methyl propionate (MP) as the main solvent (90 vol%), 10 vol% FEC was necessary to passivate the electrode surface, enabling stable cycling and reducing gas generation in graphite/NCA pouch cells.65 Similarly, methyl 3,3,3-trifluoropropionate (MTFP), a fluorinated analogue of MP, has been used as a primary low-temperature co-solvent with 10% (v/v) FEC by Holoubel et al.67 This all-fluorinated electrolyte achieved high discharge capacities at temperatures between −40 °C and −60 °C and an ionic conductivity of 0.75 mS cm−1 at −60 °C, 150 times higher than that of EC/DEC-based electrolytes (0.005 mS cm−1). Additionally, Fan et al.69 dissolved fluorinated electrolytes in highly fluorinated non-polar diluents (a flouroether), achieving high ionic conductivity across a wide temperature range (−125 °C to 70 °C). These systems reduced Li-ion desolvation energy during plating, enhancing plating/stripping reaction kinetics at low temperatures. Additionally, a LiF-rich SEI with high mechanical strength and interfacial energy was formed on the anode, improving ionic conductivity at −125 °C and mitigating Li dendrite growth. A full cell using this electrolyte maintained 56% of its room-temperature capacity at −85 °C with ultra-stable cycling performance.
Similarly, ternary or quaternary mixtures are used to expand the electrolyte's liquid range and increase its conductivity. Multicomponent systems are more tunable and usually exhibit better conductivity than single-solvent systems. Mixed-solvent systems can easily ameliorate the disordering influence on lithium's physicochemical characteristics and ion coordination.
Zhang et al.70 demonstrated that modifying the EC/EMC ratio to create the “electrolyte E5” formulation (EC/PC/EMC = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7) could improve the low-temperature electrochemical performance of electrodes. The results showed lower transfer impedance, outstanding rate performance, and good cycle stability, especially at low temperatures. The electrode's electrochemical performance with electrolyte E5 was further investigated at temperatures ranging from −30 °C to 25 °C. Fig. 9a–c shows the charge and discharge profiles of an electrode employing electrolyte E5 at room temperature, −10 °C, and −30 °C, respectively. An electrode with electrolyte E5 was able to discharge a specific capacity of 106 mA h g−1 at −30 °C (Fig. 9c). Furthermore, electrodes using electrolyte E5 demonstrated outstanding electrochemical performance at both low and high temperatures. Fig. 9d shows the rate performance of electrodes utilizing electrolyte E5 from 0.1 to 5 A g−1 at various temperatures. The electrode exhibited a high capacity of 153 mA h g−1 after 500 cycles at 2 A g−1 and −20 °C. An electrode utilizing electrolyte E5 could exhibit a capacity of 50 mA h g−1 at 5 A g−1 even at −30 °C, demonstrating exceptional low-temperature performance. The increased electrochemical performance is attributed to the lower separation energy of lithium ions between solvents and the weak interaction between Li and EMC at the optimal formulation. Given a comparable process, the electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 at low temperatures might be further improved by utilizing electrolyte E5.
7) could improve the low-temperature electrochemical performance of electrodes. The results showed lower transfer impedance, outstanding rate performance, and good cycle stability, especially at low temperatures. The electrode's electrochemical performance with electrolyte E5 was further investigated at temperatures ranging from −30 °C to 25 °C. Fig. 9a–c shows the charge and discharge profiles of an electrode employing electrolyte E5 at room temperature, −10 °C, and −30 °C, respectively. An electrode with electrolyte E5 was able to discharge a specific capacity of 106 mA h g−1 at −30 °C (Fig. 9c). Furthermore, electrodes using electrolyte E5 demonstrated outstanding electrochemical performance at both low and high temperatures. Fig. 9d shows the rate performance of electrodes utilizing electrolyte E5 from 0.1 to 5 A g−1 at various temperatures. The electrode exhibited a high capacity of 153 mA h g−1 after 500 cycles at 2 A g−1 and −20 °C. An electrode utilizing electrolyte E5 could exhibit a capacity of 50 mA h g−1 at 5 A g−1 even at −30 °C, demonstrating exceptional low-temperature performance. The increased electrochemical performance is attributed to the lower separation energy of lithium ions between solvents and the weak interaction between Li and EMC at the optimal formulation. Given a comparable process, the electrochemical performance of Li4Ti5O12 at low temperatures might be further improved by utilizing electrolyte E5.
 | ||
Fig. 9 An optimized LiBF4-based electrolyte formulation for a TiO2 anode in a LIBs: charge–discharge curves of the electrode using EC/PC/EMC (volume ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7) electrolyte at (A) room temperature, (B) −10 °C, and (C) −30 °C; (D) rate performance of the cell at different temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 70. 7) electrolyte at (A) room temperature, (B) −10 °C, and (C) −30 °C; (D) rate performance of the cell at different temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 70. | ||
Sulfites and sulfates are essential for enhancing the performance of carbonate solvents in low-temperature electrolytes. Due to its structural similarity to organic carbonates, low viscosity, and low melting point, dimethyl sulfite (DMS) has garnered significant attention. This solvent effectively reduces the resistance of the SEI layer and improves the low-temperature performance of LIBs. Li et al.71 investigated an EC/DMS/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v) electrolyte containing mixed salts (LiDFOB and LiBF4). The electrolyte exhibited excellent ionic conductivity across a temperature range of −40 °C to 20 °C. Their findings indicated that LIBs using this electrolyte could operate successfully at temperatures below −20 °C. Additionally, linear sulfates such as diethyl sulfate (DES), with their low melting points and viscosities, are promising co-solvents for improving low-temperature performance. Li et al.72 combined DMS and DES as mixed solvents, resulting in electrolytes that demonstrated good cycling performance over a broad temperature range. Furthermore, these electrolytes exhibited outstanding film-forming properties at −20 °C, suggesting their potential as alternative electrolytes for LIBs.
3 v/v) electrolyte containing mixed salts (LiDFOB and LiBF4). The electrolyte exhibited excellent ionic conductivity across a temperature range of −40 °C to 20 °C. Their findings indicated that LIBs using this electrolyte could operate successfully at temperatures below −20 °C. Additionally, linear sulfates such as diethyl sulfate (DES), with their low melting points and viscosities, are promising co-solvents for improving low-temperature performance. Li et al.72 combined DMS and DES as mixed solvents, resulting in electrolytes that demonstrated good cycling performance over a broad temperature range. Furthermore, these electrolytes exhibited outstanding film-forming properties at −20 °C, suggesting their potential as alternative electrolytes for LIBs.
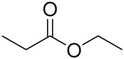
4.2.1.2. Ester family (linear and cyclic). Linear and cyclic esters, such as methyl acetate (MA), ethyl acetate (EA), ethyl butyrate (EB), methyl butyrate (MB), and methyl propionate (MP), are important organic solvents in electrolytes. Linear esters have lower melting points, lower viscosity, and higher dielectric constants than linear carbonates. These properties enable the rapid transfer of lithium ions in the bulk electrolyte, even at very low temperatures. However, compared to carbonates, esters have significant disadvantages, including high volatility, flammability, poor film-forming ability, high reactivity with reducing anodes, and a narrower electrochemical window.
For this reason, researchers have studied the effects of esters as cosolvents in carbonate-based LIBs electrolytes at low temperatures. Initially, esters were used to enhance the low-temperature performance of PC-based electrolytes.6 Subsequently, as the demand for long cycle life at room temperature grew, EC became the primary solvent. Due to the poor film-forming ability and high reactivity of esters with reductive anodes, early studies limited esters to use as cosolvents in EC-based electrolytes.73,74
Work on linear ester cosolvents for low-temperature LIBs electrolytes was conducted by Smart and collaborators.75,76 As early as 2002, they investigated the performance of EC-based electrolytes with various esters, including EA, MA, ethyl propionate (EP), and EB.73 Electrolytes containing low-molecular-weight esters enabled AA-sized cells to deliver high initial capacities at −20 °C. However, the SEI formed by electrolytes with EA and MA exhibited high resistance and insufficient protection, leading to rapid capacity decline after extended cycling.
High-molecular-weight esters, such as MB and EB, were shown to perform better as low-temperature cosolvents due to their ability to form a more stable SEI with lower resistance. Smart et al. tested the low-temperature performance of EC/EMC/MB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 v/v/v) and EC/EMC/EB (1
8 v/v/v) and EC/EMC/EB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8 v/v/v) electrolytes containing 1 M LiPF6. Both formulations retained over 80% of their room-temperature discharge capacity at −60 °C at a rate of 0.05C.77 However, due to the poor oxidative stability of high-molecular-weight esters, the charge voltage was limited to 4.1 V.
8 v/v/v) electrolytes containing 1 M LiPF6. Both formulations retained over 80% of their room-temperature discharge capacity at −60 °C at a rate of 0.05C.77 However, due to the poor oxidative stability of high-molecular-weight esters, the charge voltage was limited to 4.1 V.
While high ester content in electrolytes can achieve high discharge capacities at ultralow temperatures (−60 °C), these capacities are unsustainable without suitable film-forming additives to create a highly protective SEI. Side reactions between the esters and electrodes continue to occur, causing rapid capacity decay. Furthermore, most practical applications require batteries to perform well at low, room and elevated temperatures. High-temperature conditions impose stringent requirements for SEI stability and solvent volatility.
To address these issues, Smart et al. optimized solvent compositions, limiting esters to 20 vol% in EC/EMC/ester (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 60
60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 v/v/v) formulations.76 Among the six esters studied-MP, EP, MB, EB, propyl butyrate (PB), and butyl butyrate (BB)-MP exhibited the best low-temperature performance, delivering a discharge capacity of 5.08 A h (7 A h prismatic LIBs) at −60 °C and 0.1C. Higher-molecular-weight esters, such as PB and BB, performed better at high temperatures, suggesting a balance of high- and low-molecular-weight esters could achieve broad temperature-range stability.
20 v/v/v) formulations.76 Among the six esters studied-MP, EP, MB, EB, propyl butyrate (PB), and butyl butyrate (BB)-MP exhibited the best low-temperature performance, delivering a discharge capacity of 5.08 A h (7 A h prismatic LIBs) at −60 °C and 0.1C. Higher-molecular-weight esters, such as PB and BB, performed better at high temperatures, suggesting a balance of high- and low-molecular-weight esters could achieve broad temperature-range stability.
Fang et al.78 improved a cosolvent formulation of PC and MB, achieving a high cell capacity of 240 mA h g−1 with 28% retention at −70 °C. EA, while advantageous for its low melting point (−84 °C) and viscosity, fails to form a sufficiently stable SEI with lithiated graphite, leading to high Rct over time.79 A PC/EC/MB/EA blend retained 98% capacity at −30 °C,74 while larger esters like EB demonstrated compatibility in carbonate blends, enhancing low-temperature capacity without significant drawbacks.73
Fluorinated esters have also been explored for their improved film-forming properties and reduced flammability compared to non-fluorinated esters.75,80 Smith et al. tested various fluorinated esters-such as 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl butyrate (TFEB), 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl acetate (TFEA), and methyl pentafluoropropionate (MPFP) in EC/EMC electrolytes. Among these, the EC/EMC/TFEB (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 60
60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 v/v/v) electrolyte demonstrated the best performance.75
20 v/v/v) electrolyte demonstrated the best performance.75
Lu et al.81 further studied trifluoroacetates with varying carbon chain lengths, concluding that shorter chains are preferable for low-temperature performance. Advances in film-forming additives have enabled ester-based electrolytes (with >50 vol% esters) to achieve stable charge/discharge cycles at low temperatures. For example, Cho et al.65 proposed an MP-based electrolyte (M9F1: 1 M LiPF6 in MP/FEC 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v), which exhibited 92% capacity retention after 100 cycles at −20 °C at 0.2C. Zhang et al.82 developed a high-entropy ester-based electrolyte with six esters, achieving an ultralow freezing point (−130 °C) and ionic conductivity of 0.62 mS cm−1 at −60 °C.
1 v/v), which exhibited 92% capacity retention after 100 cycles at −20 °C at 0.2C. Zhang et al.82 developed a high-entropy ester-based electrolyte with six esters, achieving an ultralow freezing point (−130 °C) and ionic conductivity of 0.62 mS cm−1 at −60 °C.
Despite these advancements, ester-based electrolytes remain unsuitable for LMBs due to their extremely low Coulombic efficiency (6.2% for M9F1). Future work should focus on addressing these limitations to extend their application across a wider range of battery chemistries and conditions.
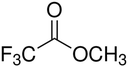
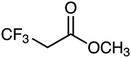
Electrolytes with fluorinated esters as the main solvents also exhibit excellent low-temperature performance with the help of FEC and are more promising than their non-fluorinated counterparts for developing LMBs cycled at low temperatures. In fact, it has been mentioned earlier that the low-temperature discharge performance of Li/NCM811 cells using MTFP electrolyte is comparable to that of Li/NCM811 cells using MP.67 Additionally, the Coulombic efficiency of LMA using MTFP is significantly better than that of LMA using MP. MTFP not only has a wider electrochemical window, but its decomposition products also help form a thinner and denser SEI. Yang et al.83 focused on the weak binding energy between the fluorinated ester and Li+, due to the strong electron-withdrawing ability of fluorine atoms. Their theoretical calculations showed that the binding energy of Li+-ETFA (10.05 kJ mol−1) is much lower than that of Li+-EA (28.18 kJ mol−1), as well as lower than the binding energy of Li+-EC (21.56 kJ mol−1) and Li+-DMC (19.07 kJ mol−1).
The ETFA/FEC electrolyte, with ETFA as the main solvent and FEC as the film-forming co-solvent (1 M LiTFSI in ETFA/FEC 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v), achieved smooth desolvation and stable SEI formation simultaneously.84 The synergy between ETFA and FEC allowed graphite/LiFePO4 (LFP) full cells to maintain a high discharge capacity of 90 mA h g−1 when charged/discharged at 30 °C. The weakly solvating solvents used for low-temperature electrolytes are summarized in Table 1. Fluorinated esters are only a minority among weakly solvating solvents.78,84 The majority of weakly solvating solvents remain ethers,85 which will be discussed subsequently. Although weakly solvating solvents have shown outstanding properties in low-temperature applications, this concept was first clearly proposed by Yao et al. for fast-charging and long-lifespan graphite anodes at room temperature.86
3 v/v), achieved smooth desolvation and stable SEI formation simultaneously.84 The synergy between ETFA and FEC allowed graphite/LiFePO4 (LFP) full cells to maintain a high discharge capacity of 90 mA h g−1 when charged/discharged at 30 °C. The weakly solvating solvents used for low-temperature electrolytes are summarized in Table 1. Fluorinated esters are only a minority among weakly solvating solvents.78,84 The majority of weakly solvating solvents remain ethers,85 which will be discussed subsequently. Although weakly solvating solvents have shown outstanding properties in low-temperature applications, this concept was first clearly proposed by Yao et al. for fast-charging and long-lifespan graphite anodes at room temperature.86
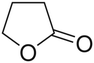
It would be remiss not to mention lactones (cyclic esters) in our discussion of ester electrolytes. Unlike linear esters, which function similarly to cyclic carbonates in electrolyte design, cyclic lactones are sufficiently polar to partially or completely replace EC/PC. Gamma-butyrolactone (GBL), the best-studied member of this family, has a dielectric constant of 42 at ambient temperature, which is lower than that of EC but still high to allow efficient ionization of lithium salts. It also has a low melting point (−44 °C) and lower viscosity than EC, which are both important characteristics for low-temperature electrolytes.87 However, like other esters, it fails to generate a passivating SEI layer on the graphite anode. This finding nearly ended the study of GBL electrolytes early in the development of LIBs. Despite the challenges in using GBL as a solvent in carbonate-based electrolytes, LiBOB-based electrolytes have been used to study GBL, since LiBOB is very weakly soluble in carbonates.88,89 Shi et al.90 made an electrolyte by mixing noncombustible hydroflurane with LiBOB and GBL. The graphite/NCM111 cells containing 1 M LiBOB in GBL/HFE (70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 v/v) demonstrated performance far superior to EC/DMC electrolyte over a wide temperature range from −50 to 60 °C. At −40 °C, the cell still delivered a discharge capacity of 74.2 mA h g−1. A follow-up investigation by the same group found that a comparable electrolyte containing LiDFOB exhibited outstanding safety features.91 Lazar et al.92 demonstrated that an all-ester electrolyte of GBL and MB (1
30 v/v) demonstrated performance far superior to EC/DMC electrolyte over a wide temperature range from −50 to 60 °C. At −40 °C, the cell still delivered a discharge capacity of 74.2 mA h g−1. A follow-up investigation by the same group found that a comparable electrolyte containing LiDFOB exhibited outstanding safety features.91 Lazar et al.92 demonstrated that an all-ester electrolyte of GBL and MB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 vol) containing 1 M LiDFOB had ionic conductivity and cycling performance equivalent to those of standard electrolytes (1 M LiPF6 in 1
1 vol) containing 1 M LiDFOB had ionic conductivity and cycling performance equivalent to those of standard electrolytes (1 M LiPF6 in 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 EC/DMC/DEC). At −10 °C, cells containing GBL/MB electrolyte exhibited considerably lower discharge performance.
1 EC/DMC/DEC). At −10 °C, cells containing GBL/MB electrolyte exhibited considerably lower discharge performance.
Aliphatic ester co-solvents have been proven to improve the ionic conductivity of electrolyte solutions at low temperatures. As the chain length increases, conductivity decreases. The features of the SEI contribute to the charge-transfer process of lithium ions and alleviate electrochemical polarization. As a result, lithium–graphite cells using long-chain electrolytes or higher-molecular-weight ester co-solvents, such as EC- and PC-based electrolytes, operate better at low temperatures.
Adding aliphatic ester cosolvents to conventional electrolytes is a practical approach to enhancing ionic conductivity and lowering the melting point, enabling satisfactory battery operation at temperatures around −30 °C. However, for carbonate-based electrolyte systems, even with the inclusion of ester additives as antifreeze agents, these measures are insufficient to ensure the operation of LIBs in extremely cold environments below −40 °C. It is well-established that electrolytes with high molecular weight and long-chain lengths can enhance electrolyte penetration and provide the necessary kinetics for Li intercalation.27,93 Additionally, stable and effective SEI layers, formed as decomposition products of the electrolyte, can reduce polarization in LIBs and facilitate the charge-transfer process of lithium ions. By incorporating ester-based solvents with higher molecular weight or longer chain lengths, the performance of LIBs can be significantly improved under ultra-low-temperature conditions. Moreover, using nonpolar alkane cosolvents holds great promise for improving the desolvation energy of Li+ cations. The combination of a rationally designed Li-ion solvation structure and carefully engineered solvents appears to be a promising strategy for enhancing electrochemical performance at temperatures below −40 °C.
4.2.1.3. Ether family (linear and cyclic). Ethers are also organic solvents in electrolytes that maintain a liquid form over a wide temperature range and have low viscosity, which leads to high ionic conductivity, especially at sub-zero temperatures. Linear and cyclic ether-based solvents exhibit similar physicochemical properties and low melting points. Compared to cyclic ethers, linear ethers have a lower viscosity, which facilitates ion movement, resulting in higher ionic conductivity. However, due to their inherent chemical instability against oxidation, their direct use in electrolytes has been commercially unsuccessful. Their operating voltage is limited to less than 4.0 V because of their intrinsic instability against oxidation.97 Furthermore, their chemical stability against reduction can enable colocalization and inhibit the growth of SEI layers, potentially leading to low capacity, poor reversibility, and inefficient intercalation chemistry.
Compared to ester-based solvents, ether-based solvents are highly flammable, volatile, and easily evaporate. These properties make ethers suitable for low-voltage LMBs, such as Li–S or Li–air batteries.98–100 Due to their high dielectric permittivity, the addition of DME can improve the solubility of lithium salts in the electrolyte. A high concentration of lithium salts can further reduce the melting point of the electrolyte. Thus, a mixture of DME and DOL is commonly used in Li–S batteries, as it exhibits an order of magnitude higher ionic conductivity (0.40 mS cm−1 at −80 °C) compared to carbonate electrolytes (0.02 mS cm−1 at −80 °C) or ester-based additives.101 Both DOL and DME have low melting points, making them ideal solvents for low-temperature electrolytes.102,103
Mikhaylik et al.104 demonstrated that a DOL/DME (86![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 14 v/v%) electrolyte can improve low-temperature performance down to −40 °C. At this temperature, cells showed a 5C discharge rate and retained more than 80% of their capacity, preventing overcharging. Holoubek et al.105 showed that the solvation structure of the electrolyte is critical for Li metal cycling at ultra-low temperatures, by comparing LiFSI diethyl ether and LiFSI DOL/DME electrolytes. The cell containing LiFSI DOL/DME electrolytes retained 76% of its room temperature capacity at −60 °C, resulting in steady performance across 50 cycles. This study demonstrated design parameters for low-temperature LMBs electrolytes, marking a significant advancement in low-temperature battery performance.
14 v/v%) electrolyte can improve low-temperature performance down to −40 °C. At this temperature, cells showed a 5C discharge rate and retained more than 80% of their capacity, preventing overcharging. Holoubek et al.105 showed that the solvation structure of the electrolyte is critical for Li metal cycling at ultra-low temperatures, by comparing LiFSI diethyl ether and LiFSI DOL/DME electrolytes. The cell containing LiFSI DOL/DME electrolytes retained 76% of its room temperature capacity at −60 °C, resulting in steady performance across 50 cycles. This study demonstrated design parameters for low-temperature LMBs electrolytes, marking a significant advancement in low-temperature battery performance.
Similarly, researchers106,107 combine DOL/DME with tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether (TEGDME), as TEGDME's high dielectric constant contributes to the dissociation of lithium salts. This hybrid ether electrolyte improves the low-temperature electrochemical behavior of Li–S batteries. Numerous studies have shown that DOL/DME stabilizes lithium dendrites and promotes cycling efficiency.102,105,108–111 Additionally, Thenuwara et al.112 showed that adding 10% FEC to an ether-based solvent electrolyte (DOL/DME) boosted and stabilized voltage profiles of LIBs at −60 °C (Fig. 10a–i).
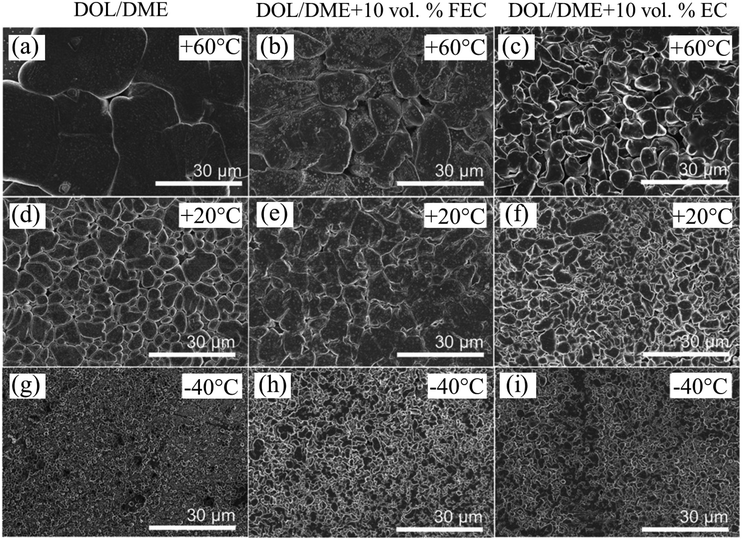 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a–i) SEM images of plated lithium on a stainless-steel electrode at different temperatures (60 °C, 20 °C, and −40 °C) in three different electrolytes at 0.5 mA cm−2. Images (a, d, g) correspond to deposition in pure ether electrolyte, (b, e, h) in FEC-modified ether electrolyte, and (c, f, i) in EC-modified ether electrolyte. Reproduced with permission from ref. 112. | ||
However, due to the weak oxidative stability of ether-based solvents (less than 4 V versus Li/Li+), they are not suitable for high-voltage systems. Wang et al.101 added allyl methyl disulfide to the conventional LiTFSI/LiNO3/DME/DOL-based electrolyte, which sustained 78.2% capacity at −40 °C and delivered a high capacity of 1563 mA h g−1 at −60 °C, resulting in an all-liquid-phase reaction mechanism.
Ether-based solvents are commonly used in the development of superconcentrated electrolytes due to their strong solvating abilities. As the salt concentration increases, the freezing point of the electrolyte drops, and ionic conductivity improves until it reaches the eutectic point.113,114 These highly concentrated ether-based electrolytes are especially valuable for low-temperature applications, as ether molecules are strongly bonded with salt, reducing volatility. However, when the lithium salt concentration exceeds 1 mol dm−3, the electrolyte can become highly viscous, which reduces ionic conductivity and negatively impacts the performance of LIBs. Pal et al.115 demonstrated that a mixture of 3.2 mol kg−1 LiFSI and DME, combined with N-propyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (C3mpyrFSI), enables rapid kinetics across a wide temperature range (−30 to 60 °C) due to the coexistence of ether DME and the FSI anion, without uncoordinated free DME solvent. Pappenfus et al.116 found that equimolar mixtures of lithium salt and tetraglyme (G4) retain an amorphous state over a broad temperature range (−100 to 300 °C), maintaining high room-temperature conductivity and electrochemical stability between 4.5 and 5.0 V (vs. Li+/Li). The salt concentration threshold is a crucial factor for these highly concentrated ether-based electrolytes; surpassing this threshold can impart distinct properties like high redox stability, aluminum anticorrosion, low volatility, high carrier density, and reduced polysulfide dissolution. Yoshida et al.117 advanced the understanding of these electrolytes, encouraging the systematic study of their unique properties.
Highly concentrated ether-based electrolytes improve electrochemical stability at both the cathode and the graphitic anode, a characteristic not found in diluted salt systems, due to the competitive solvation of Li+ ions by the ether solvents. Ren et al.118 developed a concentrated sulfone-based electrolyte with a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3
3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 molar ratio of LiTFSI, tetramethylene sulfone (TMS), and 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl-2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropyl ether (TTE), which enables operation at sub-zero temperatures (−10 °C). The addition of TTE addresses viscosity and wettability issues in sulfones, creating a localized high-concentration electrolyte.
3 molar ratio of LiTFSI, tetramethylene sulfone (TMS), and 1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl-2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropyl ether (TTE), which enables operation at sub-zero temperatures (−10 °C). The addition of TTE addresses viscosity and wettability issues in sulfones, creating a localized high-concentration electrolyte.
The low-temperature performance of Li–S cells was greatly improved by adding 1,3-dioxolane (DOL) to a tetra(ethylene glycol) dimethyl ether (TEGDME) electrolyte.119 A mixed electrolyte of MA/DOL/TEGDME (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 47.5
47.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 47.5 v/v/v) achieved a discharge capacity of 994 mA h g−1 at −10 °C, significantly higher than the 357 mA h g−1 observed with pure TEGDME electrolyte. Certain F- and phosphorus (P)-containing ethers offer wide electrochemical windows and liquid ranges, making them suitable for various electrode chemistries at low temperatures, along with flame-retardant properties for enhanced battery safety. Feng et al.120 utilized dimethyl methyl phosphonate (DMMP), a non-flammable solvent, for Li batteries, and a primary Li–MnO2 cell containing 0.8 M LiClO4 in DMMP demonstrated a discharge capacity of 100 mA h g−1 at −20 °C, about 66% of the room-temperature capacity. Naoi et al.121 explored non-flammable hydrofluoroethers in LIBs for low-temperature applications, where a carbonate-based electrolyte mixed with the branched hydrofluoroether 2-trifluoromethyl-3-methoxy-perfluoropentane (TMMP) exhibited excellent non-flammability and improved Li+ ion transport at low temperatures, achieving over 60% capacity retention at −20 °C, 20% higher than without TMMP. While many highly fluorinated ethers are highly flame-retardant, they are considered diluents rather than solvents, as they do not participate in the Li+ solvation structure.118,122 These highly fluorinated ethers will be further discussed in the section on localized high-concentration electrolytes (LHCEs).
47.5 v/v/v) achieved a discharge capacity of 994 mA h g−1 at −10 °C, significantly higher than the 357 mA h g−1 observed with pure TEGDME electrolyte. Certain F- and phosphorus (P)-containing ethers offer wide electrochemical windows and liquid ranges, making them suitable for various electrode chemistries at low temperatures, along with flame-retardant properties for enhanced battery safety. Feng et al.120 utilized dimethyl methyl phosphonate (DMMP), a non-flammable solvent, for Li batteries, and a primary Li–MnO2 cell containing 0.8 M LiClO4 in DMMP demonstrated a discharge capacity of 100 mA h g−1 at −20 °C, about 66% of the room-temperature capacity. Naoi et al.121 explored non-flammable hydrofluoroethers in LIBs for low-temperature applications, where a carbonate-based electrolyte mixed with the branched hydrofluoroether 2-trifluoromethyl-3-methoxy-perfluoropentane (TMMP) exhibited excellent non-flammability and improved Li+ ion transport at low temperatures, achieving over 60% capacity retention at −20 °C, 20% higher than without TMMP. While many highly fluorinated ethers are highly flame-retardant, they are considered diluents rather than solvents, as they do not participate in the Li+ solvation structure.118,122 These highly fluorinated ethers will be further discussed in the section on localized high-concentration electrolytes (LHCEs).
Chen et al.123 proposed an ether-based electrolyte (2 M LiPF6 in a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v mixture of THF and 2MeTHF, called mixTHF) for microsized silicon anodes (SiMPs). The high dissociation of LiPF6 in the mixTHF electrolyte raised its reduction potential to above 1.1 V, well above the decomposition potential of mixTHF, promoting the formation of a uniform LiF SEI layer on the Si surface. Thanks to this stable, thin LiF-rich SEI layer, SiMPs exhibited high reversible capacities of 2304 and 1475 mA h g−1 at −20 and −40 °C, respectively.
1 v/v mixture of THF and 2MeTHF, called mixTHF) for microsized silicon anodes (SiMPs). The high dissociation of LiPF6 in the mixTHF electrolyte raised its reduction potential to above 1.1 V, well above the decomposition potential of mixTHF, promoting the formation of a uniform LiF SEI layer on the Si surface. Thanks to this stable, thin LiF-rich SEI layer, SiMPs exhibited high reversible capacities of 2304 and 1475 mA h g−1 at −20 and −40 °C, respectively.
DEE is another weakly solvating solvent. The Li+ solvation structure in DEE-based electrolytes governs the reversibility of Li metal plating at low temperatures.105 Unlike the Solvent-Separated Ion Pair (SSIP) structure observed in conventional DOL/DME electrolytes, DEE-based electrolytes exhibit a characteristic contact-ion pairs (CIPs) structure due to the weaker Li+-DEE interaction. CIP structures are more entropically driven than SSIP structures, leading to easier desolvation. The binding energies of DEE-based and DOL/DME-based electrolytes are −280 kJ mol−1 for Li+(DEE)1.8 and −414 kJ mol−1 for Li+(DME)2.3, respectively.
The binding between Li+ and anions is not considered due to the repulsive interaction of anions near the anode surface, which is highly negatively polarized. When lithium metal full cells using perylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxydiimide functionalized with N,N′-bis(2-anthraquinone) (PTCDI-DAQ) as the cathode material were cycled at −40 °C, the low-temperature electrolyte (LTE)-based system exhibited stable performance, delivering a capacity of 57.6 mA h g−1 over 200 cycles at a current density of 100 mA g−1 (Fig. 11a). The corresponding charge and discharge curves displayed distinct voltage plateaus, indicating efficient charge transport and strong electrochemical reversibility under sub-zero conditions (Fig. 11b).124 Ma et al.31 introduced dimethoxymethane (DMM) as another weakly solvating solvent for low-temperature LMBs (Fig. 11c). Due to the weaker solvating ability of DMM, more contact-ion pairs (CIPs) and aggregates (AGGs) were present in the DMM-based electrolyte, indicating greater participation of anions in the Li+ solvation shell. These anion-rich structures not only desolvate more easily but also tend to form an inorganic-rich SEI. As a result, the DMM-based electrolyte allowed LMBs to maintain uniform deposition and achieve a capacity retention of 63.8% after 120 cycles at −40 °C (Fig. 11d).
 | ||
| Fig. 11 (a) Cycling performance and (b) charge–discharge profiles of the Li metal cell paired with PTCDI-DAQ cathode at a current density of 400 mA g−1 an −40°.124 (c) Binding energies of Li+-solvent complexes. Reproduced with permission from ref. 31. (d) Long-term cycling performance of Li/SPAN full cells with DMM-based electrolyte at −40 °C and 0.1C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 31. | ||
In addition to weakly solvating electrolytes, the Li-ether co-intercalation electrolyte strategy offers another way to reduce the activation energy for charge transfer. Yang et al. utilized the highly reversible co-intercalation of Li-DEGDME into graphite to design a solvent co-intercalation electrolyte (1.5 M LiOTF/0.2 M LiPF6 in DEGDME/DOL 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v). The incomplete stripping of the Li+ solvation sheath resulted in a very low charge transfer activation energy (0.23 eV per atom) and nearly temperature-independent chemical diffusion coefficients of solvated Li+ in graphite. Remarkably, when cycled at −60 °C, the graphite/LiNi0.65Co0.15Mn0.2O2 cell showed an initial discharge capacity of 62.1 mA h g−1 and stable cycling performance for at least 50 cycles. To date, −60 °C is the lowest temperature reported for long-term cycling of graphite-based LIBs.
1 v/v). The incomplete stripping of the Li+ solvation sheath resulted in a very low charge transfer activation energy (0.23 eV per atom) and nearly temperature-independent chemical diffusion coefficients of solvated Li+ in graphite. Remarkably, when cycled at −60 °C, the graphite/LiNi0.65Co0.15Mn0.2O2 cell showed an initial discharge capacity of 62.1 mA h g−1 and stable cycling performance for at least 50 cycles. To date, −60 °C is the lowest temperature reported for long-term cycling of graphite-based LIBs.
In conclusion, ether-based electrolytes offer significant benefits for enhancing the low-temperature performance of LIBs, yet they still face challenges related to their intrinsic interfacial properties at both electrodes. Due to the low oxidative stability of ethers, with energy levels below 4.0 V vs. Li/Li+, these electrolytes are not suitable for use with high-voltage cathodes, unlike esters. Additionally, their relatively short cycle life and poor electrochemical performance limit their broader application in LIBs. As a result, there is a pressing need for the development of ether-based electrolytes with improved oxidation stability to support both high-voltage cathodes and lithium metal. Ether-based electrolytes find a specific niche in lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries, which offer an exceptionally high theoretical energy density (2600 W h kg−1) and maintain good capacity retention at low temperatures. The high concentration of lithium salts in ether-based solvents enhances electrochemical stability at both the anode and cathode, while significantly lowering the melting point of the solvents, allowing for outstanding low-temperature performance even below −20 °C. However, the high lithium salt content increases the battery weight, which reduces the overall energy density and increases the cost of LIBs. Using a non-coordinating fluorinated solvent as a diluent can help lower the lithium salt concentration to more manageable levels, offering flexibility in forming a stable SEI, maintaining a highly aggregated coordination state, and improving viscosity and transport properties at low temperatures.
4.2.1.4. Liquefied gas. Typically, electrolytes exist in liquid or solid forms, enabling the reversible diffusion of lithium ions. However, due to weak intermolecular interactions, gaseous electrolytes at ambient temperature and pressure may lack a stable phase. Recently, gaseous electrolytes have shown promise in overcoming the limitations of narrow operational temperature ranges and low oxidation stability by altering the polarity and ion coordination within solvents. Under moderate pressures or low temperatures, some polar gases can be liquefied and used as solvents to dissolve lithium salts, forming liquefied gas electrolytes. Rustomji et al.125 identified six promising liquefied gas solvents that exhibit improved reduction and oxidation resistance. Electrostatic potential maps revealed that the regions of highest and lowest electrostatic potential increased in the order of tetrahydrofuran (THF) < fluoromethane (FM) < difluoromethane (DFM) < ethylene carbonate (EC), indicating that THF and FM possess excellent reduction stability and high solubility. The dielectric constants and viscosities of gaseous solvents are lower than those of conventional liquid solvents, resulting in poor lithium salt solubility (<0.1 mol L−1) but a high dielectric-fluidity factor (13 mS cm−1 at −60 °C). Pressurized sealed cells with monofluorinated solvents like FM and DFM perform exceptionally well at temperatures as low as −60 °C or −78 °C, and the highly fluorinated SEI layer stabilizes lithium metal deposition. At room temperature, DFM and FM exhibited the highest vapor pressures of the solvents tested, at 3.8 and 1.8 MPa, respectively, with each having a melting point below −100 °C. Interestingly, a large overpotential is observed with the FM-based liquefied gas electrolyte at −60 °C, which limits its use at high current densities. This highlights the need to investigate the exact lithium-ion coordination in different solvation structures, rather than only focusing on ionic conductivity at low temperatures. Further research by the same group demonstrated that introducing THF into FM-based liquefied gas electrolytes fully coordinates with lithium cations, improving salt dissociation and transport. The addition of THF significantly increases lithium salt solubility, with a salt-to-THF molar ratio of 1
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. The low melting points (−142 °C for FM and −108.5 °C for THF) and low viscosity of these electrolytes enable excellent low-temperature rate and cycling performance down to −60 °C.
1. The low melting points (−142 °C for FM and −108.5 °C for THF) and low viscosity of these electrolytes enable excellent low-temperature rate and cycling performance down to −60 °C.
Other co-solvents like DFM and AN have also been explored. Adding AN to the system improves its solvation structure by selectively coordinating with the Li cation, which enhances desolvation and increases ion transport.126 This new solvation structure extends the low-temperature operational range beyond that of pure FM-based liquefied gas electrolytes, which show conductivity above 4.0 mS cm−1 from −78 to 25 °C. The improved liquefied gas electrolyte system could further expand the operational temperature range of high-voltage LIBs to as low as −60 °C. To further enhance desolvation and lithium salt solubility, it is recommended to add one or more co-solvents that coordinate with the Li cation, with a focus on understanding and rationally designing the solvation shell at low temperatures. Although most reported liquefied gas electrolyte systems use FM-based solvents, there is a need to develop additional solvents and systems. Additionally, conventional cells, such as pouch, cylindrical, and button cells, are not designed to withstand the high pressure required by these electrolytes, necessitating the creation of specialized testing devices for liquefied gas electrolyte systems. Using specialized battery cases on a large scale is not economically feasible, so it is essential to design cost-effective and widely available battery enclosures for these systems. The same research group further enhanced LIBs performance by using THF127 or AN128 to increase salt concentrations. However, the high vapor pressure of these liquefied gas solvents-several megapascals under standard conditions-presents a significant challenge for practical application. Moreover, there is growing interest in fluorine-substituted organic solvents due to their superior electrochemical stability and non-flammability.129 However, gas-based electrolytes must be liquefied under high pressure, which imposes stringent requirements on battery housing design. If a leak occurs, the release of hazardous fluoromethane (FM) could present serious risks.
4.2.1.5. Ionic liquid. Research on ionic liquid electrolytes and solid-state electrolytes for low-temperature applications remains relatively limited, with most studies still in their early stages. Ionic liquid electrolytes have attracted significant interest due to their impressive advantages over traditional organic electrolytes, such as superior chemical stability, wide electrochemical windows, high safety, and elevated ionic conductivity. Ionic liquids, which are molten salts that remain liquid below 100 °C, are composed of organic cations. These characteristics help enhance the mobility of lithium ions, making ionic liquids an attractive alternative to conventional organic electrolytes, especially in extreme conditions where organic electrolytes might pose hazards.
Several ionic liquids with melting points below −10 °C have been reported, showing promise for use in low-temperature environments. These include compounds such as [EtMeIm]+[N(CF3SO2)2]− (melting point between −15 °C and −20 °C), [EtMeIm]+[CF3CO2]− (around −14 °C), [EtMeIm]+[N(CN)2]− (−21 °C), and others like [1,3-Et2-5-MeIm]+[N(CF3SO2)2]− (−22 °C) and [PrMeIm]+[BF4]− (−17 °C), which further demonstrate the potential of ionic liquids for low-temperature applications. Some of these ionic liquids have very low freezing points, indicating their ability to operate in conditions where traditional organic electrolytes would fail. Notably, Ue et al.130 explored ionic liquid electrolytes in the field of double-layer capacitors and found that a 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium fluoride (EMIF)·2.3HF-based electrolyte outperformed a 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMIBF4)-based electrolyte, exhibiting higher capacitance and better electrolytic conductivity at temperatures ranging from −40 °C to 25 °C. Additionally, Li et al.131 incorporated ionic liquid-decorated poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) nanoparticles with LiTFSI/PC/MA electrolytes, achieving a low melting point of −49 °C and high ionic conductivity of 0.915 mS cm−1 at −40 °C, further proving the potential of ionic liquids in low-temperature energy storage systems.
However, the development of ionic-liquid-based LIBs is still in its infancy. Despite the promising characteristics of ionic liquids, there are significant challenges that need to be addressed. For one, the biodegradability, toxicity, and recyclability of ionic liquids remain difficult to assess quantitatively, and their high cost presents another barrier to their widespread adoption. Practical implementation of ionic liquid electrolytes in cold environments is yet to be confirmed, and more research is needed to determine their long-term viability in real-world applications. Achieving high performance at low temperatures requires careful selection of ionic liquids that offer both high ionic conductivity and a broad electrochemical stability window. Furthermore, research into mixtures of ionic liquids with organic solvents holds promise, as these blends can improve the safety and performance of ionic liquids in low-temperature conditions, potentially making them more viable for use in LIBs.
At present, most studies on low-temperature LIBs focus on mixtures of ionic liquid electrolytes with organic solvents, as these blends combine the benefits of both components, improving performance while enhancing safety. By optimizing the solvation structure and tuning the interactions between the ionic liquids and solvents, researchers can extend the operational temperature range of LIBs, improve their cycle stability, and increase their overall efficiency in extreme environments. As research continues, a deeper understanding of the ionic liquid and organic solvent interactions will be crucial for advancing the development of low-temperature LIBs. Consequently, this area of research holds considerable promise for the next generation of energy storage technologies, especially for applications that require reliable performance in extremely cold conditions, such as aerospace and remote high-altitude environments.132–134
In summary, although ionic liquid electrolytes show considerable potential for low-temperature LIBs, further advancements are necessary to address challenges related to cost, environmental impact, and practical implementation. As studies on ionic liquid–organic solvent mixtures progress, these systems could become a key component in the future development of efficient and robust batteries for extreme conditions.
4.2.1.6. Solid-state. Among the various approaches to address challenges such as desolvation, high melting points, and safety concerns, using solid-state electrolytes made from polymers, inorganic materials, or their hybrids at low temperatures presents an effective and long-term solution. Xu et al.135 developed a modified poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)-based solid-state electrolyte with succinonitrile (SN), which shows a high discharge capacity at 0 °C. Chen et al.136 demonstrated that a zirconia-supported solid-state electrolyte operates well between −10 and 90 °C. Li et al.137 employed a mixture of covalent organic frameworks and Li2CO3 as solid electrolytes, achieving an ion conductivity of 10−5 S cm−1 at −40 °C. Wang et al.138 found that Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5P3O12-based solid electrolyte cells function effectively from −73 to 120 °C. Although photothermal materials were used for the electrodes, the solid electrolyte showed great potential for cells at ultra-low temperatures, maintaining high-capacity retention at −73 °C. However, reports on solid-state electrolytes functioning at low temperatures remain rare in the literature. The significant interfacial resistances and low ionic conductivities at room temperature are expected to make solid-state electrolytes more challenging than liquid ones at low temperatures. While solid-state electrolytes hold promise as alternatives to liquid electrolytes, there remain substantial obstacles to their practical use, even at room temperature.
To mitigate the challenges posed by low temperatures, novel electrolytes such as solid-state electrolytes have shown promising results. These electrolytes exhibit improved thermal stability, lower melting points, and higher ionic conductivity at low temperatures compared to conventional liquid organic electrolytes. The adoption of such electrolytes can help overcome the limitations of slow charge transfer kinetics and lithium plating, while simultaneously enhancing the overall safety and cycle life of LIBs.
4.2.1.7. Other solvents. Researchers have also explored organic solvents containing sulfur (S), nitrogen (N), or phosphorus (P) as potential low-temperature electrolyte solvents. Sulfites, in particular, have gained attention in the battery community for low-temperature applications because their decomposition products offer better Li-ion conductivity than Li alkylcarbonates.139 The sulfurized SEI helps reduce impedance at low temperatures. While linear sulfites have weaker film-forming properties than their cyclic counterparts, their lower melting points, lower viscosities, and appropriate dielectric constants make them ideal for low-temperature electrolytes. When DMS and diethyl sulfite (DES) were used as replacements for structurally similar linear carbonates (DMC and DEC) in EC-based electrolytes, the ionic conductivity of the electrolytes at low temperatures was notably improved. For example, a 0.8 M LiDFOB/LiBF4 (1
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) in EC/DEC/DMS (1
1 v/v) in EC/DEC/DMS (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) allowed a Li/LFP cell to maintain nearly 100% capacity retention for 50 cycles at −40 °C and 0.2C.140 Li et al. created a fully sulfided electrolyte by mixing sulfolane (SL) with DMS. This combination, along with LiDFOB, resulted in a robust, low-temperature-adaptable electrolyte due to the synergistic effects of DMS and SL.72,141
1 v/v/v) allowed a Li/LFP cell to maintain nearly 100% capacity retention for 50 cycles at −40 °C and 0.2C.140 Li et al. created a fully sulfided electrolyte by mixing sulfolane (SL) with DMS. This combination, along with LiDFOB, resulted in a robust, low-temperature-adaptable electrolyte due to the synergistic effects of DMS and SL.72,141
Isoxazole (IZ) has also been used as a primary solvent for low-temperature electrolytes, due to its excellent ionic conductivity at low temperatures. When combined with FEC and LiDFOB, IZ helps form stable SEI films. A 1 M LiDFOB in IZ/FEC (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) exhibited more than double the ionic conductivity of an EC/EMC electrolyte. A Li/graphite cell using this IZ-based electrolyte showed a high reversible capacity of 187.5 mA h g−1 at −20 °C, much higher than the 23.1 mA h g−1 achieved with an EC/EMC electrolyte.142 Xiao et al.143 introduced a high-donor-number tris(pyrrolidinophosphine) oxide (TPPO) as a multifunctional cosolvent in carbonate electrolytes. On the anode, TPPO helped LiNO3 dissolve easily in carbonate solvents, forming a robust, highly ion-conducting Li3N-rich SEI film. On the cathode, TPPO preferentially oxidized into a tough, thin N, P-rich CEI film. The simultaneous formation of superior interfacial films on both electrodes allowed the TPPO electrolyte to enable a Li/LFP cell to achieve a high initial capacity of 104 mA h g−1 and nearly 100% capacity retention after 100 cycles at −15 °C.
1 v/v) exhibited more than double the ionic conductivity of an EC/EMC electrolyte. A Li/graphite cell using this IZ-based electrolyte showed a high reversible capacity of 187.5 mA h g−1 at −20 °C, much higher than the 23.1 mA h g−1 achieved with an EC/EMC electrolyte.142 Xiao et al.143 introduced a high-donor-number tris(pyrrolidinophosphine) oxide (TPPO) as a multifunctional cosolvent in carbonate electrolytes. On the anode, TPPO helped LiNO3 dissolve easily in carbonate solvents, forming a robust, highly ion-conducting Li3N-rich SEI film. On the cathode, TPPO preferentially oxidized into a tough, thin N, P-rich CEI film. The simultaneous formation of superior interfacial films on both electrodes allowed the TPPO electrolyte to enable a Li/LFP cell to achieve a high initial capacity of 104 mA h g−1 and nearly 100% capacity retention after 100 cycles at −15 °C.
| Lithium salt | Stability | Conductivity | Thermal stability | Passivation of Al | Toxicity | Electrolyte formulation | Anode/cathode | Low temperature performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) | High | High | Low | High | Low | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Graphite/LPO | 70% of RTC at −20 °C | 144 |
1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7 v/v) 7 v/v) |
Graphite/LCO | 68.7% of RTC at −70 °C | 145 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in DEC/DMC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
LVP/C | 16% of RTC at −30 °C | 146 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC/EMC (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v/v) 1 v/v/v/v) |
LVP/C | 43% of RTC at −30 °C | 146 | ||||||
| 1 M LiPF6 in PC | LTO/NMC622 | — | 147 | ||||||
| 1 M LiPF6 | Graphite/LCO | ∼72.3% at −20 °C | 148 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Graphite/LCO | ∼60% of RTC at −40 °C and C/20 | 59 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v/v/v) 3 v/v/v/v) |
Graphite/LNCO | ∼58.96% of RTC at −40 °C and C/15 | 149 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v/v/v) 3 v/v/v/v) |
LiFePO4/C|Li cell | ∼55% of RTC at −40 °C and C/1 | 150 | ||||||
0.75 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC/ETFEC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v/v) 1 v/v/v/v) |
Li/MCMB | — | 60 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC/TFEB (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 60 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 v/v/v) 20 v/v/v) |
MCMB/LNCO | ∼85% of RTC at −20 °C and 50 mA | 75 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC/MP (20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 60 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 v/v/v) 20 v/v/v) |
MCMB/LNCO | ∼60–77% of RTC at −20 °C and C/16 | 76 | ||||||
1 M LiPF6 in MP/FEC (90![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 v/v) 10 v/v) |
Graphite/NCM111 | ∼60% of RTC at −40 °C | 65 | ||||||
2 M LiPF6 in THF/2MeTHF (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) 1 v/v) |
Li/SiMP | — | 123 | ||||||
| LiPF6 in iBN/EC | LCO/graphite | 75.8% of RTC at −40 °C and ∼68.7% of RTC at −70 °C | 151 | ||||||
| Lithium tetrafluoroborate (LiBF4) | High | Low | Medium | High | Low | 1 M LiBF4 in PA | LTO/LCO | 91% of RTC at −40 °C (0.5C) and 75% of RTC at −60 °C (0.2C) | 152 |
1 M LiBF4 in PC/EC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 w/w/w) 3 w/w/w) |
Graphite/LNO | ∼86% of RTC at −30 °C | 153 | ||||||
1 M LiBF4/LiBOB (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 m/m) in PC/EC/EMC (1 1 m/m) in PC/EC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 w/w/w) 3 w/w/w) |
Li/LFP | ∼30% of RTC at −50 °C | 154 | ||||||
1 M LiBF4/LiBOB (8![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2) in PC/EC/EMC/MB (1 2) in PC/EC/EMC/MB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v/v/v) 3 v/v/v/v) |
Li/LFP | ∼60% of RTC at −40 °C | 155 | ||||||
| Lithium bis (oxalato) borate (LiBOB) | Low | High | High | Low | Low | 1 M LiBOB in PC/EC/ECM (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Graphite/LNO | ∼74% of RTC at −30 °C | 156 |
0.7 M LiBOB in GBL/EA (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 w/w) 1 w/w) |
— | — | 157 | ||||||
1 M LiBOB in GBL/D2 (70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 w/w) 30 w/w) |
Graphite/NCM111 | >60% of RTC at −40 °C | 90 | ||||||
| Lithium (oxalato) difluoro borate (LiDFOB) | High | High | Medium | High | Low | 1 m LiDFOB in PC/EC/EMC (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 w/w/w) 4 w/w/w) |
Graphite/NCA | >20% of RTC at −40 °C | 158 |
0.9 M LiDFOB in SL/DMS (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) 1 v/v) |
Li/LFP | >20% of RTC at −40 °C | 141 | ||||||
0.9 M LiDFOB/LiBF4 (5.365![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 w/w) in EC/DMC/EMC (1 1 w/w) in EC/DMC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v/v) 3 v/v/v) |
Li/LFP; Li/graphite | >20% of RTC at −40 °C | 72 | ||||||
0.8 M LiDFOB/LiBF4 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 m/m) in EC/DEC/DMS (1 1 m/m) in EC/DEC/DMS (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Li/LFP | 55.7% of RTC at −40 °C | 159 | ||||||
1 M LiDFOB in GBL/FEPE (70![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 30 w/w) 30 w/w) |
Graphite/NCM523 | 100 mA h g−1 at −40 °C | 91 | ||||||
| Lithium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide (LiTFSI) | Medium | High | High | Low | Low | 1 M LiTFSI in DMC/FEC/MA | Graphite/NCM811 | 72% of RTC at −40 °C | 160 |
1.25 M LiTFSI in PC/MA (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v) 3 v/v) |
Li/MnO2 | >40% of RTC at −10 °C | 161 | ||||||
0.9 M LiTFSI in EC/DMC/EMC (15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 37 37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 48 w/w/w) 48 w/w/w) |
Graphite/LNCO | <30% of RTC at −40 °C | 7 | ||||||
0.5 M LiTFSI in MA/DOL/TEGDME (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 47.5 47.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 47.5 v/v/v) 47.5 v/v/v) |
Li/S | <85% of RTC at −10 °C | 119 | ||||||
1–1.4 M LiTFSI in DOL/DME/TEGDME (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Li/S | — | 162 | ||||||
1 M LiTFSI in DOL/DME (80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 v/v) 20 v/v) |
Li/Cu | — | 108 | ||||||
| 0.75 M LiTFSI in DOL | LTO/LCO | ∼60% of RTC at −80 °C and 0.1C | 163 | ||||||
1 M LiTFSI in DOL/DME (80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20 v/v) with 10 vol% FEC 20 v/v) with 10 vol% FEC |
Li/LFP | ∼50% of RTC at −60 °C | 112 | ||||||
1 M LiTFSI in EC/DEC/MB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Li/Mxene@LM | 78% of RTC at −20 °C | 164 | ||||||
| 0.5 M LiTFSI in ETFA | Li/LTO | 91% of RTC at −50 °C and 0.05C | 83 | ||||||
1 M LiTFSI in ETFA/FEC (7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 v/v) 3 v/v) |
Graphite/LFP | −40 °C and 0.02C; 82 mA h g−1 | 84 | ||||||
0.2 M LiTFSI in FM/CO2 (19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 w/w) 1 w/w) |
Li/LCO | 60.6% of RTC at −60 °C and 0.1C | 125 | ||||||
0.3 M LiTFSI, 0.3 M THF in FM/CO2 (19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 w/w) 1 w/w) |
Li/polished stainless steel | 98% of RTC at −60 °C | 127 | ||||||
1.2 M LiTFSI, 1 M AN in FM/CO2 (19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 w/w) 1 w/w) |
Li/NCM622 | 65% of RTC at −60 °C and 1.15C | 126 | ||||||
| 0.3 M LiTFSI in FM | Li/CFx | 57% of RTC at −40 °C and 10 mA h g−1 | 165 | ||||||
| Lithium bis (fluorosulfonyl) imide (LiFSI) | Low | High | High | Low | Low | LiFSI/BN in VC/FEC (1.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 m/m) 10 m/m) |
NMC111/graphite | 82.6% of RTC at −40 °C 105 mA h g−1 | 166 |
| LiFSI/AN-LHC | Graphite/NCM | 71% of RTC at −30 °C and 110 mA h g−1 | 167 | ||||||
| LiFSI/MF91 | LFP/graphite | 80.2% of RTC after 1200 cycles (2C) at −80 °C | 168 | ||||||
1 M LiFSI in EC/EMC (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 7 v/v) 7 v/v) |
Li/LCO | — | 169 | ||||||
1.4 M LiFSI in DMC/EC/D2 (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.2 0.2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 m/m/m) 3 m/m/m) |
Graphite/NCM811 | — | 170 | ||||||
1 M LiFSI in PC/MB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2 v/v) 2 v/v) |
Li/CFx | −70 °C and 0.1C; 240 mA h g−1 | 78 | ||||||
| 4 M LiFSI in DMC | Li/graphite | 85.6% at −30 °C and C/5 | 171 | ||||||
| 1 M LiFSI in DEE | Li/SPAN | 76% of RTC at −60 °C and 0.1C | 105 | ||||||
| 1 M LiFSI in DMM | Li/SPAN | 64% after 120 cycles at −40 °C and 0.1C | 31 | ||||||
LiFSI![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) DME DME![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) FB (1 FB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1.2 1.2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 m/m/m) 3 m/m/m) |
Li/S | 7.6 mA h cm−2 and −20 °C | 172 | ||||||
| 0.3 M LiFSI, 0.35 DME in DFM | Li/NCM622 | 42% of RTC at −40 °C and 0.05C | 173 | ||||||
1 M LIFSI in Me2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1.15 m/m) + TFE/PFE (7 1.15 m/m) + TFE/PFE (7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) 1 v/v) |
Li/NCM622 | −60 °C and 1.15C; 71 mA h g−1 | 174 | ||||||
| 1.28 M LiFSI in FEC/FEMC/D2 | Li/NCA | ∼56% of RTC at −85 °C | 175 | ||||||
| LiFSI in MA/FB | LCO/graphite | ∼91% of RTC at −60 °C at 0.05C | 176 | ||||||
| LiFSI and LiFTFSI | NCM/graphite | >60% of RTC at −40 °C | 177 | ||||||
| LiMe | Low | Low | Poor | Poor | Low | 1 M LiMe in MF/EC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) 1 v/v) |
Li/graphite | — | 178 |
| LiSO3CF3 | High | Moderate | High | Low | Moderate to high | 0.7 M LiSO3CF3 in DOL/DME (86![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 14 w/w) 14 w/w) |
Li/S | >60% of RTC at −40 °C | 104 |
| LiBETI | Very high | High | High | High | Moderate | 1 M LiBETI in EC/DEC/TMMP (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 45 45![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 v/v/v) 50 v/v/v) |
Li/S | >60% of RTC at −30 °C | 121 |
0.7 M LiBETI in FEC/DEC/M3 (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 14 v/v/v) 14 v/v/v) |
Li/NCM622 | — | 175 | ||||||
| Lithium perchlorate (LiClO4) | 1 M LiClO4 in EC/DMC/DEC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Li//HC | 117.9 mA h g−1 at −20 °C, and 23.3 mA h g−1 at −40 °C | 179 | |||||
1 M LiClO4 in PC/DMC/DEC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v/v) 1 v/v/v) |
Li//HC | 153.3 mA h g−1 at −20 °C, and 59.0 mA h g−1 at −40 °C | 179 | ||||||
| 0.8 M LiClO4 in DMMP | Li/MnO2 | ∼66% of RTC at −20 °C; 100 mA h g−1 | 120 |
4.2.2.1. Lithium hexafluorophosphate salts (LiPF6). Currently, LiPF6 is the most commonly used lithium salt in LIBs due to its high ionic conductivity and excellent electrochemical stability.51 It is also non-corrosive to current collectors.180 While LiPF6 can form a stable and protective SEI film, it has some limitations, including poor thermal stability. Its thermal instability can lead to the formation of PFO3, and its reaction with water produces HF, which is both harmful and corrosive. HF not only poses safety hazards but also damages other cell components, significantly reducing battery efficiency. It can also degrade interfacial protective layers and contribute to metal corrosion.181,182 Additionally, the operational temperature range for LiPF6 in organic solvents is typically from −20 to 60 °C; below −20 °C, the electrolyte experiences severe polarization, as its low diffusion rate at these temperatures causes local Li+ buildup.12,153,183 As a result, despite its widespread use in commercial cells, there is an urgent need for new advanced lithium salts to improve LIBs performance across various applications.
Plichta et al.184 found that LIBs using an EC/DMC/EMC electrolyte containing LiPF6 retained 52% of their capacity at −40 °C, demonstrating high conductivity and electrochemical stability. This electrolyte has been shown to perform well in LIBs even at temperatures as low as −40 °C. Mandal et al.7 reported that an electrolyte with LiTFSI in EC, DMC, and EMC showed good conductivity, reaching nearly 2.0 mS cm−1 at −40 °C. Elia et al.185 used an EC/DMC/DEC-based electrolyte, commonly used for low-temperature applications, and found that at −30 °C, a full cell retained 60% of its capacity at 37 mA g−1, indicating efficient performance with minimal polarization. Huang et al.186 reported that an electrolyte consisting of EC/DEC/DMC/EMC with LiPF6 maintained around 60% capacity at −30 °C.
4.2.2.2. Lithium borate salts (LiBF4, LiBOB, LiDFOB). To enhance the low-temperature performance of electrolytes from the perspective of lithium salts, researchers have extensively explored and developed specialized lithium salts to replace LiPF6. Borate (B)-containing and sulfur (S)-containing lithium salts are commonly used in low-temperature electrolytes. Borate salts are more frequently used in LIBs, while sulfur-based salts are primarily applied in LMBs, particularly Li–S batteries. Compared to LiPF6-based carbonate electrolytes, those based on lithium tetrafluoroborate (LiBF4), lithium bis(oxalato)borate (LiBOB), and lithium oxalato difluoro borate (LiDFOB) provide improved ion mobility and enhanced rate performance at low temperatures in LIBs. Specifically, electrolytes using LiBF4 and LiBOB show lower Rct.156,187 Zhang et al.153 analyzed the Nyquist plot of the impedance spectrum of a LIBs at −30 °C using electrolytes containing either 1.0 M LiPF6 or LiBF4 in an EC/PC/EMC (1
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) solvent mixture. They observed that the Rct was decoupled from the Rb, which relates to the ionic conductivity in the electrolyte. The Rct of batteries with LiBF4 was significantly lower than that with LiPF6, though LiBF4 exhibited a higher Rb. However, the exact chemical mechanisms behind this behavior remain unclear.
3) solvent mixture. They observed that the Rct was decoupled from the Rb, which relates to the ionic conductivity in the electrolyte. The Rct of batteries with LiBF4 was significantly lower than that with LiPF6, though LiBF4 exhibited a higher Rb. However, the exact chemical mechanisms behind this behavior remain unclear.
Despite LiBF4's inferior SEI properties and lower ionic conductivity, several studies12,153,183 suggest it may offer better performance for LIBs at low temperatures compared to LiPF6. Notably, a LiBF4-based cell retained 86% of its capacity at −30 °C, whereas a LiPF6-based cell only retained 72%. Moreover, the polarization in LiBF4-based electrolytes at −30 °C was minimal. The lower Rct indicated improved low-temperature performance, although LiBF4 has lower solubility in carbonate solvents than LiPF6 due to higher viscosity and reduced interfacial reactivity with graphite. Further studies have shown that the addition of LiBOB (1–5 mol%) to LiBF4 improves the SEI-forming ability on graphite anodes, mitigating substantial early cycle capacity loss and gas formation.188 Zhang et al.189,190 also synthesized LiODFB, which demonstrated high capacity retention at −30 °C. Adding 0.02 mol L−1 LiBOB to LiBF4-based electrolytes enhances SEI formation and improves cycling performance at −40 °C. Recently, LiTFSI and other organic lithium salts have gained popularity in ether-based and ionic liquid electrolytes due to their high solubility and thermal stability, offering superior conductivity, reaching 2 mS cm−1 at −40 °C.
One of the most studied lithium salts for low-temperature LIBs is LiBOB, known for its ability to protect the SEI film and prevent transition metal deposition, thus enhancing overcharge tolerance and ensuring a stable SEI on electrode surfaces.191 However, LiBOB suffers from high viscosity and poor solubility in carbonate solvents, issues that worsen at low temperatures.156 To address these drawbacks, a new lithium salt, LiDFOB, with better film-forming properties, was developed to enhance low-temperature performance. LiDFOB combines the advantages of both LiBOB and LiBF4, breaking down into an inorganic-rich SEI. To further improve low-temperature performance, binary salt systems have been developed. For example, a mixture of LiBF4/LiBOB was used to optimize low-temperature performance in Li/LFP cells. At −50 °C and 1C, a Li/LFP cell with a 1 M LiBF4/LiBOB mixture (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 m/m) in PC/EC/EMC (1
1 m/m) in PC/EC/EMC (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 w/w/w) delivered up to 30% capacity.192 This mixture enabled the Li/LFP cell to deliver a discharge capacity of 82.5 mA h g−1 at −40 °C, retaining 55.7% of the room temperature capacity. After 50 cycles, the capacity retention was close to 100%.
3 w/w/w) delivered up to 30% capacity.192 This mixture enabled the Li/LFP cell to deliver a discharge capacity of 82.5 mA h g−1 at −40 °C, retaining 55.7% of the room temperature capacity. After 50 cycles, the capacity retention was close to 100%.
Several studies have described mixed-salt electrolytes using LiBF4–LiDFOB to combine the benefits of both salts for low-temperature applications. For example, Li et al.71 studied an electrolyte with a LiDFOB/LiBF4 mixture and an EC/DMC/EMC solvent mixture, which outperformed LiPF6-based electrolytes at −20 °C, offering significantly higher capacities. Zhou et al.193 tested different LiDFOB/LiBF4 ratios over a temperature range from −20 °C to 60 °C, discovering that a 0.2 M LiBF4/0.8 M LiDFOB ratio optimized performance at −20 °C. This combination decreased the Rct by 346.3 Ω at −20 °C without compromising the efficient passivation of LiDFOB. After 100 cycles, the cell exhibited the best retention at a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 LiBF4/LiODFB ratio. Zhao et al.159 explored an electrolyte with a LiBF4/LiODFB (1
4 LiBF4/LiODFB ratio. Zhao et al.159 explored an electrolyte with a LiBF4/LiODFB (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mol%) combination in an EC/DMC/DMS (1
1 mol%) combination in an EC/DMC/DMS (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) solvent mixture, achieving a discharge capacity of 82.5 mA h g−1 at −40 °C and maintaining nearly 100% capacity after 50 cycles.
1 v/v) solvent mixture, achieving a discharge capacity of 82.5 mA h g−1 at −40 °C and maintaining nearly 100% capacity after 50 cycles.
4.2.2.3. Lithium sulfonylimide salts (LiFSI, LiTFSI). Sulfur-containing lithium salts are commonly used in low-temperature electrolyte formulations due to their enhanced electrochemical and thermal stability, which significantly boosts cycle performance and safety. Among these, LiTFSI is the most widely recognized lithium salt.194 The TFSI-anion's acidity contributes to strong chemical inertness, improving electrochemical stability against oxidation. Similarly, lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) offers high electrochemical stability, conductivity, and resistance to hydrolysis, making it versatile for enhancing cycle performance in various electrolytes. For instance, Mandal and colleagues demonstrated that LiTFSI-based electrolytes exhibit superior ionic conductivity at low temperatures (2 mS cm−1 at −40 °C) compared to LiPF6-based systems.7 LiTFSI-containing full cells perform well, and half-cells remain functional at −40 °C.
However, a notable drawback of FSI- and TFSI-anions is their tendency to cause corrosion in the aluminum current collector of the cathode. This issue is likely linked to F–S bonds in the FSI anion or residual chloride (Cl−) impurities from the synthesis process.169,195,196 This corrosion challenge makes it difficult to determine whether performance issues stem from LiF and trace HF formation or the inherent properties of the anion. Increasing lithium salt concentrations in the electrolyte can reduce aluminum corrosion, but high concentrations lead to increased viscosity, which negatively impacts low-temperature performance.51 Alternatively, adding borate ester salts can mitigate aluminum collector corrosion.197
Recently, dual-salt electrolytes like LiTFSI/LiDFOB have demonstrated good ionic conductivity at low temperatures. Additionally, combinations such as LiTFSI/LiDFOB and LiTFSI/LiBOB have proven effective in enhancing the electrochemical performance of LIBs.198
Ein-Eli et al.178 observed that Li/graphite cells with electrolytes based on LiC(SO2CF3)3 (LiMe) and LiTFSI exhibited superior cycling performance compared to those using LiPF6 electrolytes. While LiMe dissolves readily in organic solvents and offers higher ionic conductivity than LiTFSI, its use at low temperatures has been scarcely reported.155 Mikhaylik et al.104 demonstrated that Li–S cells with LiSO3CF3 electrolytes delivered significantly higher discharge capacities than those with LiSCN or LiTFSI in DME/DOL at −10 °C and a 0.5C discharge rate. However, the limited ionic conductivity of LiSO3CF3-based electrolytes has restricted their application in low-temperature studies.
LiTFSI is currently the most widely utilized sulfur-containing salt for low-temperature electrolytes due to its excellent properties, including high solubility, ionic conductivity, and improved desolvation on the cathode side.199 Mandal et al.7 compared LiTFSI and LiPF6 (0.9 M salt in EC/DMC/EMC at 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 37
37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 48 v/v/v) and found that the Rct for LiTFSI-based electrolytes was nearly an order of magnitude lower than that for LiPF6, as evidenced by Nyquist plots (Fig. 12a). This reduced Rct allowed Li/LNCO cells with LiTFSI-based electrolytes to function at temperatures as low as −40 °C. Additionally, the optimal ionic conductivity for LiTFSI-based electrolytes occurs at salt concentrations of 1.4–1.5 M (Fig. 12b).162,200
48 v/v/v) and found that the Rct for LiTFSI-based electrolytes was nearly an order of magnitude lower than that for LiPF6, as evidenced by Nyquist plots (Fig. 12a). This reduced Rct allowed Li/LNCO cells with LiTFSI-based electrolytes to function at temperatures as low as −40 °C. Additionally, the optimal ionic conductivity for LiTFSI-based electrolytes occurs at salt concentrations of 1.4–1.5 M (Fig. 12b).162,200
 | ||
Fig. 12 (a) Nyquist plots of cells featuring 0.9 M LiPF6 and LiTFSI in EC/DMC/EMC (15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 37 37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 48 v/v/v). Reproduced with permission from ref. 7. (b) Conductivity measurements of electrolytes with varying concentrations at different temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 200. (c) Schematic representation of the roles of LiTFSI and LiBOB in a dual-salt electrolyte. Reproduced with permission from ref. 195. (d) Cycling performance of a Li/NCM523 cell utilizing a LiTFSI/LiDFOB dual-salt electrolyte system at 1C and −40 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 206. 48 v/v/v). Reproduced with permission from ref. 7. (b) Conductivity measurements of electrolytes with varying concentrations at different temperatures. Reproduced with permission from ref. 200. (c) Schematic representation of the roles of LiTFSI and LiBOB in a dual-salt electrolyte. Reproduced with permission from ref. 195. (d) Cycling performance of a Li/NCM523 cell utilizing a LiTFSI/LiDFOB dual-salt electrolyte system at 1C and −40 °C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 206. | ||
Other reported sulfonylimides for low-temperature electrolytes include lithium bis(pentafluoroethylsulfonyl)imide (LiBETI) and LiFSI. Electrolytes containing 1 M LiBETI in EC-based solutions enabled MCMB/LCO cells to retain over 60% of their room-temperature capacity at −20 °C.121 However, LiBETI's high cost limits its practicality as a primary salt, making it more suitable as an additive. LiFSI-based electrolytes, on the other hand, offer higher ionic conductivity and improved interfacial stability compared to LiTFSI. As LiFSI's production process has matured, its cost has declined, making it a promising candidate for low-temperature applications.201 LiFSI has become a popular choice in advanced electrolyte systems such as highly concentrated electrolytes (HCE), localized HCEs (LHCE), and weakly solvating electrolytes.171,202,203
Despite their advantages, lithium sulfonylimides can cause corrosion of aluminum current collectors due to side reactions between the anions and aluminum.204 This issue can be mitigated by combining sulfonylimides with borate salts, significantly reducing corrosion (Fig. 12c).195,205,206 Lin et al.207 developed a blended electrolyte system using LiTFSI and LiDFOB for rapid ion dynamics in high-voltage RLBs at low temperatures. This system enabled Li/NCM523 cells to achieve 200 stable cycles at a 4.6 V cut-off voltage, 1C rate, and −40 °C (Fig. 12d).
Advancements in mixed-salt electrolytes have significantly contributed to the development of next-generation LIBs. Three key factors highlight the crucial role of lithium salt anions in determining the low-temperature performance of cells: the extent of dissociation, the SEI derived from the anion, and the likelihood of parasitic reactions. To achieve low SEI resistance, high electrolyte conductivity, and stable interfaces, future lithium salt candidates must strike a careful balance among these characteristics.
| Solvent additive | Structure | Mechanism | Temperaturea | Electrical conductivity (mS cm−1) | Ratio wt.% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Temperature is the lowest operating temperature that can be achieved by a cell composed of this electrolyte. | ||||||
| Allyl sulfide (AS) |

|
Facilitates the charge transfer reaction on the graphite surface | −30 | 0.6 | 2 | 209 |
| Phenyl methanesulfonate (PhMS) |
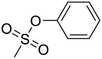
|
Improves the migration kinetics of Li+ in the graphite anode and reduces the lithium-ion deposition on the graphite anode surface | −20 | 5.26 | 1 | 210 |
| 1,3,2-Dioxathiolane-2,2-dioxide (DTD) |
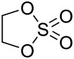
|
Leads to reduction paths creating large amounts of dimeric sulfur-based species to create an advantageous SEI | −20 | 0.058 | 1 | 211 |
| Dimethyl sulfite (DMS) |

|
Has a unique molecular structure and appropriate reduction activity | −20 | 0.033 | 0.5 | 212 |
| Tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite (TMSP) |

|
Contributes to the formation of a robust and ultrathin film on cathodes and consumes HF produced in LiPF6-based electrolytes during cycling | −40 | 14.28 | 0.5 | 36 and 213 |
| Fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) |

|
Suppresses the decomposition of electrolytes and decreases the charge-transfer resistance | −40 | 0.004 | 2 | 67 and 214 |
| Vinylene carbonate (VC) |

|
Provides surface protection on both electrodes | −40 | 0.075 | 2 | 215 and 216 |
Additives are incorporated into electrolytes to enhance their performance, addressing properties such as SEI film formation, flammability, and resistance to high pressures, typically comprising no more than 5% of the electrolyte by mass. They are also crucial for improving low-temperature performance. The primary categories of additives include organic compounds, inorganic salts, and siloxanes.217,218 Some additives decompose or polymerize on electrode surfaces to form protective films that prevent further redox reactions of the electrolyte, while others chelate with reaction centers on electrodes to inhibit electrolyte decomposition. As a result, electrolyte additives in LIBs improve SEI properties, enhance ionic conductivity, and protect cathode materials from dissolution and overcharging.219
Fig. 13 illustrates the development of additives in recent years by comparing the conductivity of a standard salt (1 M LiPF4) before and after adding various additives at low temperatures. Fig. 13 demonstrates that certain salts (e.g., LiDFOB, LiPO2F2) or organic additives like phenyl methanesulfonate (PhMS) and tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite (TMSP) maintain high conductivity in the electrolyte. Early use of organic additives, such as allyl sulfide (AS) and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), significantly improved electrolyte conductivity (as shown on the left side of Fig. 13).
4.3. Aqueous electrolytes
Due to its unique dielectric and fluid properties, water is an excellent conductor for electrolytes, facilitating faster kinetics during the discharge/charge processes.220,221 Compared to organic electrolytes, water is more affordable and safer than lithium-ion technology. However, it's very low electrochemical stability window limits the energy density of LIBs. For LIBs to function at temperatures below −20 °C, water's freezing point presents a significant challenge, as pure water freezes below 0 °C, hindering low-temperature applications. However, the freezing point of aqueous electrolytes can be lowered by several tens of degrees below the thermodynamic value through the addition of lithium salts and other additives.220 In recent years, numerous aqueous electrolyte approaches have been suggested to significantly enhance the operating range and stability of aqueous lithium batteries at low temperatures. A summary of some key low-temperature aqueous electrolytes is provided in Table 5.| Electrolyte formulation | Anode/cathode | Low-temperature performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 M LiTFSI aqueous solution | LiTiO2(PO4)3/Li3V2(PO4)3 | 60% of RTC at −20 °C and 6C | 222 |
20 M LiPTFSI/LiOTf (15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 m/m) aqueous solution 5 m/m) aqueous solution |
Activated carbon (AC)/LiMn2O4 | −10 °C and 1C | 220 |
| Over 100 mA h g−1 | |||
15.3 M LITFSI in water/AN (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 m/m) 1 m/m) |
LTO/LMO | 95% (110 70 mA h g−1) after 120 cycles at 0 °C and 1C | 223 |
| 5.2 M LiTFSI in water | AC/LMO | 66.4% of RTC at −40 °C and 2C | 224 |
| 5 M LiTFSI in water saturated with CO2 | Mo6S8/LMO | −40 °C and 0.5C | 225 |
| Over 70 mA h g−1 | |||
| Saturated aqueous solution of LiCl | Li0.75CoO2/LiCoO2 | ∼72% of RTC at −40 °C and 0.22C | 226 |
| 0.5 M Li2SO4 aqueous solution + 30 mol% DMSO | AC/LiTi2(PO4)3@C | 62% of RTC at −50 °C and 0.5C | 227 |
| 1 M Li2SO4 aqueous solution + 40 mol% EtG | AC/LFP | −20 °C and 1C | 228 |
| Over 40 mA h g−1 | |||
SL![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O H2O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) LiClO4 (12 LiClO4 (12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3 m/m/m) 3 m/m/m) |
LTO/LMO | 87% after 200 cycles at −20 °C and 200 mA h g−1 | 229 |
Based on colligative properties, the freezing point depression can be calculated using the following equation:
| ΔTf = Twater − Tsoln = Kf·m | (4) |
The “water-in-salt” (WIS) electrolyte concept was introduced by Suo et al., who developed a highly concentrated aqueous electrolyte containing 21 M LiTFSI in water.222 This WIS electrolyte significantly reduced the electrochemical activity of water and formed a dense SEI on the anode surface due to anion reduction. These advantages allowed the WIS electrolyte to achieve an expanded electrochemical stability window of 3.0 V. Additionally, due to colligative properties, the freezing point of highly concentrated or even saturated salt solutions can be lowered by several tens of degrees compared to pure water.9,230 The broad electrochemical window, strong film-forming ability, and low freezing point of the WIS electrolyte make it suitable for the stable operation of high-energy-density aqueous LIBs at low temperatures. For example, the 21 M LiTFSI aqueous electrolyte resolved the fading issue of the Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode and allowed LiTi2(PO4)3/Li3V2(PO4)3 batteries to achieve a high initial Coulombic efficiency of 86.7% and excellent rate performance at −20 °C.222
Ramanujapuram and Yushin226 explored aqueous electrolytes with three types of lithium salts (LiCl, Li2SO4, and LiNO3) and demonstrated that cells with LiCl-saturated electrolytes perform well even at low temperatures as low as −45 °C. These cells exhibit lower charge transfer resistance and excellent rate performance at low temperatures. Unlike organic electrolytes, cells with aqueous electrolytes and layered cathodes do not experience rapid capacity fading or a significant increase in Rct as the temperature decreases. Certain anion salts, such as LiTFSI and its derivatives, show remarkable electrochemical stability due to their unique solvation structure in aqueous electrolytes, where water molecules are strongly coordinated with lithium ions and confined within anion-containing lithium ion solvation sheaths.231,232
Lithium salts in WIS electrolytes benefit from the presence of asymmetric anions and organized structures that minimize crystallization, though the mechanisms behind this remain unclear.233,234 Yue et al. revisited WIS electrolytes by incorporating a CO2 additive into a traditional salt-in-water (SIW) framework, forming a novel aqueous interphase.225 This research draws on earlier electrolyte studies that initially investigated CO2 in organic systems and employed SIW formulations, such as a 5 M LiNO3 solution.229 The interaction between CO2 and LiTFSI allows CO2 to dissolve effectively in a 5 M LiTFSI SIW electrolyte, producing a Li2CO3-rich layer on the anode. This layer is critical for reducing hydrogen evolution at the anode and enabling the reduction of TFSI. The reduction of the CO2-TFSI complex creates a robust aqueous interphase featuring both LiF and Li2CO3. Compared to WIS electrolytes, the CO2-SIW formulation offers notable benefits, including lower viscosity, enhanced ionic conductivity, and resistance to crystallization. These properties improve electrochemical performance and enable superior operation at low temperatures. For example, a Mo6S8/LMO full cell using the CO2-SIW electrolyte achieved stable cycling at −40 °C, delivering over 70 mA h g−1 at 0.5C (see Fig. 14).
 | ||
| Fig. 14 (a) Initial charge/discharge profiles of a Mo6S8/LMO aqueous full cell using CO2-SIW and WIS electrolytes. (b) Cycling stability of the Mo6S8/LMO aqueous full cell with CO2-SIW electrolyte at −40 °C and 0.5C. Reproduced with permission from ref. 225. | ||
To enhance the low-temperature performance of aqueous electrolytes, various cosolvents and additives such as acetonitrile (AN), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and ethylene glycol (EG) have been introduced. For example, the crystallization temperature of an aqueous electrolyte decreases significantly from −4.6 °C to −24.6 °C as the EG concentration is increased from 0 to 40 wt%.235 Among these additives, DMSO is notable for its ability to form strong hydrogen bonds with water molecules. By integrating into the cation solvation sheath and replacing some coordinating water molecules, DMSO effectively suppresses interfacial electrochemical reactions, thereby enabling the electrolyte to operate at lower temperatures. Nian et al. demonstrated that incorporating DMSO into an aqueous electrolyte results in an extremely low freezing point of less than −130 °C, while maintaining a sufficient ionic conductivity of 0.11 mS cm−1 at −50 °C.227 Additionally, Dou et al. reported that AN significantly reduces the viscosity of aqueous electrolytes, enhances ionic conductivity, and supports operation over a wide temperature range from −30 °C to 50 °C.236
In traditional LiTFSI-based aqueous electrolytes, lithium ions are strongly coordinated by water molecules and TFSI anions, resulting in robust cation–anion interactions. However, the introduction of AN disrupts this interaction. With its smaller size and weaker steric hindrance compared to TFSI anions, AN molecules coordinate with lithium ions, effectively separating them from TFSI anions. This separation prevents further coordination between lithium ions and TFSI anions, improving the stability and performance of the electrolyte under various conditions.236
Li et al. introduced AN as a cosolvent in an aqueous electrolyte, creating a super-concentrated hybrid electrolyte with 15.3 M LiTFSI in a water/AN mixture.237 This hybrid electrolyte outperforms the WIS electrolyte by offering a broader electrochemical stability window of 4.5 V and a lower freezing point. These advantages enable the support of high-capacity LTO anode chemistry in aqueous batteries. When cycled at 1C and 0 °C, the LTO/LMO full cell demonstrated a discharge capacity of 110 mA h g−1 and a capacity retention of 95% after 120 cycles. In a subsequent study, a water/sulfone binary electrolyte was developed, further extending the low-temperature operating range of LMO/LTO full cells. Sulfone disrupts the large-scale hydrogen bond network by competing for hydrogen bonds with water molecules, which lowers the glass-transition temperature of the water/sulfone binary electrolyte to −110 °C. The LTO/LMO full cell using this water/sulfone binary electrolyte achieved a high-capacity retention of 87% and an average Coulombic efficiency of 99.8% after 200 cycles at 200 mA h g−1 and −20 °C.
Low-temperature aqueous electrolytes are still less effective than organic electrolytes because water has a higher freezing point compared to most organic solvents. Much of the research aimed at enhancing the low-temperature performance of aqueous electrolytes focuses on using highly concentrated lithium salts (∼20 mol L−1), which increases the cost. A key approach to improving aqueous electrolyte performance at low temperatures is to reduce cation–anion interactions. Organic additives and concentration enhancers can help optimize the solvation structure and extend the operational temperature range of aqueous electrolytes. However, greater attention should be given to cost reduction and ensuring the electrolytes retain their inherent safety following these improvements.
5. Future directions for low-temperature LIBs
Despite significant progress in the development of low-temperature LIBs, several challenges remain to be addressed to enable their widespread adoption in practical applications. One of the most critical challenges is the development of electrolytes with low viscosity and high ionic conductivity at sub-zero temperatures. This can be achieved through the use of advanced solvents, such as fluorinated esters and ethers, which exhibit low melting points and weak solvation structures. Additionally, the incorporation of functional additives, such as FEC and VC, can promote the formation of stable and conductive SEI and CEI layers, thereby improving cyclic stability at low temperatures.Another promising direction is the development of solid-state electrolytes, which offer improved safety and stability at low temperatures. However, the high interfacial resistance and poor ion transport in solid-state electrolytes remain significant challenges that need to be overcome. Future research should focus on optimizing the interfacial compatibility between solid-state electrolytes and electrodes, as well as developing novel materials with enhanced ionic conductivity at sub-zero temperatures.
In addition to electrolyte optimization, the development of advanced electrode materials is essential for improving the low-temperature performance of LIBs. For example, the use of silicon-based anodes and high-voltage cathodes can enhance the energy density and rate capability of LIBs at low temperatures. However, these materials often suffer from poor cycling stability and mechanical degradation, which need to be addressed through innovative electrode designs and protective coatings. Tailoring electrode surfaces with materials such as Al2O3 and Li3PO4 can improve the mechanical and electrochemical stability of SEI/CEI layers, while self-healing materials could help repair cracks and defects that form during cycling at low temperatures.
While notable progress has been made in the development of sub-zero LIBs, the field is still in its infancy. Moving forward, it is essential to focus on understanding the interactions between electrolyte components and surface chemistries across a wide temperature spectrum to enable the broader use of LIBs in extreme environments. The integration of advanced nanomaterials in battery component manufacturing and a more comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing low-temperature LIB performance, supported by accurate simulations, could pave the way for significant advancements, including large-scale industrial production. These innovations are anticipated to grow rapidly in the coming decade, greatly expanding the potential applications of LIBs across various industries.
Finally, the development of large-format pouch cells for low-temperature applications remains a significant challenge. The increased cell size and complexity can exacerbate issues such as electrolyte distribution, thermal management, and mechanical stress. Future research should focus on optimizing cell designs and manufacturing processes to enable the widespread adoption of low-temperature LIBs in practical applications. Key strategies include:
1. Optimization of electrolyte composition: Developing advanced electrolyte formulations with low-viscosity solvents, functional additives, and high-concentration electrolytes.
2. Scalable electrolyte formulations: Developing electrolyte systems that can uniformly form stable SEI/CEI layers across large-format electrodes.
3. Advanced thermal management: Integrating efficient thermal management systems, such as internal heating mechanisms and phase-change materials, to regulate temperature distribution within pouch cells.
4. Interfacial engineering: Tailoring electrode surfaces with protective coatings and functional binders to improve interfacial stability and reduce side reactions.
5. In situ diagnostics and modeling: Leveraging advanced in situ characterization techniques and computational models to understand and optimize the dynamic behavior of SEI/CEI layers in pouch cells under real-world operating conditions.
By addressing these challenges, the performance and safety of high-energy pouch cells at low temperatures can be significantly improved, paving the way for their widespread adoption in demanding applications such as electric vehicles, aerospace, and grid-scale energy storage systems.
6. Summary
This review has thoroughly examined the challenges and recent advancements in low-temperature lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), highlighting the critical limitations such as reduced ionic conductivity, sluggish charge transfer kinetics, lithium dendrite formation, and sluggish diffusion coefficients in the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) and cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI) layers. Significant progress has been made in addressing these issues through innovative electrolyte designs, including the use of advanced solvents, lithium salts, and additives, which have shown promising results in enhancing LIB performance at sub-zero temperatures.While significant progress has been made in addressing low-temperature challenges in small-scale test cells, scaling these advancements to large-format pouch cells presents additional challenges. In particular, high-energy pouch cells, which are commonly used in electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems, require electrolytes that can perform reliably at sub-zero temperatures while maintaining high energy density and long cycle life. The increased size and different geometries of pouch cells lead to larger internal resistance and uneven temperature distribution during charging and discharging, which can exacerbate the existing low-temperature issues such as poor ionic conductivity and formation of detrimental SEI/CEI layers. Furthermore, mechanical stresses and thermal management in pouch cells need to be optimized for consistent performance across the entire battery.
To address these challenges, future research must focus on the development of electrolyte formulations that can better withstand the scaling effects of pouch cell configurations. Advances in solid-state electrolytes, fluorinated electrolytes, ether- and ester-based systems, liquid gas electrolytes, and advanced additives, and cathode/anode optimization will be critical in improving the structural stability of the SEI and CEI layers in larger battery formats. Additionally, integrating intelligent thermal management systems and better separators will help mitigate temperature-induced degradation, ensuring the cells maintain high performance even in harsh low-temperature environments. It should also be noted that these solutions have their own limitations, including increased costs, weight, and compatibility issues, which need to be addressed for wider commercialization.
The rapid expansion of LIB applications across various sectors has driven remarkable technological advancements, yet their performance in cold environments remains a critical hurdle. Direct optimization of electrolyte systems has emerged as a cost-effective and efficient approach to enhance low-temperature performance. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanisms influencing electrolyte behavior at low temperatures and offers guidance for improving LIB applicability in cold climates. While significant progress has been made, further research is essential to develop new solvents, salts, and additives that can extend the operational range and improve the commercial viability of low-temperature LIBs. By addressing these challenges, LIBs can be widely adopted in critical applications such as electric vehicles, aerospace, and renewable energy storage systems, ensuring reliable performance even in extreme conditions.
Abbreviations
| e | Unit charge |
| K f | Freezing point depression constant |
| m | Molality of constant |
| n i | Number of free ions |
| r | Radius of the solute ion |
| R | Gas constant |
| R ct | Charge transfer resistance |
| T | Temperature |
| T water | Freezing point of the water |
| T soln | Freezing point of the solution |
| z i | Charge capacity |
| σ | Ionic conductivity |
| μ i | Ion mobility of different ions |
| η | Viscosity |
| ΔTf | Depression of the freezing point |
| CEI | Cathode electrolyte interface |
| DRT | Distribution of relaxation times |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectra |
| LIBs | Lithium-ion battery |
| LMBs | Lithium-metal battery |
| RTC | Room temperature capacity |
| SEI | Solid electrolyte interface |
| SIW | Salt-in-water |
| WIS | Water-in-salt |
Data availability
All the data presented and analyzed in this review article have been obtained from previously published studies and publicly available sources. As such, no new experimental or computational data were generated for this work. The original datasets are available through the references cited in the manuscript.To ensure transparency and reproducibility, readers are encouraged to refer to the cited works for detailed datasets and ESI.† These sources adhere to the principles of findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability (FAIR) and can be accessed via the respective repositories or ESI† documents associated with the original publications.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge The University of Tulsa, and Faculty Development Summer Fellowship Program for supporting us (A.A) financially. We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the Rusell School of Chemical Engineering and Multifunctional Energy Storage lab.References
- Y. Yang, W. Yang, H. Yang and H. Zhou, Electrolyte design principles for low-temperature lithium-ion batteries, eScience, 2023, 3(6), 100170 Search PubMed.
- Z. Li, Y. X. Yao, S. Sun, C. B. Jin, N. Yao, C. Yan and Q. Zhang, 40 Years of Low–Temperature Electrolytes for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries, Angew. Chem., 2023, 135(37), e202303888 Search PubMed.
- X. Su, Y. Xu, Y. Wu, H. Li, J. Yang, Y. Liao, R. Qu and Z. Zhang, Liquid electrolytes for low-temperature lithium batteries: main limitations, current advances, and future perspectives, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 56, 642–663 Search PubMed.
- Y. Ge, J. Chen, G. Ma, R. Huang, F. Meng and R. Hu, Low-Temperature-Sensitivity Materials for Low-Temperature Lithium-Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2025, 17(9), 13232–13245 Search PubMed.
- S. Sun, K. Wang, Z. Hong, M. Zhi, K. Zhang and J. Xu, Electrolyte design for low-temperature Li-metal batteries: challenges and prospects, Nano–Micro Lett., 2024, 16(1), 35 Search PubMed.
- K. Xu, Nonaqueous Liquid Electrolytes for Lithium-Based Rechargeable Batteries, Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(10), 4303–4418 Search PubMed.
- B. K. Mandal, A. K. Padhi, Z. Shi, S. Chakraborty and R. Filler, New low temperature electrolytes with thermal runaway inhibition for lithium-ion rechargeable batteries, J. Power Sources, 2006, 162(1), 690–695 Search PubMed.
- N. Yao, X. Chen, X. Shen, R. Zhang, Z. H. Fu, X. X. Ma, X. Q. Zhang, B. Q. Li and Q. Zhang, An atomic insight into the chemical origin and variation of the dielectric constant in liquid electrolytes, Angew. Chem., 2021, 133(39), 21643–21648 Search PubMed.
- J. Huang, X. Dong, N. Wang and Y. Wang, Building low-temperature batteries: Non-aqueous or aqueous electrolyte?, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2022, 33, 100949 Search PubMed.
- L. Yan, S. Zhang, Q. Kang, X. Meng, Z. Li, T. Liu, T. Ma and Z. Lin, Iodine conversion chemistry in aqueous batteries: Challenges, strategies, and perspectives, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 54, 339–365 Search PubMed.
- B. Pal, S. Yang, S. Ramesh, V. Thangadurai and R. Jose, Electrolyte selection for supercapacitive devices: a critical review, Nanoscale Adv., 2019, 1(10), 3807–3835 Search PubMed.
- Y. Ji, Y. Zhang and C.-Y. Wang, Li-Ion Cell Operation at Low Temperatures, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2013, 160(4), A636 Search PubMed.
- W. Zhang, X. Sun, Y. Tang, H. Xia, Y. Zeng, L. Qiao, Z. Zhu, Z. Lv, Y. Zhang and X. Ge, Lowering charge transfer barrier of LiMn2O4 via nickel surface doping to enhance Li+ intercalation kinetics at subzero temperatures, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(36), 14038–14042 Search PubMed.
- R. Xu, C. Yan, Y. Xiao, M. Zhao, H. Yuan and J.-Q. Huang, The reduction of interfacial transfer barrier of Li ions enabled by inorganics-rich solid-electrolyte interphase, Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 28, 401–406 Search PubMed.
- K. Xu, A. von Cresce and U. Lee, Differentiating Contributions to “Ion Transfer” Barrier from Interphasial Resistance and Li+ Desolvation at Electrolyte/Graphite Interface, Langmuir, 2010, 26(13), 11538–11543 Search PubMed.
- Q. Li, D. Lu, J. Zheng, S. Jiao, L. Luo, C.-M. Wang, K. Xu, J.-G. Zhang and W. Xu, Li+-Desolvation Dictating Lithium-Ion Battery's Low-Temperature Performances, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(49), 42761–42768 Search PubMed.
- J. Bae, Y. Choi and Y. Kim, Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs) Immersed in Fire Prevention Material for Fire Safety and Heat Management, Energies, 2024, 17(10), 2418 Search PubMed.
- M. Sohaib, A. S. Akram and W. Choi, Analysis of Aging and Degradation in Lithium Batteries Using Distribution of Relaxation Time, Batteries, 2025, 11(1), 34 Search PubMed.
- Q. Li, S. Jiao, L. Luo, M. S. Ding, J. Zheng, S. S. Cartmell, C.-M. Wang, K. Xu, J.-G. Zhang and W. Xu, Wide-Temperature Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(22), 18826–18835 Search PubMed.
- D. Hubble, D. E. Brown, Y. Zhao, C. Fang, J. Lau, B. D. McCloskey and G. Liu, Liquid electrolyte development for low-temperature lithium-ion batteries, Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15(2), 550–578 Search PubMed.
- T. Waldmann, B.-I. Hogg and M. Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, Li plating as unwanted side reaction in commercial Li-ion cells – A review, J. Power Sources, 2018, 384, 107–124 Search PubMed.
- Y. Liu, Y. Zhu and Y. Cui, Challenges and opportunities towards fast-charging battery materials, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(7), 540–550 Search PubMed.
- X. Li, P. Xu, Y. Tian, A. Fortini, S. H. Choi, J. Xu, X. Tan, X. Liu, G. Chen, C. Zhang, X. Lu, L. Jin, Q. Wang, L. Shen and Y. Lu, Electrolyte Modulators toward Polarization-Mitigated Lithium-Ion Batteries for Sustainable Electric Transportation, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(7), 2107787 Search PubMed.
- N. Piao, X. Gao, H. Yang, Z. Guo, G. Hu, H.-M. Cheng and F. Li, Challenges and development of lithium-ion batteries for low temperature environments, eTransportation, 2022, 11, 100145 Search PubMed.
- A. Tomaszewska, Z. Chu, X. Feng, S. O'Kane, X. Liu, J. Chen, C. Ji, E. Endler, R. Li, L. Liu, Y. Li, S. Zheng, S. Vetterlein, M. Gao, J. Du, M. Parkes, M. Ouyang, M. Marinescu, G. Offer and B. Wu, Lithium-ion battery fast charging: A review, eTransportation, 2019, 1, 100011 Search PubMed.
- T. Waldmann, B.-I. Hogg, M. Kasper, S. Grolleau, C. G. Couceiro, K. Trad, B. P. Matadi and M. Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, Interplay of Operational Parameters on Lithium Deposition in Lithium-Ion Cells: Systematic Measurements with Reconstructed 3-Electrode Pouch Full Cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2016, 163(7), A1232 Search PubMed.
- Y.-X. Yao, N. Yao, X.-R. Zhou, Z.-H. Li, X.-Y. Yue, C. Yan and Q. Zhang, Ethylene-Carbonate-Free Electrolytes for Rechargeable Li-Ion Pouch Cells at Sub-Freezing Temperatures, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(45), 2206448 Search PubMed.
- C. von Lüders, V. Zinth, S. V. Erhard, P. J. Osswald, M. Hofmann, R. Gilles and A. Jossen, Lithium plating in lithium-ion batteries investigated by voltage relaxation and in situ neutron diffraction, J. Power Sources, 2017, 342, 17–23 Search PubMed.
- B. Ng, P. T. Coman, E. Faegh, X. Peng, S. G. Karakalos, X. Jin, W. E. Mustain and R. E. White, Low-Temperature Lithium Plating/Corrosion Hazard in Lithium-Ion Batteries: Electrode Rippling, Variable States of Charge, and Thermal and Nonthermal Runaway, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3(4), 3653–3664 Search PubMed.
- J. Holoubek, H. Liu, Z. Wu, Y. Yin, X. Xing, G. Cai, S. Yu, H. Zhou, T. A. Pascal and Z. Chen, Tailoring electrolyte solvation for Li metal batteries cycled at ultra-low temperature, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6(3), 303–313 Search PubMed.
- T. Ma, Y. Ni, Q. Wang, W. Zhang, S. Jin, S. Zheng, X. Yang, Y. Hou, Z. Tao and J. Chen, Optimize lithium deposition at low temperature by weakly solvating power solvent, Angew. Chem., 2022, 134(39), e202207927 Search PubMed.
- G. Zhang, X. Wei, G. Han, H. Dai, J. Zhu, X. Wang, X. Tang and J. Ye, Lithium plating on the anode for lithium-ion batteries during long-term low temperature cycling, J. Power Sources, 2021, 484, 229312 Search PubMed.
- Y. Xiao, R. Xu, C. Yan, J.-Q. Huang, Q. Zhang and M. Ouyang, A Toolbox of Reference Electrodes for Lithium Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(13), 2108449 Search PubMed.
- L. Liao, P. Zuo, Y. Ma, Y. An, G. Yin and Y. Gao, Effects of fluoroethylene carbonate on low temperature performance of mesocarbon microbeads anode, Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 74, 260–266 Search PubMed.
- Y. Lu, C.-Z. Zhao, J.-Q. Huang and Q. Zhang, The timescale identification decoupling complicated kinetic processes in lithium batteries, Joule, 2022, 6(6), 1172–1198 Search PubMed.
- G. Xu, S. Huang, Z. Cui, X. Du, X. Wang, D. Lu, X. Shangguan, J. Ma, P. Han, X. Zhou and G. Cui, Functional additives assisted ester-carbonate electrolyte enables wide temperature operation of a high-voltage (5 V-Class) Li-ion battery, J. Power Sources, 2019, 416, 29–36 Search PubMed.
- J. Chen, L. Xing, X. Yang, X. Liu, T. Li and W. Li, Outstanding electrochemical performance of high-voltage LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode achieved by application of LiPO2F2 electrolyte additive, Electrochim. Acta, 2018, 290, 568–576 Search PubMed.
- J. Wang, P. Nie, G. Xu, J. Jiang, Y. Wu, R. Fu, H. Dou and X. Zhang, High-Voltage LiNi0.45Cr0.1Mn1.45O4 Cathode with Superlong Cycle Performance for Wide Temperature Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(4), 1704808 Search PubMed.
- R. Huang, G. Wei, X. Wang, B. Jiang, J. Zhu, J. Chen, X. Wei and H. Dai, Revealing the low-temperature aging mechanisms of the whole life cycle for lithium-ion batteries (nickel-cobalt-aluminum vs. graphite), J. Energy Chem., 2025, 106, 31–43 Search PubMed.
- H. Li, C. Yan and S. Wang, Solvation chemistry in liquid electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries at low temperatures, EcoEnergy, 2025, 1–35, DOI:10.1002/ece2.94.
- C. Liu, L. Sheng and L. Jiang, Research on performance constraints and electrolyte optimization strategies for lithium-ion batteries at low temperatures, RSC Adv., 2025, 15(10), 7995–8018 Search PubMed.
- G. Wang, G. Wang, L. Fei, L. Zhao and H. Zhang, Structural engineering of anode materials for low-temperature lithium-ion batteries: mechanisms, strategies, and prospects, Nano–Micro Lett., 2024, 16(1), 150 Search PubMed.
- U. Awan, K. Ghabraie, A. Zolfagharian and B. Rolfe, Impact of Vibrations on Lithium-ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles: Sources, Degradation Mechanisms, and Testing Standards, J. Phys.: Energy, 2025, 7(2), 022003 Search PubMed.
- Y. Peng, J. Chen, G. Liu, Y. Yin, X. Fang, Y. Wang, X. Dong and Y. Xia, Highly Adaptable Electrode–Electrolyte Interphases Constructed by Dual-Additive-Optimized Electrolyte for 4.5 V Lithium Metal Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2025, 2501489 Search PubMed.
- L. Wang, F.-D. Yu, L.-F. Que, X.-G. Zhang and K.-Y. Xie, Degradation behavior of A h-level Li-ion pouch cell during repeated fast charging within a wide temperature region, Energy Storage Mater., 2025, 104096 Search PubMed.
- J. Xu, in Corrosion and Degradation in Fuel Cells, Supercapacitors and Batteries, ed. V. S. Saji, Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, 2024, pp. 307–324. DOI:10.1007/978-3-031-57012-4_13.
- Q. Sun, Z. Gong, T. Zhang, J. Li, X. Zhu, R. Zhu, L. Wang, L. Ma, X. Li, M. Yuan, Z. Zhang, L. Zhang, Z. Qian, L. Yin, R. Ahuja and C. Wang, Molecule-Level Multiscale Design of Nonflammable Gel Polymer Electrolyte to Build Stable SEI/CEI for Lithium Metal Battery, Nano-Micro Lett., 2024, 17(1), 18 Search PubMed.
- J. Liu, M. Ma, Y. Su, S. Wang, T. Han, Y. Huan and T. Wei, Low-temperature piezoelectric/ferroelectric coating layer driving lithium-ion rapid diffusion and structure stability of LiCoO2 cathode, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2025, 979, 118929 Search PubMed.
- D. Rossi, Y. Wu, G. Wu, D. Bilby, A. B. Getsoian, N. J. Kempema and Z. Chen, In Operando and Ex Situ Investigation of the Formation and Aging Processes of SEI/CEI C–H Chemistry in Liquid Electrolyte Lithium-Ion Batteries, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2025, 2759–2763, DOI:10.1021/acs.jpclett.5c00348.
- K. Xie, Y. Ji, L. Yang and F. Pan, Electrolyte Design Strategies to Construct Stable Cathode-Electrolyte Interphases for High-Voltage Sodium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2025, 2405301 Search PubMed.
- J. Zheng, J. A. Lochala, A. Kwok, Z. D. Deng and J. Xiao, Research Progress towards Understanding the Unique Interfaces between Concentrated Electrolytes and Electrodes for Energy Storage Applications, Adv. Sci., 2017, 4(8), 1700032 Search PubMed.
- H. Q. Pham, H.-Y. Lee, E.-H. Hwang, Y.-G. Kwon and S.-W. Song, Non-flammable organic liquid electrolyte for high-safety and high-energy density Li-ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2018, 404, 13–19 Search PubMed.
- M.-T. F. Rodrigues, G. Babu, H. Gullapalli, K. Kalaga, F. N. Sayed, K. Kato, J. Joyner and P. M. Ajayan, A materials perspective on Li-ion batteries at extreme temperatures, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2(8), 17108 Search PubMed.
- Q. Zhao, N. W. Utomo, A. L. Kocen, S. Jin, Y. Deng, V. X. Zhu, S. Moganty, G. W. Coates and L. A. Archer, Upgrading carbonate electrolytes for ultra–stable practical lithium metal batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61(9), e202116214 Search PubMed.
- Y. Li, J. Zhao, Q. Hu, T. Hao, H. Cao, X. Huang, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, D. Lin and Y. Tang, Prussian blue analogs cathodes for aqueous zinc ion batteries, Mater. Today Energy, 2022, 101095 Search PubMed.
- X. Li, M. Banis, A. Lushington, X. Yang, Q. Sun, Y. Zhao, C. Liu, Q. Li, B. Wang, W. Xiao, C. Wang, M. Li, J. Liang, R. Li, Y. Hu, L. Goncharova, H. Zhang, T.-K. Sham and X. Sun, A high-energy sulfur cathode in carbonate electrolyte by eliminating polysulfides via solid-phase lithium-sulfur transformation, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 4509 Search PubMed.
- L. F. Xiao, Y. L. Cao, X. P. Ai and H. X. Yang, Optimization of EC-based multi-solvent electrolytes for low temperature applications of lithium-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2004, 49(27), 4857–4863 Search PubMed.
- G. K. P. Dathar, D. Sheppard, K. J. Stevenson and G. Henkelman, Calculations of Li-Ion Diffusion in Olivine Phosphates, Chem. Mater., 2011, 23(17), 4032–4037 Search PubMed.
- M. C. Smart, B. V. Ratnakumar and S. Surampudi, Electrolytes for Low–Temperature Lithium Batteries Based on Ternary Mixtures of Aliphatic Carbonates, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1999, 146(2), 486–492 Search PubMed.
- M. Smart, B. Ratnakumar, V. Ryan-Mowrey, S. Surampudi, G. Prakash, J. Hu and I. Cheung, Improved performance of lithium-ion cells with the use of fluorinated carbonate-based electrolytes, J. Power Sources, 2003, 119, 359–367 Search PubMed.
- J. Alvarado, M. A. Schroeder, T. P. Pollard, X. Wang, J. Z. Lee, M. Zhang, T. Wynn, M. Ding, O. Borodin, Y. S. Meng and K. Xu, Bisalt ether electrolytes: a pathway towards lithium metal batteries with Ni-rich cathodes, Energy Environ. Sci., 2019, 12(2), 780–794 Search PubMed.
- S. S. Zhang, K. Xu, J. L. Allen and T. R. Jow, Effect of propylene carbonate on the low temperature performance of Li-ion cells, J. Power Sources, 2002, 110(1), 216–221 Search PubMed.
- Y. H. Ren, C. W. Yang, B. R. Wu, C. Z. Zhang, S. Chen and F. Wu, Novel Low-Temperature Electrolyte for Li-Ion Battery, Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, 287–290, 1283–1289 Search PubMed.
- J. Holoubek, Y. Yin, M. Li, M. Yu, Y. S. Meng, P. Liu and Z. Chen, Exploiting Mechanistic Solvation Kinetics for Dual-Graphite Batteries with High Power Output at Extremely Low Temperature, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58(52), 18892–18897 Search PubMed.
- Y.-G. Cho, M. Li, J. Holoubek, W. Li, Y. Yin, Y. S. Meng and Z. Chen, Enabling the Low-Temperature Cycling of NMC||Graphite Pouch Cells with an Ester-Based Electrolyte, ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6(5), 2016–2023 Search PubMed.
- X.-Q. Zhang, X.-B. Cheng, X. Chen, C. Yan and Q. Zhang, Fluoroethylene Carbonate Additives to Render Uniform Li Deposits in Lithium Metal Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(10), 1605989 Search PubMed.
- J. Holoubek, M. Yu, S. Yu, M. Li, Z. Wu, D. Xia, P. Bhaladhare, M. S. Gonzalez, T. A. Pascal, P. Liu and Z. Chen, An All-Fluorinated Ester Electrolyte for Stable High-Voltage Li Metal Batteries Capable of Ultra-Low-Temperature Operation, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5(5), 1438–1447 Search PubMed.
- T. Subburaj, W. Brevet, F. Farmakis, D. Tsiplakides, S. Balomenou, N. Strataki, C. Elmasides, B. Samaniego and M. Nestoridi, Silicon/LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 lithium-ion pouch cells charging and discharging at −40 °C temperature, Electrochim. Acta, 2020, 354, 136652 Search PubMed.
- X. Fan, X. Ji, L. Chen, J. Chen, T. Deng, F. Han, J. Yue, N. Piao, R. Wang, X. Zhou, X. Xiao, L. Chen and C. Wang, All-temperature batteries enabled by fluorinated electrolytes with non-polar solvents, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(10), 882–890 Search PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, T. Hu, Q. Sun, Y. Chen, Q. Yang and Y. Li, The optimized LiBF4 based electrolytes for TiO2(B) anode in lithium ion batteries with an excellent low temperature performance, J. Power Sources, 2020, 453, 227908 Search PubMed.
- S. Li, X. Li, J. Liu, Z. Shang and X. Cui, A low-temperature electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries, Ionics, 2015, 21(4), 901–907 Search PubMed.
- S. Li, W. Zhao, Z. Zhou, X. Cui, Z. Shang, H. Liu and D. Zhang, Studies on Electrochemical Performances of Novel Electrolytes for Wide-Temperature-Range Lithium-Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(7), 4920–4926 Search PubMed.
- M. C. Smart, B. V. Ratnakumar and S. Surampudi, Use of Organic Esters as Cosolvents in Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries with Improved Low Temperature Performance, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2002, 149(4), A361 Search PubMed.
- S. Herreyre, O. Huchet, S. Barusseau, F. Perton, J. M. Bodet and P. Biensan, New Li-ion electrolytes for low temperature applications, J. Power Sources, 2001, 97–98, 576–580 Search PubMed.
- K. A. Smith, M. C. Smart, G. K. S. Prakash and B. V. Ratnakumar, Electrolytes Containing Fluorinated Ester Co-Solvents for Low-Temperature Li-Ion Cells, ECS Trans., 2008, 11(29), 91 Search PubMed.
- M. C. Smart, B. V. Ratnakumar, K. B. Chin and L. D. Whitcanack, Lithium-Ion Electrolytes Containing Ester Cosolvents for Improved Low Temperature Performance, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2010, 157(12), A1361 Search PubMed.
- M. C. Smart, B. V. Ratnakumar, A. Behar, L. D. Whitcanack, J. S. Yu and M. Alamgir, Gel polymer electrolyte lithium-ion cells with improved low temperature performance, J. Power Sources, 2007, 165(2), 535–543 Search PubMed.
- Z. Fang, Y. Yang, T. Zheng, N. Wang, C. Wang, X. Dong, Y. Wang and Y. Xia, An all-climate CFx/Li battery with mechanism-guided electrolyte, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 42, 477–483 Search PubMed.
- R. Petibon, C. P. Aiken, L. Ma, D. Xiong and J. R. Dahn, The use of ethyl acetate as a sole solvent in highly concentrated electrolyte for Li-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 154, 287–293 Search PubMed.
- M. C. Smart, B. V. Ratnakumar, L. D. Whitcanack, K. B. Chin, S. Surampudi, H. Croft, D. Tice and R. Staniewicz, Improved low-temperature performance of lithium-ion cells with quaternary carbonate-based electrolytes, J. Power Sources, 2003, 119–121, 349–358 Search PubMed.
- W. Lu, K. Xie, Y. Pan, Z.-X. Chen and C.-M. Zheng, Effects of carbon-chain length of trifluoroacetate co-solvents for lithium-ion battery electrolytes using at low temperature, J. Fluorine Chem., 2013, 156, 136–143 Search PubMed.
- W. Zhang, H. Xia, Z. Zhu, Z. Lv, S. Cao, J. Wei, Y. Luo, Y. Xiao, L. Liu and X. Chen, Decimal Solvent-Based High-Entropy Electrolyte Enabling the Extended Survival Temperature of Lithium-Ion Batteries to −130 °C, CCS Chem., 2021, 3(4), 1245–1255 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yang, P. Li, N. Wang, Z. Fang, C. Wang, X. Dong and Y. Xia, Fluorinated carboxylate ester-based electrolyte for lithium ion batteries operated at low temperature, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56(67), 9640–9643 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yang, Z. Fang, Y. Yin, Y. Cao, Y. Wang, X. Dong and Y. Xia, Synergy of weakly–solvated electrolyte and optimized interphase enables graphite anode charge at low temperature, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61(36), e202208345 Search PubMed.
- Z. Wang, H. Wang, S. Qi, D. Wu, J. Huang, X. Li, C. Wang and J. Ma, Structural regulation chemistry of lithium ion solvation for lithium batteries, EcoMat, 2022, 4(4), e12200 Search PubMed.
- Y.-X. Yao, X. Chen, C. Yan, X.-Q. Zhang, W.-L. Cai, J.-Q. Huang and Q. Zhang, Regulating Interfacial Chemistry in Lithium-Ion Batteries by a Weakly Solvating Electrolyte, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60(8), 4090–4097 Search PubMed.
- S.-C. Kinoshita, M. Kotato, Y. Sakata, M. Ue, Y. Watanabe, H. Morimoto and S.-I. Tobishima, Effects of cyclic carbonates as additives to γ-butyrolactone electrolytes for rechargeable lithium cells, J. Power Sources, 2008, 183(2), 755–760 Search PubMed.
- D. Belov and D.-T. Shieh, GBL-based electrolyte for Li-ion battery: thermal and electrochemical performance, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2012, 16(2), 603–615 Search PubMed.
- K. Xu, Tailoring Electrolyte Composition for LiBOB, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155(10), A733 Search PubMed.
- P. Shi, S. Fang, J. Huang, D. Luo, L. Yang and S.-I. Hirano, A novel mixture of lithium bis(oxalato)borate, gamma-butyrolactone and non-flammable hydrofluoroether as a safe electrolyte for advanced lithium ion batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(37), 19982–19990 Search PubMed.
- Y. Gu, S. Fang, L. Yang and S.-I. Hirano, A safe electrolyte for high-performance lithium-ion batteries containing lithium difluoro(oxalato)borate, gamma-butyrolactone and non-flammable hydrofluoroether, Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 394, 139120 Search PubMed.
- M. L. Lazar and B. L. Lucht, Carbonate Free Electrolyte for Lithium Ion Batteries Containing γ-Butyrolactone and Methyl Butyrate, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2015, 162(6), A928 Search PubMed.
- B. Li, C. Xing, H. Zhang, L. Hu, J. Zhang, D. Jiang, P. Su and S. Zhang, Kinetic-matching between electrodes and electrolyte enabling solid-state sodium-ion capacitors with improved voltage output and ultra-long cyclability, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 421, 127832 Search PubMed.
- W. Zhang, H. Xia, Z. Zhu, Z. Lv, S. Cao, J. Wei, Y. Luo, Y. Xiao, L. Liu and X. Chen, Decimal solvent-based high-entropy electrolyte enabling the extended survival temperature of lithium-ion batteries to −130 C, CCS Chem., 2021, 3(4), 1245–1255 Search PubMed.
- T. Ma, Y. Ni, Q. Wang, W. Zhang, S. Jin, S. Zheng, X. Yang, Y. Hou, Z. Tao and J. Chen, Optimize Lithium Deposition at Low Temperature by Weakly Solvating Power Solvent, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61(39), e202207927 Search PubMed.
- Y. Li, J. Zhao, Q. Hu, T. Hao, H. Cao, X. Huang, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, D. Lin, Y. Tang and Y. Cai, Prussian blue analogs cathodes for aqueous zinc ion batteries, Mater. Today Energy, 2022, 29, 101095 Search PubMed.
- D. Guyomard and J. M. Tarascon, Rechargeable Li1+xMn2O4/Carbon Cells with a New Electrolyte Composition: Potentiostatic Studies and Application to Practical Cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1993, 140(11), 3071 Search PubMed.
- L. Du, H. Wang, M. Yang, L. Liu and Z. Niu, Free-Standing Nanostructured Architecture as a Promising Platform for High-Performance Lithium–Sulfur Batteries, Small Struct., 2020, 1(3), 2000047 Search PubMed.
- K. Yuan, L. Yuan, J. Chen, J. Xiang, Y. Liao, Z. Li and Y. Huang, Methods and Cost Estimation for the Synthesis of Nanosized Lithium Sulfide, Small Struct., 2021, 2(3), 2000059 Search PubMed.
- Q. Jin, X. Qi, F. Yang, R. Jiang, Y. Xie, L. Qie and Y. Huang, The Failure Mechanism of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries under Lean-Ether-Electrolyte Conditions, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 38, 255–261 Search PubMed.
- Z. Wang, H. Ji, L. Zhou, X. Shen, L. Gao, J. Liu, T. Yang, T. Qian and C. Yan, All-liquid-phase reaction mechanism enabling cryogenic Li–S batteries, ACS Nano, 2021, 15(8), 13847–13856 Search PubMed.
- H.-J. Peng, J.-Q. Huang, X.-B. Cheng and Q. Zhang, Review on High-Loading and High-Energy Lithium–Sulfur Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7(24), 1700260 Search PubMed.
- X. Shen, H. Liu, X.-B. Cheng, C. Yan and J.-Q. Huang, Beyond lithium ion batteries: Higher energy density battery systems based on lithium metal anodes, Energy Storage Mater., 2018, 12, 161–175 Search PubMed.
- Y. V. Mikhaylik and J. R. Akridge, Low Temperature Performance of Li/S Batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(3), A306 Search PubMed.
- J. Holoubek, H. Liu, Z. Wu, Y. Yin, X. Xing, G. Cai, S. Yu, H. Zhou, T. A. Pascal, Z. Chen and P. Liu, Tailoring electrolyte solvation for Li metal batteries cycled at ultra-low temperature, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6(3), 303–313 Search PubMed.
- R. Fang, S. Zhao, Z. Sun, D.-W. Wang, H.-M. Cheng and F. Li, More Reliable Lithium-Sulfur Batteries: Status, Solutions and Prospects, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(48), 1606823 Search PubMed.
- J. Gao, M. A. Lowe, Y. Kiya and H. D. Abruña, Effects of Liquid Electrolytes on the Charge–Discharge Performance of Rechargeable Lithium/Sulfur Batteries: Electrochemical and in situ X-ray Absorption Spectroscopic Studies, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(50), 25132–25137 Search PubMed.
- A. C. Thenuwara, P. P. Shetty and M. T. McDowell, Distinct Nanoscale Interphases and Morphology of Lithium Metal Electrodes Operating at Low Temperatures, Nano Lett., 2019, 19(12), 8664–8672 Search PubMed.
- S. Jiao, X. Ren, R. Cao, M. H. Engelhard, Y. Liu, D. Hu, D. Mei, J. Zheng, W. Zhao, Q. Li, N. Liu, B. D. Adams, C. Ma, J. Liu, J.-G. Zhang and W. Xu, Stable cycling of high-voltage lithium metal batteries in ether electrolytes, Nat. Energy, 2018, 3(9), 739–746 Search PubMed.
- Q. Liu, A. Cresce, M. Schroeder, K. Xu, D. Mu, B. Wu, L. Shi and F. Wu, Insight on lithium metal anode interphasial chemistry: Reduction mechanism of cyclic ether solvent and SEI film formation, Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 17, 366–373 Search PubMed.
- S. Zhu and J. Chen, Dual strategy with Li-ion solvation and solid electrolyte interphase for high Coulombic efficiency of lithium metal anode, Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 44, 48–56 Search PubMed.
- A. C. Thenuwara, P. P. Shetty, N. Kondekar, S. E. Sandoval, K. Cavallaro, R. May, C.-T. Yang, L. E. Marbella, Y. Qi and M. T. McDowell, Efficient Low-Temperature Cycling of Lithium Metal Anodes by Tailoring the Solid-Electrolyte Interphase, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5(7), 2411–2420 Search PubMed.
- L. Suo, Y.-S. Hu, H. Li, M. Armand and L. Chen, A new class of solvent-in-salt electrolyte for high-energy rechargeable metallic lithium batteries, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4(1), 1481 Search PubMed.
- X. Ge and X. Wang, Estimation of freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, and vaporization enthalpies of electrolyte solutions, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2009, 48(4), 2229–2235 Search PubMed.
- U. Pal, F. Chen, D. Gyabang, T. Pathirana, B. Roy, R. Kerr, D. R. MacFarlane, M. Armand, P. C. Howlett and M. Forsyth, Enhanced ion transport in an ether aided super concentrated ionic liquid electrolyte for long-life practical lithium metal battery applications, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(36), 18826–18839 Search PubMed.
- T. M. Pappenfus, W. A. Henderson, B. B. Owens, K. R. Mann and W. H. Smyrl, Complexes of lithium imide salts with tetraglyme and their polyelectrolyte composite materials, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2004, 151(2), A209 Search PubMed.
- K. Yoshida, M. Tsuchiya, N. Tachikawa, K. Dokko and M. Watanabe, Correlation between battery performance and lithium ion diffusion in glyme–lithium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) amide equimolar complexes, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2012, 159(7), A1005 Search PubMed.
- X. Ren, S. Chen, H. Lee, D. Mei, M. H. Engelhard, S. D. Burton, W. Zhao, J. Zheng, Q. Li and M. S. Ding, Localized high-concentration sulfone electrolytes for high-efficiency lithium-metal batteries, Chem, 2018, 4(8), 1877–1892 Search PubMed.
- H.-S. Ryu, H.-J. Ahn, K.-W. Kim, J.-H. Ahn, K.-K. Cho, T.-H. Nam, J.-U. Kim and G.-B. Cho, Discharge behavior of lithium/sulfur cell with TEGDME based electrolyte at low temperature, J. Power Sources, 2006, 163(1), 201–206 Search PubMed.
- J. K. Feng, X. P. Ai, Y. L. Cao and H. X. Yang, Possible use of non-flammable phosphonate ethers as pure electrolyte solvent for lithium batteries, J. Power Sources, 2008, 177(1), 194–198 Search PubMed.
- K. Naoi, E. Iwama, N. Ogihara, Y. Nakamura, H. Segawa and Y. Ino, Nonflammable Hydrofluoroether for Lithium-Ion Batteries: Enhanced Rate Capability, Cyclability, and Low-Temperature Performance, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2009, 156(4), A272 Search PubMed.
- X. Cao, H. Jia, W. Xu and J.-G. Zhang, Review—Localized High-Concentration Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2021, 168(1), 010522 Search PubMed.
- J. Chen, X. Fan, Q. Li, H. Yang, M. R. Khoshi, Y. Xu, S. Hwang, L. Chen, X. Ji, C. Yang, H. He, C. Wang, E. Garfunkel, D. Su, O. Borodin and C. Wang, Electrolyte design for LiF-rich solid–electrolyte interfaces to enable high-performance microsized alloy anodes for batteries, Nat. Energy, 2020, 5(5), 386–397 Search PubMed.
- L. Cheng, Y. Wang, J. Yang, M. Tang, C. Zhang, Q. Zhu, S. Wang, Y. Li, P. Hu and H. Wang, An Ultrafast and Stable Li–Metal Battery Cycled at −40 °C, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33(11), 2212349 Search PubMed.
- C. S. Rustomji, Y. Yang, T. K. Kim, J. Mac, Y. J. Kim, E. Caldwell, H. Chung and Y. S. Meng, Liquefied gas electrolytes for electrochemical energy storage devices, Science, 2017, 356(6345), eaal4263 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yang, Y. Yin, D. M. Davies, M. Zhang, M. Mayer, Y. Zhang, E. S. Sablina, S. Wang, J. Z. Lee and O. Borodin, Liquefied gas electrolytes for wide-temperature lithium metal batteries, Energy Environ. Sci., 2020, 13(7), 2209–2219 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yang, D. M. Davies, Y. Yin, O. Borodin, J. Z. Lee, C. Fang, M. Olguin, Y. Zhang, E. S. Sablina, X. Wang, C. S. Rustomji and Y. S. Meng, High-Efficiency Lithium-Metal Anode Enabled by Liquefied Gas Electrolytes, Joule, 2019, 3(8), 1986–2000 Search PubMed.
- W. Zhao, F. Ren, Q. Yan, H. Liu and Y. Yang, A facile synthesis of non-aqueous LiPO2F2 solution as the electrolyte additive for high performance lithium ion batteries, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2020, 31(12), 3209–3212 Search PubMed.
- M. Tesemma, F.-M. Wang, A. M. Haregewoin, N. L. Hamidah, P. Muhammad Hendra, S. D. Lin, C.-S. Chern, Q.-T. Pham and C.-H. Su, Investigation of the Dipole Moment Effects of Fluorofunctionalized Electrolyte Additives in a Lithium Ion Battery, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7(7), 6640–6653 Search PubMed.
- M. Ue, M. Takeda, A. Toriumi, A. Kominato, R. Hagiwara and Y. Ito, Application of low-viscosity ionic liquid to the electrolyte of double-layer capacitors, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150(4), A499 Search PubMed.
- Y. Li, K. W. Wong, Q. Dou, W. Zhang and K. M. Ng, Improvement of lithium-ion battery performance at low temperature by adopting ionic liquid-decorated PMMA nanoparticles as electrolyte component, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1(6), 2664–2670 Search PubMed.
- M. Armand, F. Endres, D. R. MacFarlane, H. Ohno and B. Scrosati, Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8(8), 621–629 Search PubMed.
- R.-S. Kühnel, N. Böckenfeld, S. Passerini, M. Winter and A. Balducci, Mixtures of ionic liquid and organic carbonate as electrolyte with improved safety and performance for rechargeable lithium batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56(11), 4092–4099 Search PubMed.
- A. Amiri, R. Sellers, M. Naraghi and A.A Polycarpou, Multifunctional Quasi-Solid-State Zinc–Sulfur Battery, ACS Nano, 2023, 17(2), 1217–1228, DOI:10.1021/acsnano.2c09051.
- S. Xu, Z. Sun, C. Sun, F. Li, K. Chen, Z. Zhang, G. Hou, H. M. Cheng and F. Li, Homogeneous and fast ion conduction of PEO–based solid–state electrolyte at low temperature, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(51), 2007172 Search PubMed.
- R. Chen, W. Qu, J. Qian, N. Chen, Y. Dai, C. Guo, Y. Huang, L. Li and F. Wu, Zirconia-supported solid-state electrolytes for high-safety lithium secondary batteries in a wide temperature range, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(47), 24677–24685 Search PubMed.
- X. Li, Q. Hou, W. Huang, H.-S. Xu, X. Wang, W. Yu, R. Li, K. Zhang, L. Wang and Z. Chen, Solution-processable covalent organic framework electrolytes for all-solid-state Li–organic batteries, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5(11), 3498–3506 Search PubMed.
- S. Wang, H. Song, X. Song, T. Zhu, Y. Ye, J. Chen, L. Yu, J. Xu and K. Chen, An extra-wide temperature all-solid-state lithium-metal battery operating from −73 °C to 120 °C, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 39, 139–145 Search PubMed.
- F. Wu, Q. Zhu, R. Chen, N. Chen, Y. Chen and L. Li, Ionic liquid electrolytes with protective lithium difluoro(oxalate)borate for high voltage lithium-ion batteries, Nano Energy, 2015, 13, 546–553 Search PubMed.
- G. H. Wrodnigg, J. O. Besenhard and M. Winter, Cyclic and acyclic sulfites: new solvents and electrolyte additives for lithium ion batteries with graphitic anodes?, J. Power Sources, 2001, 97–98, 592–594 Search PubMed.
- S. Li, W. Zhao, X. Cui, Y. Zhao, B. Li, H. Zhang, Y. Li, G. Li, X. Ye and Y. Luo, An improved method for synthesis of lithium difluoro(oxalato)borate and effects of sulfolane on the electrochemical performances of lithium-ion batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 91, 282–292 Search PubMed.
- S. Tan, U. N. D. Rodrigo, Z. Shadike, B. Lucht, K. Xu, C. Wang, X.-Q. Yang and E. Hu, Novel Low-Temperature Electrolyte Using Isoxazole as the Main Solvent for Lithium-Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(21), 24995–25001 Search PubMed.
- P. Xiao, R. Luo, Z. Piao, C. Li, J. Wang, K. Yu, G. Zhou and H.-M. Cheng, High-Performance Lithium Metal Batteries with a Wide Operating Temperature Range in Carbonate Electrolyte by Manipulating Interfacial Chemistry, ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6(9), 3170–3179 Search PubMed.
- C. Wang, Y. Xie, Y. Huang, S. Zhou, H. Xie, H. Jin and H. Ji, Li3PO4-Enriched SEI on Graphite Anode Boosts Li+ De–Solvation Enabling Fast–Charging and Low–Temperature Lithium–Ion Batteries, Angew. Chem., 2024, 136(21), e202402301 Search PubMed.
- L. Luo, K. Chen, H. Chen, H. Li, R. Cao, X. Feng, W. Chen, Y. Fang and Y. Cao, Enabling Ultralow-Temperature (−70 °C) Lithium-Ion Batteries: Advanced Electrolytes Utilizing Weak-Solvation and Low-Viscosity Nitrile Cosolvent, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(5), 2308881 Search PubMed.
- Y. Oh, S. Song, M. Li, S. Vallem and J. Bae, Advanced electrolyte coupled with Li3V2 (PO4)3/C cathode for enhanced low-temperature lithium-ion battery performance, SSRN, 2024.
- K. S. Han, M.-S. Lee, N. Kim, D. Choi, S. Chae, J. Ryu, G. Piccini, R. Rousseau and E. C. Thomsen, Lithium-ion hopping weakens thermal stability of LiPF6 carbonate electrolytes, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci., 2024, 5(1), 101768 Search PubMed.
- S. Yuan, S. Cao, X. Chen, J. Wei, Z. Lv, H. Xia, J. Li, H. Zhang, L. Liu, C. Tian, L. Chen, W. Zhang, Z. Xing, H. Li, S. Li, Q. Zhu, X. Feng and X. Chen, Deshielding Anions Enable Solvation Chemistry Control of LiPF6-Based Electrolyte toward Low-Temperature Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(16), 2311327 Search PubMed.
- M. Smart, B. Ratnakumar, L. Whitcanack, K. Chin, M. Rodriguez and S. Surampudi, Performance characteristics of lithium ion cells at low temperatures, IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag., 2002, 17(12), 16–20 Search PubMed.
- X.-Z. Liao, Z.-F. Ma, Q. Gong, Y.-S. He, L. Pei and L.-J. Zeng, Low-temperature performance of LiFePO4/C cathode in a quaternary carbonate-based electrolyte, Electrochem. Commun., 2008, 10(5), 691–694 Search PubMed.
- L. Luo, K. Chen, H. Chen, H. Li, R. Cao, X. Feng, W. Chen, Y. Fang and Y. Cao, Enabling Ultralow–Temperature (−70 °C) Lithium–Ion Batteries: Advanced Electrolytes Utilizing Weak–Solvation and Low–Viscosity Nitrile Cosolvent, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(5), 2308881 Search PubMed.
- Q. Chen, P. Luo, L. Liao, Y. Shen, X. Luo, X. Li, X. Wen, J. Song, B. Yu, J. Chen, B. Guo, M. Wang, Y. Huang, F. Liu, J. Liu, Z. Li, J. Ma, S. Wang and X. Li, Regulating Diffusion Coefficient of Li+ by High Binding Energy Anion towards Ultra-Low Temperature Lithium-Ion Batteries, Batteries Supercaps, 2024, 7(11), e202400246 Search PubMed.
- S. S. Zhang, K. Xu and T. R. Jow, A new approach toward improved low temperature performance of Li-ion battery, Electrochem. Commun., 2002, 4(11), 928–932 Search PubMed.
- S. Zhang, K. Xu and T. Jow, An improved electrolyte for the LiFePO4 cathode working in a wide temperature range, J. Power Sources, 2006, 159(1), 702–707 Search PubMed.
- Y. Lai, B. Peng, Z. Zhang and J. Li, A wide operating temperature range electrolyte containing lithium salts mixture and a co-solvent for the LiFePO4 cathode, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2014, 161(6), A875 Search PubMed.
- T. R. Jow, M. S. Ding, K. Xu, S. S. Zhang, J. L. Allen, K. Amine and G. L. Henriksen, Nonaqueous electrolytes for wide-temperature-range operation of Li-ion cells, J. Power Sources, 2003, 119–121, 343–348 Search PubMed.
- F. Azeez and P. S. Fedkiw, Conductivity of libob-based electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2010, 195(22), 7627–7633 Search PubMed.
- S. S. Zhang, An unique lithium salt for the improved electrolyte of Li-ion battery, Electrochem. Commun., 2006, 8(9), 1423–1428 Search PubMed.
- Q. Zhao, Y. Zhang, F. Tang, J. Zhao and S. Li, Mixed Salts of Lithium Difluoro (Oxalate) Borate and Lithium Tetrafluorobotate Electrolyte on Low-Temperature Performance for Lithium-Ion Batteries, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2017, 164(9), A1873–A1880 Search PubMed.
- N. Chen, M. Feng, C. Li, Y. Shang, Y. Ma, J. Zhang, Y. Li, G. Chen, F. Wu and R. Chen, Anion-Dominated Conventional-Concentrations Electrolyte to Improve Low-Temperature Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 34(33), 2400337 Search PubMed.
- E. Plichta and S. Slane, Conductivity of lithium imide in mixed aprotic solvents for lithium cells, J. Power Sources, 1997, 69(1–2), 41–45 Search PubMed.
- R. Dharavath, A. Murali, A. W. Tarapathi, B. Trichy Srinivasan and R. Kammili, Low–Temperature Conductivity Study of Multiorganic Solvent Electrolyte for Lithium–Sulfur Rechargeable Battery Application, Int. J. Electrochem., 2019, 2019(1), 8192931 Search PubMed.
- J. Xu, X. Wang, N. Yuan, J. Ding, S. Qin, J. M. Razal, X. Wang, S. Ge and Y. Gogotsi, Extending the low temperature operational limit of Li-ion battery to −80 C, Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 23, 383–389 Search PubMed.
- M. Zhang, X. Lei, Y. Lv, X. Liu and Y. Ding, Reversible Low Temperature Li–Storage in Liquid Metal Based Anodes via a Co–Solvent Strategy, Chin. J. Chem., 2021, 39(10), 2801–2807 Search PubMed.
- G. Cai, Y. Yin, D. Xia, A. A. Chen, J. Holoubek, J. Scharf, Y. Yang, K. H. Koh, M. Li, D. M. Davies, M. Mayer, T. H. Han, Y. S. Meng, T. A. Pascal and Z. Chen, Sub-nanometer confinement enables facile condensation of gas electrolyte for low-temperature batteries, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 3395 Search PubMed.
- H. Shahali, D. Stufflebam and A. Amiri, Elucidating Passivation Layer Effects on Low-Temperature Performance of Nitrile-Based Electrolytes in Lithium-Ion Batteries, Energy Fuels, 2025, 39(15), 7538–7549 Search PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, S. Li, J. Shi, J. Lai, Z. Zhuang, J. Liu, W. Yang, L. Ma, Y.-P. Cai, J. Xu and Q. Zheng, Revealing the key role of non-solvating diluents for fast-charging and low temperature Li-ion batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2024, 94, 171–180 Search PubMed.
- Z. Li, Y.-X. Yao, M. Zheng, S. Sun, Y. Yang, Y. Xiao, L. Xu, C.-B. Jin, X.-Y. Yue, T. Song, P. Wu, C. Yan and Q. Zhang, Electrolyte Design Enables Rechargeable LiFePO4/Graphite Batteries from −80 °C to 80 °C, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2025, 137(2), e202409409 Search PubMed.
- H.-B. Han, S.-S. Zhou, D.-J. Zhang, S.-W. Feng, L.-F. Li, K. Liu, W.-F. Feng, J. Nie, H. Li and X.-J. Huang, Lithium bis (fluorosulfonyl) imide (LiFSI) as conducting salt for nonaqueous liquid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries: Physicochemical and electrochemical properties, J. Power Sources, 2011, 196(7), 3623–3632 Search PubMed.
- X. Zhang, L. Zou, Y. Xu, X. Cao, M. H. Engelhard, B. E. Matthews, L. Zhong, H. Wu, H. Jia and X. Ren, Advanced electrolytes for fast–charging high–voltage lithium–ion batteries in wide–temperature range, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(22), 2000368 Search PubMed.
- J. Wang, Q. Zheng, M. Fang, S. Ko, Y. Yamada and A. Yamada, Concentrated Electrolytes Widen the Operating Temperature Range of Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Sci., 2021, 8(18), 2101646 Search PubMed.
- Z. Jiang, Z. Zeng, X. Liang, L. Yang, W. Hu, C. Zhang, Z. Han, J. Feng and J. Xie, Fluorobenzene, a low–density, economical, and bifunctional hydrocarbon cosolvent for practical lithium metal batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(1), 2005991 Search PubMed.
- D. M. Davies, Y. Yang, E. S. Sablina, Y. Yin, M. Mayer, Y. Zhang, M. Olguin, J. Z. Lee, B. Lu, D. Damien, O. Borodin, C. S. Rustomji and Y. S. Meng, A Safer, Wide-Temperature Liquefied Gas Electrolyte Based on Difluoromethane, J. Power Sources, 2021, 493, 229668 Search PubMed.
- Q. K. Zhang, X. Q. Zhang, L. P. Hou, S. Y. Sun, Y. X. Zhan, J. L. Liang, F. S. Zhang, X. N. Feng, B. Q. Li and J. Q. Huang, Regulating solvation structure in nonflammable amide–based electrolytes for long–cycling and safe lithium metal batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(24), 2200139 Search PubMed.
- X. Fan, X. Ji, L. Chen, J. Chen, T. Deng, F. Han, J. Yue, N. Piao, R. Wang and X. Zhou, All-temperature batteries enabled by fluorinated electrolytes with non-polar solvents, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(10), 882–890 Search PubMed.
- S. Lei, Z. Zeng, H. Yan, M. Qin, M. Liu, Y. Wu, H. Zhang, S. Cheng and J. Xie, Nonpolar Cosolvent Driving LUMO Energy Evolution of Methyl Acetate Electrolyte to Afford Lithium–Ion Batteries Operating at −60 °C, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33(34), 2301028 Search PubMed.
- J. Xu, V. Koverga, A. Phan, A. Min Li, N. Zhang, M. Baek, C. Jayawardana, B. L. Lucht, A. T. Ngo and C. Wang, Revealing the Anion–Solvent Interaction for Ultralow Temperature Lithium Metal Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36(7), 2306462 Search PubMed.
- Y. Ein-Eli, S. Thomas, R. Chadha, T. Blakley and V. Koch, Li–ion battery electrolyte formulated for low–temperature applications, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1997, 144(3), 823 Search PubMed.
- J. Yang, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, G. Duan, Z. Liang, J. Han, Y. Huang, X. Han, C. Zhang, S. He and S. Jiang, Design of cyclic carbonate-based electrolytes for HC anodes towards improved low-temperature performance in lithium-ion batteries system, Fuel, 2025, 379, 133048 Search PubMed.
- R. Weber, M. Genovese, A. J. Louli, S. Hames, C. Martin, I. G. Hill and J. R. Dahn, Long cycle life and dendrite-free lithium morphology in anode-free lithium pouch cells enabled by a dual-salt liquid electrolyte, Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(8), 683–689 Search PubMed.
- A. S. Wotango, W.-N. Su, E. G. Leggesse, A. M. Haregewoin, M.-H. Lin, T. A. Zegeye, J.-H. Cheng and B.-J. Hwang, Improved Interfacial Properties of MCMB Electrode by 1-(Trimethylsilyl)imidazole as New Electrolyte Additive To Suppress LiPF6 Decomposition, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(3), 2410–2420 Search PubMed.
- Z. Geng, J. Lu, Q. Li, J. Qiu, Y. Wang, J. Peng, J. Huang, W. Li, X. Yu and H. Li, Lithium metal batteries capable of stable operation at elevated temperature, Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 23, 646–652 Search PubMed.
- L. J. Krause, W. Lamanna, J. Summerfield, M. Engle, G. Korba, R. Loch and R. Atanasoski, Corrosion of aluminum at high voltages in non-aqueous electrolytes containing perfluoroalkylsulfonyl imides; new lithium salts for lithium-ion cells, J. Power Sources, 1997, 68(2), 320–325 Search PubMed.
- E. J. Plichta and W. K. Behl, A low-temperature electrolyte for lithium and lithium-ion batteries, J. Power Sources, 2000, 88(2), 192–196 Search PubMed.
- G. A. Elia, F. Nobili, R. Tossici, R. Marassi, A. Savoini, S. Panero and J. Hassoun, Nanostructured tin–carbon/LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 lithium-ion battery operating at low temperature, J. Power Sources, 2015, 275, 227–233 Search PubMed.
- C. K. Huang, J. S. Sakamoto, J. Wolfenstine and S. Surampudi, The Limits of Low–Temperature Performance of Li–Ion Cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2000, 147(8), 2893 Search PubMed.
- S. S. Zhang, K. Xu and T. R. Jow, Study of LiBF4 as an Electrolyte Salt for a Li-Ion Battery, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2002, 149(5), A586 Search PubMed.
- S. Zhang, K. Xu and T. Jow, Low-temperature performance of Li-ion cells with a LiBF4-based electrolyte, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2003, 7(3), 147–151 Search PubMed.
- S. Zhang, K. Xu and T. Jow, Enhanced performance of Li-ion cell with LiBF4-PC based electrolyte by addition of small amount of LiBOB, J. Power Sources, 2006, 156(2), 629–633 Search PubMed.
- S. S. Zhang, Electrochemical study of the formation of a solid electrolyte interface on graphite in a LiBC2O4F2-based electrolyte, J. Power Sources, 2007, 163(2), 713–718 Search PubMed.
- B. S. Parimalam and B. L. Lucht, Reduction Reactions of Electrolyte Salts for Lithium Ion Batteries: LiPF6, LiBF4, LiDFOB, LiBOB, and LiTFSI, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165(2), A251 Search PubMed.
- K. Xu, U. Lee, S. Zhang, J. L. Allen and T. R. Jow, Graphite/Electrolyte Interface Formed in LiBOB-Based Electrolytes: I. Differentiating the Roles of EC and LiBOB in SEI Formation, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2004, 7(9), A273 Search PubMed.
- H. Zhou, K. Xiao and J. Li, Lithium difluoro(oxalate)borate and LiBF4 blend salts electrolyte for LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode material, J. Power Sources, 2016, 302, 274–282 Search PubMed.
- K. Qian, Y. Liu, X. Zhou, D. J. Gosztola, H. Nguyen and T. Li, Decoupling the degradation factors of Ni-rich NMC/Li metal batteries using concentrated electrolytes, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 41, 222–229 Search PubMed.
- G. Xu, X. Shangguan, S. Dong, X. Zhou and G. Cui, Formulation of Blended-Lithium-Salt Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59(9), 3400–3415 Search PubMed.
- S.-T. Myung, Y. Hitoshi and Y.-K. Sun, Electrochemical behavior and passivation of current collectors in lithium-ion batteries, J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(27), 9891–9911 Search PubMed.
- K. Park, S. Yu, C. Lee and H. Lee, Comparative study on lithium borates as corrosion inhibitors of aluminum current collector in lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide electrolytes, J. Power Sources, 2015, 296, 197–203 Search PubMed.
- T. Zheng, J. Xiong, B. Zhu, X. Shi, Y.-J. Cheng, H. Zhao and Y. Xia, From −20 °C to 150 °C: a lithium secondary battery with a wide temperature window obtained via manipulated competitive decomposition in electrolyte solution, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(14), 9307–9318 Search PubMed.
- L. A. Dominey, V. R. Koch and T. J. Blakley, Thermally stable lithium salts for polymer electrolytes, Electrochim. Acta, 1992, 37(9), 1551–1554 Search PubMed.
- B. Wen, Z. Deng, P.-C. Tsai, Z. W. Lebens-Higgins, L. F. J. Piper, S. P. Ong and Y.-M. Chiang, Ultrafast ion transport at a cathode–electrolyte interface and its strong dependence on salt solvation, Nat. Energy, 2020, 5(8), 578–586 Search PubMed.
- W. Li, A. Dolocan, J. Li, Q. Xie and A. Manthiram, Ethylene Carbonate-Free Electrolytes for High-Nickel Layered Oxide Cathodes in Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(29), 1901152 Search PubMed.
- I. A. Shkrob, T. W. Marin, Y. Zhu and D. P. Abraham, Why Bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide Is a “Magic Anion” for Electrochemistry, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118(34), 19661–19671 Search PubMed.
- L.-L. Jiang, C. Yan, Y.-X. Yao, W. Cai, J.-Q. Huang and Q. Zhang, Inhibiting Solvent Co-Intercalation in a Graphite Anode by a Localized High-Concentration Electrolyte in Fast-Charging Batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60(7), 3402–3406 Search PubMed.
- B. Nan, L. Chen, N. D. Rodrigo, O. Borodin, N. Piao, J. Xia, T. Pollard, S. Hou, J. Zhang and X. Ji, Enhancing Li+ transport in NMC811|| graphite lithium–ion batteries at low temperatures by using low–polarity–solvent electrolytes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61(35), e202205967 Search PubMed.
- H. Yang, K. Kwon, T. M. Devine and J. W. Evans, Aluminum Corrosion in Lithium Batteries An Investigation Using the Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2000, 147(12), 4399 Search PubMed.
- H. Xiang, P. Shi, P. Bhattacharya, X. Chen, D. Mei, M. E. Bowden, J. Zheng, J.-G. Zhang and W. Xu, Enhanced charging capability of lithium metal batteries based on lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide-lithium bis(oxalato)borate dual-salt electrolytes, J. Power Sources, 2016, 318, 170–177 Search PubMed.
- S. Lin, H. Hua, P. Lai and J. Zhao, A Multifunctional Dual-Salt Localized High-Concentration Electrolyte for Fast Dynamic High-Voltage Lithium Battery in Wide Temperature Range, Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11(36), 2101775 Search PubMed.
- J. Chen, A. Naveed, Y. Nuli, J. Yang and J. Wang, Designing an intrinsically safe organic electrolyte for rechargeable batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 31, 382–400 Search PubMed.
- S. Jurng, S. Park, T. Yoon, H.-S. Kim, H. Jeong, J. H. Ryu, J. J. Kim and S. M. Oh, Low-Temperature Performance Improvement of Graphite Electrode by Allyl Sulfide Additive and Its Film-Forming Mechanism, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2016, 163(8), A1798 Search PubMed.
- Y. Lin, X. Yue, H. Zhang, L. Yu, W. Fan and T. Xie, Using phenyl methanesulfonate as an electrolyte additive to improve performance of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2/graphite cells at low temperature, Electrochim. Acta, 2019, 300, 202–207 Search PubMed.
- P. Jankowski, N. Lindahl, J. Weidow, W. Wieczorek and P. Johansson, Impact of Sulfur-Containing Additives on Lithium-Ion Battery Performance: From Computational Predictions to Full-Cell Assessments, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2018, 1(6), 2582–2591 Search PubMed.
- R. Guo, Y. Che, G. Lan, J. Lan, J. Li, L. Xing, K. Xu, W. Fan, L. Yu and W. Li, Tailoring Low-Temperature Performance of a Lithium-Ion Battery via Rational Designing Interphase on an Anode, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(41), 38285–38293 Search PubMed.
- B. Liu, Q. Li, M. H. Engelhard, Y. He, X. Zhang, D. Mei, C. Wang, J.-G. Zhang and W. Xu, Constructing robust electrode/electrolyte interphases to enable wide temperature applications of lithium-ion batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(24), 21496–21505 Search PubMed.
- G. Cai, J. Holoubek, D. Xia, M. Li, Y. Yin, X. Xing, P. Liu and Z. Chen, An ester electrolyte for lithium–sulfur batteries capable of ultra-low temperature cycling, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56(64), 9114–9117 Search PubMed.
- E. R. Logan, E. M. Tonita, K. L. Gering, J. Li, X. Ma, L. Y. Beaulieu and J. R. Dahn, A Study of the Physical Properties of Li-Ion Battery Electrolytes Containing Esters, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2018, 165(2), A21 Search PubMed.
- J.-P. Jones, M. C. Smart, F. C. Krause and R. V. Bugga, The Effect of Electrolyte Additives upon Lithium Plating during Low Temperature Charging of Graphite-LiNiCoAlO2 Lithium-Ion Three Electrode Cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, 167(2), 020536 Search PubMed.
- J. Zheng, M. H. Engelhard, D. Mei, S. Jiao, B. J. Polzin, J.-G. Zhang and W. Xu, Electrolyte additive enabled fast charging and stable cycling lithium metal batteries, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2(3), 17012 Search PubMed.
- J. Liu, X. Song, L. Zhou, S. Wang, W. Song, W. Liu, H. Long, L. Zhou, H. Wu, C. Feng and Z. Guo, Fluorinated phosphazene derivative – A promising electrolyte additive for high voltage lithium ion batteries: From electrochemical performance to corrosion mechanism, Nano Energy, 2018, 46, 404–414 Search PubMed.
- H. Gao, F. Maglia, P. Lamp, K. Amine and Z. Chen, Mechanistic Study of Electrolyte Additives to Stabilize High-Voltage Cathode–Electrolyte Interface in Lithium-Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(51), 44542–44549 Search PubMed.
- M. Becker, R.-S. Kühnel and C. Battaglia, Water-in-salt electrolytes for aqueous lithium-ion batteries with liquidus temperatures below −10 °C, Chem. Commun., 2019, 55(80), 12032–12035 Search PubMed.
- Y. Zhao, Z. Chen, F. Mo, D. Wang, Y. Guo, Z. Liu, X. Li, Q. Li, G. Liang and C. Zhi, Aqueous rechargeable metal–ion batteries working at subzero temperatures, Adv. Sci., 2021, 8(1), 2002590 Search PubMed.
- L. Suo, O. Borodin, T. Gao, M. Olguin, J. Ho, X. Fan, C. Luo, C. Wang and K. Xu, “Water-in-salt” electrolyte enables high-voltage aqueous lithium-ion chemistries, Science, 2015, 350(6263), 938–943 Search PubMed.
- J. Chen, J. Vatamanu, L. Xing, O. Borodin, H. Chen, X. Guan, X. Liu, K. Xu and W. Li, Improving Electrochemical Stability and Low-Temperature Performance with Water/Acetonitrile Hybrid Electrolytes, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(3), 1902654 Search PubMed.
- H.-I. Kim, E. Shin, S.-H. Kim, K. M. Lee, J. Park, S. J. Kang, S. So, K. C. Roh, S. K. Kwak and S.-Y. Lee, Aqueous eutectic lithium-ion electrolytes for wide-temperature operation, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 36, 222–228 Search PubMed.
- J. Yue, J. Zhang, Y. Tong, M. Chen, L. Liu, L. Jiang, T. Lv, Y.-S. Hu, H. Li, X. Huang, L. Gu, G. Feng, K. Xu, L. Suo and L. Chen, Aqueous interphase formed by CO2 brings electrolytes back to salt-in-water regime, Nat. Chem., 2021, 13(11), 1061–1069 Search PubMed.
- A. Ramanujapuram and G. Yushin, Understanding the exceptional performance of lithium–ion battery cathodes in aqueous electrolytes at subzero temperatures, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(35), 1802624 Search PubMed.
- Q. Nian, J. Wang, S. Liu, T. Sun, S. Zheng, Y. Zhang, Z. Tao and J. Chen, Aqueous batteries operated at −50 °C, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58(47), 16994–16999 Search PubMed.
- A. Tron, S. Jeong, Y. D. Park and J. Mun, Aqueous lithium-ion battery of nano-LiFePO4 with antifreezing agent of ethyleneglycol for low-temperature operation, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7(17), 14531–14538 Search PubMed.
- J. Liu, C. Yang, X. Chi, B. Wen, W. Wang and Y. Liu, Water/sulfolane hybrid electrolyte achieves ultralow–temperature operation for high–voltage aqueous lithium–ion batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(1), 2106811 Search PubMed.
- J. Xu and C. Wang, Perspective—Electrolyte Design for Aqueous Batteries: From Ultra-High Concentration to Low Concentration?, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2022, 169(3), 030530 Search PubMed.
- L. Jiang, D. Dong and Y.-C. Lu, Design strategies for low temperature aqueous electrolytes, Nano Res. Energy, 2022, 1(1), e9120003 Search PubMed.
- J. Hou, M. Yang, D. Wang and J. Zhang, Fundamentals and challenges of lithium ion batteries at temperatures between −40 and 60 °C, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(18), 1904152 Search PubMed.
- M. S. Ding and K. Xu, Phase Diagram, Conductivity, and Glass Transition of LiTFSI–H2O Binary Electrolytes, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122(29), 16624–16629 Search PubMed.
- D. Reber, R.-S. Kühnel and C. Battaglia, Suppressing Crystallization of Water-in-Salt Electrolytes by Asymmetric Anions Enables Low-Temperature Operation of High-Voltage Aqueous Batteries, ACS Mater. Lett., 2019, 1(1), 44–51 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yamada, K. Furukawa, K. Sodeyama, K. Kikuchi, M. Yaegashi, Y. Tateyama and A. Yamada, Unusual stability of acetonitrile-based superconcentrated electrolytes for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(13), 5039–5046 Search PubMed.
- Q. Dou, S. Lei, D.-W. Wang, Q. Zhang, D. Xiao, H. Guo, A. Wang, H. Yang, Y. Li and S. Shi, Safe and high-rate supercapacitors based on an “acetonitrile/water in salt” hybrid electrolyte, Energy Environ. Sci., 2018, 11(11), 3212–3219 Search PubMed.
- W. Chen, J. Vatamanu, L. D. Xing, O. Borodin, H. Y. Chen, X. C. Guan, X. Liu, K. Xu and W. S. Li, Improving electrochemical stability and low-temperature performance with water/acetonitrile hybrid electrolytes, Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(3), 1902654 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5eb00013k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |