DOI:
10.1039/C9RA10169A
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2020,
10, 3775-3788
Catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate with manganese cobaltite nanoparticles for the degradation of organic dyes†
Received
4th December 2019
, Accepted 9th January 2020
First published on 22nd January 2020
Abstract
In this work, we report the facile hydrothermal synthesis of manganese cobaltite nanoparticles (MnCo2O4.5 NPs) which can efficiently activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for the generation of sulfate free radicals (SO4˙−) and degradation of organic dyes. The synthesized MnCo2O4.5 NPs have a polyhedral morphology with cubic spinel structure, homogeneously distributed Mn, Co, and O elements, and an average size less than 50 nm. As demonstrated, MnCo2O4.5 NPs showed the highest catalytic activity among all tested catalysts (MnO2, CoO) and outperformed other spinel-based catalysts for Methylene Blue (MB) degradation. The MB degradation efficiency reached 100% after 25 min of reaction under initial conditions of 500 mg L−1 Oxone, 20 mg L−1 MnCo2O4.5, 20 mg L−1 MB, unadjusted pH, and T = 25 °C. MnCo2O4.5 NPs showed a great catalytic activity in a wide pH range (3.5–11), catalyst dose (10–60 mg L−1), Oxone concentration (300–1500 mg L−1), MB concentration (5–40 mg L−1), and temperature (25–55 °C). HCO3−, CO32− and particularly Cl− coexisting anions were found to inhibit the catalytic activity of MnCo2O4.5 NPs. Radical quenching experiments revealed that sulfate radicals are primarily responsible for MB degradation. A reaction sequence for the catalytic activation of PMS was proposed. The as-prepared MnCo2O4.5 NPs could be reused for at least three consecutive cycles with small deterioration in their performance due to low metal leaching. This study suggests a facile route for synthesizing MnCo2O4.5 NPs with high catalytic activity for PMS activation and efficient degradation of organic dyes.
1. Introduction
Organic dyes are universally found in the wastewater of paint, printing and textile industries. Their high solubility, low biodegradability, and toxicity cause severe environmental pollution and threaten human health. To deal with these problems, many different methods have been exploited for the removal and degradation of organic dyes, and it is found that advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) are very promising due to their high efficiency. During traditional AOPs such as Fenton's reagent, photo-Fenton, electro-Fenton, ozonation, and UV/TiO2 treatment, the highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (·OH, reduction potential E0 = 2.8 V) are in situ generated and unselectively oxidize organic contaminants to smaller and less harmful molecules.1 Nevertheless, classic AOPs have intrinsic limitations for practical applications such as sludge generation, strong pH-dependent efficiency, and cost ineffectiveness. Recently, sulfate free radicals (SO4˙−) have been attracting increasing attention due to its advantages such as stronger oxidity (E0 = 2.5–3.1 V), longer half-life (30–40 μs, vs. 10−3 μs for ·OH), higher selectivity (to organic compounds), and the ability to work in a wide pH range.2 Ultimately, these lead to the acceleration of the degradation of dissolved organic pollutants and improvement of degradation yield. SO4˙− radicals are commonly generated from persulfate (PS) or peroxymonosulfate (PMS) through different activation methods using UV irradiation,3 heat,4 base,5 ultrasound,6 and catalyst.2,7 Differing from other methods, catalytic activation requires no high-energy input or sophisticated equipments and thus has great potential for practical applications. In addition, PMS has its own advantage as compared to PS for the generation of SO4˙−, thanks to its asymmetric molecular structure and large length of O–O bonds which greatly promote the activation process.2
The catalytic activation of PMS is mostly based on transition metals such as Fe, Mn, Ni, Co, Cu and Ag in the forms of homogeneous or heterogeneous catalysts.8 Although Co, Cu and Ag are excellent PMS activators, their relatively high toxicity (especially Co) and low abundance have hindered their practical uses. Moreover, the utilization of these transitional metals ions as homogeneous activators has several drawbacks such as difficult recovery of activators and secondary pollution. Compared to homogeneous activation, heterogeneous activators show excellent PMS activation capability, chemical stability, low solubility (less metal leaching), easy separation and reuse. Therefore, the development of efficient heterogeneous catalysts for PMS activation becomes a priority in many studies. So far, Co(II)-based heterogeneous catalysts such as CoFe2O4,9,10 CoMn2O4,11 CoxMn3−xO4,12 CoNi2O4, and CoCu2O4 have been extensively studied. Recently, Co(III)-based spinels with general formula MCo2Ox (M is transition metals) have been paid great attention due to their excellent electrochemical properties.13,14 For PMS activation, these compounds exhibit several key advantages such as high catalytic activity and low Co leachability in acidic environment (CuCo2O4 (ref. 15)). CoxMn3−xO4 showed greater catalytic performance than that of the component oxides (Co3O4 and Mn2O3), which indicates the synergistic effects of Co and Mn species.12 Therefore, exploring novel routes for the synthesis and catalytic performance of cobaltite in PMS activation is of great importance in environmental remediation.
In this work, manganese cobaltite nanoparticles (MnCo2O4.5 NPs) have been prepared by a combined hydrothermal treatment/annealing route and applied as a heterogeneous catalyst to activate PMS for the degradation of various synthetic dyes, with Methylene Blue (MB) selected as a model pollutant. Our main goals are to: (i) investigate the influence of initial reaction parameters (MB and Oxone concentration, catalyst dosage, pH, reaction temperature) and the presence of common co-existing anions on MB degradation; (ii) identify the major radical species, reaction pathways, and mechanism; (iii) assess the reusability of the catalyst. The crystal structure, morphology, chemical composition and oxidation states of the elements in MnCo2O4.5 NPs were investigated. The influence of various parameters on catalytic activity of MnCo2O4.5 NPs for PMS activation towards degradation of MB was studied. The mechanism for generating free radicals was investigated based on quenching experiments. We also evaluated the capability of MnCo2O4.5 NPs as heterogeneous catalyst for the treatment of textile wastewater and landfill leachate.
2. Experiments
2.1. Chemicals
Manganese chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O), urea ((NH2)2CO), manganese(IV) oxide (MnO2), cobalt(II) oxide (CoO), Oxone (KHSO5·0.5KHSO4·0.5K2SO4), ethanol (C2H5OH, 99.5%), Methylene Blue (MB), Rhodamine B (RhB), Orange G (OG), and Methyl Orange (MO) were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Bio-Chem Technology Co., Ltd. All the reagents were used without further purification.
2.2. Synthesis of MnCo2O4.5
MnCo2O4.5 nanomaterials were synthesized by hydrothermal method using Mn2+, Co2+ chloride salts and urea as precursors. Typically, MnCl2·4H2O (5 mmol), CoCl2·6H2O (10 mmol) and urea (0.9 g) were dissolved in 75 mL DI H2O and magnetically stirred for 30 min, then transferred to a Teflon-lined autoclave and maintained at 120 °C for 6 h. In this condition, urea is hydrolyzed and decomposed into ammonia and carbon dioxide, which also undergo immediate hydrolysis to generate carbonate and hydroxyl anions. They combine with Mn2+ and Co2+ cations to form metal(II) hydroxycarbonates. The reactions involved in the hydrothermal treatment can be described by the following equations:
| CO(NH2)2 + H2O → 2NH3 + CO2 |
| M2+ + 2OH− + CO32− → M2(OH)2CO3 (M = Mn, Co) |
The resulting mixed metal hydroxycarbonates was washed with distilled water and ethanol several times, and dried at 60 °C for 12 h. Finally, the obtained pink powder was annealed in air at 400 °C for 2 h, during which the following reaction occurs:
| 2Mn2(OH)2CO3 + 4Co2(OH)2CO3 + 3O2 → 4MnCo2O4.5 + 6CO2 + 6H2O |
The as-synthesized MnCo2O4.5 sample was obtained in the blackish and powdery form.
2.3. Characterization of MnCo2O4.5
The as-synthesized MnCo2O4.5 sample was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD; Siemens D5005 X-ray diffractometer; Cu-Kα radiation, λ = 1.5418 Å; voltage/current 30 kV/40 mA; scan rate 0.9°/min; scan step 0.03°; 2θ from 10 to 70°), scanning electron microscopy (SEM; Hitachi S4800 field-emission scanning electron microscope), scanning TEM (STEM; JEOL JEM-ARM200F microscope; high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) detector; voltage 200 kV; spherical aberration corrector; nominal resolution 0.8 Å), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS; Shimadzu Kratos AXIS-ULTRA DLD; monochromated Al Kα radiation). The average crystallite size of MnCo2O4.5 particles was calculated using Scherrer equation:16| |
d = k × λ/(β × cos![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) θ) θ)
| (1) |
where λ is the wavelength of Cu Kα irradiation, λ = 1.5418 Å, β is the full width at maximal half (FWHM), θ is Bragg diffraction angle (peak position), and k = 0.9.
2.4. Catalysis studies
The catalytic activity of MnCo2O4.5 NPs for PMS activation was evaluated through the degradation of organic dyes in batch experiments. We first prepared the stock suspension/solutions of MnCo2O4.5 NPs, MB, and Oxone (1000, 100, and 5000 mg L−1, respectively) by dispersing pre-weighted amount of respective materials in deionized (DI) water using volumetric flasks. The calculated concentration of PMS (KHSO5, M = 152.2) in the Oxone stock solution is 2475.76 mg L−1. In a typical experiment, a known volume of catalyst suspension was introduced into a 5 mL volumetric flask containing a predetermined volume of MB solution and stirred for 30 min to reach adsorption equilibrium. Then, a known volume of Oxone solution was added to the above solution and shaken to commence the catalytic activation for dye degradation. Immediately after adding Oxone, the resulting solution was mixed well and transferred to a cuvette for UV-Vis measurement (ca. 4 mL), with the reference solution containing MnCo2O4.5 and Oxone of the same concentrations with those of the studied samples (without the presence of MB). The MB degradation by Oxone in the absence of MnCo2O4.5 catalyst was also performed using the same concentration of MB (20 mg L−1) and Oxone (500 mg L−1), employing a 500 mg L−1 Oxone solution as a reference. When necessary, initial solution pH was adjusted by adding 10 mM NaOH or 10 mM HNO3 solution. At various time intervals, the remaining concentration of MB was calculated according to UV-Vis data (Biochrom SP60, optical absorbance at 664 nm) and Beer–Lambert law. The degradation efficiency of MB (γ) was calculated using the formula:| | |
γ (%) = (Co − Ct) × 100/Co
| (2) |
where Co is the initial concentration and Ct is the real-time concentration of MB. The term γΔt indicates the degradation efficiency of MB obtained after Δt min of treatment. The investigated experimental parameters were catalyst dose (10, 20, 30, 40, and 60 mg L−1), Oxone concentration (100, 300, 500, 700, 1000, and 1500 mg L−1), MB concentration (5, 10, 15, 20, 30, and 40 mg L−1), temperature (25, 35, 45, and 55 °C), initial solution pH (3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0, 11.0, and 12.5), type of dye (RhB, MO, OG, and MB), reaction sequence, co-existing anions (Cl−, HCO3−, CO32−, NO3−), type of oxidant (PS, PMS, and H2O2). In the experiment to investigate the influence of temperature, the radical-generating reactions were stopped by quickly adding 0.2 mL of Na2SO3 0.1 M and the catalyst NPs were removed by centrifugation. The influence of different coexisting anions on MB degradation was investigated by using their corresponding sodium salts at concentration of 0–20 mM. Quenching tests were performed by adding a predetermined amount of quencher into MB solution before adding Oxone. In this work, tert-butyl alcohol (TBA), ethanol (EtOH), and phenol have been employed as quenchers. Cycling tests were carried out by centrifugation, washed with double distilled water and EtOH till neutral, dried at 60 °C, then re-used. The concentration of possibly leached Mn and Co ionic species was quantified using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS, PerkinElmer NexION® 2000).
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Synthesis and characteristics of the as-prepared MnCo2O4.5 NPs
The catalyst was synthesized in two steps, as illustrated in Fig. 1a. In the first step, an aqueous solution containing Mn2+, Co2+, and urea is hydrothermally treated to form a pink precursor. In the second step, the precursor is annealed to get the final black solid. Its major XRD peaks (Fig. 1b) occurring at 18.6, 31.4, 36.7, 44.3, 59.1 and 64.6° are well indexed to (111), (220), (311), (422), (511) and (440) planes of MnCo2O4.5 (JCPDS #32-0297), correspondingly. This material possesses cubic spinel structure and space group Fd![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m (227), with Mn ions occupying octahedral sites, and Co ions occupying both octahedral and tetragonal sites, as shown in Fig. 1c. In the FT-IR spectrum (Fig. 1d), the wide and weak bands observed at 3347.2 and 1633.3 cm−1 are respectively associated with –OH stretching and bending vibrations of adsorbed water molecules. The sharp and strong peaks observed at 652.8 and 547.2 cm−1 correspond to stretching vibrations of metal–oxygen bondings at tetrahedral and octahedral sites.17 The peak occurred at 1118.1 cm−1 indicates the presence of C–O bondings, possibly due to the presence of adventitious carbon species. TG curve of the catalyst (Fig. 1e) displays two major events of the weight loss, which represent the dehydration and deoxygenation of the catalyst, respectively. The percentages of both weight losses were only 1.2 and 0.8%, indicating the high thermal stability of the material.
m (227), with Mn ions occupying octahedral sites, and Co ions occupying both octahedral and tetragonal sites, as shown in Fig. 1c. In the FT-IR spectrum (Fig. 1d), the wide and weak bands observed at 3347.2 and 1633.3 cm−1 are respectively associated with –OH stretching and bending vibrations of adsorbed water molecules. The sharp and strong peaks observed at 652.8 and 547.2 cm−1 correspond to stretching vibrations of metal–oxygen bondings at tetrahedral and octahedral sites.17 The peak occurred at 1118.1 cm−1 indicates the presence of C–O bondings, possibly due to the presence of adventitious carbon species. TG curve of the catalyst (Fig. 1e) displays two major events of the weight loss, which represent the dehydration and deoxygenation of the catalyst, respectively. The percentages of both weight losses were only 1.2 and 0.8%, indicating the high thermal stability of the material.
 |
| | Fig. 1 (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation method for MnCo2O4.5 catalyst; (b) XRD patterns; (c) structural model; (d) FT-IR spectrum; and (e) TG curve of MnCo2O4.5 NPs. | |
The morphology and structure of the catalyst were studied using SEM and STEM. As shown in Fig. 2a and b, the MnCo2O4.5 catalyst consists of polyhedral nanoparticles (NPs) with an average size less than 50 nm. These MnCo2O4.5 NPs are composed of Mn, Co, and O elements, as confirmed by STEM-HAADF image and EDS elemental mappings (Fig. 2b). These elements are homogeneously distributed throughout all NPs, indicating that the manganese cobaltite has been successfully formed. To identify the oxidation state of these elements, XPS analyses were performed. The presence of Mn, Co, and O in MnCo2O4.5 NPs is well confirmed in the XPS survey spectra (Fig. 2c), in which C peak is due to adventitious carbon contamination. The XPS core-level spectra of Mn 2p, Co 2p, and O 1s were calibrated using C 1s line as reference, background subtracted, deconvoluted and fitted by Gaussian method. The deconvoluted Mn 2p spectrum (Fig. 2d) showed four peaks, which can be ascribed to spin–orbit characteristics of Mn3+ (655.3 and 642.9 eV) and Mn2+ (653.4 and 641.0 eV),18 respectively. The spin–orbit splitting of Mn 2p was observed to be 11.7 eV. Fig. 2e shows that the XPS Co 2p spectrum is deconvoluted into Co2+ (796.2 and 780.4 eV), Co3+ (794.1 and 779.3 eV), and shake-up satellites peaks of Co (804.6 and 789 eV).19 The deconvoluted O 1s spectrum (Fig. 2f) showed O species in the metal–oxygen bonding (529.3 eV) and in surface defect sites (531 eV).20 The presence of Mn2+, Mn3+, Co2+, Co3+, and O species on the surface of MnCo2O4.5 NPs clearly indicates that MnCo2O4.5 NPs have been successfully formed using our synthetic route.
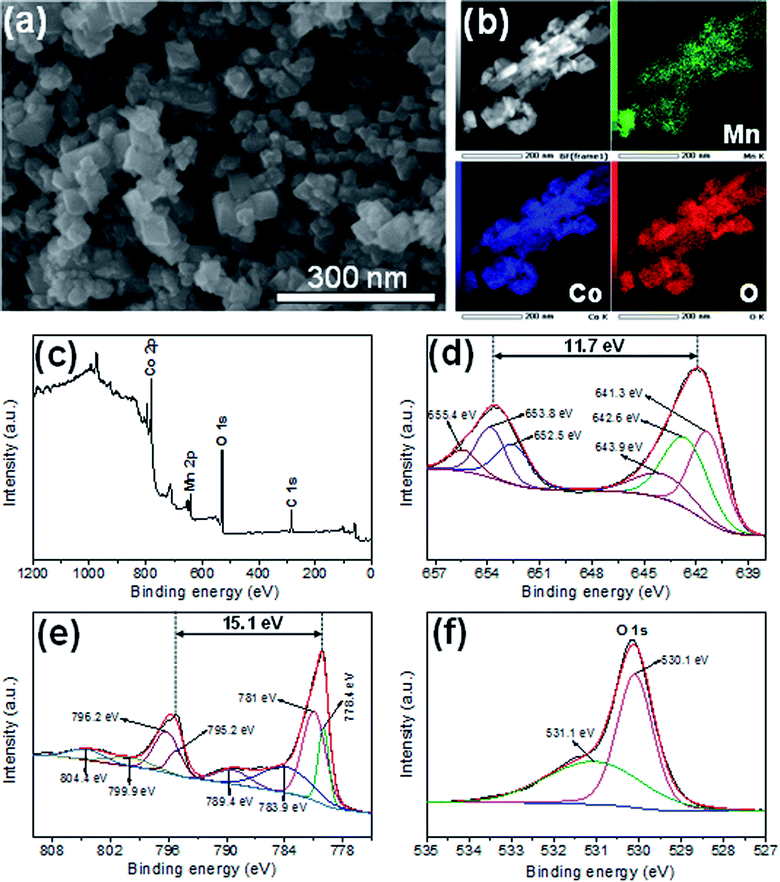 |
| | Fig. 2 (a) SEM image; (b) dark-field image and elemental mapping; XPS survey (c) and high-resolution spectra for Mn 2p (d); Co 2p (e); and O 1s (f). | |
3.2. Performance evaluation
3.2.1. Comparison of related catalysts. We firstly investigated MB degradation in the presence of various catalyst samples without pH adjustment, and the results are shown in Fig. 3a. When only MnCo2O4.5 was present, the degradation efficiency was very low (γ20 = 5.2%), indicating that the degradation of MB by this catalyst itself was low in the absence of PMS. When PMS was used alone, the MB degradation proceeded more considerably, with γ20 reached 10.9%. The combination of PMS with commercially available MnO2 and CoO bulky powders resulted in a γ20 of 25.8% and 25.3%, correspondingly. The homogeneous Mn2+/PMS system gave a γ20 of only 22.9%, slightly lower than that of MnO2, indicating that Mn2+ cations are weak catalysts for PMS activation. The homogeneous Co2+ (at a very small concentration of 0.4 mg L−1) displayed a high γ20 of 44.0%, as well documented in literatures.2,7 When MnCo2O4.5 NPs were used, 96.7% of MB had been degradated after only 20 min. These comparisons show that MnCo2O4.5 catalyst performed better than its oxide components (commercial MnO2 and CoO powder) and homogeneous Mn2+. The excellent catalytic performance of MnCo2O4.5 NPs might originate from several aspects, namely (i) their small particle size (as observed by TEM) and a high density of surface hydroxyl groups (as characterized by FTIR), and (ii) synergistic coupling of Mn–Co as previously observed and proposed for Mn–Fe,21 Cu–Fe,22 and Fe–Co.23
 |
| | Fig. 3 (a) MB degradation in different comparison experiments. (b) UV-Vis spectra and (c) digital photos of MnCo2O4.5/PMS/MB solution taken at different durations. Initial concentrations: [MB]0 = 20 mg L−1, [Oxone]0 = 500 mg L−1, [MnCo2O4.5]0 = 20 mg L−1, [MnO2]0 = 20 mg L−1, [Mn2+]0 = 20 mg L−1, [Co2+]0 = 0.4 mg L−1, [CoO]0 = 20 mg L−1, unadjusted pH, T = 25 °C. | |
3.2.2. Influence of catalyst dosage, initial Oxone and MB concentrations, and temperature. The influence of initial reaction parameters on MB degradation is shown in Fig. 4. As seen in Fig. 4a, the MB degradation proportionally increases with MnCo2O4.5 dosage. After 10 min of treatment, the MB degradation increased from 37.8 to 99.2% when MnCo2O4.5 dosage increased from 10 to 60 mg L−1. This indicates that MnCo2O4.5 catalyst can be implemented at high dosages upon necessity without losing its activity, which is attributed to its excellent dispersibility and stability. Fig. 4b shows MB degradation at different concentrations of Oxone. When Oxone concentration was increased from 100 to 300 mg L−1, the γ20 increased from 56.2% to 91.8% due to the increase of SO4˙− concentration. At higher concentrations of Oxone (500–1500 mg L−1), MB degradation was completed after 20 min. However, the MB degradation percentage increased very slowly with Oxone concentration, which might be caused by quenching reactions of redundant SO4˙− radicals (eqn (3)–(5)). The generation of SO5˙− radicals does not affect the degradation yield of MB since they are weak oxidants (E0 = 1.1 V)7,24| | |
SO4˙− + HSO5− → SO5˙− + HSO4−
| (3) |
| | |
SO4˙− + SO4˙− → S2O82−
| (4) |
| | |
HO˙ + HSO5− → SO5˙− + H2O
| (5) |
 |
| | Fig. 4 Influence of initial parameters on MB degradation in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system: (a) MnCo2O4.5 dosage; (b) Oxone concentration; (c) initial concentration of MB; and (d) temperature. Except for the examined parameter, other ones were fixed: [MB]0 = 20 mg L−1; [Oxone]0 = 500 mg L−1; [MnCo2O4.5]0 = 20 mg L−1; unadjusted pH; T = 25 °C. | |
The γ value is also influenced by initial concentration of MB, as shown in Fig. 4c. Generally, the γ value decreases with increasing MB concentration, because a higher concentration of PMS is required to degrade MB completely. At small concentrations (5, 10, and 15 mg L−1), high degradation percentage of 97.6, 95.1, and 97.6% was obtained after 8, 10, and 16 min of reaction, correspondingly. After 20 min, the γ of MB solutions having initial concentration of 20, 30, and 40 mg L−1 was 96.7, 85.2, and 69.2%, respectively. Herein, increasing MB concentration might limit the diffusion process to and from catalyst surface,21 therefore it required longer time for complete degradation of MB.25 This result shows that the MnCo2O4.5/PMS reaction system is capable of working in a vast range of dye concentration. It is well known that the reaction temperature has a great influence on the degradation of contaminants.7 The influence of reaction temperature on MB degradation was examined in the range of 25–55 °C. As seen in Fig. 4d, MB degradation was dramatically increased with increasing temperature. At 25, 35, 45, and 55 °C, the MB degradation reached 96.7% (20 min), 96.6% (14 min), 96.6% (8 min), and 91.5% (4 min), respectively. This result suggested that the generation of reactive radicals was promoted at high temperature.
3.2.3. Influence of initial solution pH. The pH value of natural and polluted water varies in a broad range, which might affect the generation of free radicals. Herein, we investigated the influence of initial solution pH (3.5–12.5) on MB degradation. We first examined the evolution of pH values of the reaction solution before and after catalysis tests. Without adjusting pH, mixing Oxone (pH ≈ 3.1–3.2) with MB solution (pH ≈ 7) and MnCo2O4.5 NPs resulted in a solution with a pH value of ca. 3.5. When the initial solution pH was adjusted to either acidic or neutral conditions (pH ≤ 7), the final solution was still acidic with pH < 4. The similar behavior was also observed in other catalyst systems such as Co3O4–Bi2O3/PMS, and mentioned as “buffering capacity”.26,27 The acidic pH of the post-reaction environment might be possibly caused by the decomposition of PMS and the reaction of SO4˙− with water (SO4˙− + H2O → SO42− + HO˙ + H+) and MB which produces additional protons and small acidic molecules such as formic, acetic or oxalic acids.28,29 However, when the initial solution pH was adjusted to more alkaline conditions (pH > 7), the buffering capacity of MnCo2O4.5/PMS system decreased, and at strongly alkaline conditions (pH ≥ 11), the MnCo2O4.5/PMS system completely lost its buffering capacity. In order to elucidate the pH dependence of MB degradation in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system, we investigated the surface charge of MnCo2O4.5 NPs as a function of solution pH. As shown in Fig. 5a, the point of zero charge (pHpzc) of as-synthesized MnCo2O4.5 NPs was 7.22, indicating that MnCo2O4.5 NPs is positively charged at pH < 7.22, and negatively charged at pH > 7.22. It is also known that H2SO5 acid has pKa1 < 0 (H2SO5 ↔ HSO5− + H+) and pKa2 ≈ 9.4 (HSO5− ↔ SO52− + H+).2 Therefore, PMS primarily exists as SO52− in a strong alkaline solution (pH > 9.4), as HSO5− in acidic, neutral and mild alkaline solutions (pH < 9.4), and as both HSO5− and SO52− at pH around 9.4.2,30–33
 |
| | Fig. 5 (a) The isoelectric point of MnCo2O4.5 NPs at different pH. (b) Influence of initial solution pH on MB degradation in MnCo2O4.5/PMS/MB system. Initial conditions: [MB]0 = 20 mg L−1; [Oxone]0 = 500 mg L−1; [MnCo2O4.5]0 = 20 mg L−1; T = 25 °C. | |
The influence of the initial solution pH on MB degradation is presented in Fig. 5b. As observed, the γ20 was highest in the range of pH from 4.5 to 7.0, where a nearly complete elimination of MB was achieved within ca. 14 min (96.4% at pH 4.5, 96.1% at pH 5.5, and 96.2% at pH 7.0). The high γ20 obtained in this pH range could be attributed to strong Coulomb attraction force between positively charged MnCo2O4.5 NPs and anionic species generated by PMS. This result is consistent with earlier judgements that the maximal efficiency in PMS activation is achieved in mild acidic and neutral solutions.34–36 The γ20 was declined in stronger acidic (pH = 3.5) or alkaline solutions (pH ≥ 8), possibly due to several following factors: In acidic pH, the formation of H-bond between H+ and the O–O groups of HSO5− becomes significant and thus hinders the interaction between HSO5− and positively charged catalyst surface.37 In alkaline pH, MnCo2O4.5 catalyst is negatively charged and repulsive to both HSO5− and SO52−. Moreover, SO4˙− radicals may combine with hydroxyl anions in alkaline environment to form the weaker oxidant, HO˙ (SO4˙− + HO− → SO42− + HO˙). The great efficiency of MnCo2O4.5/PMS system at neutral and mild acidic pH suggested that this process can be employed for the treatment of ground and surface waters. This process also offers more advantages in comparison with Fenton processes, which are workable only in relatively limited pH ranges.38
3.2.4. The degradation of different dyes. The versatility of MnCo2O4.5/PMS system was examined for the degradation of various types of dyes. As shown in Fig. 6a, the degradation decreased following the order of MO > OG > RhB > MB. Under the same initial conditions (Oxone 500 mg L−1, MnCo2O4.5 20 mg L−1, MB 20 mg L−1, unadjusted pH, T = 25 °C), the degradation efficiencies of MB, RhB, OG, and MO were 96.7% (after 20 min), 95.6% (after 16 min), 91.0% (after 10 min), and 96.3% (after 6 min), respectively. The difference in degradation yield of these four dyes was due to their differences in molecular structure (Fig. 6b) and degradation mechanism.39 The azo dyes (MO and OG) contain color centers (–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–), in which π-bondings are easily dissociated to form naphthalene ring.40 The xanthene dye (RhB) is disrupted through the degradation of its conjugated structure and subsequent N-demethylation.41 The degradation of the thiazine dye (MB) first occurred on aromatic ring-bonded nitrogen atoms due to the presence of electron-donating groups (–N(CH3)2).40 All of these organic dyes can be degraded in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system, indicating that this catalyst can be employed in a wide range of organic pollutant environments.
N–), in which π-bondings are easily dissociated to form naphthalene ring.40 The xanthene dye (RhB) is disrupted through the degradation of its conjugated structure and subsequent N-demethylation.41 The degradation of the thiazine dye (MB) first occurred on aromatic ring-bonded nitrogen atoms due to the presence of electron-donating groups (–N(CH3)2).40 All of these organic dyes can be degraded in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system, indicating that this catalyst can be employed in a wide range of organic pollutant environments.
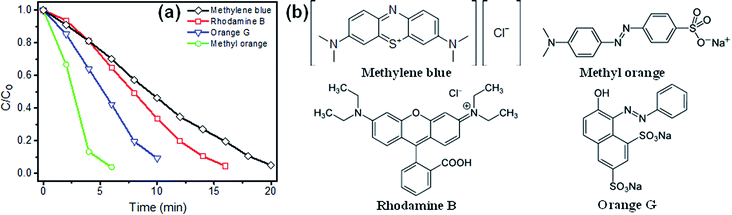 |
| | Fig. 6 (a) The degradation of different dyes by MnCo2O4.5/PMS system. Initial conditions: [dye]0 = 20 mg L−1; [Oxone]0 = 500 mg L−1; [MnCo2O4.5]0 = 20 mg L−1; T = 25 °C; unadjusted pH. (b) The molecular structure of MB, RhB, OG, and MO. | |
3.2.5. Influence of reaction sequence. The sequence of adding MB dye, MnCo2O4.5 catalyst, and Oxone into reaction flask (reaction sequence) might have an impact on the degradation yield. In this work, six possible reaction sequences were carefully examined (other initial conditions were same) and the obtained result is shown in Fig. S1.† As seen, the degradation obtained for these sequences were not significantly different. The MB–MnCo2O4.5–PMS sequence was selected for further experiments because of its high degradation efficiency and minimal self-decomposition of PMS caused by sonication.
3.2.6. Influence of coexisting anions. Real wastewater sources are commonly encountered with different coexisting anions (water matrix species) such as chloride (Cl−), nitrate (NO3−), bicarbonate (HCO3−) and carbonate (CO32−) at ppm concentration, and their presence might affect the degradation process. The influence of these anions (in the concentration range of 0–20 mM) has been investigated and the results are shown in Fig. 7.
 |
| | Fig. 7 Influence of different coexisting anions on MB degradation in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system. (a) Cl−; (b) HCO3−; (c) CO32−; (d) the degradation of MB in the presence of different coexisting anions at a concentration of 20 mM. (e) Comparison of γ20 in the presence of different coexisting anions at various concentrations. Initial conditions: [MB]0 = 20 mg L−1; [Oxone]0 = 500 mg L−1; [MnCo2O4.5]0 = 20 mg L−1; T = 25 °C; unadjusted pH. | |
As shown in Fig. 7a, the inhibition of MB degradation could be observed at a concentration of Cl− as low as 1 mM. The γ20 dramatically decreased from 95.8 to 35.2% when Cl− concentration was increased from 1 to 10 mM, but gradually decreased to 30.6 and 27.1 when Cl− concentration was subsequently increased to 15 and 20 mM, respectively. These results show that Cl− strongly inhibit SO4˙− free radicals, and the inhibition mechanism can be explained as following: SO4˙−/SO42− redox couple has higher reduction potential (E0 = 2.5 V) as compared to that of Cl2/2Cl− (E0 = 1.4 V) and HOCl/Cl− (E0 = 1.48 V). Therefore, SO4˙− can oxidize Cl− ions to form weaker oxidants such as Cl˙, ClOH˙−, and Cl2˙− as described by Table S1.† The influence of bicarbonate on MB degradation is shown in Fig. 7b. At a very low concentration of HCO3− (1 mM), MB seems to degrade more quickly. If HCO3− was employed at higher concentrations, MB degradation was retarded, which obviously demonstrated the inhibition role of HCO3− towards PMS. It is not clear why the γ20 increased from 74.3 to 78.5% when HCO3− concentration increased from 5 to 15 mM. However, at the highest concentration of HCO3− examined in this work (20 mM), the γ20 reached only 58.6%. The involved reactions between HCO3− and PMS are also represented in Table S1.† The influence of CO32− anions was relatively similar to that of HCO3− (Fig. 7c). In contrast, the presence of NO3− anions seemed not to affect MB degradation yield (Fig. S2†), indicating that free radicals were not inhibited by them. Fig. 7d compares the degradation of MB upon employing different coexisting anions at the same concentration (20 mM), and Fig. 7e visualizes the influence of different coexisting anions at various concentrations to the γ20 of MB. The γ20 was 96.7, 81.8, 58.6, and 27.1% for NO3−, CO32−, HCO3−, and Cl−, respectively. These results point out that the concentration of Cl−, HCO3−, and CO32− ions must be carefully controlled within allowed limitation before Oxone treatment for optimal performance.
3.2.7. Comparison of different oxidants (PMS, PS, and H2O2). In addition to PMS, PS and H2O2 are also employed as oxidants in AOPs.42 Herein we have compared the capability of MnCo2O4.5 NPs as a catalytic activator for these oxidants in MB degradation. As shown in Fig. 8, the γ20 of MnCo2O4.5/PMS, MnCo2O4·5/PS, and MnCo2O4.5/H2O2 systems was 96.7, 48.5, and 39.4%, correspondingly. The stronger oxidation power of the first two systems might be associated with the fact that O–O bonding energy in PMS and PS is smaller that of H2O2 (Table S2†), which makes the activation of PMS and PS easier in terms of energy. Although it is not clear why the degradation efficiency of PMS is higher than that of PS, one possible cause is the activation of PMS is more convenient due to its asymmetric structure.
 |
| | Fig. 8 Comparison of different oxidants on MB degradation using MnCo2O4.5 catalyst. Initial conditions: [MB]0 = 20 mg L−1; [oxidant]0 = 500 mg L−1; [MnCo2O4.5]0 = 20 mg L−1; T = 25 °C; unadjusted pH. | |
3.2.8. Identification of contribution of different radicals based on quenching experiments. In order to explore activation mechanism, it is necessary to find the dominant species which cause the activation of PMS. The heterogeneous activation of PMS, particularly by transition metal oxides, is known to be strongly associated with the generation of SO4˙−, HO˙ and SO5˙− free radicals.2 MB degradation due to SO5˙− can be neglected because the standard reduction potential of SO5˙− at neutral solution is only 1.1 V,15 much lower than that of SO4˙− and HO˙. In this work, the role of SO4˙− and HO˙ free radicals in MB degradation has been determined through quenching experiments using EtOH, phenol, and TBA quenchers. The rate constant of EtOH with HO˙ (1.2–2.8 × 109 M−1 s−1) is 36–75 times greater than that of SO4˙− (1.6–7.7 × 107 M−1 s−1).43 The rate constants of phenol with both HO˙− and SO4˙− are very high (6.6 × 109 and 8.8 × 109 M−1 s−1, correspondingly).44 The rate constant of TBA with HO˙ (3.8–7.6 × 108 M−1 s−1) is 835 to 950 times greater than that of SO4˙− (4.0–9.1 × 105 M−1 s−1). Therefore, EtOH and phenol have been employed as scavenger for both SO4˙− and HO˙ while TBA is scavenger for HO˙. Fig. 9 shows the influence of different quenchers on MB degradation in a wide range of quencher concentration (0–200 mM). Without any quenchers (EtOH, phenol and TBA), 96.7% MB was eliminated after 20 min. In the presence of quenchers (EtOH and TBA) of increasing concentration (0–200 mM), the MB degradation yield decreased to 85.2% and 87.3% in 20 min, correspondingly. Whereas, with the increase of phenol concentration from 0 to 100 mM, MB degradation yield decreased to 18.0% in 20 min. These results point out that sulfate and hydroxyl radicals are generated from MnCo2O4.5/PMS system, and sulfate radicals play a major role in MB degradation.
 |
| | Fig. 9 Influence of different radical scavengers on MB degradation in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system. (a) EtOH; (b) phenol; (c) TBA. Initial concentrations: [MB]0 = 20 mg L−1, [Oxone]0 = 500 mg L−1, [MnCo2O4.5]0 = 20 mg L−1, unadjusted pH, T = 25 °C. | |
3.2.9. Cobalt leaching test. Metal leaching is a major concern in heterogeneous catalysts because metallic species such as Co2+ have been known as excellent PMS activator.2,45 Our own experiment also demonstrated the excellent catalytic activity of Co2+ (Fig. 3a) therefore the leaching of cobalt from corresponding heterogeneous catalysts must be carefully taken into account. Our ICP-MS analysis showed that the leaching concentration (percentage) of Co2+ and Mn2+ after the first run was 1.669 and 0.467 mg L−1, respectively. The reported Co leaching concentration was 0.662 mg L−1 for CoFe2O4/TiO2,9 0.928 mg L−1 for CoFe2O4,9 1.167 mg L−1 for SrCoO3,29 2.45 mg L−1 for CoFe2O4/SBA-15,19 ca. 9.0 mg L−1 for Co-BTC46 and 9.8 mg L−1 for PrBaCo2O5+δ.47 Although the measured leached Co concentration in our work is acceptable as compared to previous reports, future efforts should be made in order to meet environmental standard for surface water. A potential solution is to grow MnCo2O4.5 NPs on a suitable support such as carbon nanotube, which can simultaneously improve catalytic performance and suppress leaching ions.
3.2.10. Proposed mechanism of PMS activation on MnCo2O4.5 NPs. Based on the above results and previous researches, a mechanism for PMS activation on MnCo2O4.5 NPs is proposed as following: In the presence of MnCo2O4.5 NPs, PMS is activated to form SO5˙− and SO4˙− radicals (eqn (6) and (8)). Subsequently, ·OH radicals are generated due to the reaction of SO5˙− and hydroxylated metallic sites (M3+–H3O+) (eqn (10) and (11)) or the reaction between SO4˙− and H2O or OH− (eqn (12) and (13)). The two latter equations could be also considered as the quenching reactions of SO4˙−.48 Mn2+ and Co3+ can be regenerated as described by eqn (7) and (9). The generated radicals attack dye molecules, open the aromatic rings and form intermediate products (mostly oxalic and small-weight carboxylic acids) which are ultimately mineralized into CO2, H2O and SO42− (eqn (15)).| | |
Co3+ + HSO5− → Co2+ + SO5˙− + H+
| (6) |
| | |
Co2+ + HSO5− → Co3+ + SO4˙− + OH−
| (7) |
| | |
Mn2+ + HSO5− → Mn3+ + SO4˙− + OH−
| (8) |
| | |
Mn3+ + HSO5− → Mn2+ + SO5˙− + H+
| (9) |
| | |
M3+ − H3O+ + SO5˙− → M3+ − ·OHOSO3 + H2O
| (10) |
| | |
M3+ − ·OHOSO3 + 2e− → M2+ + SO4˙− + ·OH
| (11) |
| | |
SO4˙− + H2O → ·OH + H+ + SO42−
| (12) |
| | |
SO4˙− + OH− → ·OH + SO42−
| (13) |
| | |
MB + SO4˙−/·OH → intermediate compounds → CO2 + H2O + SO42−
| (15) |
3.2.11. Comparison with other spinel catalysts. Table 1 compares the performance of several spinel-based catalysts/PMS systems for MB degradation. Our MnCo2O4.5/PMS system exhibited a high degradation efficiency of 96.7% after 20 min, and 100% after 25 min (data not shown here), while for other systems it usually requires 30–60 min to achieve 100% degradation of MB. In addition, the amount of MnCo2O4.5 catalyst employed in our experiments was 20 mg L−1, much smaller than that of previous studies (50–300 mg L−1). This comparison showed that the performance of MnCo2O4.5/PMS system is excellent and promising for practical applications in environmental remediation.
Table 1 Comparison of various spinel-based catalysts as PMS activator for MB degradation
| Catalyst |
Synthesis method |
Reaction conditions |
Performance |
Reference |
| Co3O4–Bi2O3 |
Co-precipitation |
[MB] = 7.5 mg L−1; [catalyst] = 50 mg L−1; [PMS] = 0.5 mM; pH = 3.4; T = 25 °C |
98% (10 min) Co leaching: 43 μg L−1 (acidic pH) and 31 μg L−1 (pH 7.0) |
49 |
| CoMoO4 |
Hydrothermal |
[MB] = 100 mg L−1; [catalyst] = 100 mg L−1; [Oxone] = 2 mM; unadjusted pH; T = 25 °C |
100% (40 min) |
50 |
| Fe3O4/Mn3O4/rGO |
Co-precipitation |
[MB] = 50 mg L−1; [catalyst] = 100 mg L−1; [Oxone] = 300 mg L−1; pH = 7.0; T = 25 °C |
98.8% (30 min) |
21 |
| Fe3O4@MnO2 |
Co-precipitation |
[MB] = 30 mg L−1; [catalyst] = 300 mg L−1; [PMS] = 20 mM; pH = 7.0; T = 25 °C |
99.8% (30 min) |
51 |
| CuFe2O4/AC |
Co-precipitation/calcination |
[MB] = 20 mg L−1; [catalyst] = 200 mg L−1; [PMS]/[dye] = 200 mg L−1; pH = 5.0; T = 25 °C |
100% (60 min) |
52 |
| MnCo2O4.5 |
Hydrothermal/calcination |
[MB] = 20 mg L−1; [MnCo2O4.5] = 20 mg L−1; [Oxone] = 500 mg L−1; T = 30 °C; pH = 3.5 |
96.7% (20 min); 100% (25 min) |
This work |
3.2.12. The reusability of as-prepared MnCo2O4.5 catalyst. The reusability and stability of MnCo2O4.5 catalyst are important aspects for practical applications, and were evaluated for three successive runs. After each run, MnCo2O4.5 NPs were washed with ethanol and redispersed for the next catalysis reaction. As observed in Fig. 10, MnCo2O4.5 NPs sustained an excellent γ20 of 89.9% at the third run, indicating its very good reusability and high stability.
 |
| | Fig. 10 MB degradation in three consecutive runs by MnCo2O4.5/PMS system. Initial conditions: [MB] = 20 mg L−1, [MnCo2O4.5] = 20 mg L−1, [Oxone] = 500 mg L−1, T = 25 °C, unadjusted pH. | |
3.2.13. Evaluation of COD removal efficiency for real wastewater treatment application. Real wastewater such as leachate or textile discharges is a complex environment contains a diverse range of organic compound at high concentration, and COD is a parameter of major concern when treating civilian and industrial discharges. Here the COD removal efficiency of MnCo2O4.5/PMS system was evaluated for three different sources: MB solution (20 mg L−1), textile wastewater, and leachate. The textile wastewater was collected at Hopex Textile Co., Ltd. in Hai Duong Province, Vietnam. Random leachate samples were collected at Quang Hanh co-disposal landfill in Quang Ninh Province, Vietnam. The results are presented in Fig. 11. The input COD of MB solution, textile wastewater, and leachate was determined to be 144, 416, and 339.2 mg L−1, respectively. After treatment with MnCo2O4.5/PMS system for 20 min, the measured output CD was 22.4, 54.4, and 169.6 mg L−1, correspondingly. The calculated COD removal efficiency for MB, textile wastewater, and leachate was 83.3, 86.9, and 50%, indicating dissolved organic matters have been significantly degraded in these systems. These results show that employing MnCo2O4.5 to activate PMS could be an alternative method to cope with real wastewaters.
 |
| | Fig. 11 COD removal efficiency of MnCo2O4.5/PMS system for different sources of contaminant. | |
4. Conclusions
In summary, well-crystallined, pure-phase spinel MnCo2O4.5 NPs are successfully synthesized via a new hydrothermal/calcination protocol. The synthesized MnCo2O4.5 NPs show the highest catalytic activity for PMS activation among all tested heterogeneous catalyst (MnO2, CoO) and outperform other spinel-based heterogeneous catalysts for dye degradation, which can be credited to its organic-free synthesis route and the synergy between Mn2+ and Co3+. The catalyst dosage, initial Oxone and MB concentrations, reaction temperature, initial solution pH, and coexisting anions are found to influence the degradation of MB. The presence of HCO3−, CO32− and particularly Cl− ions reduces the MB degradation rate, while NO3− ions do not inhibit the generation sulfate radicals. A complex mechanism for the activation of PMS is proposed, whereas the generation of SO4˙−, rather than ·OH, is primarily responsible for MB degradation. MnCo2O4.5 NPs can be separated, reused and displayed good catalytic performance after three consecutive cycles of use with small deterioration. This work thus suggests a promising route for the preparation of MnCo2O4.5 NPs with high catalytic activity for PMS activation for efficient degradation of organic dyes.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED).
References
- M. A. Oturan and J.-J. Aaron, Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: principles and applications. A review, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, 44, 2577–2641 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Ghanbari and M. Moradi, Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 310, 41–62 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sharma, I. Mishra, D. D. Dionysiou and V. Kumar, Oxidative removal of Bisphenol A by UV-C/peroxymonosulfate (PMS): kinetics, influence of co-existing chemicals and degradation pathway, Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 276, 193–204 CrossRef CAS.
- R. H. Waldemer, P. G. Tratnyek, R. L. Johnson and J. T. Nurmi, Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by heat-activated persulfate: kinetics and products, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2007, 41, 1010–1015 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Qi, X. Liu, J. Ma, C. Lin, X. Li and H. Zhang, Activation of peroxymonosulfate by base: implications for the degradation of organic pollutants, Chemosphere, 2016, 151, 280–288 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Su, W. Guo, C. Yi, Y. Leng and Z. Ma, Degradation of amoxicillin in aqueous solution using sulphate radicals under ultrasound irradiation, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2012, 19, 469–474 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang and S. Wang, Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 334, 1502–1517 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Deng, C. Ya, Y. Ge, Y. Cheng, Y. Chen, M. Xu and H. Wang, Activation of peroxymonosulfate by metal (Fe, Mn, Cu and Ni) doping ordered mesoporous Co3O4 for the degradation of enrofloxacin, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 2338–2349 RSC.
- Y. Du, W. Ma, P. Liu, B. Zou and J. Ma, Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on titanate nanotubes (CoFe2O4/TNTs) as a novel heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of organic pollutants, J. Hazard Mater., 2016, 308, 58–66 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Tabit, O. Amadine, Y. Essamlali, K. Dânoun, A. Rhihil and M. Zahouily, Magnetic CoFe2O4 nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide (CoFe2O4/GO) with high catalytic activity for peroxymonosulfate activation and degradation of rhodamine B, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 1351–1360 RSC.
- C.-X. Li, C.-B. Chen, J.-Y. Lu, S. Cui, J. Li, H.-Q. Liu, W.-W. Li and F. Zhang, Metal organic framework-derived CoMn2O4 catalyst for heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate and sulfanilamide degradation, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 337, 101–109 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yao, Y. Cai, G. Wu, F. Wei, X. Li, H. Chen and S. Wang, Sulfate radicals induced from peroxymonosulfate by cobalt manganese oxides (CoxMn3−xO4) for Fenton-like reaction in water, J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 296, 128–137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Shakir, M. Sarfraz, U. A. Rana, M. Nadeem and M. A. Al-Shaikh, Synthesis of hierarchical porous spinel nickel cobaltite nanoflakes for high performance electrochemical energy storage supercapacitors, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 21386–21389 RSC.
- M. G. Bellino, J. G. Sacanell, D. G. Lamas, A. G. Leyva and N. E. Walsöe de Reca, High-performance solid-oxide fuel cell cathodes based on cobaltite nanotubes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3066–3067 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Feng, J. Liu, D. Wu, Z. Zhou, Y. Deng, T. Zhang and K. Shih, Efficient degradation of sulfamethazine with CuCo2O4 spinel nanocatalysts for peroxymonosulfate activation, Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 280, 514–524 CrossRef CAS.
- T. V. Thu and S. Maenosono, Synthesis of high-quality Al-doped ZnO nanoink, J. Appl. Phys., 2010, 107, 014308 CrossRef.
- N. Padmanathan and S. J. I. Selladurai, Mesoporous MnCo2O4 spinel oxide nanostructure synthesized by solvothermal technique for supercapacitor, Ionics, 2014, 20, 479–487 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Liao, X. Han, Y. Zhang, C. Xu and H. Chen, Solvothermal synthesis of porous MnCo2O4.5 spindle-like microstructures as high-performance electrode materials for supercapacitors, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44, 22622–22631 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Yunyun, L. Xu, Z. Wankun, Z. Yuxuan, Y. Yunhan, Q. Honglin, X. Xuetang and W. Fan, Spinel CoMn2O4 nanosheet arrays grown on nickel foam for high-performance supercapacitor electrode, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 357, 2013–2021 CrossRef.
- J. F. Marco, J. R. Gancedo, M. Gracia, J. L. Gautier, E. Ríos and F. J. Berry, Characterization of the Nickel Cobaltite, NiCo2O4, Prepared by Several Methods: An XRD, XANES, EXAFS, and XPS Study, J. Solid State Chem., 2000, 153, 74–81 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Yang, Z. Tian, B. Wang, Z. Sun, L. Zhang, Y. Guo, H. Li and S. Yan, Facile synthesis of Fe3O4/hierarchical-Mn3O4/graphene oxide as a synergistic catalyst for activation of peroxymonosulfate for degradation of organic pollutants, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 20674–20683 RSC.
- W.-D. Oh, Z. Dong, Z.-T. Hu and T.-T. Lim, A novel quasi-cubic CuFe2O4–Fe2O3 catalyst prepared at low temperature for enhanced oxidation of bisphenol A via peroxymonosulfate activation, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 22208–22217 RSC.
- H. Wang, C. Wang, J. Qi, Y. Yan, M. Zhang, X. Yan, X. Sun, L. Wang and J. J. N. Li, Spiderweb-Like Fe-Co Prussian Blue Analogue Nanofibers as Efficient Catalyst for Bisphenol-A Degradation by Activating, Peroxymonosulfate, 2019, 9, 402 CAS.
- W.-D. Oh, Z. Dong and T.-T. Lim, Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: current development, challenges and prospects, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 194, 169–201 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Gong, F. Chen, Q. Yang, K. Luo, F. Yao, S. Wang, X. Wang, J. Wu, X. Li and D. Wang, Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by Fe-Co layered doubled hydroxide for efficient catalytic degradation of Rhoadmine B, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 321, 222–232 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Hu, G. Zhang, M. Liu, Q. Wang and P. Wang, Enhanced degradation of bisphenol A (BPA) by peroxymonosulfate with Co3O4-Bi2O3 catalyst activation: effects of pH, inorganic anions, and water matrix, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 338, 300–310 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-H. Guan, J. Ma, Y.-M. Ren, Y.-L. Liu, J.-Y. Xiao, L.-q. Lin and C. Zhang, Efficient degradation of atrazine by magnetic porous copper ferrite catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation via the formation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals, Water Res., 2013, 47, 5431–5438 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Li, Z. Wang, B. Zhang, A. I. Rykov, M. A. Ahmed and J. Wang, FexCo3−xO4 nanocages derived from nanoscale metal–organic frameworks for removal of bisphenol A by activation of peroxymonosulfate, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 181, 788–799 CrossRef CAS.
- S. B. Hammouda, F. Zhao, Z. Safaei, V. Srivastava, D. L. Ramasamy, S. Iftekhar and M. Sillanpää, Degradation and mineralization of phenol in aqueous medium by heterogeneous monopersulfate activation on nanostructured cobalt based-perovskite catalysts ACoO3 (A= La, Ba, Sr and Ce): characterization, kinetics and mechanism study, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 215, 60–73 CrossRef.
- Y.-H. Guan, J. Ma, Y.-M. Ren, Y.-L. Liu, J.-Y. Xiao, L.-q. Lin and C. Zhang, Efficient degradation of atrazine by magnetic porous copper ferrite catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation via the formation of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals, Water Res., 2013, 47, 5431–5438 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Nie, J. Huang, Y. Hu, Y. Ding, X. Han and H. Tang, Heterogeneous catalytic activation of peroxymonosulfate for efficient degradation of organic pollutants by magnetic Cu0/Fe3O4 submicron composites, Chin. J. Catal., 2017, 38, 227–239 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Hu, G. Zhang, M. Liu, Q. Wang and P. Wang, Enhanced degradation of Bisphenol A (BPA) by peroxymonosulfate with Co3O4-Bi2O3 catalyst activation: Effects of pH, inorganic anions, and water matrix, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 338, 300–310 CrossRef CAS.
- S. K. Rani, D. Easwaramoorthy, I. M. Bilal and M. Palanichamy, Studies on Mn (II)-catalyzed oxidation of α-amino acids by peroxomonosulphate in alkaline medium-deamination and decarboxylation: a kinetic approach, Appl. Catal., A, 2009, 369, 1–7 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Wu, H. Li, X. Li, H. He and C. Yang, Performances and mechanisms of efficient degradation of atrazine using peroxymonosulfate and ferrate as oxidants, Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 353, 533–541 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ji, C. Dong, D. Kong and J. Lu, New insights into atrazine degradation by cobalt catalyzed peroxymonosulfate oxidation: kinetics, reaction products and transformation mechanisms, J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 285, 491–500 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Zhang, H. Zhu and J.-P. Croueé, Production of sulfate radical from peroxymonosulfate induced by a magnetically separable CuFe2O4 spinel in water: efficiency, stability, and mechanism, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 2784–2791 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Zhang, H. Zhu and J.-P. Croue, Production of sulfate radical from peroxymonosulfate induced by a magnetically separable CuFe2O4 spinel in water: efficiency, stability, and mechanism, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 2784–2791 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. V. Nidheesh, R. Gandhimathi and S. T. Ramesh, Degradation of dyes from aqueous solution by Fenton processes: a review, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2013, 20, 2099–2132 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yao, Y. Cai, F. Lu, F. Wei, X. Wang and S. Wang, Magnetic recoverable MnFe2O4 and MnFe2O4-graphene hybrid as heterogeneous catalysts of peroxymonosulfate activation for efficient degradation of aqueous organic pollutants, J. Hazard Mater., 2014, 270, 61–70 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhao, C. Niu, L. Zhang, H. Guo, X. Wen, C. Liang and G. Zeng, Co-Mn layered double hydroxide as an effective heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of organic dyes by activation of peroxymonosulfate, Chemosphere, 2018, 204, 11–21 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Hisaindee, M. Meetani and M. Rauf, Application of LC-MS to the analysis of advanced oxidation process (AOP) degradation of dye products and reaction mechanisms, Trac. Trends Anal. Chem., 2013, 49, 31–44 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Yang, P. Wang, X. Yang, L. Shan, W. Zhang, X. Shao and R. Niu, Degradation efficiencies of azo dye Acid Orange 7 by the interaction of heat, UV and anions with common oxidants: persulfate, peroxymonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide, J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 179, 552–558 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. P. Anipsitakis and D. D. Dionysiou, Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, 38, 3705–3712 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Deng, S. Feng, X. Ma, C. Tan, H. Wang, S. Zhou, T. Zhang and J. Li, Heterogeneous degradation of Orange II with peroxymonosulfate activated by ordered mesoporous MnFe2O4, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2016, 167, 181–189 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Chen, J. Chen, X. Qiao, D. Wang and X. Cai, Performance of nano-Co3O4/peroxymonosulfate system: kinetics and mechanism study using Acid Orange 7 as a model compound, Appl. Catal., B, 2008, 80, 116–121 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Li, J. Wan, Y. Ma, Y. Wang, X. Chen and Z. Guan, Degradation of refractory dibutyl phthalate by peroxymonosulfate activated with novel catalysts cobalt metal-organic frameworks: Mechanism, performance, and stability, J. Hazard. Mater., 2016, 318, 154–163 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Su, X. Duan, J. Miao, Y. Zhong, W. Zhou, S. Wang and Z. Shao, Mixed conducting perovskite materials as superior catalysts for fast aqueous-phase advanced oxidation: a mechanistic study, ACS Catal., 2016, 7, 388–397 CrossRef.
- K. Wang, Y. Yang, T. C. Zhang, Y. Liang and Q. Wang, Degradation of methylene blue with magnetic Co-doped Fe3O4@ FeOOH nanocomposites as heterogeneous catalysts of peroxymonosulfate, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 17664–17673 RSC.
- Y. Ding, L. Zhu, A. Huang, X. Zhao, X. Zhang and H. Tang, A heterogeneous Co3O4–Bi2O3 composite catalyst for oxidative degradation of organic pollutants in the presence of peroxymonosulfate, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, 2, 1977–1984 RSC.
- Y. Fan, W. Ma, J. He and Y. Du, CoMoO4 as a novel heterogeneous catalyst of peroxymonosulfate activation for the degradation of organic dyes, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 36193–36200 RSC.
- S. Zhang, Q. Fan, H. Gao, Y. Huang, X. Liu, J. Li, X. Xu and X. Wang, Formation of Fe3O4@MnO2 ball-in-ball hollow spheres as a high performance catalyst with enhanced catalytic performances, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 1414–1422 RSC.
- W.-D. Oh, S.-K. Lua, Z. Dong and T.-T. Lim, Performance of magnetic activated carbon composite as peroxymonosulfate activator and regenerable adsorbent via sulfate radical-mediated oxidation processes, J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 284, 1–9 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Influence of reaction sequence and NO3− concentration on MB degradation, the proposed reactions of coexisting anions with free radicals, and some physicochemical properties of H2O2, PS and PMS. See DOI: 10.1039/c9ra10169a |
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here.  Open Access Article
Open Access Article *b,
To Van Nguyena,
Bui Minh Thuya,
Masahito Hatsukanoc,
Koichi Higashiminec,
Shinya Maenosono
*b,
To Van Nguyena,
Bui Minh Thuya,
Masahito Hatsukanoc,
Koichi Higashiminec,
Shinya Maenosono c and
Ziyi Zhong
c and
Ziyi Zhong d
d
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) θ)
θ)
![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m (227), with Mn ions occupying octahedral sites, and Co ions occupying both octahedral and tetragonal sites, as shown in Fig. 1c. In the FT-IR spectrum (Fig. 1d), the wide and weak bands observed at 3347.2 and 1633.3 cm−1 are respectively associated with –OH stretching and bending vibrations of adsorbed water molecules. The sharp and strong peaks observed at 652.8 and 547.2 cm−1 correspond to stretching vibrations of metal–oxygen bondings at tetrahedral and octahedral sites.17 The peak occurred at 1118.1 cm−1 indicates the presence of C–O bondings, possibly due to the presence of adventitious carbon species. TG curve of the catalyst (Fig. 1e) displays two major events of the weight loss, which represent the dehydration and deoxygenation of the catalyst, respectively. The percentages of both weight losses were only 1.2 and 0.8%, indicating the high thermal stability of the material.
m (227), with Mn ions occupying octahedral sites, and Co ions occupying both octahedral and tetragonal sites, as shown in Fig. 1c. In the FT-IR spectrum (Fig. 1d), the wide and weak bands observed at 3347.2 and 1633.3 cm−1 are respectively associated with –OH stretching and bending vibrations of adsorbed water molecules. The sharp and strong peaks observed at 652.8 and 547.2 cm−1 correspond to stretching vibrations of metal–oxygen bondings at tetrahedral and octahedral sites.17 The peak occurred at 1118.1 cm−1 indicates the presence of C–O bondings, possibly due to the presence of adventitious carbon species. TG curve of the catalyst (Fig. 1e) displays two major events of the weight loss, which represent the dehydration and deoxygenation of the catalyst, respectively. The percentages of both weight losses were only 1.2 and 0.8%, indicating the high thermal stability of the material.


![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N–), in which π-bondings are easily dissociated to form naphthalene ring.40 The xanthene dye (RhB) is disrupted through the degradation of its conjugated structure and subsequent N-demethylation.41 The degradation of the thiazine dye (MB) first occurred on aromatic ring-bonded nitrogen atoms due to the presence of electron-donating groups (–N(CH3)2).40 All of these organic dyes can be degraded in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system, indicating that this catalyst can be employed in a wide range of organic pollutant environments.
N–), in which π-bondings are easily dissociated to form naphthalene ring.40 The xanthene dye (RhB) is disrupted through the degradation of its conjugated structure and subsequent N-demethylation.41 The degradation of the thiazine dye (MB) first occurred on aromatic ring-bonded nitrogen atoms due to the presence of electron-donating groups (–N(CH3)2).40 All of these organic dyes can be degraded in MnCo2O4.5/PMS system, indicating that this catalyst can be employed in a wide range of organic pollutant environments.









