Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleMetal-mediated peptide processing. How copper and iron catalyze diverse peptide modifications such as amidation and crosslinking
Ninian J.
Blackburn

Department of Chemical Physiology and Biochemistry, Oregon Health & Sciences University, Portland, OR 97239, USA. E-mail: blackbni@ohsu.edu
First published on 6th June 2025
Abstract
Peptide processing is an important post-translational function that converts newly synthesized pro-peptides into their biologically active mature forms. In this review we discuss two such processes, peptide amidation and ribosomally synthesized post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) synthesis. The first step in peptide amidation is catalyzed by copper, utilizing a single enzyme peptidylglycine monooxygenase (PHM), while RiPP chemistry can utilize Fe-containing radical SAM enzymes and in a more recent discovery Cu-containing burpitide cyclases. For PHM we describe the canonical mechanism built on three decades of structural, spectroscopic and computational work that posits mononuclear reactivity coupled to long range electron transfer. We discuss this alongside new experimental evidence that suggests instead an open-to-closed conformationally gated mechanism where a binuclear copper entity is the reactive species. Next we describe new insights into RiPP chemistry of thioether formation formed via cysteine to peptidyl-C crosslinking in the radical SAM enzymes PapB and Tte1186. Here Se edge XAS has documented selenocysteine to Fe binding at an auxiliary FeS cluster as an important step in S/Se to peptidyl-C coupling. Finally we examine analogous radical-induced peptide crosslinking in a new class of peptide cyclases termed burpitide cyclases (BpCs) some of which exhibit a striking similarity to PHM, yet show catalytic chemistry leading to a different product profile. These comparisons emphasize how nature leverages very specific properties of metal ions, and their ability to underpin catalysis via radical processes to bring about a variety of important biochemical and biological outcomes.
Introduction
Peptide processing is an important post-translational function that converts newly synthesized pro-peptides into their biologically active mature forms.1–4 Most bioactive peptides are synthesized in their pro-peptide form where the N-terminal sequence is used for trafficking or for recognition of cognate enzyme partners. Important peptide processing pathways involve C-terminal amidation, and ribosomally encoded post-translational peptide synthesis (RiPP) which generate active neuropeptide hormones and cross-linked bioactive molecules respectively.Amidated peptides are important regulators of cellular function via interactions with GPCRs at the cell membrane to initiate a molecular cascade leading to production of essential hormones.3,5,6 A contemporary example is the action of glucogen-like peptide 1 (GLP1) on pancreatic beta cells to regulate the production of insulin leading to the current use of GLP1-related drugs in the treatment of T2 diabetes.6 While native GLP1 peptides are susceptible to proteolysis, minor changes in sequence can generate synthetic analogues with improved pharmacokinetics – the semaglutide class of drugs that include Ozempic and Wegovy. These drugs have been shown to have remarkable success in the treatment of obesity, so much so that that they are now used as designer drugs for cosmetic weight loss. However, the GLP1s do have side effects, most notably an increased risk of medullary thyroid cancer. Understanding the biochemical mechanisms that underpin native synthesis and degradation of amidated peptides is important because other neuropeptides can have opposite physiological effects which complicate therapeutic outcomes. For example, neuropeptide Y expressed predominately in GABAergic neurons of the hypothalmus and hippocampus acts post-synaptically on GPCR Y receptors to regulate food intake, fat storage, and bring about reduction in pain perception, anxiety, and alcohol intake. Its function appears opposite to GLP1s in that high levels lead to obesity via a process that includes stimulation of gluconeogenesis, down-regulation of leptin and/or its receptor and induction of insulin resistance.5 These examples illustrate the important and often antagonistic roles of amidated peptides in human health, and given the broad scope of these molecules in hormonal regulation, they remain good targets for drug interventions provided that their complex interactions can be fully understood. Other examples of amidated peptides include thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), oxytocin (OT), calcitonin (CT), growth hormone releasing factor (GHRF), and more.
Peptide processing via other pathways is also known to be a major source of new lead compounds for antibacterial, antiviral and anticancer therapeutics. Traditionally non-ribosomal peptide synthesis (NRPS) has generated many of the common antibiotics in use today,7 but increasing resistance has spurred new discovery science focused on finding alternatives with different modes of action. A class of natural products with enormous potential are the ribosomal synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides or RiPPs which encompass a new class of antibiotics based on lanthipeptides, thiopeptides, sactipeptides, and ranthipeptides many of which carry modifications involving α-, β-, or γ-thioether crosslinks.2,4 These compounds show activity against Gram positive bacteria, especially S. aureus (MRSA) and are therefore of great pharmacological interest. RiPP synthesis involves a precursor peptide and its associated maturase (cyclase) which is often a metalloprotein such as a radical SAM enzyme.8 The precursor peptide (substrate) is itself comprised of a leader sequence which recognizes the maturase, and a “core” peptide which contains the sequence that will be modified. The reactions involve radical mediated crosslinking reactions and are terminated via tailoring of the N- and C-termini by proteases to release the mature products.
Peptide processing reactions are often mediated by metals and/or are catalyzed by metalloenzymes. Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) is the only enzyme able to catalyze peptide amidation, via a mechanism that first converts the glycine-extended pro-peptide to an α-hydroxyglycyl intermediate in a Cu-dependent reaction catalyzed by the PHM (peptidylglycine alpha hydroxylating monooxygenase) domain followed by hydrolysis of the carbinolamide to form the peptide amide and glyoxalate in a Zn/Ca-dependent process catalyzed by the PAL (peptidylglycine alpha amidating lyase) domain (Fig. 1(a)).3,9 AhyBURP is a member of an emerging class of copper-dependent peptide cyclases (burpitide cyclases or BpCs) within the broader class of RiPP enzymes which install tyrosine or tryptophan crosslinks.1,10–12 BpCs are unusual since often a single protein contains both the core peptide and its maturase, such that the ribosomally encoded precursor is autocatalytic. Although unrelated in sequence or protein fold, the AhyBURP active site bears a remarkable resemblance to PHM in metal site coordination and separation, the presence of an unusual disulfide staple at each of the two copper sites, and the proposal for a parallel reaction mechanism.10 Both AhyBURP and PHM generate a substrate radical via oxygen chemistry at their homologous Cu(I) His2Met copper centers but thereafter the reactions diverge. In PHM, the product is an α-hydroxyglycine modified C-terminus which is further processed to an amide, while in BURP radical coupling generates two sequential cross-linked products. As mentioned above other RiPP cyclases utilize radical SAM enzymes where the S-adenosylmethionine cofactor and its associated Fe/S cluster initiate radical chemistry which is further directed into peptidyl crosslinks via downstream auxiliary Fe/S cluster-peptide interactions.8
 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) Reaction catalyzed by peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PHM and PAL). (b) Subdomains of the PHM structure showing the Cu atoms in gold separated by 11 A. The M-subdomain is on the left, the H subdomain is on the right. (c) Active site of the substrate-bound enzyme showing the positions of the Cu ligands and substratedi-iodo YG substrate in the pocket. From pdb file 1OPM. | ||
Copper monooxygenases related to PHM also play important roles in neurotransmitter biosynthesis. Dopamine β-monooxygenase (DBM)13–15 and its insect homologue tyramine β-monooxygenase (TBM)16 catalyze the biosynthesis of nor-epinephrine and octopamine respectively. Other non-related monooxygenases include particulate methane monooxygenase (pMMO) and lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase (LPMO), both important in climate mitigation.17–21 pMMO converts the greenhouse gas methane to methanol while LPMOs catalyze the oxidation of polysaccharides at C1 and/or C4, an important stimulus for biomass degradation. Understanding their underlying reaction mechanisms is therefore important to the health of the planet and its inhabitants.
Peptide amidation
Structure, spectroscopy and canonical reaction mechanism
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Structures of the diatomic adducts of PHM bound at the M center. The adducts are shown as colored sticks designated as follows: cyan, peroxide complex of the Cu(II) enzyme(pdb: 4E4Z); red, oxygen complex formed from reduced enzyme + ascorbate (oxidation state undetermined, pdb 1SDW); yellow, CO complex of the reduced enzyme (pdb:3MLJ). | ||
KIE studies on the H-site variant H172A provided an important and surprising codicil to the mechanistic interpretation of isotope effects.47 While the mutation lowered rates of substrate binding and electron transfer 400–2000 fold, a much larger effect was observed for the HAA step where the rate was reduced by a factor of 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 relative to WT. This implies that H172A has a large influence on the reorganizational energy and/or dynamics required to form the transition state within which HAA chemistry can proceed. While this might involve solvent-induced reorganization of H-bonding pathways or global conformational effects that perturb the structure of the ES complex, the magnitude of the effect suggests direct structural involvement of this ligand in the transition state. This is a remarkable result for a residue located 8–11 Å from the active site and will be discussed in more detail later in this review.
000 relative to WT. This implies that H172A has a large influence on the reorganizational energy and/or dynamics required to form the transition state within which HAA chemistry can proceed. While this might involve solvent-induced reorganization of H-bonding pathways or global conformational effects that perturb the structure of the ES complex, the magnitude of the effect suggests direct structural involvement of this ligand in the transition state. This is a remarkable result for a residue located 8–11 Å from the active site and will be discussed in more detail later in this review.
Carbon monoxide binding as a probe of oxygen reactivity and substrate triggering
![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) O bond weakens since electrons are populating its antibonding levels and this translates into a decrease in bond order and C
O bond weakens since electrons are populating its antibonding levels and this translates into a decrease in bond order and C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) O stretching frequency, and second, the magnitude of this effect and thus the observed frequency red-shift measured by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) depends on the electron density residing on the metal ion which itself is strongly influenced by the other coordinated ligands. For example, since imidazole-N is more electron donating than thioether-S, histidine ligands decrease the ν(CO) more than methionine ligands. The magnitude of the red-shift is also expected to scale with the number of each ligand type in the complex.
O stretching frequency, and second, the magnitude of this effect and thus the observed frequency red-shift measured by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) depends on the electron density residing on the metal ion which itself is strongly influenced by the other coordinated ligands. For example, since imidazole-N is more electron donating than thioether-S, histidine ligands decrease the ν(CO) more than methionine ligands. The magnitude of the red-shift is also expected to scale with the number of each ligand type in the complex.
| Sample | Ligand set (excluding CO) | Coord. No (including CO) | ν(C ≡ O) (cm−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBM | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2089 | 58 |
| PHM | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2093 | 60 |
| PHM + AcYVG | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2093, 2063 | 60 |
| PHM + Benzoylglycine | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2093, 2075 | 60 |
| PHM M314H | 3N(His) | 4 | 2075 | 36 |
| PHM M314H + AcYVG | 3N(His) | 4 | 2075, 2051 | 36 |
| PHM H172A | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2092 | 75 |
| PHM H172A + AcYVG | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2092, 2065 | 75 |
| PHM H107A | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2092 | 36 |
| PHM H107A + AcYVG | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2092 | 36 |
| PHM H108A | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2093 | 36 |
| PHM H108A + AcYVG | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2087 | 36 |
| PHM H107AH108A | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2090 | 36 |
| PHM H107AH108A + AcYVG | 2N(His) 1S(Met) | 4 | 2083 | 36 |
| PHM H242A | No peak | 36 | ||
| CusF W44A | 1N(His)2S(Met) | 4 | 2108 | 73 |
| CusF W44AM49H (M-site model) | 2N(His)S(Met) | 4 | 2089 | 71 |
| CusF W44AM47HM49H | 3N(His) | 4 | 2075 | 73 |
| SeM CusF W44AM49H (M-site model) | 2N(His)Se(Met) | 4 | 2087 | 72 |
| Aβ(10–14) YEVHH | 2N(His) | 3 | 2110 | 39 |
| Histidylhistidine (Nδ coordinated) | 2N(His) | 3 | 2110–2105 weak | 40 |
| Histidylhistidine + N-methylimidazole | 2N(His)N(imid) | 4 | 2075 strong | 40 |
| HisXHis (X = Gly) (Nε coordinated) | 2N(His) | 3 | 2092 strong | 76 |
| Hc (mollusk) | 3N(His) + Cu–Cu | 4 | 2062 | 77 |
| Hc (limulus) | 3N(His) + Cu–Cu | 4 | 2053 | 77 |
| Hc (arthropod) | 3N(His) + Cu–Cu | 4 | 2043 | 77 |
| aa3-cytochrome oxidase | 3N(His) + Cu–Fe | 4 | 2066, 2054, 2039 | 78 |
| ba3-cytochrome oxidase | 3N(His) + Cu–Fe | 4 | 2054 | 78 |
| bis-dimethylimidazole ([Cu-(Me2imid)2]+) | 2N(imid) | No reaction | 79 | |
| Tris-dimethylimidazole ([Cu-(Me2imid)3]+) | 3N(imid) | 4 | 2069 | 79 |
| Tris-(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate | 3N(pyrazole) | 4 | 2081 | 80 |
| Tris-(2-methylpyridyl)amine (TMPA) | 3N(py) and 4N(py) | 4 and 5 | 2094, 2075 | 81 |
| 1H-(imidazol-4-yl)-N,N-bis((pyridin-2-yl)methyl)ethanamine | 2N(py)N(imid) | Probably 4 | 2082 | 81 |
The next question was how to interpret the 30 cm−1 red-shift induced by substrate binding. Curiously, no difference in coordination was observed by EXAFS at the M center. One possibility was a change in H-bonding interaction with the distal-N of coordinated His residues.61 CuM ligand H242 is H-bonded to the side-chain amide of Q272 with a short 2.8 Å N⋯H⋯O bond. We tested whether strengthening this H-bond would decrease the frequency by making the imidazole of residue H242 more “imidazolate-like”. A substrate-free Q272E variant gave a CO complex with ν(CO) of 2088 cm−1 insufficient to account for the magnitude of red-shift (unpublished data) but of greater consequence this frequency did not shift in the presence of Ac-YVG. H-site mutants had disparate effects. H172A showed a normal Ac-YVG red-shift but H107A and H108A showed no substrate effect. The data point to a substrate-induced structural change that activates the enzyme (providing complete coupling) and involves both the M site (red-shifted CO complex) and the H-site (requirement for either H107 or H108).
 | ||
| Fig. 5 An accurate protein-based model for the PHM M-site derived from the W44AM49H variant of the metallochaperone CusF. (a) Comparison of structural models adapted from pdb files 3PHM (reduced PHM) and 3E6Z (W44A CusF) respectively. (b) left panel FTIR and right panel EXAFS spectra for the complexes of the fully reduced M-site model with CO. (c) Geometry optimized structures for Cu(I)–CO complexes with variable His:Met ratios calculated using ORCA. (d) plot of experimental versus theoretical frequencies for the complexes in (c). Frequencies were calculated in ORCA. | ||
Evidence for closed conformers and flexible sub-domain dynamics
 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) Structure of the H108A variant of PHM in the presence of citrate pdb 6ALA. The single Cu(II) ion is shown as a pink sphere bound to H242, H244, and H107. A bidentate interaction with citrate completes the 5-coordinate structure of the Cu(II) ion. The positions of the Cu atoms in the oxidized structure (Cu–Cu = 11 Å, 1PHM) are shown as transparent spheres (b) Overlay of H107A + citrate (closed, gold, 6ALA), oxidized (Cu–Cu = 11 Å, slate, 1PHM) and oxidized anaerobic (Cu–Cu = 14 Å, green, 8DSJ) with the structures aligned on the H domain. | ||
A new open-to closed mechanism for DBM catalysis from QM/MM calculations
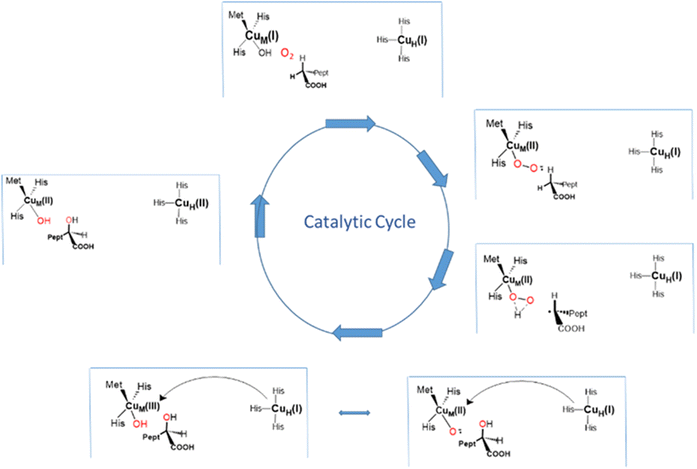
For an open to closed transition to be mechanistically feasible, it would have to proceed with an activation energy lower than that required for HAA chemistry. Wu et al.49 have recently explored the energy landscape for such a mechanism for the reaction of DBM with hippuric acid using a QM/MM approach. The starting point for comparing the energetics of an open mechanism with one involving domain closure is assessing the reactivity of the CuM(II)–O2˙ cupric superoxo species in the open conformation. An important premise of the work is that excess ascorbate is present during catalysis such the cupric superoxo has the choice of abstracting a H atom from bound substrate or from the ascorbate HAsc− anion which is freely accessible to the active site. Energy calculations suggest that HAA from ascorbate (10.2 kcal mol−1) is more favorable than HAA from hippuric acid (DBM, 26.1 kcals mol−1) or formylglycine (PHM, 22 kcals mol−1) by a large amount making the formation of a Cu(II)M–OOH hydroperoxide and ascorbate radical a more likely outcome. They further calculate that the energy of H2O2 formation via dissociative protonation (8 kcal mol−1) exceeds that for domain closure (DBM,1.3 kcal mol−1; PHM, 2.1 kcals mol−1) suggesting that once formed the Cu(II)M–OOH species would undergo domain closure rather than release the hydrogen peroxide ensuring that the reaction would remain completely coupled. Domain closure leads to formation of the mixed valence binuclear complex μ-OOH–Cu(II)MCu(I)H that undergoes internal ET from Cu(I)H to break the O–O bond and form an oxyl-bridged HOCuM(II)–(O˙)–CuH(II) species capable of HAA from the bound substrate. OH radical rebound, domain opening and further ascorbate reduction and substrate binding to the open conformer complete the catalytic cycle.Like the canonical mechanism discussed earlier this mechanism predicts primary and secondary KIE values for the chemical step that are comparable with experiment, but otherwise its predicted intermediates remain unverified. Notwithstanding, the role of ascorbate as the initiator of the process leading to domain closure is testable. In a series of experiments we examined the role of ascorbate in pre-steady-state single turnover reactions of PHM using dansyl-YVG as substrate.30 The enzyme was first reduced with ascorbate, and the excess ascorbate removed anaerobically. This ascorbate-free preparation was then reacted with dansyl-YVG and O2 and the reaction quenched at appropriate times using rapid chemical quench methodology. Hydroxylated product was determined by HPLC separation and fluorescent detection to obtain rates and stoichiometries of product formation with the expectation that the ratio of product formed to reduced enzyme starting material would approach unity at the end point of the single turnover. Surprisingly, ascorbate-free reduced enzyme generated <15 percent of the expected hydroxylated peptide, with the result confirmed for the extent of enzyme copper oxidation by RFQ (rapid freeze quench) EPR spectroscopy. The ratio could be increased to about 70 percent if ascorbate was added back to the reaction mixture in a process that was proven not to be due to multiple turnovers. Measurement of reaction rates as a function of ascorbate concentration indicated saturating behavior with a KD for ascorbate of 117 μM an order of magnitude less than the Km measured from steady state suggesting a role distinct from Cu(II) reduction. The most intriguing aspect of ascorbate activation was a correlation between ascorbate concentration and the intensity of the 2063 cm−1 substrate induced Cu(I)M–CO band (vide supra) when the latter was formed by CO reaction with an ascorbate-reduced di-Cu(I) sample of PHM. This result suggested that the mode of activation might correlate with the open-to-closed transition (Fig. 9).
 | ||
| Fig. 9 A new mechanism derived from QM/MM calculations based on a conformationally gated open-to-closed catalytic cycle. The structure of the proposed intermediate mixed-valence intermediate is shown in the center of the figure. Figure constructed from concepts proposed in ref. 49. | ||
Capturing a fully metalated binuclear state in solution
 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) Titration of oxidized PHM with the AAF-hCys peptide. (b) Suggested mixed valence species responsible for the broad absorption around 925 nm. | ||
Despite these similarities the PHM MV complex appears structurally distinct. The CuA system is a fully delocalized Cu(1.5+)Cu(1.5+) species (class III) MV complex,90,94–96 and is found in a variety of other systems, including N2O reductase,97–99 purple copper azurin,100,101 and pMMOD102 while the PHM complex is valence localized. The canonical CuA site exists as a pseudo planar NCuS2CuN diamond core with a 7-line Cu-hyperfine pattern in the EPR spectrum that implies full electron delocalization. The extremely short Cu–Cu distance (2.4 Å) facilitates the delocalization via direct Cu–Cu bonding where the dimer-coupled dx2−y2 orbitals form a σu* HOMO with a direct sigma interaction along the Cu–Cu axis. The PHM system on the other hand gives rise to an EPR spectrum which shows a 4-line pattern typical of what is termed a class II mixed valence system where the unpaired electron localizes onto one of the copper centers. In this respect it is more similar to the halide-bridged complexes of half-met hemocyanin103 which exhibit intervalence transitions above 900 nm but 4-line rather than 7-line Cu-hyperfine patterns indicative of spin localization with Cu–Cu distances of ∼3–4 Å based on known structures of oxy and deoxy hemocyanin.104,105 In PHM the spin localization is likely due to the presence of only one bridging thiolate in contrast to the two thiolate bridges and Cu–Cu bond found in CuA.
The stability of the MV complexes of the AAF-hCys/hSeCys with PHM is remarkable. For the S-containing homocysteine peptide the deep purple color of the MV complex is stable indefinitely at room temperature, and bleaches over a period of hours when exposed to ascorbate as a reductant. The seleno complex is reduced faster which is anticipated for a selenolate complex.107,108 However, stable MV complexes are generally utilized for specific functions in metalloproteins. The CuA systems described above are used to accelerate long range electron transfer, as (with a few notable exceptions) are iron–sulfur clusters. The proposal (vide supra) for a catalytic MV peroxo intermediate adds significance to the PHM MV complex: although certainly off-pathway, the mono-bridging thiolate complex is likely to have a geometry that mimics the proposed μ-1,1-peroxo intermediate, and demonstrates that a conformation that could accommodate the intermediate is possible. One may speculate that the enzyme could supply a bridging group such as imidazole from histidine or OH from serine/threonine that might help stabilize a MV intermediate during catalysis.
We suggested a plausible mechanism for domain closure in PHM based on simple electrostatics.61 The oxidized enzyme in the absence of substrate contains five positive charges in the active site cleft which are subject to modification by reduction and substrate binding. These include two each from the Cu(II) centers and one from the guanidinium group of Arg240. When the enzyme is reduced and binds substrate the positive charge is reduced by 3, as the substrate forms its salt bridge with R240 and the Cu atoms are reduced to Cu(I). If ascorbate binds in the active site pocket as HAsc− this would reduce the net positive charge to 1. Given the energy for domain closure is a mere 2 kcal mol−1, the decrease in electrostatic repulsion between the two sub-domains as the result of this decrease in net positive charge could be sufficient to induce domain closure. It is worth noting that this mechanism would not work as well for DBM where the substrate dopamine in uncharged. However, as noted above DBM may utilize a distinct pathway for domain closure orchestrated by allosteric effects in either the DOMON domain or dimerization domain or both, which may result in the two catalytic cores of each active dimer to exist in asymmetric open and closed conformers. This would explain why monomeric DBM protomers appear to be inactive.
Ribosomally synthesized and post translationally modified peptides (RiPPs)
Radical SAM RiPP chemistry
We turn next to systems that generate natural peptide products that have gained function through post-translational modification. The more common examples of this class of bioactive molecules are derived from non-ribosomal peptide synthesis (NRPS) and will not be discussed further. Here we will examine metal-mediated peptide transformations in the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides or RiPPs which encompass a large class of bioactive molecules produced by all classes of microorganisms often with specific antimicrobial properties that suggest importance in host defense. There are many subclasses of RiPPs with diverse function4 where the enzymatic products include nisin (an antibacterial food additive), bottromycin (active against MRSA) and plantazolicin (active against B. anthracis) as specific examples. Of interest to this review are RiPPs containing thioether crosslinks such as the antibacterials subtilosin A and thuricin H where a cysteine S of the substrate peptide reacts at an activated C atom catalyzed by the associated maturase. The advent of inexpensive genome sequencing has aided the discovery of these systems since the substrate peptide and its associated maturase are generally clustered in the same operon and can be identified by data mining techniques.Sactipeptides and ranthipeptides4,109,110 contain thioether crosslinks between a cysteine S and the alpha, beta or gamma C of another amino acid. The maturases PapB, Tte1186 and CteB are homologous radical SAM (RS) enzymes that catalyze thioether crosslinking reactions using the RS cluster together with two additional FeS auxiliary clusters all of which are essential to the crosslinking reaction.8,111 The radical SAM cluster is a site-differentiated FeS cluster where one out of the four Fe atoms binds the S-adenosylmethionine cofactor via the α-amino and α-carboxylate of the methionine. The reduced form of the cluster initiates reductive cleavage of the coordinated SAM moiety to form a 5-deoxyadenosyl radical Ado˙ which is capable of HAA from the peptide substrate to form a peptidyl substrate radical. In the case of sactipeptide thioether crosslinking reactions the cysteine-S must then couple with the radical in a process that also requires an electron and a proton. The absolute requirement for both auxiliary clusters in completing the chemistry points to their mechanistic importance but does not immediately suggest how it is achieved.
The crystal structure of CteB from Clostridium thermocellum provides some insight into the function of the auxiliary clusters and their interaction with the RS cluster.112 CteB has an RS-SPASM structure where the RS cluster is located in a characteristic triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) barrel, with the two auxiliary clusters AC1 and AC2 located in a separate C-terminal cysteine rich domain called a SPASM domain. Interestingly, the structure of CteB with its peptide substrate shows an interaction between an Fe atom in AC1 and a cysteine-S of the substrate, although this Cys (C21) is not the one that forms the crosslink (C32). However, this structure suggests that a function of the auxiliary cluster might be to bind and activate the reactive cysteine while its proximity to AC2 might provide a conduit for transfer of the second electron needed to complete the reaction. The structure of the CteB homologue and its substrate complex is shown in Fig. 11.
 | ||
| Fig. 11 Structure of the radical SAM (RS) RiPP maturase CteB. (a) Full length protein showing TIMM and SPASM domains with bound peptide shown as a salmon strand. (b) Close up of the cluster region showing the RS cluster (Fe atoms in orange), AC1 cluster (Fe atoms in purple), and AC2 cluster (Fe atoms in cyan). From pdb file 5WGG. The cysteine bound at AC1 is C21 rather than the crosslinking C32 residue. | ||
We used the concept of substrate coordination to an Fe atom of an auxiliary cluster to design an experiment that would provide spectroscopic evidence for this mode of action.8 Using the peptidyl substrate for PapB (C19U msPapA) we substituted the reactive cysteine for selenocysteine and then showed that in the presence of PapB, SAM and sodium dithionite this homologue underwent enzyme-dependent reaction to form a selenoether via crosslinking to a residue between positions 19 and 23, similar to what had been reported for the Cys-containing peptide. Next we examined the EXAFS of the PapB-C19UPapA complex at the Se edge which indicated strong scattering between the Se absorber and an Fe atom of one of the clusters (Fig. 12). Of significance, samples prepared under catalytically active conditions showed an increase in the intensity of the Se-C peak in the Fourier transform, indicating that selenocysteine (1C per Se) had undergone partial conversion into the selenoether (2C per Se). We could then use cluster-deletion variants of the Tte1186 homologue to localize the binding to auxiliary cluster 1 which is expected to occupy a position analogous to that shown in the CteB structure. This work highlighted the role of a site-differentiated Fe center in the auxiliary clusters in RS RiPP maturases for both peptidyl substrate binding and potentially catalytic activation, where electron donation from the cluster increases the electron density on the thiol/selenol for radical coupling to a carbon-based radical on a nearby residue generated by reaction with Ado˙. It is possible, perhaps likely, that auxiliary cluster 2 might aid in this activation process via supplying the electron necessary to complete the radical coupling.
Copper mediated RiPP chemistry
An emerging class of RiPPs that install tryptophan and tyrosine crosslinks has been described in plants1,11 and more recently in fungi.12 The plant systems termed BURP domains or burpitide cyclases (BpCs) are unusual since often a single open reading frame codes for both peptide substrate (core peptide) and its maturase, such that the ribosomally encoded precursor is autocatalytic and destroys itself during the formation of the RiPP products. The cyclization reactions require copper atoms, and unlike the radical SAM dependent enzymes that function under strict anaerobiosis, the BpCs appear to utilize oxygen in their catalytic chemistry.In 2024 Kersten, Mydy and coworkers reported the first crystal structure of a BpC, the AhyBURP domain reconstituted with Cu(II). The structure revealed new Cu-dependent RiPP chemistry involving indole-N and tyrosyl-O coupling to an unactivated C in the core peptide.10 The core peptide has the sequence Q79PYGVYTW86 and undergoes autocatalytic processing to form two crosslinks, one between G82 and W86 to form lyciumin, and the second between Q79 and Y84 to form the double macrocycle legumenin (Fig. 13). The structure of AhyBURP has a novel protein fold and an active site comprised of two Cu atoms that face each other across a 7 Å wide cleft (Fig. 13). Each Cu center is built from a Cys–His repeating motif –(CH–Xn)4- creating a bis-histidine binding site, stapled on the backside by a disulfide formed from the Cys residues. The Cus are flanked by conserved Met residues that are positioned at too long a distance to be Cu(II) ligands but may potentially bind to the Cu(I) form. The core peptide straddles the cleft and the amide oxygen of Gly82, the residue destined for a crosslink with W86 in the first cyclization, forms a weak bond with one of the Cu centers. The disulfide staple appears to constrain the His residues to be cis to one another, a strategy that could potentially prevent them from attaining a preferred linear coordination in the Cu(I) form and opening up a vacant coordination position for oxygen binding. Both sites are required for autocatalysis, since His to Ala mutations at any of the His residues abrogate peptide crosslinking. Mutagenesis of the core peptide itself is consistent with initial formation of the W86 to G82 crosslink followed by a sequential cyclization that couples Q79 with Y84. It is also apparent that some chemistry can still persist with core peptide mutants that lack the native crosslinking residues, often leading to Y81–Y84 crosslinks suggestive of radical coupling initiated by the copper center itself. The authors used a novel radical trap (CHANT) capable of trapping short lived radicals to capture a transient radical associated with the core peptide residues Y81–W86, consistent with radical formation in the first cyclization. Together their data supported an active site comprised of a pair of Cu(His)2 centers that react with oxygen to form an oxy-intermediate capable of hydrogen atom abstraction from a residue in the core peptide followed by radical coupling of G82 and W86. The process is then repeated in a second cyclization that crosslinks Q79 and Y84.
 | ||
| Fig. 13 Copper-mediated RiPP chemistry. (a) Crosslinking reactions of the the AhyBURP protein. (b) Crystal structure of Cu(II)AhyBURP showing coordination of a Cu ion in its bis-His site. The core peptide is shown in pink from pdb file 8SY3. | ||
It is hard not to notice the strong similarity between the active site structure of the Cu centers in AhyBURP and the Cu centers particularly the CuM center of PHM. As described earlier in this review, PHM generates a glycine radical via oxygen chemistry at its homologous Cu(I) His2Met site and in another unusual twist, the Met residue coordinates Cu only in its Cu(I) state. The understanding of the reaction chemistry of BpCs is still in its infancy, yet it is intriguing that the Cu centers in the crystal structure of AhyBURP appear to be placed at a distance in between the open and closed conformers of PHM and DBM. While too early to speculate, it seems at least a possibility that the reaction chemistry of BpCs may also utilize open and closed conformers and/or binuclear states.
Conclusions
Posttranslational peptide processing generates important products that benefit the organism whether as neuropeptide signaling molecules or cyclic derivatives that assist in host defense. The one-electron redox chemistry inherent to metal ions such as copper and iron provide mechanisms for generating peptidyl radicals that act as intermediates for both amidation and crosslinking reactions.For the copper-mediated peptide amidation, we have reviewed evidence that is beginning to challenge the canonical “mononuclear” mechanism in favor of one proceeding through a binuclear and possibly mixed valence intermediate. The canonical mechanism was based on two tenets – first that the Cu–Cu distance was invariant and second that the reaction was initiated by a CuM–dioxygen complex and could proceed to products within the crystal implying that it retained the conformation observed in the structure – viz an open conformation – throughout the catalytic cycle. Revisiting the mechanistic landscape after the premise of invariant sub-domain separation had been disproved, led to the formulation and later discovery of states with binuclear configurations. Both mechanisms account equally well for the observed reaction energetics and kinetic isotope data, but the binuclear mechanism is better able to accommodate a number of other experimental findings. For example, contrary to expectation from model studies in organic solvents at low-temperature O2 was unreactive towards our water soluble mononuclear M-site protein analogue built from the CusF scaffold emphasizing the need for enzyme activation. Additional evidence not previously introduced includes peroxide-shunt chemistry113 where product could be formed catalytically from oxidized PHM and hydrogen peroxide but led to 60 percent O isotope scrambling with ambient O2 in the hydroxylated product when H218O2 was used as the source of O in the product. This result required the reaction to cycle through an intermediate where a Cu(II)-peroxide or hydroperoxide is in equilibrium with a Cu(I) dioxygen species and strongly suggested the intermediacy of a species similar to that of the binuclear copper centers of hemocyanin and tyrosinase, as also discussed for the origin of the substrate-induced red-shifted M-site CO band. Lastly we noted the unusually large effect on the rate of HAA from the H172A mutant suggesting that the ligand H172 at CuH has a major effect on the structure of the transition state located at CuM.
The essential role of Met314 in PHM catalysis is an experimental finding that has been difficult to rationalize by either mechanism. The canonical mechanism relies on conclusions from Cu(II)-superoxo reactivity that seem to suggest that thioether coordination enhances the HAA potential of the cupric superoxo. For example a recent study of the [(TMGN3S)CuII(O2˙−)]+ CuM model superoxo complex found an increase of ∼1.5 fold in the second order rate of HAA with the TEMPOH substrate over the analogous [(TMGN4)CuII(O2˙−)]+ species.114 The difference in rate between N- and S- coordinated complexes is small, and certainly insufficient to account for that observed in the enzyme. Wang et al. on the other hand explain the M314H result by calculating an O–O cleavage barrier 3.1 kcal mol−1 higher than that for the WT.49 At a qualitative level one may speculate that the highly fluxional and weakly bound Met residue71,72 may facilitate the necessary movement to the CuM atom as it toggles between open and closed states, and indeed the S(M314) thioether sulfur is displaced by almost 3 Å away from the copper center in the closed H108A structure.87 The more strongly bound His residue may be energetically restrained from accommodating this movement.
The similarities in both ligand-set and dioxygen-induced peptide radical formation argue forcibly for mechanistic correlations between PHM and BpCs. It is possible, perhaps likely that nature has discovered metal-mediated reactivities that are accessible to many different systems where product outcomes diverge in response to small perturbations in enzyme active sites. Understanding the detailed mechanisms of these metal-mediated processing reactions is important in the quest to expand the utility of these molecules as drug targets, and to develop synthetic biological protocols for their production.
Abbreviations
| RiPP | Ribosomally synthesized and post translational modified peptide synthesis |
| PAM | Peptidylglycine alpha amidating monooxygenase |
| PHM | Peptidylglycine alpha hydroxylating monooxygenase |
| PHMcc | PHM catalytic core |
| BURP | BNM2, USP, RD22, and PG1beta |
| BpC | Burpitide cyclase |
| SAM | S-adenosyl methionine |
| RS | Radical SAM enzyme |
| DBM | Dopamine beta monooxygenase |
| Ac-YVG | Acetyl-tyr-val-gly |
| XAS | X-ray absorption |
| EXAFS | Extended X-ray absorption fine structure |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| RFQ | Rapid freeze quench |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infra red |
| KIE | Kinetic isotope effect |
| HAA | Hydrogen atom abstraction |
| QM/MM | Quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| ET | Electron transfer |
| PCET | Proton coupled electron transfer |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| MV | Mixed valence |
| IVCT | Intervalence charge transfer |
Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included, and no new data were generated or analyzed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The work was funded by a grant to NJB from the National Institutes of Health NIGMS R35 GM136239. The work described herein is that of many talented post-doctoral fellows and graduate students over the years who have made important contributions to Blackburn lab publications. Recent studies form our lab on characterizing the binuclear state of PHM have been particularly aided by colleagues Dr Vahe Bandarian, Dr Renee Arias, Dr Katherine Rush Dr Karsten Eastman and Dr Evan Welch. XAS data were measured at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource and we are particularly grateful for the help and expertise of the beam line staff.References
- D. N. Chigumba, L. S. Mydy, F. de Waal, W. Li, K. Shafiq, J. W. Wotring, O. G. Mohamed, T. Mladenovic, A. Tripathi, J. Z. Sexton, S. Kautsar, M. H. Medema and R. D. Kersten, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2022, 18, 18–28 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. A. Hudson and D. A. Mitchell, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2018, 45, 61–69 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. J. Merkler, A. J. Hawley, B. A. Eipper and R. E. Mains, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2022, 179, 3306–3324 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Montalban-Lopez, T. A. Scott, S. Ramesh, I. R. Rahman, A. J. van Heel, J. H. Viel, V. Bandarian, E. Dittmann, O. Genilloud, Y. Goto, M. J. Grande Burgos, C. Hill, S. Kim, J. Koehnke, J. A. Latham, A. J. Link, B. Martinez, S. K. Nair, Y. Nicolet, S. Rebuffat, H. G. Sahl, D. Sareen, E. W. Schmidt, L. Schmitt, K. Severinov, R. D. Sussmuth, A. W. Truman, H. Wang, J. K. Weng, G. P. van Wezel, Q. Zhang, J. Zhong, J. Piel, D. A. Mitchell, O. P. Kuipers and W. A. van der Donk, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2021, 38, 130–239 RSC.
- S. P. Brothers and C. Wahlestedt, EMBO Mol. Med., 2010, 2, 429–439 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Jones, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2022, 179, 492–510 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Zhang, C. Wang, K. Chen, W. Zhong, Y. Xu and I. Molnar, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2023, 40, 62–88 RSC.
- K. W. Rush, K. A. S. Eastman, W. M. Kincannon, N. J. Blackburn and V. Bandarian, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 10167–10177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. F. Welch, K. W. Rush, R. J. Arias and N. J. Blackburn, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2022, 231, 111780 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. S. Mydy, J. Hungerford, D. N. Chigumba, J. R. Konwerski, S. C. Jantzi, D. Wang, J. L. Smith and R. D. Kersten, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2024, 20, 530–540 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Chekan, L. S. Mydy, M. A. Pasquale and R. D. Kersten, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2024, 41, 1020–1059 RSC.
- C. Y. Chiang, M. Ohashi and Y. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 8113–8117 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Klinman, J. Biol. Chem., 2006, 281, 3013–3016 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Klinman, Chem. Rev., 1996, 1996, 2541–2561 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. V. Vendelboe, P. Harris, Y. Zhao, T. S. Walter, K. Harlos, K. El Omari and H. E. Christensen, Sci. Adv., 2016, 2, E1500980 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. R. Hess, J. P. Klinman and N. J. Blackburn, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2010, 15, 1195–1207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. W. Koo and A. C. Rosenzweig, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 3424–3436 RSC.
- F. J. Tucci, R. J. Jodts, B. M. Hoffman and A. C. Rosenzweig, Nat. Catal., 2023, 6, 1194–1204 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. J. Tucci and A. C. Rosenzweig, Chem. Rev., 2024, 124, 1288–1320 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. O. Ipsen, M. Hallas-Moller, S. Brander, L. Lo Leggio and K. S. Johansen, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 2021, 49, 531–540 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. C. Schroder, W. B. O'Dell, S. P. Webb, P. K. Agarwal and F. Meilleur, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 13303–13320 RSC.
- S. T. Prigge, A. S. Kolhekar, B. A. Eipper, R. E. Mains and L. M. Amzel, Science, 1997, 278, 1300–1305 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. T. Prigge, A. S. Kolhekar, B. A. Eipper, R. E. Mains and L. M. Amzel, Nat. Struct. Biol., 1999, 6, 976–983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. T. Prigge, B. A. Eipper, R. E. Mains and L. M. Amzel, Science, 2004, 304, 864–867 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Rudzka, D. M. Moreno, B. Eipper, R. Mains, D. A. Estrin and L. M. Amzel, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 18, 223–232 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. E. Chufan, S. T. Prigge, X. Siebert, B. A. Eipper, R. E. Mains and L. M. Amzel, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 15565–15572 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Siebert, B. A. Eipper, R. E. Mains, S. T. Prigge, N. J. Blackburn and L. M. Amzel, Biophys. J., 2005, 89, 3312–3319 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Chen, J. Bell, B. A. Eipper and E. I. Solomon, Biochemistry, 2004, 43, 5735–5747 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. A. Eipper, A. S. W. Quon, R. E. Mains, J. S. Boswell and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 1995, 34, 2857–2865 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. F. Welch, K. W. Rush, R. J. Arias and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2022, 61, 665–677 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. Boswell, B. J. Reedy, R. Kulathila, D. J. Merkler and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 1996, 35, 12241–12250 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. C. Freeman, J. J. Villafranca and D. J. Merkler, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 4923–4924 CrossRef CAS.
- N. J. Blackburn, M. Concannon, S. Khosrow Shahiyan, F. E. Mabbs and D. Collison, Biochemistry, 1988, 27, 6001–6008 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. J. Blackburn, F. C. Rhames, M. Ralle and S. Jaron, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2000, 5, 341–353 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. T. Bauman, B. A. Broers, C. D. Kline and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2011, 50, 10819–10828 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Kline and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2016, 55, 6652–6661 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chauhan, C. D. Kline, M. Mayfield and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2014, 53, 1069–1080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. D. Kline, M. Mayfield and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2013, 52, 2586–2596 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. Himes, G. Y. Park, G. S. Siluvai, N. J. Blackburn and K. D. Karlin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 9084–9087 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. Himes, Y. G. Park, A. N. Barry, N. J. Blackburn and K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 5352–5353 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. J. Pickering, G. N. George, C. T. Dameron, B. Kurz, D. R. Winge and I. G. Dance, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 9498–9505 CrossRef CAS.
- N. R. McIntyre, E. W. Lowe, Jr., J. L. Belof, M. Ivkovic, J. Shafer, B. Space and D. J. Merkler, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 16393–16402 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. A. Francisco, D. J. Merkler, N. J. Blackburn and J. P. Klinman, Biochemistry, 1998, 37, 8244–8252 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. A. Francisco, M. J. Knapp, N. J. Blackburn and J. P. Klinman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 8194–8195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Evans, K. Ahn and J. P. Klinman, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278, 49691–49698 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Klinman, Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 2006, 1757, 981–987 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Evans, N. J. Blackburn and J. P. Klinman, Biochemistry, 2006, 45, 15419–15429 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Crespo, M. A. Marti, A. E. Roitberg, L. M. Amzel and D. A. Estrin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 12817–12828 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Wu, F. Fan, J. Song, W. Peng, J. Liu, C. Li, Z. Cao and B. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 19776–19789 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Chen and E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 4991–5000 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Chen and E. I. Solomon, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, 101, 13105–13110 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. E. Cowley, L. Tian and E. I. Solomon, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113, 12035–12040 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Ginsbach, R. L. Peterson, R. E. Cowley, K. D. Karlin and E. I. Solomon, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 12872–12874 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Debnath, S. Laxmi, O. McCubbin Stepanic, S. Y. Quek, M. van Gastel, S. DeBeer, T. Kramer and J. England, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 23704–23716 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pasquali and C. Floriani, in Copper Coordination Chemistry, Biochemical and Inorganic Perspectives, ed K. D. Karlin and J. Zubieta, Adenine Press, New York, 1984, pp. 311–330 Search PubMed.
- H. C. Fry, H. R. Lucas, A. A. Sarjeant, K. D. Karlin and G. J. Meyer, Inorg. Chem., 2008, 47, 241–256 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Sanyal, K. D. Karlin, R. W. Strange and N. J. Blackburn, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 11259–11270 CrossRef CAS.
- N. J. Blackburn, T. M. Pettingill, K. S. Seagraves and R. T. Shigeta, J. Biol. Chem., 1990, 265, 15383–15386 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. M. Pettingill, R. W. Strange and N. J. Blackburn, J. Biol. Chem., 1991, 266, 16996–17003 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jaron and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 1999, 38, 15086–15096 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Arias, E. F. Welch and N. J. Blackburn, Protein Sci., 2023, 32, e4615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Chen, D. E. Root, C. Campochiaro, K. Fujisawa and E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 466–474 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. L. Peterson, J. W. Ginsbach, R. E. Cowley, M. F. Qayyum, R. A. Himes, M. A. Siegler, C. D. Moore, B. Hedman, K. O. Hodgson, S. Fukuzumi, E. I. Solomon and K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 16454–16467 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. Woertink, L. Tian, D. Maiti, H. R. Lucas, R. A. Himes, K. D. Karlin, F. Neese, C. Wurtele, M. C. Holthausen, E. Bill, J. Sundermeyer, S. Schindler and E. I. Solomon, Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49, 9450–9459 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. L. Peterson, R. A. Himes, H. Kotani, T. Suenobu, L. Tian, M. A. Siegler, E. I. Solomon, S. Fukuzumi and K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 1702–1705 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Tano, Y. Okubo, A. Kunishita, M. Kubo, H. Sugimoto, N. Fujieda, T. Ogura and S. Itoh, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 10431–10437 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kunishita, M. Z. Ertem, Y. Okubo, T. Tano, H. Sugimoto, K. Ohkubo, N. Fujieda, S. Fukuzumi, C. J. Cramer and S. Itoh, Inorg. Chem., 2012, 51, 9465–9480 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kunishita, M. Kubo, H. Sugimoto, T. Ogura, K. Sato, T. Takui and S. Itoh, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 2788–2789 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kim, J. Y. Lee, R. E. Cowley, J. W. Ginsbach, M. A. Siegler, E. I. Solomon and K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2796–2799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. N. Sanchez-Eguia, M. Flores-Alamo, M. Orio and I. Castillo, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 11134–11137 RSC.
- K. B. Alwan, E. F. Welch, R. J. Arias, B. F. Gambill and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2019, 58, 3097–3108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. B. Alwan, E. F. Welch and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2019, 58, 4436–4446 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. W. Rush, K. B. Alwan, A. T. Conner, E. F. Welch and N. J. Blackburn, Inorg. Chem., 2024, 63, 21519–21530 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Arias, E. F. Welch and N. J. Blackburn, Protein Sci., 2023, 32, e4615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jaron, R. E. Mains, B. A. Eipper and N. J. Blackburn, Biochemistry, 2002, 41, 13274–13282 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Y. Park, J. Y. Lee, R. A. Himes, G. S. Thomas, N. J. Blackburn and K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 12532–12535 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Y. Fager and J. O. Alben, Biochemistry, 1972, 11, 4786–4792 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. B. Dyer, O. Einarsdottir, P. M. Killough, G. J. J. Lopez and W. H. Woodruff, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 7657–7659 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Sanyal, K. D. Karlin, R. W. Strange and N. J. Blackburn, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 11259–11270 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kealy, A. J. P. White, A. D. Gee and N. J. Long, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2014, 1896–1905 CrossRef.
- Y. Lee, G. Y. Park, H. R. Lucas, P. L. Vajda, K. Kamaraj, M. A. Vance, A. E. Milligan, J. S. Woertink, M. A. Siegler, A. A. Narducci Sarjeant, L. N. Zakharov, A. L. Rheingold, E. I. Solomon and K. D. Karlin, Inorg. Chem., 2009, 48, 11297–11309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. B. Ray, X.-Y. Li, J. A. Ibers, J. L. Sessler and T. G. Spiro, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 162–176 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Einarsdottir, P. M. Killough, J. A. Fee and W. H. Woodruff, J. Biol. Chem., 1989, 264, 2405–2408 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. Ramsden and P. A. Riley, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2014, 22, 2388–2395 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Klabunde, C. Eicken, J. C. Sacchettini and B. Krebs, Nat. Struct. Biol., 1998, 5, 1084–1090 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Miller and J. P. Klinman, Biochemistry, 1985, 24, 2114–2127 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Maheshwari, C. Shimokawa, K. Rudzka, C. D. Kline, B. A. Eipper, R. E. Mains, S. B. Gabelli, N. Blackburn and L. M. Amzel, Commun. Biol., 2018, 1, 74 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. D. Erion, J. Tan, M. Wong and A. Y. Jeng, J. Med. Chem., 1994, 37, 4430–4437 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. W. Rush, K. A. S. Eastman, E. F. Welch, V. Bandarian and N. J. Blackburn, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 5074–5080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. R. Gamelin, D. W. Randall, M. T. Hay, R. P. Houser, T. C. Mulder, G. W. Canters, S. de Vries, W. B. Tolman, Y. Lu and E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 5246–5263 CrossRef CAS.
- R. P. Houser, V. G. J. Young and W. B. Tolman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 2101–2102 CrossRef CAS.
- K. N. Chacon and N. J. Blackburn, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 16401–16412 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chakraborty, M. J. Polen, K. N. Chacon, T. D. Wilson, Y. Yu, J. Reed, M. J. Nilges, N. J. Blackburn and Y. Lu, Biochemistry, 2015, 54, 6071–6081 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. A. Williams, N. J. Blackburn, D. Sanders, H. Bellamy, E. A. Stura, J. A. Fee and D. E. McRee, Nat. Struct. Biol., 1999, 6, 509–516 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. J. Blackburn, S. de Vries, M. E. Barr, R. P. Houser, W. B. Tolman, D. Sanders and J. A. Fee, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 6135–6143 CrossRef CAS.
- K. R. Williams, D. R. Gamelin, L. B. Lacroix, R. P. Houser, W. B. Tolman, M. C. Mulder, S. de Vries, B. Hedman, K. O. Hodgson and E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 613–614 CrossRef.
- T. Haltia, K. Brown, M. Tegoni, C. Cambillau, M. Saraste, K. Mattila and K. Djinovic-Carugo, Biochem. J., 2003, 369, 77–88 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. M. H. Kroneck, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2018, 23, 27–39 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. N. Morgada, D. H. Murgida and A. J. Vila, Met. Ions Life Sci., 2020, 20 DOI:10.1515/9783110589757-010.
- M. T. Hay, M. C. Ang, D. R. Gamelin, E. I. Solomon, W. E. Antholine, M. Ralle, N. J. Blackburn, P. D. Massey, X. Wang, A. H. Kwon and Y. Lu, Inorg. Chem., 1998, 37, 191–198 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Robinson, M. C. Ang, Y.-G. Gao, M. T. Hay, Y. Lu and A. H.-J. Wang, Biochemistry, 1999, 38, 5677–5683 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. O. Ross, O. S. Fisher, M. N. Morgada, M. D. Krzyaniak, M. R. Wasielewski, A. J. Vila, B. M. Hoffman and A. C. Rosenzweig, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 4678–4686 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. D. Westmoreland, D. E. Wilcox, M. J. Baldwin, W. B. Mims and E. I. Solomon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 6106–6123 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Hazes, K. A. Magnus, C. Bonaventura, J. Bonaventura, Z. Dauter, K. H. Kalk and W. G. Hol, Prot. Sci., 1993, 2, 597–619 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. A. Magnus, B. Hazes, H. Ton-That, C. Bonaventura, J. Bonaventura and W. G. J. Hol, Proteins: Struct., Funct., Genet., 1994, 19, 302–309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. F. Welch, K. W. Rush, K. A. S. Eastman, V. Bandarian and N. J. Blackburn, Dalton Trans., 2025, 54, 4941–4955 RSC.
- M. M. Kimani, J. L. Brumaghim and D. VanDerveer, Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49, 9200–9211 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. N. Sánchez-Eguía, H. Hernández-Toledo, S. Lidin, M. Flores-Alamo, E. Nordlander, S. Bertaina, M. Orio and I. Castillo, ChemCatChem, 2025, 17, e202401330 CrossRef.
- Y. Chen, J. Wang, G. Li, Y. Yang and W. Ding, Front. Chem., 2021, 9, 595991 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. A. Latham, I. Barr and J. P. Klinman, J. Biol. Chem., 2017, 292, 16397–16405 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. A. Bruender, J. Wilcoxen, R. D. Britt and V. Bandarian, Biochemistry, 2016, 55, 2122–2134 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. L. Grove, P. M. Himes, S. Hwang, H. Yumerefendi, J. B. Bonanno, B. Kuhlman, S. C. Almo and A. A. Bowers, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 11734–11744 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. T. Bauman, E. T. Yukl, K. Alkevich, A. L. McCormack and N. J. Blackburn, J. Biol. Chem., 2006, 281, 4190–4198 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Bhadra, W. J. Transue, H. Lim, R. E. Cowley, J. Y. C. Lee, M. A. Siegler, P. Josephs, G. Henkel, M. Lerch, S. Schindler, A. Neuba, K. O. Hodgson, B. Hedman, E. I. Solomon and K. D. Karlin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 3707–3713 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |