Structures and terahertz dynamics of an imidazolium-based ionic liquid on a gold electrode studied using surface-enhanced Raman scattering†
Ryo
Ueno
 ,
Kenta
Motobayashi
,
Kenta
Motobayashi
 and
Katsuyoshi
Ikeda
and
Katsuyoshi
Ikeda
 *
*
Program of Applied Physics, Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya Institute of Technology, Gokiso-cho, Nagoya 466-8555, Japan. E-mail: kikeda@nitech.ac.jp
First published on 3rd June 2025
Abstract
Room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) have been extensively studied for decades as a potential electrolyte alternative. The structural and dynamic properties of RTILs in an electrical double layer (EDL), formed at the electrode/electrolyte interface, differ from those in their bulk phase. Despite the importance of the interfacial properties of RTILs in electrical devices, such behaviours of denser ion structuring in EDL are poorly understood owing to the delicate anion–cation interplay among various intermolecular interactions such as Coulombic interaction, hydrogen bonding interaction, and π-type interaction. Herein, an advanced spectroscopy technique based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is used to achieve simultaneous observation of electronic, chemical, and terahertz-dynamic behaviours of an imidazolium-based ionic liquid, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ([BMI]PF6), on a gold electrode. Physisorption and desorption of PF6 anions on the Au surface are of particular importance in understanding the hysteresis behaviour of potential-induced anion–cation replacement in the EDL. It is also highlighted that the restructuring dynamics of the EDL is correlated with the enhancement of translational terahertz motions among cations and anions on a charged surface.
Introduction
Room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs), consisting entirely of ions, are believed to be fascinating liquid electrolytes with several advantages over conventional electrolyte solutions containing both ions and neutral solvent molecules. These solvent-free liquid electrolytes exhibit very low vapor pressure, high thermal stability, and a wide electrochemical window.1–4 Their physicochemical behaviours are largely influenced by the structural and chemical nature of constituent ions, unlike ordinary electrolyte solutions containing solvent molecules; contributions of intermolecular interactions such as van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, and steric effects are strong in RTILs, resulting in nanoscale structuring even in the bulk phase.5,6 Thus, several aspects of the relationship between the microheterogeneity and macroscopic properties of RTILs still remain controversial or not fully answered.7 At electrochemical interfaces, such nanostructuring of RTILs is further modified by the presence of a charged solid surface, resulting in discrete layering of charges in the electrical double layer (EDL).8–13 Although such interfacial structuring should impact their electrochemical behaviours, there is a dearth of information about the molecular-scale details of the structure, dynamics, and interactions of RTILs at electrochemical interfaces. In particular, far less information is available on the nature of intermolecular interactions in the EDL because of the difficulty in the surface-selective detection of relatively weak intermolecular forces.Surface-selective vibrational spectroscopies such as vibrational sum-frequency generation (VSFG), surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy (SEIRAS), and attenuated total reflection-IR spectroscopy (ATR-IR) have been widely used to study the electrochemical characteristics of RTILs.14–18 However, these spectroscopic methods are operated mostly in the mid-infrared (MIR) frequency region between 4000 and 400 cm−1, where many intramolecular (chemical bond) vibrations exist. Given that intermolecular (external) vibrations are found in the terahertz (THz) region below 300 cm−1,19–21 it is necessary to obtain THz information and MIR information of RTILs at electrochemical interfaces, which is difficult for ordinary vibrational spectroscopies. By contrast, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) can, in principle, simultaneously measure MIR and THz responses at electrochemical interfaces.22–25 Indeed, structural and dynamic properties of hydrogen-bond networks of water have recently been observed on a charged surface using volume-Bragg-grating (VBG)-based SERS spectroscopy.26,27
As for the applicability of SERS, it has also been demonstrated that SERS can provide information about the surface charge density of electrodes; the SERS spectrum is composed of two different types of Raman signals: electronic SERS (eSERS) and vibrational SERS (vSERS).28–33 The former, i.e., plasmon-enhanced Raman signals scattered by free electrons of the metal substrate, gives a background continuum in the SERS spectrum, while the latter, i.e., plasmon-enhanced Raman signals scattered by molecular vibrations, appends discrete peaks on the continuum. Importantly, the eSERS intensity is nearly proportional to the surface charge density of the electrode.34,35 Given that the magnitude of the surface charge of the electrode is equal to the net counter charge of the electrolyte phase in the EDL, SERS spectroscopy seems to be a great method to understand the EDL structure and charging dynamics at the molecular level.
Herein, we report the in situ observation of eSERS and vSERS (e/vSERS) for 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, [BMI]PF6, on an Au electrode in a wide frequency range of 8–1800 cm−1 covering both MIR-intramolecular and THz-external vibrations. Among various types of RTILs, [BMI]PF6 is one of the most widely studied ionic liquids with hydrogen bonding between anions and cations.5,14,36–40 We demonstrate that molecular-level changes of EDL-layering structures, monitored by vSERS, conform well to the EDL-charging behaviour, probed by eSERS. The potential-induced anion–cation replacement in the EDL is closely related to the desorption and adsorption of PF6 anions on the Au surface, resulting in hysteresis behaviour of the EDL restructuring. For THz dynamics of ions in the EDL, the interionic hydrogen-bond vibration exhibits an increase in intensity and softening in frequency during the restructuring of the EDL, which resembles phonon softening in structural phase transitions of a crystalline solid.41 This comprehensive information helps our understanding of how the EDL restructuring takes place at the molecular level.
Methods
Electrochemical and spectroscopic measurements
[BMI]PF6 (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd, 98%) was dried in a vacuum at 80 °C overnight to eliminate water impurity and stored in an Ar-filled glove box with −90 °C dew point and 0.2 ppm O2 (Glovebox Japan inc., GBJF100). Karl–Fischer titration measurements (Mitsubishi Chemical, CA 200) indicated that the water content of the dried [BMI]PF6 was lower than 5 ppm. The potential of zero charge (pzc) of the gold electrode in [BMI]PF6 was measured by the electrode immersion method42 in the glove box using a potentiostat (ECstat-300, EC Frontier). The measurement of the charge at each potential was repeated 10 times. The pzc was estimated by linear least squares fitting in the charge-potential plot.A SERS-active Au electrode was prepared on a smooth Au substrate by drop casting of Au colloidal solution containing Au nanoparticles with a diameter of 100 nm (Tanaka Precious Metals, SC100). The obtained electrode was cleaned in 0.1 NaClO4 solution by applying oxidation–reduction cycles. After being rinsed with ultra-pure water, the electrode was dried in a vacuum at 120 °C for 1 hour. Then, it was transferred into the glove box and placed in a home-built air-sealed spectroelectrochemical cell filled with dried [BMI]PF6 so that the electrode was not exposed to ambient air after vacuum-drying. The electrode surface was further cleaned by applying potential cycles in [BMI]PF6 before use. A Pt wire was used as the counter electrode. Electrochemical potentials were measured with respect to a Pt quasi-reference electrode, which were converted against the ferrocene redox (Fc/Fc+) potential.
Normal Raman and SERS spectra of [BMI]PF6 were recorded in the air-sealed cell using a home-built inverted microscope Raman system with an objective (40 ×, 0.6 N.A.).25 A He–Ne laser radiation of 632.8 nm was further filtered using an ultra-narrow-band laser-line filter with a bandwidth of less than 0.4 nm FWHM (reflecting volume Bragg grating (VBG) line filter, OptiGrate Corp). The excitation laser power was typically less than 0.02 mW at the focal point for SERS. The backscattered Raman signals from the sample were monitored by using a single-stage spectrometer with a CCD detector (IsoPlane & PIXIS 100BR eX-I, Princeton Instruments) after Rayleigh scattering was removed by ultra-narrow-band VBG notch filters (OptiGrate Corp). The normal Raman spectrum of [BMI]PF6 in the bulk phase showed a fluorescence background,43 which was removed by smooth fitting. For SERS, the contribution of the fluorescence from [BMI]PF6 was negligible due to the quenching effect on the Au surface. To perform vibrational analysis in the low-frequency region, measured spectra were converted to the density of states (DOS) format for both normal Raman18,44 and SERS31,32 (for details, see ESI†).
Computational method
Vibrational calculations of the PF6-anion, BMI-cation with trans–trans conformation, NHC (reductively deprotonated BMI), Au4-PF6−, Au4-NHC, and dimeric NHC were carried out using density functional theory (DFT) at the M06 level of theory with the def2-SVPD basis set, which were performed with the Gaussian09 ver.9.0 program. The calculated Raman spectra were scaled by 0.995 in the low-frequency range below 1000 cm−1 and by 0.982 in the mid-frequency range between 1000 and 2000 cm−1.45Results and discussion
Electrochemical behaviour of [BMI]PF6
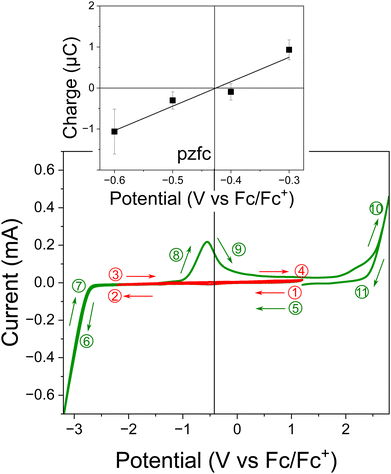
Fig. 1 shows the cyclic voltammograms of dry [BMI]PF6 (with water impurity of less than 5 ppm) in both capacitive and faradaic regions measured on a SERS-active Au electrode. The electrochemical window between the anodic and cathodic limits is clearly more than 4 V, which agrees with the reported value. When the potential was scanned more negatively beyond the cathodic limit, there appeared an anodic peak at around −0.8 V vs. Fc/Fc+ in the reverse scan, which is ascribed to the oxidation of reduced BMI, i.e., N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC).46,47 The potential of zero charge (pzc) was found near the center of the electrochemical window (see the inset). Incidentally, the measured pzc should be the potential of zero free charge (pzfc) rather than the potential of zero total charge (pztc) because of the presence of adsorbed anions on the surface as shown later. SERS measurement of [BMI]PF6 was performed in the entire potential range, but we could not obtain SERS spectra in the potential range above the anodic limit because of the strong fluorescence from oxidative reaction products. Therefore, we focus on the electrochemical behavior of [BMI]PF6 in the potential region more negative than the pzfc.Normal Raman and SERS spectra of [BMI]PF6
The normal Raman spectrum for dry [BMI]PF6, measured with 632.8 nm excitation, is presented in the top panel of Fig. 2 (the vibrational Raman scattering spectrum is converted into the density of states (DOS) format, denoted as χ′′vRS, by reducing the Bose–Einstein thermal factor18,44). The most intense peak at 740 cm−1 is assigned to the symmetric stretching mode of the PF6 anion, νs(PF6−). The peaks at 565 cm−1 and 468 cm−1 are also attributed to the vibration modes of the PF6-anion. All other peaks found in the fingerprint region are attributed to the vibrational modes of the BMI-cation (DFT calculation results are presented in ESI†). In addition to these intramolecular vibrations, there is a broad feature below 200 cm−1, which is assigned to the interionic vibration band: stretching of the cation–anion hydrogen bond, ν(H⋯F).21 The bottom panel of Fig. 2 shows the SERS spectrum of dry [BMI]PF6 on the Au electrode measured at pzfc, which is converted to the DOS format, denoted as χ′′SERS, by reducing the Purcell factor as well as the Bose–Einstein thermal factor.31,32 There appear several vSERS peaks on a broad eSERS background. (It is emphasized that the background is not caused by fluorescence from [BMI]PF6; when the SERS spectrum is measured in the absence of [BMI]PF6, a similar spectral background is observed without vSERS peaks as shown in ESI†) In the fingerprint region, the observed vSERS peaks are in good agreement with those of the normal Raman spectrum. In the low-frequency region, the interionic vibration is not clearly seen at this potential. Instead, a remarkable peak appears at 188 cm−1. This feature can be assigned to the external mode of the PF6-anion adsorbed on Au, νAu-PF6−, because the adsorption of PF6 anions on the Au surface has been confirmed in RTILs.48 The DFT calculation result for an adsorbed PF6 anion also supports this peak assignment. As mentioned in Fig. 1, the existence of adsorbed anions at pzc means that the measured pzc should be pzfc rather than pztc.Potential dependence of SERS in the capacitive region
When electrochemical potential cycles are applied to [BMI]PF6 within the electrochemical window, the SERS spectrum shows reversible changes; the potential dependences of SERS spectra and their difference spectra are presented in Fig. 3. When the electrochemical potential was scanned toward the negative direction, the eSERS background gradually increased in intensity, and then the increased intensity of eSERS recovered to the initial level when the potential was reversely scanned (see Fig. 3a). For the vSERS peaks, BMI-cation peaks and the adsorbed PF6-anion peak (νAu-PF6−) showed opposite behaviors, as clearly seen in Fig. 3b. That is, the νAu-PF6− peak vanished when the applied potential was changed to around −1.6 V, indicating that PF6− anions were desorbed from the Au surface. Instead, the BMI-cation peaks increased in intensity. These spectral variations can be interpreted as the anion–cation replacement in the first layer of the EDL;16,49 the first and second layers of the EDL near pzfc were initially enriched with adsorbed PF6-anions and BMI-cations, respectively, and then the ion replacement in the first layer started with desorption of PF6-anions under the negative-going scan. It should also be noted that the interionic hydrogen-bonding vibration in the THz region, ν(H⋯F), evolved synchronously with this ion replacement. More precisely, this stretching mode of the hydrogen bond initially appeared at around 110 cm−1 when the νAu-PF6− peak started to decrease (see the blue spectrum at pzfc), and then it was softened to 58 cm−1 at more negative potentials (see the red spectrum at −1.6 V, for example). Because this interionic vibration is composed of relative translational motions between PF6-anions and BMI-cations, the increase in the band intensity means that the discrete interfacial layering structure fluctuates under the applied potential more negative than pzfc. Such interlayer ionic motions should play a central role in facilitating the anion–cation replacement in the first layer of the EDL. Moreover, the softening of the vibrational mode during the restructuring of interfacial layers implies that the induced restructuring became stable under the more negative potential application; it resembles the so-called phonon softening in structural phase transition of crystalline solids.41Fig. 4 illustrates a concise model for potential-dependent EDL structures obtained from MIR-vibrations and dynamic restructuring between these structures probed by THz-vibrations. | ||
| Fig. 4 Concise model of the potential-dependent EDL structures obtained from MIR-vibrations and dynamic restructuring probed by THz-vibrations. | ||
For BMI-cations, distinct Raman bands are found at 1350, 1394, 1418, and 1567 cm−1, as indicated by the dotted lines in Fig. 3. Among these bands, the 1418 cm−1 peak, assigned to alkyl chain vibration, δsym(CH3),37 was less sensitive to the potential change. By contrast, the other three peaks, assigned to imidazolium ring vibrations,37 were more sensitive to the potential change, suggesting that the positively charged imidazolium ring rather than the neutral alkyl chain approaches the Au surface when the electrode surface is charged negatively. Fig. 5 shows potential dependences of the imidazolium ring vibration at 1567 cm−1 and two PF6-anion bands at 190 cm−1 and 741 cm−1, along with the cyclic voltammogram in the corresponding potential range. Stepwise intensity variations of the BMI-ring mode during the potential cycle well agreed with the capacitive responses observed in the CV. Besides, the behavior of the adsorbed PF6-anions, νAu-PF6− at 190 cm−1, was roughly opposite to that of the BMI-cations. This suggests that the EDL charging (discharging) involves the accumulation (diminution) of BMI-cations and desorption (adsorption) of PF6-anions in the first layer of the EDL. On the other hand, the intensity of free PF6-anions, νPF6− at 741 cm−1, was nearly invariant to the potential change, implying that free PF6-anions mostly exist in the outer layers of the EDL. Fig. 5 also shows that this potential-induced anion–cation replacement process exhibits hysteresis behavior. In fact, the origin of such hysteretic behavior in the EDL restructuring of RTILs is still under discussion, with several predominant mechanisms proposed: the ion-substrate interaction, nonequilibrium restructuring due to the slow response of RTILs, and the energy barrier for restructuring.16 In the case of [BMI]PF6, the adsorption/desorption of PF6-anions seems to have a large impact on the hysteretic behavior in the EDL restructuring. One can say that SERS is more powerful for studying the electrochemical behaviors of RTILs while SEIRAS and VSFG are not very useful for detecting surface adsorbates.
Potential dependence of SERS in the faradaic region
When the electrochemical potential is scanned negatively beyond the cathodic limit of the electrochemical window, BMI-cations are decomposed reductively. Fig. 6 shows SERS spectral changes under such a wide potential scan. For the eSERS background, it gradually increased in intensity, as already shown in Fig. 3a, but suddenly decreased when the applied potential became more negative than −2.0 V. At the same time, there appeared a new vibrational peak at 146 cm−1. The reductive deprotonation of BMI-cations can yield neutral NHCs in the vicinity of the Au surface. Because NHCs have a single lone pair of electrons, they can form a single dative bond with the Au surface.50 Indeed, the 146 cm−1 peak can be assigned to the external mode of NHC adsorbed on the Au surface, νAu-NHC, according to the DFT calculation result. Incidentally, when the potential was reversely scanned after the formation of chemisorbed NHCs on Au, the νAu-NHC peak remained until −1.2 V (see ESI†). In the more negative potential range beyond −2.4 V, faradaic current was observed in the voltammetric response (Fig. 6c). In this potential range, the νAu-NHC peak vanished. Alternatively, another new peak appeared at 1618 cm−1, which is assigned to the ring mode of dimeric NHC, νring(NHC)2. At the same time, the eSERS intensity also recovered partially.For more detailed analysis of Fig. 6, potential dependences of the eSERS intensity at 1700 cm−1 (where no vSERS peak is found) and the vSERS intensity of the νAu-NHC peak are presented in Fig. 7, along with the voltammetric response in the same potential range. Under the negative-going potential scan in the range between 0.0 and −2.0 V, the eSERS intensity showed stepwise increases at around −1.0 V and −1.6 V. It is again emphasized that the eSERS intensity is nearly proportional to the surface charge density on Au.34 Therefore, the variation of the eSERS intensity reveals the stepwise negative charging of the Au surface under the negative-going potential scan. Indeed, the trend of the eSERS intensity variations was consistent with capacitive current responses found in the same potential region in the voltammogram. The negative charging of the Au surface leads to an increase in the net counter charge of the EDL in the electrolyte phase, which is accomplished by the first-layer replacement between PF6-anions and BMI-cations, as confirmed by the vSERS changes in Fig. 3 and 5. That is, simultaneous monitoring of eSERS and vSERS can provide molecular insights into the potential-induced changes of EDL structures for both the electrolyte and electrode. Next, chemisorbed NHCs were formed on the Au surface at around −2.0 V due to the reductive deprotonation of BMI-cations, as indicated by the evolution of νAu-NHC. The synchronous decrease in the eSERS intensity can be understood by the fact that NHCs are powerful σ-donors;46 free electrons on the Au surface are pushed inside by chemisorbed NHCs. (By contrast, physisorption of PF6-anions above pzc did not affect the eSERS intensity because of the relatively weak interaction.) Interestingly, the peak intensity of νAu-NHC, i.e., the surface density of adsorbed NHCs, gradually decreased in the potential range between −2.0 and −2.6 V, and then, dimeric NHCs were suddenly generated at the cathodic limit of −2.6 V. This implies that the dimeric NHCs are generated not by a chemical combination of two adsorbed NHCs but by an electrochemical process through the formation of intermediates like NHC-BMI+ pairs.43 Indeed, NHC adlayers on Au seem to behave as a passivation layer towards the reductive decomposition of BMI-cations. It is known that imidazolium-based cations form the so-called solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on the cathode of Li-ion batteries.51–53 The passivation layer-like behavior of chemisorbed NHCs on Au may have some connection with the SEI formation in the presence of Li. Decomposition of imidazolium-based cations, including the formation of NHCs, has been identified in the presence of Li metal.51 The presence of reductively generated NHCs may promote the formation of a Li3N-rich SEI.52,53 However, the EDL structure near the cathodic limit becomes more complicated due to the existence of Li cations coordinated by anions.17 Further experimental studies would be needed for discussing the connection with this potential implication.
 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) Linear sweep voltammogram, which is the same as Fig. 5c, but the current axis is enlarged. (b) Potential dependencies of the eSERS intensity at 1700 cm−1 and vSERS intensity of νAu-NHC at 146 cm−1 under negative-going potential scan. | ||
Conclusions
The potential-induced behaviour of imidazolium-based RTILs in the EDL was studied at the [BMI]PF6/Au interface using e/vSERS spectroscopy in a wide frequency range covering both THz-intermolecular and MIR-intramolecular vibrations. As reported in previous conventional SERS studies,37,40,54 MIR-intramolecular vibrations revealed potential-induced changes in the composition or orientation of ions in the EDL. In addition to such ensemble-averaged structural information, THz-intermolecular vibrations were able to provide dynamic information like potential-induced structural fluctuations in the EDL (Fig. 4). We succeeded in achieving the direct observation of interionic hydrogen-bond interactions among anions and cations in the EDL under the application of potential cycles. The obtained spectral changes revealed that the potential-induced ion replacement in the first layer of the EDL is promoted by fluctuations of layering structures associated with translational THz-dynamic motions of hydrogen-bonded ion pairs. The hysteretic behaviour of the EDL restructuring is affected by the existence of physisorbed PF6-anions when the potential is scanned within the electrochemical window. It was also found that the reductive formation of NHCs from BMI cations occurred in the potential range more positive than the apparent cathodic limit in the voltammogram, which also causes the large hysteretic behaviour of the EDL restructuring. Direct monitoring of EDL charging using eSERS also helped comprehensive understanding of EDL behaviours. This spectroscopic technique will shed some light on the molecular level understanding of EDL structures and THz-dynamics.Author contributions
K. Ikeda conceived the project, R. Ueno performed SERS studies, K. Motobayashi advised the experimental procedures for RTILs, K. Ikeda performed data analysis and drafted the manuscript, and all the co-authors contributed to reviewing and editing the manuscript into its final format.Data availability
All additional data are in the ESI† associated with this publication.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (No. JP21H01882 and JP25K01743) and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (No. JP22H04537) from JSPS, Japan. The Iwatani Naoji Foundation also support this research. The authors would like to thank the Equipment Sharing Division, Organization for Co-Creation Research and Social Contributions, Nagoya Institute of Technology, for SEM analyses of the samples.Notes and references
- P. Hapiot and C. Lagrost, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 2238–2264 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
A. Torriero and M. Shiddiky, Electrochemical Properties and Applications of Ionic Liquids, Nova, New York, 2011 Search PubMed
.
-
H. Ohno, Electrochemical Aspects of Ionic Liquids, Wiley, Hoboken, 2011 Search PubMed
.
- S. Zhang, N. Sun, X. He, X. Lu and X. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 2006, 35, 1475–1517 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. N. A. Canongi Lopes and A. A. H. Pádua, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 3330–3335 CrossRef PubMed
.
- Y.-L. Wang, A. Laaksonen and M. D. Fayer, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2017, 121, 7173–7179 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- B. Kirchner, F. Malberg, D. S. Firaha and O. Hollóczki, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2015, 27, 463002 CrossRef PubMed
.
- M. Mezger, H. Schröder, H. Reichert, S. Schramm, J. S. Okasinski, S. Schöder, V. Honkimäki, M. Deutsch, B. M. Ocko, J. Ralston, M. Rohwerder, M. Stratmann and H. Dosch, Science, 2008, 322, 424–428 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. V. Fedorov and A. A. Kornyshev, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 2978–3036 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Hayes, G. G. Warr and R. Atkin, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 1709–1723 RSC
.
- D. Bedrov, J.-P. Piquemal, O. Borodin, A. D. Mackerell, Jr., B. Roux and C. Schröder, Chem. Rev., 2019, 119, 7940–7995 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Pedro de Souza, Z. A. H. Goodwin, M. McEldrew, A. A. Kornyshev and M. Z. Bazant, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2020, 125, 116001 CrossRef PubMed
.
- D. S. Silvester, R. Jamil, S. Doblinger, Y. Zhang, R. Atkin and H. Li, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125, 13707–13720 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Rivera-Rubero and S. Baldelli, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 4756–4765 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- W. Zhou, S. Inoue, T. Iwahashi, K. Kanai, K. Seki, T. Miyamae, D. Kim, Y. Katayama and Y. Ouchi, Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 12, 672–675 CrossRef CAS
.
- K. Motobayashi, K. Minami, N. Nishi, T. Sakka and M. Osawa, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2013, 4, 3110–3114 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. Kakinoki, A. Imanishi, S. Kondow, I. Tanabe and K. Fukui, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2025, 27, 6056 RSC
.
- F. Zaera, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 2920–2986 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C. J. Hirschmugl, G. P. Williams, F. M. Hoffmann and Y. J. Chabal, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1990, 65, 480 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Amo and Y. Tominaga, Physica A, 2000, 276, 401–412 CrossRef CAS
.
- V. H. Paschoal, L. F. O. Faria and M. C. C. Ribeiro, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 7053–7112 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Fleischmann, P. J. Hendra, I. R. Hill and M. E. Pemble, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1981, 117, 243–255 CrossRef CAS
.
- G. M. Brown and G. A. Hope, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1995, 382, 179–182 CrossRef
.
- S. Kania and R. Holze, Surf. Sci., 1998, 408, 252–259 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Inagaki, K. Motobayashi and K. Ikeda, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8, 4236–4240 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Kamimura, S. Maeda, T. Hayashi, K. Motobayashi and K. Ikeda, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 22327–22334 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- T. Isogai, M. Uranagase, K. Motobayashi, S. Ogata and K. Ikeda, Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 6531–6537 RSC
.
- J. T. Hugall and J. J. Baumberg, Nano Lett., 2015, 15, 2600–2604 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Carlex, M. Bayle, P. Benzo, G. Benassayag, C. Bonafos, G. Cacciato and V. Privitera, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2015, 92, 174302 CrossRef
.
- S. Dey, M. Banik, E. Hulkko, K. Rodriguez, V. A. Apkarian, M. Galperin and A. Nitzan, Phys. Rev. B, 2016, 93, 035411 CrossRef
.
- M. Inagaki, T. Isogai, K. Motobayashi, K.-Q. Lin, B. Ren and K. Ikeda, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 9807–9817 RSC
.
- R. Kamimura, T. Kondo, K. Motobayashi and K. Ikeda, Phys. Status Solidi B, 2022, 259, 2100589 CrossRef CAS
.
- Y. Zhao, C. Xiao, E. Mejia, A. Garg, J. Song, A. Agrawal and W. Zhou, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 8634–8645 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- T. Isogai, K. Motobayashi and K. Ikeda, J. Chem. Phys., 2021, 155, 204702 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Inagaki, K. Motobayashi and K. Ikeda, Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 22988–22994 RSC
.
- R. W. Berg, M. Deetlefs, K. R. Seddon, I. Shim and J. M. Thompson, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 19018–19025 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- V. O. Santos, Jr., M. B. Alves, M. S. Carvalho, P. A. Z. Suarez and J. C. Rubim, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 111, 20379–20385 CrossRef PubMed
.
- T. Endo, T. Kato, K. Tozaki and K. Nishikawa, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010, 114, 407–411 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. Zhang, Y.-X. Zhong, J.-W. Yan, Y.-Z. Su, M. Zhang and B.-W. Mao, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 582–584 RSC
.
- M. Zhang, L.-J. Yu, Y.-F. Huang, J.-W. Yan, G.-K. Liu, D.-Y. Wu, Z.-Q. Tian and B.-W. Mao, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 14740 RSC
.
- W. Cochran, Adv. Phys., 1960, 9, 387–423 CrossRef CAS
.
- V. Jendrašić, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem., 1969, 22, 157–164 CrossRef
.
- A. Paul and A. Samanta, J. Chem. Sci., 2006, 118, 335–340 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. Fukasawa, T. Sato, J. Watanabe, Y. Hama, W. Kunz and R. Buchner, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, 95, 197802 CrossRef PubMed
.
- J. C. Zapata Trujillo and L. K. McKemmish, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2023, 127, 1715–1735 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. N. Hopkinson, C. Richter, M. Schedler and F. Glorius, Nature, 2014, 510, 485–496 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. A. Gokturk, S. E. Donmez, B. Ulgut, Y. E. Türkmen and S. Suzer, New J. Chem., 2017, 41, 10299 RSC
.
- G.-B. Pan and W. Freyland, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2006, 427, 96–100 CrossRef CAS
.
- K. Motobayashi, N. Nishi, Y. Inoue, K. Minami, T. Sakka and M. Osawa, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2017, 800, 126–133 CrossRef CAS
.
- O. Sadek, J. Rabah, S. Ba Sowid, D. Mercier, P. Marcus, C. Chauvier, F. Ribot, L. Fensterbank and E. Maisonhaute, Electrochim. Acta, 2024, 507, 145189 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Schmitz, R. Jakelski, M. Pyschik, K. Jalkanen, S. Nowak, M. Winter and P. Bieker, ChemSusChem, 2017, 10, 876–883 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. Dong, W. Chen, X. Ge, S. Wang, X. Zhang, Z. Xing, Q. Zhang and Z.-X. Wang, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2025, 682, 124–134 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- W. Wang, W. Ma, Q. Yang, Z. Lin, J. Tang, M. Wang, Y. He, C. Fan and K. Sun, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2022, 61, 10883–10890 CrossRef CAS
.
- T. C. Niu, Y. X. Yuan, J. L. Yao, F. Lu and R. A. Gu, Sci. China: Chem., 2011, 54, 200–204 CrossRef CAS
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Normal Raman and SERS spectra in density of states (DOS) formats. eSERS spectrum of Au substrate. Electrochemical SERS behaviours of [BMI]PF6 on Au electrode. DFT calculated Raman spectra. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5cp01606a |
| This journal is © the Owner Societies 2025 |