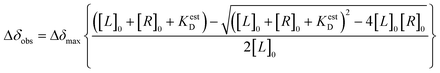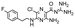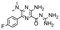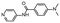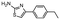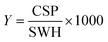Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
NMR 1H,19F-based screening of the four stem-looped structure 5_SL1–SL4 located in the 5′-untranslated region of SARS-CoV 2 RNA†
Daniel
Hymon‡
a,
Jason
Martins‡
a,
Christian
Richter
a,
Sridhar
Sreeramulu
a,
Anna
Wacker
a,
Jan
Ferner
a,
Neeraj N.
Patwardhan
b,
Amanda E.
Hargrove
 b and
Harald
Schwalbe
b and
Harald
Schwalbe
 *a
*a
aInstitute for Organic Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Center for Biomolecular Magnetic Resonance (BMRZ), Goethe-University Frankfurt, Max-von-Laue-Str. 7, 60438 Frankfurt/Main, Germany. E-mail: schwalbe@nmr.uni-frankfurt.de
bDepartment of Chemistry, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina 27708, USA
First published on 28th November 2023
Abstract
Development of new antiviral medication against the beta-coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (SCoV2) is actively being pursued. Both NMR spectroscopy and crystallography as structural screening technologies have been utilised to screen the viral proteome for binding to fragment libraries. Here, we report on NMR screening of elements of the viral RNA genome with two different ligand libraries using 1H-NMR-screening experiments and 1H and 19F NMR-screening experiments for fluorinated compounds. We screened against the 5′-terminal 119 nucleotides located in the 5′-untranslated region of the RNA genome of SCoV2 and further dissected the four stem-loops into its constituent RNA elements to test specificity of binding of ligands to shorter and longer viral RNA stretches. The first library (DRTL-F library) is enriched in ligands binding to RNA motifs, while the second library (DSI-poised library) represents a fragment library originally designed for protein screening. Conducting screens with two different libraries allows us to compare different NMR screening methodologies, describe NMR screening workflows, validate the two different fragment libraries, and derive initial leads for further downstream medicinal chemistry optimisation.
Introduction
The global pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 (ScoV2) has seen the successful use of vaccines but also challenges for their efficacy against the variants of concern that have emerged during viral evolution.1 The first-generation oral therapeutics, molnupiravir and the combinational drug Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir (also known as PF-07321332) plus ritonavir) were initially heralded as revolutionary until clinical-trial data revealed lower-than-expected efficacy.2–4 Therefore, continued efforts in developing new antivirals not only against the validated viral targets (proteases and polymerases) but also exploring other targets are required to evade resistance.5The virus contains a small proteome of 27 proteins and an RNA genome of a little less than 30.000 nucleotides. Most efforts to develop antiviral drugs focus on targeting proteins, because some viral proteins have been classified as validated targets, and technologies, including fragment screening by X-ray crystallography, have been established.6–10 By stark contrast, only recently, targeting antiviral RNA has gained interest.11–15 In fact, targeting conserved structural motifs of viral RNAs with molecules of low molecular weight (small molecules) would provide vast opportunities in developing alternative approaches to inhibit viral proliferation.16 Such targeting of RNAs by small molecules is not only relevant towards developing antivirals but holds great promise also for other diseases for which modulating RNA function has been shown to affect disease outcome.17,18
Rapid and large-scale (ScoV2) RNA genome sequencing has revolutionised the availability of the sequence data and thus contributes towards understanding the dynamics of viral evolution. Finding small molecules that can bind to conserved and structured regions of the non-coding parts of a viral RNA with high affinity and specificity is a powerful strategy to target the untranslated part of the genome of SCoV2, for which few mutations have been reported up to now.
The genome of SCoV2 contains four regulatory stem-loops in the 5′-untranslated region (5′-UTR), which are highly conserved among betacoronaviruses.19–21 Targeting such structured RNA elements to interfere with their regulatory function is regarded as a promising antiviral strategy, and targeting the SL1 stem-loop by antisense oligonucleotides has been shown to offer great therapeutic potential.22–25
In March 2020, the global consortium Covid19-NMR was formed.26 It was its mission to make viral proteins and RNAs amenable to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic studies including protein and RNA preparation and the optimisation of sample conditions. RNA secondary structures were determined for all conserved RNA elements along with their NMR-based resonance assignment, thus providing a basis for investigations of the interaction of small molecules or viral and host proteins with the viral genome.27 Two massive fragment screening campaigns involving 20 RNA elements and 25 proteins from SCoV2 resulted in the identification of 69 and 311 high-quality hits against the viral RNAs and proteins, respectively.28–31
Here, we investigated and compared the general targetability of the 5′-terminal region of the 5′-UTR of SCoV2, consisting of the four stem-loops SL1, SL2, SL3, and SL4 (5_SL1234) and its three constituting sub-elements 5_SL1, 5_SL2 + 3ext, and 5_SL4 (Fig. 1) using an RNA-dedicated library32 (DRTL-F library) and a non-RNA-dedicated fragment library (DSI-PL).33,34 The DSI-PL and the DRTL-F library consist of 768 compound fragments (200–250 Da) and 49 compounds (222–439 Da), respectively.
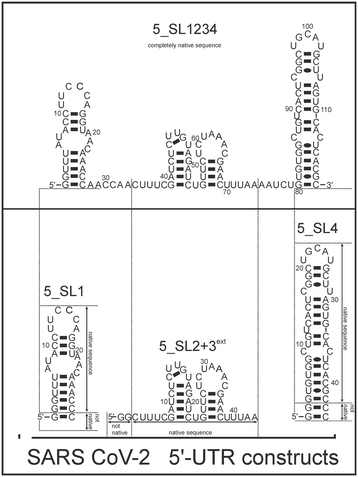 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic secondary structures of our chosen RNA sub constructs of the SCoV2 5′-UTR as previously determined.27 | ||
In general, NMR spectroscopy is well suited for fragment screening and many such screens have been conducted in academia and in the pharmaceutical industry.30,31,35 The ability to detect weak binding, the comparably low amount of sample required and the ability to detect binding to non-modified molecular targets including proteins, nucleic acids and their complexes in a non-destructive manner in solution are particular advantages of NMR-based fragment screening. In addition to 1H-detected NMR experiments, 19F-detected NMR experiments have been recently advertised because binding can often be monitored on a single, background-free 19F signal in 19F-1D NMR experiments. 19F resonances show chemical shift dispersions that are large compared to the 1H or 13C chemical shift dispersions, allowing detection of binding-induced chemical shift perturbations (CSPs) and screening of mixtures containing a larger number of molecules compared to screening mixtures if 1H detection is used.35,36 Compared to 13C detection, 19F offers two advantages: 19F is a pure isotope (100% natural abundance) and it has a comparatively high sensitivity. The combined readout of 1H- & 19F-CSPs provides more reliable data for RNA screening in comparison to conventional STD experiments used for protein screening, since reduced proton density within RNA in contrast to protein leads to reduced STD effects upon (transient) binding.37,38
The goals of our study reported were:
(i) To compare the hit rates of the DSI-PL versus the DRTL-F library.
(ii) To investigate the validity of using isolated RNA sub-elements for such NMR-based screening approaches.
(iii) To evaluate the utility of 19F and 1H chemical shift perturbations (CSPs) and changes in T2 relaxation rates upon binding to RNA as proxies reporting on binding in NMR-based screening.
(iv) Evaluation of simultaneous NMR detection of CSPs for 1H and 19F ligands. Such dual detection scheme has become possible with the introduction of dual NMR receivers in the newest generation of NMR consoles. In principle, dual or parallel detection leads to a reduction of measurement time by a factor of two.39
We can show that the DRTL-F library is enriched in molecules that bind RNA and the binders derived from this library bind more tightly compared to molecules from the DSI-PL.
19F screening provides a small, but significant improvement in detecting binding compared to 1H screening, including detection and quantification of low affinity binding.
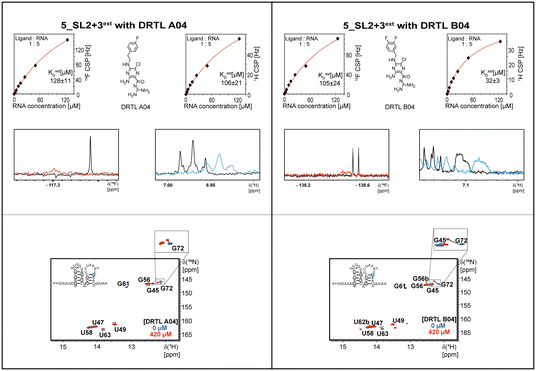
Most importantly, the RNA binders show selectivity for the 5_SL2 + 3ext element of the 5′-terminal SCoV2 RNA. In order to map the RNA binding site to this preferred target RNA, we assigned the 1H,15N imino chemical shifts utilising NOESY, HSQC, and HNN-COSY experiments. These chemical shift assignments allow for rapid mapping of the RNA binding site by comparing chemical shift changes upon addition of RNA binders.
Experimental
RNA synthesis and purification
All RNA constructs of SCoV2 were synthesised by in vitro transcription using T7-polymerase and purified under the same conditions. First, DNA sequences for 5_SL1, 5_SL2 + 3ext, 5_SL4 and 5_SL1234 were obtained by cloning DNA oligomers encoding the T7 polymerase promotor (5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAG-3′) these RNA constructs into a plasmid based on the pSP64 vector. The plasmids also encode an HDV ribozyme, and the genes of interest were cloned into the plasmid using the EcoRI and NcoI restriction sites upstream of the ribozyme sequence to allow transcription of the RNA as an HDV fusion construct to avoid 3′ inhomogeneities of the RNA constructs.40Transcriptions were performed at 15 mL scale, and the conditions were optimized for maximum yield and purity for each construct. Purification was carried out by preparative PAGE, HPLC and buffer exchange with screening buffer (25 mM KPi; 50 mM KCl; pH 6.2). After the PAGE, the desired RNA was visualized by UV-shadowing, cutted out and eluted with 0.3 M NaOAc. By using rpHPLC with a Kromasil RP 18 column and a gradient from non-polar to polar (0.1 M acetonitrile/triethylammonium acetate), the remaining PAA was removed. Concentrations of the samples were analysed by UV/vis spectroscopy using the following molar extinction coefficients (OD260): 5_SL1: 257.4 1/mM; 5_SL2 + 3ext: 390.0 1/mM; 5_SL4: 388.7 1/mM and 5_SL1234: 1064.1 1/mM, and analytical PAGE was performed to verify the purity.
Sample preparation
For each RNA screened, there were two samples (one with and one without the fragment to be screened). Each screening sample contained 4 μM of RNA, 5% of D2O and 5% of [d6]DMSO, and the fragment at 0 μM or 40 μM concentration resulting in an [RNA]/[ligand]-ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10. The screening buffer was 25 mM KPi (pH 6.2), 50 mM KCl in H2O. Titration samples contained 25 μM of the fragment, 5% [d6]DMSO (which was used as lock solvent), and RNA at concentrations from 0–125 μM.
10. The screening buffer was 25 mM KPi (pH 6.2), 50 mM KCl in H2O. Titration samples contained 25 μM of the fragment, 5% [d6]DMSO (which was used as lock solvent), and RNA at concentrations from 0–125 μM.
NMR spectroscopy
Spectra were recorded on a 600 MHz Bruker spectrometer equipped with a Neo console and a 5 mm cryogenic quadruple resonance 1H[13C,15N,19F] QCI probe and a SampleJet automatic sample changer. Measurements were performed in 3 mm sample tubes with a final volume of 170 μL. 1H 1Ds, 19F 1Ds and 19F T2-CPMG experiments were measured to identify binders (19F experiments were only measured for the fluorinated compounds). CPMG measurements were conducted with mixing times of 0, 16, 64, 128 and 256 ms.35,41,42 For the CSP evaluation, titrations were performed by 1H 1D measurements (and 19F 1D for all fluorinated fragments) on 8 samples with RNA concentrations varying from 0–125 μM and fixed ligand concentration of 25 μM. All NMR-measurements were conducted at 298 K. 5% [d6]DMSO was used as locking solvent for the spectrometer and shim optimization was done for every sample in an identical manner with a shimming-script loaded into the IconNMR-Automation Software. In 1H 1D screening experiments as well as titration experiments, a conventional excitation sculpting sequence was used to suppress the water.431H 1D experiments were performed with 16k points, 1k scans, a spectral width of 8 kHz and a 53 min runtime each. 19F 1D experiments were performed with 150k points, 256 scans, a spectral width of 75 kHz and 9 min runtime. All data were processed and analysed using the software package TopSpin 4.0.7.To assign the imino region of the 5_SL2 + 3ext RNA, an 1H–1H-NOESY, an 1H–15N-BEST-TROSY and an HNN-COSY experiment were conducted. The spectra were recorded with 430 μM 15N-labelled 5_SL2 + 3ext RNA. The experiments were performed at a 800 MHz Bruker spectrometer equipped with an Avance III HD console and a 5 mm cryogenic triple resonance 1H[13C, 15N] TCI probe. The measurements were carried out with the RNA in RNA buffer (25 mM KPi, pH 6.2 and 50 mM KCl) as much as 95% H2O/5% D2O. The 1H–1H-NOESY was run for 30 h with 400 points in the indirect dimension and 256 scans. The 1H–15N-BEST-TROSY was performed with 256 points in the indirect dimension and 16 scans for 35 min. The HNN-COSY was conducted with 192 points in the indirect dimension and 64 scans for 11 h runtime. All three spectra were recorded at 283 K.
For NMR-based binding site mapping detecting changes in the NMR spectra of G and U imino resonances in 1H,15N heteronuclear correlation experiments, two 1H–15N-BEST-TROSY spectra were recorded with 84 μM 15N-labelled 5_SL2 + 3ext RNA alone and after addition of 420 μM ligand (ratio 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5) under equal conditions. The measurements were run with a 800 MHz Bruker spectrometer equipped with an Avance III HD console and a 5 mm cryogenic triple resonance 1H[13C, 15N] TCI probe. The sample buffer was 25 mM KPi, pH 6.2 and 50 mM KCl. For locking of the spectrometer frequency, 5% D2O was added to the pure RNA sample and 5% D2O plus 5% [d6]DMSO was added to the RNA–ligand sample. Both measurements of the RNA alone and RNA plus ligand were performed with 256 points in the indirect dimension, 32 scans and 45 min runtime.
5) under equal conditions. The measurements were run with a 800 MHz Bruker spectrometer equipped with an Avance III HD console and a 5 mm cryogenic triple resonance 1H[13C, 15N] TCI probe. The sample buffer was 25 mM KPi, pH 6.2 and 50 mM KCl. For locking of the spectrometer frequency, 5% D2O was added to the pure RNA sample and 5% D2O plus 5% [d6]DMSO was added to the RNA–ligand sample. Both measurements of the RNA alone and RNA plus ligand were performed with 256 points in the indirect dimension, 32 scans and 45 min runtime.
The dual detection experiments were performed on a 600 MHz spectrometer equipped with a Bruker Avance Neo console and a cryogenic probe for 1H, 19F [13C, 15N] (QCI). This type of console combines frequency generation with a digital receiver for each channel to ease implementation of dual receive experiments. Individual reference 1H and 19F-1D experiments were acquired with 512 scans and a relaxation delay of 1.4 s at an acquisition time of 1 s (1H) and 0.5 s (19F) in 20 min (1H) and 16 min (19F). The same settings were used for the dual receive experiment, recorded in 20 min. Water suppression for the proton experiment was achieved with a SOGGY sequence.44 This sequence was shown to be robust for use in screening experiments.31 The measurements were carried out with the ligand DRTL A04 at a concentration of 100° μM in RNA buffer and 95% H2O/5% DMSO.
Analysis of NMR data
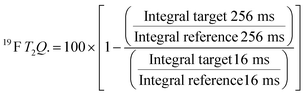
For every screening sample, the following three experiments were conducted: 1H 1D, 19F 1D and 19F T2-CMPG (Fig. 2). As hit criterion, we defined changes in all three parameters to be required (CSP (1H) ≥ 3 Hz; CSP (19F) ≥ 5 Hz; intensity decrease in the 19F T2-CPMG experiment 19F T2Q. ≥ 30%).35,41,42 The T2-reduction in percentage between peak integrals of samples containing ligand and RNA and sample containing only ligand with each 16 ms CPMG and 256 ms CPMG was calculated for all screening samples.where “integral target” describes ligand with RNA and “integral reference” is only the ligand peak integral.
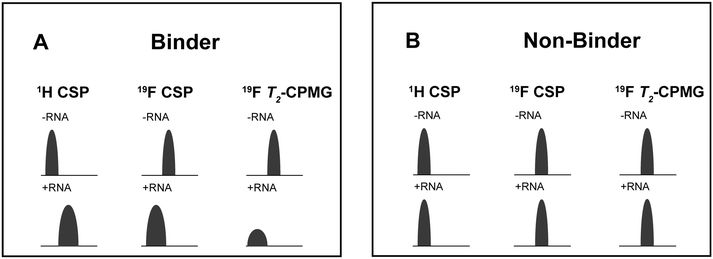 | ||
| Fig. 2 Ligand-based NMR screening and binding classification: schematic illustration of conducted experiments and criteria to identify binders A and non-binders B. | ||
CSP-based calculation of the estimated dissociation constant (KestD) was done by plotting the changes in CSP values during NMR-titration experiments against RNA concentration and non-linear fitting. For this analysis, OriginLab Software was used.
Results
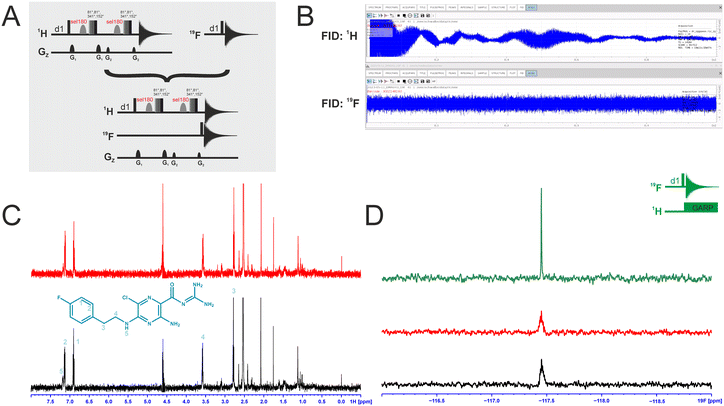
Dual-detected NMR experiments
We attempted to improve NMR screening technologies utilising dual detection schemes that allow detection of the 1H and the 19F at the same time (Fig. 3).45 In principle, such dual detection reduces the measurement time by combining detection of the response of two different NMR signals upon addition of ligands at the same time. Implementation of such approach, while feasible in principle, meets several challenges.Typically, sensitivity of probes can only be optimised for detection of a single nucleus at a time. Thus, 19F-detected experiments require the inner coil to be tuned to 19F so that the detection coil picks up the rf-output of the 19F NMR signals, optimally exploiting the largest filling factor.
The presence of 1H–19F long-range couplings (nJ(H,F) with n = 2–5) leads to splittings of both, 1H and 19F spectra that, while being information-rich, require expert analysis. Thus, typically 1H decoupling is used employing a second outer coil for probes that are optimised for 19F detection. Probes optimised for 1H detection can implement only band-selective 1H decoupling. If both nuclei are detected at the same time in dual detection mode, decoupling of either one of the two nuclei cannot be implemented. Decoupling is, however, not required for molecules that contain CF3-groups as these methyl groups typically do not feature large nJ(H,F) couplings.
We tested the feasibility of dual 1H and 19F detection. The DRTL-F (RNA-dedicated) library contains compounds with CF3-groups as well as fluorinated aromatic systems.
Simultaneous detection of 1H and 19F NMR signals was established using DRTL A04 as ligand (Fig. 3C). Each acquisition parameter was optimised individually and recorded under these conditions and compared with the parallel detected spectra (Fig. 3C and D). The signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) is identical in both cases for 1H and 19F. DRTL A04 carries a fluorine atom in a 1,4 di-substituted aromatic ring. 2J(H,F) and 3J(H,F) couplings cannot be suppressed in these experiments, so the S/N for the 19F experiments is worse compared to the decoupled 19F-1D. The less sensitive 19F-CPMG experiment can therefore not be performed in a reasonable time. Thus, while dual detection experiments can be performed for molecules carrying CF3 ligands, for ligands with sizeable scalar J(H,F) couplings, gains in measurement time due to dual detection cannot be realised as the heteronuclear couplings cannot be decoupled.
Ligand-based screening via NMR spectroscopy
We screened two fragment libraries for binding to four RNA constructs derived from the 5′-UTR of the SCoV2 genome using ligand-based NMR experiments detecting either of the two NMR-active isotopes 1H or 19F.19,27,36,46 Before screening the various ligands, we verified that DMSO-induced shifts up to the volume percentage of 5% used in the screening experiments did not affect the chemical shifts of the RNA signals (ESI† Fig. S1).The experimental design allows comparison of screening results based on either of the two detected NMR nuclei in parallel and in comparison to each other. Two libraries were used for screening: (i) the DSI-PL of fragments with 768 compounds, and (ii) the DRTL-F library developed by the Hargrove lab,32 containing 49 compounds.
While quality control NMR had already been conducted for the first library, we also conducted quality control NMR experiments for the DRTL-F library, in particular to determine solubilities of all compounds in the RNA NMR screening buffer by 1H 1D and 19F 1D spectroscopy.34
Definition for binding within the screening
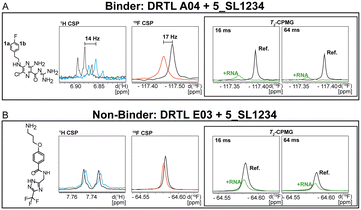
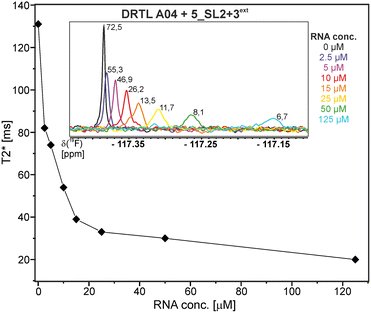
First, we screened the 4-stem-loop construct 5_SL1234 containing 119 nucleotides against both libraries. The most pronounced effects were observed for binding of compound DRTL A04 to 5_SL1234. We detected large CSPs in the 1H 1D (14 Hz) and the 19F 1D (17 Hz) and a signal decrease the 19F signal at ([ligand]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [RNA] = 10
[RNA] = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) for T2 relaxation times of 16 ms or 64 ms, respectively, compared to the reference signal without the RNA (Fig. 4A).
1) for T2 relaxation times of 16 ms or 64 ms, respectively, compared to the reference signal without the RNA (Fig. 4A).
For comparison, we show the signature of the compound DRTL E03 that we classified as non-binder because neither a significant CSPs nor strong signal intensity attenuation in the T2-CPMG experiment could be detected (Fig. 4B).
Applying the hit criteria defined in Fig. 2A, we found 10 binders out of the 49 compounds from the DRTL-F library (Fig. 5). 5 out of 768 fragments of the DSI-PL were reported to bind previously.30 These numbers translate to a hit rate of 20.4% for the DRTL-F library versus 0.7% for the DSI-PL. The binding profiles of the 10 compounds from the DRTL-F library (Table S1†) and the 5 compounds from the DSI-PL (Table S2†) binding to 5_SL1234 are given in the ESI.†
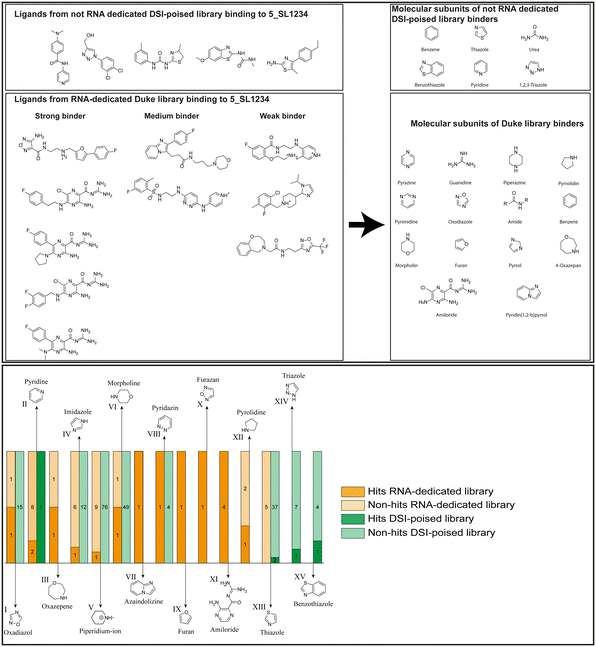 | ||
| Fig. 5 Comparison of all DRTL-F library and DSI-PL binders and their molecular subunits and chemotype comparison for the hits of both libraries. | ||
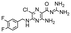
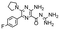
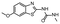
In the next step, we screened the three sub-elements 5_SL1, 5_SL2 + 3ext and 5_SL4 against the four most promising binders to 5_SL1234 from the DRTL-F library. All these ligands were amiloride derivatives.47,48
Apparently, those four amilorides did not bind to all three RNA sub-elements (Table 1), although they were found to be strong binders in the screening with the entire 5_SL1234 RNA before. This finding confirms that there is binding specificity for structured RNA motifs. The secondary structures of the three RNA sub-elements 5_SL1, 5_SL2 + 3ext and 5_SL4 differ significantly: the secondary structure of 5_SL1 features an internal loop, 5_SL4 shows pyrimidine mismatches and 5_SL2 + 3ext is the most flexible RNA sub-element and contains two structured stem regions and two loops of which one is a large loop.
| RNAs | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRTL A04 | DRTL B04 | DRTL D04 | DRTL A05 | |||||||||
| 1H CSP | 19F CSP | 19F T2Q. | 1H CSP | 19F CSP | 19F T2Q. | 1H CSP | 19F CSP | 19F T2Q. | 1H CSP | 19F CSP | 19F T2Q. | |
| 5_SL1234 | 14 | 17 | 78 | 13 | 27 | 96 | 26 | 6.5 | 100 | 20 | 1.6 | 100 |
| 5_SL1 | 3 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 78 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 20 |
| 5_SL2 + 3ext | 8 | 24 | 100 | 3 | 17 | 100 | 0.7 | 0 | 39 | 1.8 | 7 | 43 |
| 5_SL4 | 3 | 13 | 17 | 3 | 7 | 92 | 2 | 2 | 48 | 0.8 | 6 | 11 |
Binding of amilorides to RNA involves electrostatic interactions. Our initial screening protocol uses a buffer system containing 50 mM KPi and 25 mM KCl, in accordance with optimal NMR spectral quality. We thus tested the influence of increased salt concentration up to 250 mM KCl on the binding of DRTL A04 to SL2 + 3ext. Interestingly, we observe largest 1H and 19F CSPs and substantially increased line widths at the lowest salt concentration. These large CSPs become smaller at higher salt concentration, but the large line widths remain. Such salt dependence on the primary NMR output could be consistent with more unspecific binding events involving more than a single site at higher KCl salt concentration (ESI† Fig. S2).
Interestingly, 5_SL2 + 3ext binds two out of four screened compounds following the criteria applied for 5_SL1234, while 5_SL1 binds none and 5_SL4 only binds to DRTL B04 (Table 1).
While five fragments of the DSI-PL showed binding to 5_SL1234, there was no binder found at all in the screening of that library for 5_SL2 + 3, five for 5_SL1 and seven for 5_SL4.
Apparently, the (not-RNA dedicated) DSI-PL contains less compounds that bind RNA compared to the RNA-dedicated DRTL-F library. Closer analysis of the constitution of the binding compounds found in the two libraries shows that chemotypes for RNA binding differ as well (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 summarises graphically the identified 15 chemotypes: Six chemotypes (III, VII, IX, X, XI) are unique for the DRTL-F library and two chemotypes (XIV, XV) are unique for the DSI-PL. The DSI-PL is enriched in several chemotypes (oxadiazol I, 15 fragments; imidazole IV, 12 fragments; piperidinium-ion V, 76 fragments; morpholine VI, 49 fragments) that are not found within its binders but are part of the binders of the DRTL-F library. Thiazole fragment XIII is found in 39 DSI_PL fragments of which two bind but is found to not be part of a binder in the DRTL-F library. Chemotype V, piperidinium-ion, is also found in ten DRTL-F library compounds but is only present in one binder, while one of the two DRTL-F library compounds containing chemotype morpholine VI is found to bind. The 6-membered nitrogen-carrying chemotypes V and VI often increase solubility, but apparently do not contribute to RNA binding. The amiloride chemotype 11 within the DRTL-F library stands out for its binding capability and represents a high-affinity non-specific tag for RNA binding, at least in part because the acyl guanidinium group is capable of forming hydrogen bonds on the Hoogsteen-edge in particular for a guanine nucleobase within the target RNA. An overview of the compounds screened within the DRTL-F library is given in Fig. 6.
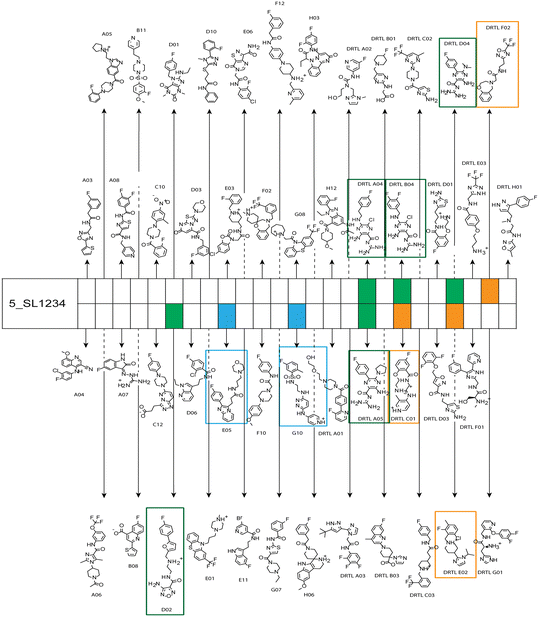 | ||
| Fig. 6 Overview of screening results from screening of 5_SL1234 with 49 compounds of the DRTL-F library. Strong binders are marked green, medium binders blue and weak binders yellow. | ||
Estimation of relative binding affinities by 1H and 19F NMR titration
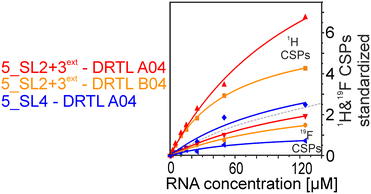
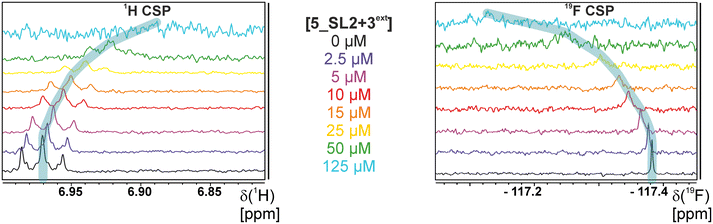
The initial hit identification for the DRTL-F library was conducted using a tenfold excess of ligand over RNA target. We determined binding affinities for each of the amilorides prioritised for the RNAs to the three RNA sub-elements by 1H and 19F NMR titration. Here, the ligand concentration was fixed to 25 μM and increasing amounts of RNA were added up to a concentration of 125 μM. Compound CSPs were monitored for the titrations by 1H and 19F 1D spectra. Estimated KD values (KestD) were calculated by fitting the CSPs as function of RNA concentration (Fig. 7). From analysis of the data, the sub-element 5_SL2 + 3ext was found to be the best targetable RNA element. So, NMR-based binding site mapping was performed with 5_SL2 + 3ext using changes of G and U imino resonances in 1H,15N heteronuclear correlation experiments of RNA alone compared to RNA with ligand as indicator of binding (Fig. 7). To do so, it was necessary to predominantly assign resonances of the imino region of 5_SL2 + 3ext, which was done by performing 1H–1H-NOESY, 1H–15N-BEST-TROSY and HNN-COSY experiments. Finally, since a small but detectable percentage of this RNA sub-element forms a secondary conformation, the experiments were performed at 283 K, which corresponds to the temperature range where the second conformation is least pronounced (ESI† Fig. S3).To further compare the binding affinities of hits derived from either of the two libraries, the five fragments from the DSI-PL identified to bind to 5_SL1234 were titrated and affinities to the 5_SL2 + 3ext were determined using 1H NMR of the non-fluorinated compounds. We found approximate affinities to range between 250 to 780 μM for these fragments (Table 2).
NMR titration of hits identified in both libraries show that the dedicated RNA-library contains compounds that bind significantly stronger than those from the DSI-PL. Only for fragments ligand 1 and ligand 3 from the DSI-PL, binding affinities in the high micromolar range could be detected. By contrast, several low micromolar binding events for the amilorides of the DRTL-F library were observed.
We further compared the affinities determined by 1H versus19F CSPs for three RNA-compound pairs. The CSPs shown in Fig. 8 are standardised to the respective spectral dispersion
Discussion and conclusion
Herein, we screened and titrated several compounds using 1H and 19F NMR to detect and characterise their binding to conserved RNA elements from the 5′UTR of the SCoV2 genome. All three elements of the 5_SL1234 untranslated region feature regular A-form secondary structures disrupted either by bulges or loops. Our findings suggest, that there must be binding specificity for either the structured RNA motifs of the sub-elements or unstructured spacer regions present in 5_SL1234 and not present in either of the sub-constructs. Each of the RNAs consists of unique structural elements. CSP can be detected both on the 1H and 19F resonances but weaker binding can be detected by 19F screening as its chemical shift dispersion (in Hertz) is larger than for 1H. Fig. 8 illustrates the CSP behaviour of 1H and 19F ligand resonances during titration with an RNA target. In addition, Fig. 9 shows the decrease in transverse relaxation T2 (19F) for DRTL A04 upon titration with 5_SL2 + 3ext. We found that standardisation of the observed CSPs with the spectral dispersion (accessible chemical shift range) for 1H and 19F, respectively, lead to a higher consistency between each compound–RNA-pair. In addition, after normalisation, the range of 19F CSPs is smaller and they are clustered.Measuring both 1H and 19F experiments on identical samples allowed us to compare advantages and limitations with such experimental setup.
After detection of binding at one fixed concentration ratio of ligand over RNA ([ligand]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) [RNA] = 10
[RNA] = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), binding affinities for those positive hits are characterised by suitable follow-up NMR experiments.
1), binding affinities for those positive hits are characterised by suitable follow-up NMR experiments.
Here and in previous works, we propose to detect binding in a ligand-observed method by recording CSPs at a fixed ligand concentration and variable target concentrations.28,30,31,34 Especially for low affinity RNA binders (KD of 100 μM–1 mM), estimates of ligand affinity are quick and easy to perform and provide a valuable checkpoint prior to performing detailed characterisation of the observed RNA binding. The latter method is more challenging in terms of sample amount, adjustment of experimental conditions, and ligand solubility. There is especially a problem with weaker binders that require a higher excess of RNA, where the ligand concentration must be sufficiently high to record NMR experiments within a reasonable time. Addition of DMSO to improve ligand solubility is limited: RNA folding, and thus binding site architecture, can be compromised at DMSO concentrations greater than 5%, which we often found to be the minimum required to keep compounds soluble during our experiments.
From the ligand-based affinity titrations conducted here, there are mainly two factors that determine the range of affinities that can be reliably quantified by NMR: signal-to-noise limits the lowest KD that can be detected: from our experience, 1H and 19F experiments require ligands at a concentration of at least 10 μM. In 1H experiments, we prepared samples with [ligand] = 25 μM and added RNA up to a concentration of 125 μM.
Depending on the chemical shift of the ligand signal, we often observed spectral overlap in 1H spectra starting at a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio of compound to RNA. Obviously, this resonance overlap was circumvented in 19F-detected titrations. Additionally, 19F does not require solvent suppression and is not compromised by the presence of additional impurities from either RNA, buffer or ligand in general, although such impurities were not an issue in the work conducted here.
1 ratio of compound to RNA. Obviously, this resonance overlap was circumvented in 19F-detected titrations. Additionally, 19F does not require solvent suppression and is not compromised by the presence of additional impurities from either RNA, buffer or ligand in general, although such impurities were not an issue in the work conducted here.
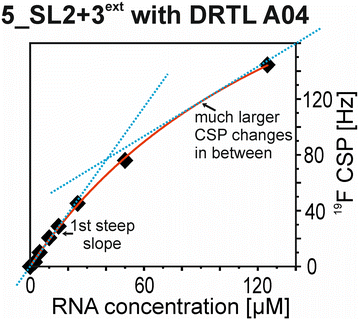
The affinities we detect here represent relative estimates rather than highly precise KDs. Thus, we refer to estimated affinities (KestD), because the signal-to-noise ratio of the ligand signal often limits us with respect to the lowest possible ligand concentrations, which does not allow us to add sufficient excess of RNA to accurately determine the endpoints of the titration.49 Especially for 19F, we often observe substantial line broadening when RNA is added in excess over ligand (Fig. 10). This line broadening is presumably caused by several aspects: especially for 19F, the kinetics of the interaction change from fast exchange to intermediate exchange. The change in exchange regimes can be more readily observed for 19F than for 1H resonances, in line with larger chemical shift changes for 19F. In addition, some of the titration data suggest that the interaction of the ligand with RNA is not restricted to a single binding site, but two or several binding sites are involved. Here, we refrained from quantitatively describing these more complex interaction models, but especially for DRTL A04 binding to 5_SL2 + 3ext (Fig. 11), we observed an initial steep CSP response followed by a second CSP change at higher RNA![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ligand ratios.
ligand ratios.
From Fig. 11 it is apparent that there is a much larger region between the titration steps of 50 μM added and 125 μM added compared to the start of the curve where the titration steps, and respectively the gaps between CSP values, are much smaller. Thus, the chemical shift changes at higher RNA concentrations are larger than those at low RNA concentrations. This observation is consistent with a two-binding-site-scenario featuring a first binding site at ∼10 μM and a second, weaker binding and may account for frequent differences between NMR-detected affinities compared to other biophysical methods. In line with this, we observed different values for each RNA/fragment-pair depending on which of the CSPs we used (1H or 19F resonances) (Fig. 7 and 8). The reason for these differences could be that there are multiple binding events for the fragments to the RNA.
The exact nature of each individual interaction is likely different among all binding events, especially if the molecular encounter is driven by electrostatic or by stacking interactions, which are redundantly present in every RNA. The result is an ensemble of several local CSPs representing an average of all interaction events of either the fluorinated site of the compound or one proton resonance and RNA on the same timescale. In fact, we were able to detect such “delocalized” binding in our RNA-observed experiments (Fig. 7).
Towards the development of drugs targeting RNA optimised from initial fragment binders, we recommend using 1D and 2D NMR techniques to validate binding for those fragments that should be prioritised from initial ligand-based screens. NMR is particularly well suited for reliably selecting promising candidates in the lower affinity regime (3-digit μM) because it can distinguish between specific and non-specific binding.
The latter is a common issue with compounds targeting RNA rather than targeting proteins due to the large electrostatic contributions to binding and the inherent structural redundancy of many RNA motifs. Importantly, low-affinity binders that are selective for a particular RNA motif may be readily tuned to higher affinities for the same reasons, provided that detailed structural information about the binding site is available. Thus, by using the NMR methods presented here in the early stages of ligand development, the number of false positives leading to fruitless follow-up efforts can be reduced, and the same is true for the number of false negatives that may have been wrongly discarded. Especially when affinities in the single-digit micro molar range have been developed, additional biophysical methods need to be in place to accurately determine affinities. For example, fluorescent-based methods exploiting the inherent fluorescence of ligands or of fluorescent 2-aminopurine RNA residues introduced within the RNA target are options to pursue.
In conclusion, we demonstrate that RNAs can be targeted with substantial affinity and selectivity even by fragments. Enrichment of RNA binders in such fragment libraries accelerates the process of rapidly detecting binders in the 10–50 μM range. Our data support the notion that selectivity of 1–2 orders of magnitude in differential binding affinity can be reached over the set of RNAs investigated here even with low molecular weight molecules that are fragments but not yet optimized by extensive follow-up medicinal chemistry campaigns. The fluorinated library, that was used, is a subset of the Duke RNA-targeted Library (DRTL)32 with accompanying synthetic molecules and is not optimised for ease of NMR detection. Methodological NMR-centred screens often use compound libraries s containing only CF3-groups. The design of the library was guided in part by medicinal chemistry considerations including optimisation of affinity and selectivity as well as ease of follow-up chemistry in the hit-to-lead process and thus contain 19F groups where they may improve the binding properties of the hit but are not optimal for dual NMR detection. 19F screening provides advantages and limitations compared to 1H screening, we thus advocate to use both NMR screening technologies in parallel. While feasible in principle, dual detection schemes in NMR screening campaigns is hampered by insufficient S/N with the currently available probe technology and we recommend conducting individually optimised 1H and 19F experiments. However, methodological improvements are currently being developed to conduct such screens with a single sample strictly in parallel by dual detection methodology and with the right hardware and the correspondingly designed library, a lot of measurement time can be saved in the near future. The work reported will support the vast number of efforts to make also the RNA genome of viruses targetable by small molecules, both for mechanistic studies as an RNA target specific chemical probe but also towards antiviral medication. For such research, NMR spectroscopy is an indispensable tool to support medicinal chemistry campaigns.
Author contributions
D. H., J. M., C. R., S. S., conducted research. N. N. P. synthesized the amiloride derivatives used. D. H., H. S. wrote the initial draft. All authors contributed in the iterative process of improving the initial draft. H. S. supervised the project. A. H. supervised synthesis and curation of the DRTL-F. A. H., H. S. acquired funding.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Work at BMRZ is supported by the state of Hesse. The work is supported by the EU project Fragment-Screen, grant agreement ID: 101094131. J. M. and H. S. are members of the DFG-funded graduate college “CLIC”. Library synthesis and curation was supported by NIH R35GM124785 and U54 AI170660 to A. H. Sarah Wicks is acknowledged for assistance with curation of the DRTL-F library. We are grateful to the reviewer for suggesting to investigate the salt dependence on the NMR screening results.Notes and references
- Y. Dong, T. Dai, B. Wang, L. Zhang, L. H. Zeng, J. Huang, H. Yan, L. Zhang and F. Zhou, Signal Transduction Targeted Ther., 2021, 6, 387 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. R. Painter, M. G. Natchus, O. Cohen, W. Holman and W. P. Painter, Curr. Opin. Virol., 2021, 50, 17–22 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kozlov, Nature, 2021 DOI:10.1038/d41586-021-03667-0.
- J. Liu, X. Pan, S. Zhang, M. Li, K. Ma, C. Fan, Y. Lv, X. Guan, Y. Yang, X. Ye, X. Deng, Y. Wang, L. Qin, Z. Xia, Z. Ge, Q. Zhou, X. Zhang, Y. Ling, T. Qi, Z. Wen, S. Huang, L. Zhang, T. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Huang, W. Li, H. Du, Y. Chen, Y. Xu, Q. Zhao, R. Zhao, D. Annane, J. Qu and D. Chen, Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac., 2023, 100694 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Kozlov, Nature, 2022, 601, 496 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Yu, L. Chen, R. Lan, R. Shen and P. Li, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, 2020, 56, 106012 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Günther, P. Y. A. Reinke, Y. Fernández-Garciá, J. Lieske, T. J. Lane, H. M. Ginn, F. H. M. Koua, C. Ehrt, W. Ewert, D. Oberthuer, O. Yefanov, S. Meier, K. Lorenzen, B. Krichel, J. D. Kopicki, L. Gelisio, W. Brehm, I. Dunkel, B. Seychell, H. Gieseler, B. Norton-Baker, B. Escudero-Pérez, M. Domaracky, S. Saouane, A. Tolstikova, T. A. White, A. Hänle, M. Groessler, H. Fleckenstein, F. Trost, M. Galchenkova, Y. Gevorkov, C. Li, S. Awel, A. Peck, M. Barthelmess, F. Schlünzen, P. L. Xavier, N. Werner, H. Andaleeb, N. Ullah, S. Falke, V. Srinivasan, B. A. Francą, M. Schwinzer, H. Brognaro, C. Rogers, D. Melo, J. J. Zaitseva-Doyle, J. Knoska, G. E. Penã-Murillo, A. R. Mashhour, V. Hennicke, P. Fischer, J. Hakanpaä, J. Meyer, P. Gribbon, B. Ellinger, M. Kuzikov, M. Wolf, A. R. Beccari, G. Bourenkov, D. Von Stetten, G. Pompidor, I. Bento, S. Panneerselvam, I. Karpics, T. R. Schneider, M. M. Garcia-Alai, S. Niebling, C. Günther, C. Schmidt, R. Schubert, H. Han, J. Boger, D. C. F. Monteiro, L. Zhang, X. Sun, J. Pletzer-Zelgert, J. Wollenhaupt, C. G. Feiler, M. S. Weiss, E. C. Schulz, P. Mehrabi, K. Karnïcar, A. Usenik, J. Loboda, H. Tidow, A. Chari, R. Hilgenfeld, C. Uetrech, R. Cox, A. Zaliani, T. Beck, M. Rarey, S. Günther, D. Turk, W. Hinrichs, H. N. Chapman, A. R. Pearson, C. Betzel and A. Meents, Science, 2021, 372, 642–646 CrossRef PubMed.
- O. Guven, M. Gul, E. Ayan, J. A. Johnson, B. Cakilkaya, G. Usta, F. B. Ertem, N. Tokay, B. Yuksel, O. Gocenler, C. Buyukdag, S. Botha, G. Ketawala, Z. Su, B. Hayes, F. Poitevin, A. Batyuk, C. H. Yoon, C. Kupitz, S. Durdagi, R. G. Sierra and H. Demirci, Crystals, 2021, 11, 1–14 CrossRef.
- A. Douangamath, D. Fearon, P. Gehrtz, T. Krojer, P. Lukacik, C. D. Owen, E. Resnick, C. Strain-Damerell, A. Aimon, P. Ábrányi-Balogh, J. Brandão-Neto, A. Carbery, G. Davison, A. Dias, T. D. Downes, L. Dunnett, M. Fairhead, J. D. Firth, S. P. Jones, A. Keeley, G. M. Keserü, H. F. Klein, M. P. Martin, M. E. M. Noble, P. O'Brien, A. Powell, R. N. Reddi, R. Skyner, M. Snee, M. J. Waring, C. Wild, N. London, F. von Delft and M. A. Walsh, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 1–11 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. A. Newman, A. Douangamath, S. Yadzani, Y. Yosaatmadja, A. Aimon, J. Brandão-Neto, L. Dunnett, T. Gorrie-stone, R. Skyner, D. Fearon, M. Schapira, F. von Delft and O. Gileadi, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 1–11 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Ursu, J. L. Childs-Disney, R. J. Andrews, C. A. O'Leary, S. M. Meyer, A. J. Angelbello, W. N. Moss and M. D. Disney, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 7252–7270 RSC.
- C. Maucort, D. D. Vo, S. Aouad, C. Charrat, S. Azoulay, A. Di Giorgio and M. Duca, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 899–906 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. L. Kelly, C. C. Chu, H. Shi, L. R. Ganser, H. P. Bogerd, K. Huynh, Y. Hou, B. R. Cullen and H. M. Al-Hashimi, RNA, 2021, 27, 12–26 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Meyer, C. C. Williams, Y. Akahori, T. Tanaka, H. Aikawa, Y. Tong, J. L. Childs-Disney and M. D. Disney, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 7167–7199 RSC.
- J. L. Childs-Disney, X. Yang, Q. M. R. Gibaut, Y. Tong, R. T. Batey and M. D. Disney, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2022, 21, 736–762 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. D. Warner, C. E. Hajdin and K. M. Weeks, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2018, 17, 547–558 Search PubMed.
- O. O. Abudayyeh, J. S. Gootenberg, P. Essletzbichler, S. Han, J. Joung, J. J. Belanto, V. Verdine, D. B. T. Cox, M. J. Kellner, A. Regev, E. S. Lander, D. F. Voytas, A. Y. Ting and F. Zhang, Nature, 2017, 550, 280–284 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. F. Bennett and E. E. Swayze, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 2010, 50, 259–293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rangan, I. N. Zheludev, R. J. Hagey, E. A. Pham, H. K. Wayment-Steele, J. S. Glenn and R. Das, RNA, 2020, 26, 937–959 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Yang and J. L. Leibowitz, Virus Res., 2015, 206, 120–133 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. J. Andrews, C. A. O'leary, V. S. Tompkins, J. M. Peterson, H. S. Haniff, C. Williams, M. D. Disney and W. N. Moss, NAR: Genomics Bioinf., 2021, 3, 1–14 CAS.
- H. S. Haniff, Y. Tong, X. Liu, J. L. Chen, B. M. Suresh, R. J. Andrews, J. M. Peterson, C. A. O'Leary, R. I. Benhamou, W. N. Moss and M. D. Disney, ACS Cent. Sci., 2020, 6, 1713–1721 Search PubMed.
- T. Hermann, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: RNA, 2016, 7, 726–743 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Richter, K. F. Hohmann, S. Toews, D. Mathieu, N. Altincekic, J. K. Bains, O. Binas, B. Ceylan, E. Duchardt-Ferner, J. Ferner, B. Fürtig, J. T. Grün, M. Hengesbach, D. Hymon, H. R. A. Jonker, B. Knezic, S. M. Korn, T. Landgraf, F. Löhr, S. A. Peter, D. J. Pyper, N. S. Qureshi, A. Schlundt, R. Schnieders, E. Stirnal, A. Sudakov, J. Vögele, J. E. Weigand, J. Wirmer-Bartoschek, K. Witt, J. Wöhnert, H. Schwalbe and A. Wacker, Biomol. NMR Assignments, 2021, 15, 467–474 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Joshi, J. Parkar, A. Ansari, A. Vora, D. Talwar, M. Tiwaskar, S. Patil and H. Barkate, Int. J. Infect. Dis., 2021, 102, 501–508 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Duchardt-Ferner, J. Ferner, B. Fürtig, M. Hengesbach, C. Richter, A. Schlundt, S. Sreeramulu, A. Wacker, J. E. Weigand, J. Wirmer-Bartoschek and H. Schwalbe, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62(14), e202217171 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Wacker, J. E. Weigand, S. R. Akabayov, N. Altincekic, J. K. Bains, E. Banijamali, O. Binas, J. Castillo-Martinez, E. Cetiner, B. Ceylan, L. Y. Chiu, J. Davila-Calderon, K. Dhamotharan, E. Duchardt-Ferner, J. Ferner, L. Frydman, B. Fürtig, J. Gallego, J. T. Grün, C. Hacker, C. Haddad, M. Hähnke, M. Hengesbach, F. Hiller, K. F. Hohmann, D. Hymon, V. de Jesus, H. Jonker, H. Keller, B. Knezic, T. Landgraf, F. Löhr, L. Luo, K. R. Mertinkus, C. Muhs, M. Novakovic, A. Oxenfarth, M. Palomino-Schätzlein, K. Petzold, S. A. Peter, D. J. Pyper, N. S. Qureshi, M. Riad, C. Richter, K. Saxena, T. Schamber, T. Scherf, J. Schlagnitweit, A. Schlundt, R. Schnieders, H. Schwalbe, A. Simba-Lahuasi, S. Sreeramulu, E. Stirnal, A. Sudakov, J. N. Tants, B. S. Tolbert, J. Vögele, L. Weiß, J. Wirmer-Bartoschek, M. A. Wirtz Martin, J. Wöhnert and H. Zetzsche, Nucleic Acids Res., 2020, 48, 12415–12435 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Berg, M. A. W. Martin, N. Altincekic, I. Alshamleh, J. K. Bains, J. Blechar, B. Ceylan, V. de Jesus, K. Dhamotharan, C. Fuks, S. L. Gande, B. Hargittay, K. F. Hohmann, M. T. Hutchison, S. M. Korn, R. Krishnathas, F. Kutz, V. Linhard, T. Matzel, N. Meiser, A. Niesteruk, D. J. Pyper, L. Schulte, S. Trucks, K. Azzaoui, M. J. J. Blommers, Y. Gadiya, R. Karki, A. Zaliani, P. Gribbon, M. da Silva Almeida, C. D. Anobom, A. L. Bula, M. Bütikofer, Í. P. Caruso, I. C. Felli, A. T. Da Poian, G. C. de Amorim, N. K. Fourkiotis, A. Gallo, D. Ghosh, F. Gomes-Neto, O. Gorbatyuk, B. Hao, V. Kurauskas, L. Lecoq, Y. Li, N. C. Mebus-Antunes, M. Mompeán, T. C. Neves-Martins, M. Ninot-Pedrosa, A. S. Pinheiro, L. Pontoriero, Y. Pustovalova, R. Riek, A. J. Robertson, M. J. A. Saad, M. Treviño, A. C. Tsika, F. C. L. Almeida, A. Bax, K. Henzler-Wildman, J. C. Hoch, K. Jaudzems, D. V. Laurents, J. Orts, R. Pierattelli, G. A. Spyroulias, E. Duchardt-Ferner, J. Ferner, B. Fürtig, M. Hengesbach, F. Löhr, N. Qureshi, C. Richter, K. Saxena, A. Schlundt, S. Sreeramulu, A. Wacker, J. E. Weigand, J. Wirmer-Bartoschek, J. Wöhnert and H. Schwalbe, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61(46), e202205858 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zafferani, C. Haddad, L. Luo, J. Davila-Calderon, L. Y. Chiu, C. S. Mugisha, A. G. Monaghan, A. A. Kennedy, J. D. Yesselman, R. J. Gifford, A. W. Tai, S. B. Kutluay, M. L. Li, G. Brewer, B. S. Tolbert and A. E. Hargrove, Sci. Adv., 2021, 7, 1–15 Search PubMed.
- S. Sreeramulu, C. Richter, H. Berg, M. A. W. Martin, B. Ceylan, T. Matzel, J. Adam, N. Altincekic, K. Azzaoui, J. K. Bains, M. J. J. Blommers, J. Ferner, B. Fürtig, M. Göbel, J. T. Grün, M. Hengesbach, K. F. Hohmann, D. Hymon, B. Knezic, J. N. Martins, K. R. Mertinkus, A. Niesteruk, S. A. Peter, D. J. Pyper, N. S. Qureshi, U. Scheffer, A. Schlundt, R. Schnieders, E. Stirnal, A. Sudakov, A. Tröster, J. Vögele, A. Wacker, J. E. Weigand, J. Wirmer-Bartoschek, J. Wöhnert and H. Schwalbe, Angew. Chem., 2021, 60, 19191–19200 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Berg, M. A. Wirtz Martin, A. Niesteruk, C. Richter, S. Sreeramulu and H. Schwalbe, J. Visualized Exp., 2021, 172, e62262 Search PubMed.
- S. L. Wicks, B. S. Morgan, A. W. Wilson and A. E. Hargrove, Probing Bioactive Chemical Space to Discover RNA-Targeted Small Molecules, bioRxiv, 2023, preprint, DOI:10.1101/2023.07.31.551350.
- J. Vögele, J. P. Ferner, N. Altincekic, J. K. Bains, B. Ceylan, B. Fürtig, J. T. Grün, M. Hengesbach, K. F. Hohmann, D. Hymon, B. Knezic, F. Löhr, S. A. Peter, D. Pyper, N. S. Qureshi, C. Richter, A. Schlundt, H. Schwalbe, E. Stirnal, A. Sudakov, A. Wacker, J. E. Weigand, J. Wirmer-Bartoschek, J. Wöhnert and E. Duchardt-Ferner, Biomol. NMR Assignments, 2021, 15, 335–340 Search PubMed.
- S. Sreeramulu, C. Richter, T. Kuehn, K. Azzaoui, M. J. J. Blommers, R. Del Conte, M. Fragai, N. Trieloff, P. Schmieder, M. Nazaré, E. Specker, V. Ivanov, H. Oschkinat, L. Banci and H. Schwalbe, J. Biomol. NMR, 2020, 74, 555–563 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Binas, V. de Jesus, T. Landgraf, A. E. Völklein, J. Martins, D. Hymon, J. Kaur Bains, H. Berg, T. Biedenbänder, B. Fürtig, S. L. Gande, A. Niesteruk, A. Oxenfarth, N. S. Qureshi, T. Schamber, R. Schnieders, A. Tröster, A. Wacker, J. Wirmer-Bartoschek, M. A. W. Martin, E. Stirnal, K. Azzaoui, C. Richter, S. Sreeramulu, M. J. J. Blommers and H. Schwalbe, ChemBioChem, 2021, 22, 423–433 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Dalvit, P. E. Fagerness, D. T. A. Hadden, R. W. Sarver and B. J. Stockman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 7696–7703 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mayer and B. Meyer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 1999, 38, 1784–1788 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mayer and T. James, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 13376–13377 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Kupče, R. Freeman and B. K. John, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 9606–9607 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Schürer, K. Lang, J. Schuster and M. Mörl, Nucleic Acids Res., 2002, 30(12), e56 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Y. Carr and E. M. Purcell, Phys. Rev., 1954, 94, 630–638 Search PubMed.
- S. Meiboom and D. Gill, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1958, 29, 688–691 Search PubMed.
- T. Hwang and A. Shaka, J. Magn. Reson., 1995, 112, 275–279 CrossRef CAS.
- B. D. Nguyen, X. Meng, K. J. Donovan and A. J. Shaka, J. Magn. Reson., 2007, 184, 263–274 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Kovacs and Ē. Kupče, Magn. Reson. Chem., 2016, 544–560 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pellecchia, I. Bertini, D. Cowburn, C. Dalvit, E. Giralt, W. Jahnke, T. L. James, S. W. Homans, H. Kessler, C. Luchinat, B. Meyer, H. Oschkinat, J. Peng, H. Schwalbe and G. Siegal, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2008, 7, 738–745 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. N. Patwardhan, L. R. Ganser, G. J. Kapral, C. S. Eubanks, J. Lee, B. Sathyamoorthy, H. M. Al-Hashimi and A. E. Hargrove, MedChemComm, 2017, 8(5), 1022–1036 RSC.
- N. N. Patwardhan, Z. Cai, A. Umuhire Juru and A. E. Hargrove, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17(42), 9313–9320 RSC.
- I. Jarmoskaite, I. Alsadhan, P. P. Vaidyanathan and D. Herschlag, eLife, 2020, 9, 1–34 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3md00322a |
| ‡ The two authors are joint first authors. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |