Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleNaphthalimide based smart sensor for CN−/Fe3+ and H2S. Synthesis and application in RAW264.7 cells and zebrafish imaging†
Sanay Nahaa,
Shu-Pao Wu *b and
Sivan Velmathi
*b and
Sivan Velmathi *a
*a
aOrganic and Polymer Synthesis Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, India. E-mail: velmathis@nitt.edu
bDepartment of Applied Chemistry, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan. E-mail: spwu@mail.nctu.edu.tw
First published on 28th February 2020
Abstract
Achieving selective detection of target analytes in aqueous media continues to be an arduous proposition. Herein, we report the conceptualization and synthesis of a novel tailor-fit molecular probe R based on 1,8-naphthalimide which acts as a trifunctional molecular sensor for CN−, Fe3+ and H2S. R shows colorimetric and fluorometric “on–off” relay recognition for CN− (red colour and orange emission) and Fe3+ (no colour and no emission) in 5% H2O + DMSO medium which is experimentally ascertained to be a tandem deprotonation–protonation process and is supported by 1H-NMR titration. Among all RSS (Reactive Sulphur Species), R shows selectivity for H2S through red colouration. Other coexistent anions, cations and RSS cause no discernible perturbation to the detection process. The detection of H2S is attributed to a chemodosimetric reduction of the nitro to amino group as evidenced by a potentiometric titration assay. The experimental observations are well supported by DFT theoretical calculation. The Ka for CN−/Fe3+ are 1.4 × 104 M−1, 6.07 × 104 M−1 respectively and photochemical yield of R + CN− is 0.86. Limit of detections for CN−, Fe3+ and H2S are 17.5 nM, 8.69 μM and 8.1 μM respectively. Receptor R is effective for real time applications, bio-compatible and has been successfully employed for confocal fluorescence imaging of RAW264.7 cell and zebrafish.
Introduction
There has been an unchecked increase in the release of toxic inorganic effluents from industrial sources into terrestrial water resources. This necessitates the development of techniques for the detection and quantification of inorganic pollutants. The adverse health consequences of ions such as cyanide, are well documented such as complications of vascular, visual, central nervous, cardiac, endocrine and metabolic systems.1–8 Chemically, cyanide ion is a resilient nucleophile, sufficiently basic in nature, and can act as an ambidentate ligand and most importantly a pseudohalide. Cyanide is chosen as an exemplar since it finds widespread application in metallurgy, mining, electroplating and polymer synthesis.9–11 According to the WHO guideline, the optimum tolerance limit of cyanide is 0.07 mg L−1 in drinking water and about 0.5–3.5 mg kg−1 of cyanide to an adult is lethal.12Alongside cyanide, metals, specifically transition metals are copiously used for catalytic redox reactions in biological systems. Among transition metals, iron is the third most abundant metal ion present in humans and plays a pivotal role in oxygen transport, electron transport, balancing ionic pressure and is an integral part of the heme protein in our blood.13,14 Like all inorganic ions, an untethered increase in iron concentration can prove harmful. Apart from ionic analytes, there are some neutral species available in waste which are equally dangerous to mankind. Of these, H2S is predominant. Due to fungal activity and direct use, there has been a steady accumulation of H2S in wastewater.15–18 Therefore, methods for the quantitative and qualitative detection of cyanide, iron and H2S assume ample significance.
Numerous well-established techniques are known for qualitative and quantitative estimation of analytes. These include atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS),19 inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ICPMS),20 inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry (ICPES),21 chromatography (HPLC and LC),22 voltammetry23 and so on. But these processes suffer from pitfalls such as frantic sample preparation procedures, requirement of sophisticated instrumentation, non-portability and high costs. Most of these processes are time-consuming. On the contrary, colorimetric and fluorescent sensors have marked advantages as they are easy to use, exhibit fast response times, involve simple synthetic procedures, are affordable, reusable, portable and most importantly involve real time bare-eye observation.
For detection, there are various strategies that have been adopted till date. These include single analyte and dual analyte detection. However, multifunctional receptors have not been equally explored. The development of multifunctional molecular sensors based on a single molecular structure has attracted a lot of attention in recent years.24–31 In this regard, many reports are available which involve extensive investigations for the multifunctional sensor molecules towards cation–cation, or, anion–anion, or, anion–cation, or, cation–anion, or, ionic–neutral or neutral–ionic analytes combinations.32 There are few reports available on Fe3+–CN− recognition.33–38 However, triple analyte selective receptors are not common.39
Herein, we report a simple 1,8-naphthalimide based probe as tailor-fit triple action smart chemosensor R for the sequential detection of CN− and Fe3+ via colorimetric and fluorometric ‘on–off’ method and H2S through colorimetric method in semi-aqueous media over a wide pH range. DFT calculations supported the experimental findings and results are in correlation with experimental data. The receptor is capable of detecting analytes in biological systems. The results are documented in subsequent paragraphs.
Results and discussion
The receptor R was characterized using IR, 1H & 13C-NMR and HR-mass spectroscopic methods. The synthesized receptor R has an interesting molecular framework which consists of binary interacting sites. One is the amide moiety where a nucleophilic attack or deprotonation can take place, and another is the nitro functional group which is susceptible to reduction in the presence of reducing analytes (Scheme 1). Based on this assumption, the receptor was examined for triple action anion, cation and reactive species sensing in various solvents and investigated using UV-Visible, fluorescence, and 1H-NMR spectroscopic techniques. Density Functional Theory (DFT) was employed for theoretical calculation to support the observed results. Prior to sensing studies, the dependence of receptor's efficiency in different solvents was determined. The receptor did not show appreciable effect in less-polar solvents like THF, toluene, MeOH, EtOH and DIOX. Rather, the receptor is quite efficacious in polar solvents like ACN, DMF and DMSO. Among polar solvents, the performance in DMSO is conducive for photo-physical studies (Fig. S5†).Visual selectivity experiment
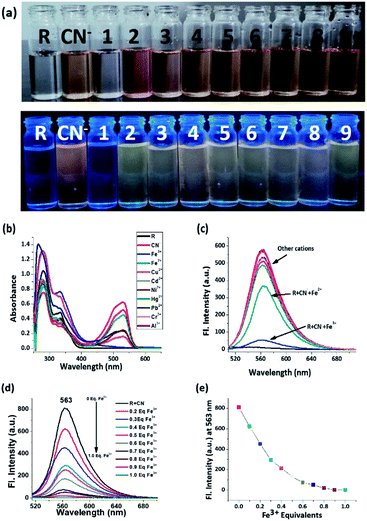
The receptor contains multiple heteroatoms which can provide satisfactory binding sites for metal ions and on this note the receptor was exempted for naked eye cation recognition. But, there was no specificity and selectivity for a particular cation, as none of the metal ions show any significant interference neither by colorimetric nor by emissive approaches. Subsequently, the receptor is applied for anion selectivity and to do so, 2 equivalents of all anions such as CN−, F−, Cl−, Br−, I−, AcO−, HSO4−, H2PO4−, NO3−, OH−, ClO4−, H2S, N3− and PF6− were added to 3 mL (15 μM) of R solution in DMSO. Among the library of anions, only CN− selectively shows an intense and drastic color change from no colour to an intense red and an orange fluorescence ‘turn-on’. Alongside CN−, H2S also shows rapid and intense colour change to red colour but without any ‘turn-on’ emission. Other anions like I− AcO−, HSO4−, H2PO4−, NO3−, SCN−, N3− and ClO4− show a bright golden-yellow emission but no change in colour (Fig. S6†). After determining the effect of water on CN− detection via emissive mode (Fig. S7 and S8†), a sensing medium of 5% aqueous DMSO is used, where only CN− selectively and specifically shows an intense red colouration and orange emission ‘turn-on’ (Fig. 1). The change in color and ‘turn-on’ of fluorescence can be attributed to deprotonation of the acidic hydrazide [–NH].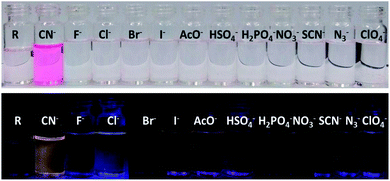 | ||
| Fig. 1 Bared eye colour change and turn-on emission under UV-light for cyanide in 5% aqueous-DMSO solvent. | ||
Electronic and emission response
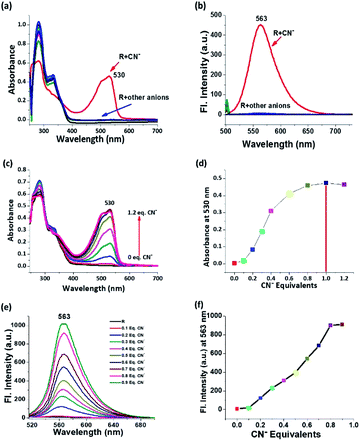
The spectroscopic responses were recorded for anion sensing studies which depicted the selectivity for cyanide among competitive anions. The electronic spectra of receptor in 5% aqueous solution shows two absorption peaks at around 280 nm due to σ–σ* transition and 332 nm due to π–π* transition and almost all the anions in the chosen ensemble yield the same trends in their corresponding electronic spectra. In the case of cyanide, the peak position of σ–σ* transition does not change but the intensity reduces abruptly followed by the disappearance of the 332 nm peak. Along with that, the appearance of a peak around 530 nm is attributed to n–π* transition of the de-protonated receptor and the drastic change in colour is justified (Fig. 2a). On deprotonation, the formed negative charge leads to the red shift in λmax, and this shift in λmax is conspicuously correlated with the molecular orbitals and the energy of transition from HOMO to LUMO. On the other hand, the emission spectrum is self-explanatory for cyanide selectivity which proceeds via ‘turn-on’ emission. On excitation at 530 nm, an emission is observed at λem 563 nm, which is the region for orange emission (Fig. 2b). Titrimetric analysis of the receptor via both UV-Vis and fluorescence methods shows a saturation limit of receptor with one equivalent of cyanide, and on further addition, no appreciable change is observed (Fig. 2c–f). The receptor is selective and specific for CN− even in the presence of other competing analytes (Fig. S9†).Relay recognition experiment
As the receptor shows optimum specificity for cyanide, the R–CN− ensemble was employed for the sequential recognition of cationic analytes and the cyanide treated receptor is capable of recognizing Fe3+ via both decolorization and rapid ‘turn-off’ emission which is evident from the colour change from intense red to colourless and the quenching of orange emission under UV-light (Fig. 3a). Other metal ions did not show any comparative interference in this context. From the electronic spectrum it can be inferred that the absorption peak at around 332 nm reappears and the peak at 530 nm disappears upon introduction of Fe3+ (Fig. 3b). Similarly, in the emission spectrum, the intensity of R + CN− is decreased by 12 fold after Fe3+ addition (Fig. 3c). In the titration between R + CN− vs. Fe3+, the decrease of emission intensity follows a specific pattern and at 1 equivalent of Fe3+ concentration, emission gets quenched completely. On further addition, no discernible change is observed (Fig. 3d and e).Naked eye H2S selectivity
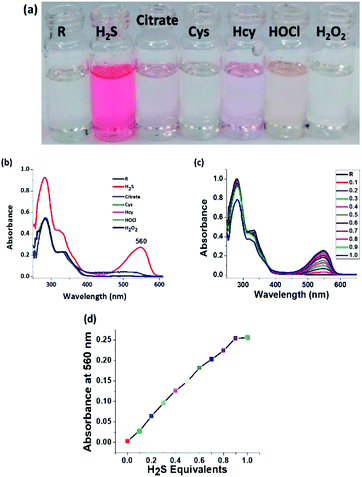
Since the receptor is tailor-made for H2S sensing due to the presence of a nitro group, the receptor is examined for interference from other reactive sulphur species (RSS). And as expected, the receptor precisely and selectively shows an intense colorimetric response only for H2S (Fig. 4a). The electronic spectra illustrate the specificity of the probe towards H2S. The appearance of a new peak at 560 nm is attributed to the formation of an amine chromophore (Fig. 4b). Both cyanide and H2S show an intense red colouration, but the absorption peak position for H2S is red shifted by almost 30 nm when compared to CN− (Fig. 4c). Incremental titration of receptor R by H2S shows a saturation limit of 1 equivalent. It can therefore be said that the chemodosimetric reduction of the nitro group follows a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 stoichiometric ratio (Fig. 4d).
1 stoichiometric ratio (Fig. 4d).
pH effect
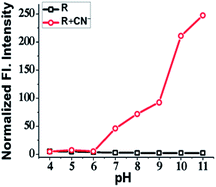
The effect of pH on the sensitivity and efficacy of a receptor is an important factor that needs to be consider while developing a molecular probe. The bio-applicability of a receptor invariably depends on pH. So, to examine pH effect, 3 mL of 15 μM solution of R in various pH values were prepared using HEPES buffer and the emission of each pH solution was recorded before and after addition of CN−. The receptor R showed an intense orange emission in the pH range from 7 to 11, which can be attributed to the stability of the deprotonated R in that pH range. Since the reason behind emission is the deprotonation, basic medium certainly supports deprotonation of acidic/replaceable protons. The receptor R is therefore efficient within a range of pH 7 to 11 and can be used for fluorescence cell imaging of CN− (Fig. 5).Quantitative calculation
The authenticity of a developed analytical method is always evaluated on the basis of suitability and sustainability of its intended purpose, recovery, standardization requirements, sensitivity and specificity, ease of analysis, skill subset required, time and cost. Limit of detection is an important performance characteristic of any analytical method. These parameters stand to describe the smallest concentration of an analyte that can be reliably measured by an analytical method. Job's plot for CN− and Fe3+ showed a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 stoichiometry for the sensing process (Fig. S10†). However, since H2S detection involves a chemodosimetric reduction process, a Job's plot construction is not applicable since no stable binding is taking place. The calculated association constants (Ka) for sequential recognition of CN−/Fe3+ are 1.4 × 104 M−1 and 6.07 × 104 M−1 respectively. Limit of detection (LOD) for CN−, Fe3+ and H2S are found to be 17.5 nM, 8.69 μM and 8.1 μM respectively (Fig. S11, S12 and S13) (Table S1†). The standard iodometric method for standardization of H2S dissolved in water has been opted for reference and according to the iodometric method, the concentration of H2S used for quantification is found to be 10 μM which is well correlated to known limits. Hence, this method can be considered as an efficient approach for H2S detection. The quantum yield of CN−/Fe3+ recognition process has been calculated with respect to rhodamine B. The quantum yields (ϕ) for R, R + CN− and R + CN− + Fe3+ are 0.01, 0.86 and 0.01 respectively (Table S2†).
1 stoichiometry for the sensing process (Fig. S10†). However, since H2S detection involves a chemodosimetric reduction process, a Job's plot construction is not applicable since no stable binding is taking place. The calculated association constants (Ka) for sequential recognition of CN−/Fe3+ are 1.4 × 104 M−1 and 6.07 × 104 M−1 respectively. Limit of detection (LOD) for CN−, Fe3+ and H2S are found to be 17.5 nM, 8.69 μM and 8.1 μM respectively (Fig. S11, S12 and S13) (Table S1†). The standard iodometric method for standardization of H2S dissolved in water has been opted for reference and according to the iodometric method, the concentration of H2S used for quantification is found to be 10 μM which is well correlated to known limits. Hence, this method can be considered as an efficient approach for H2S detection. The quantum yield of CN−/Fe3+ recognition process has been calculated with respect to rhodamine B. The quantum yields (ϕ) for R, R + CN− and R + CN− + Fe3+ are 0.01, 0.86 and 0.01 respectively (Table S2†).
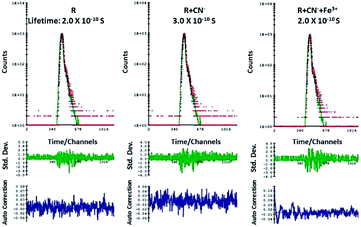
Lifetime experiment
According to the emission spectra, the emission maxima of R + CN− is at 563 nm and to perform luminescence lifetime decay experiment a 550 nano-LED source was used. The average decay time of the excited state of only R was found to be 0.2 ns. After the addition of 10 μM of CN− ions to R, the average luminescence lifetime of R + CN− increased to 0.3 ns. When this was followed by the addition of 10 μM Fe3+ to the resultant R + CN− solution, the average lifetime again decreased and revert back to 0.2 ns. The lifetime decay curve of only R, R + CN− and R + CN− + Fe3+ were fitted to a triple-exponential decay curve using theoretical calculations. The 0.1 ns resultant increment of the average lifetime before and after addition of cyanide implies that the excited state of ‘R + CN−’ is comparatively stable in comparison to the excited state of free receptor R. As a result, there is a delay of 0.1 ns in the decay rate, when cyanide ion deprotonates the receptor; hence it is proved that there is a scope for the enhancement of fluorescence in the case of R–CN− interaction. Whereas, the resultant decrement of average lifetime after addition of Fe3+ to the deprotonated R is 0.1 ns, which implies that the increase in decay rate and hence quenching of emission is favorable (Fig. 6).Theoretical studies
Theoretical calculations were performed for only R, deprotonated R and reduced R to support the deprotonation process taking place upon introduction of cyanide and the reduction of nitro group to amine group by H2S. The structural optimization and quantum mechanical calculations were performed using Gaussian 09 software. The Gauss View 5 GUI was used for visualization of results. Geometry optimizations for ground state of only R and reduced R were conducted using DFT/B3LYP/6-31g basis set and excited state of deprotonated R was conducted using TD-DFT/B3LYP/6-31g basis set alongside solvent effect of DMSO respectively. Highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) for the respective form of R were generated from their optimized structures (Fig. 7a and b). The calculated energy gap between HOMO and LUMO of only R is 3.08 eV which after deprotonation of amide –NH by cyanide ions decreases to 2.1 eV (excited state of deprotonated R). Similarly, the energy gap between HOMO and LUMO of only R and reduced R also decreases to 2.15 eV from 3.08 eV. The calculated energy for only R, deprotonated R and reduced R corresponds to wavelengths of 402 nm, 589 nm and 576 nm respectively and well coincided with the experimental values.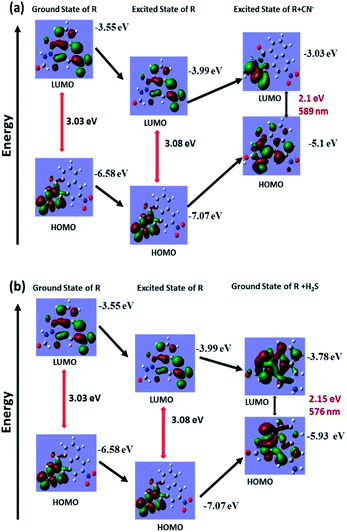 | ||
| Fig. 7 Theoretical calculation for ground state and excited state energy of (a) receptor R and R + CN− for cyanide recognition and (b) receptor R and R + H2S for H2S recognition. | ||
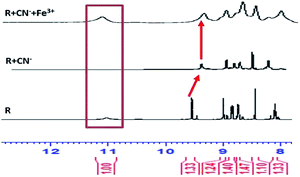
1H-NMR titration
The successive detection of cyanide and Fe3+ by R was supported by 1H NMR titration. A solution of R (0.01 M in DMSO-d6), TBACN (0.01 M in DMSO-d6) and FeCl3 (0.01 M in DMSO-d6) were used for the 1H NMR titrations (Fig. 8). In the NMR spectrum, the peak at 11 ppm corresponds to the only acidic [–N–H] proton present in the receptor and on addition of 1 equivalent cyanide ion to R, the peak at 11 ppm disappears. Furthermore, the peak position of aldehyde proton is shifted downfield due to the localization of the electronic field. On addition of CN−, the obvious dense electron density around the napthalimide moiety has no discernible impact on its proton signals in the 1H NMR spectra. Due to the lack of extended conjugation, the accrued negative charge on N-atom in the molecular framework got static dissipation. As a result, the molecule does feel the electron density over a specific position which results in an internal charge transfer (ICT) process. It follows, upon addition of Fe3+ to the resultant mixture, regeneration of [–NH] appears at around 10.9 ppm which confirms the binding of cyanide with Fe3+.Potentiometric titration
The reductive chemodosimetric approach adopted by the receptor for H2S sensing is supported by potentiometric titration and recorded using a cyclic voltammeter. In aqueous solutions, H2S exists either as HS− or even as S2− which impart significant reducing character and current flow. In a typical experiment, Pt electrodes were used as both working and counter electrodes and Ag/AgCl electrode was used as a reference electrode. The three electrodes were dipped in a 10 μM 20 mL aqueous solution, the oxidation–reduction potential of the resultant cell assembly was measured. Only H2S solution shows a reduction potential of −0.5 V with a current of −0.00135 mA. On sequential addition of 1.1 equivalent receptor R to the H2S solution, the concentration of reduced sulphur decreases as evidenced by the decrease in current from −0.00135 mA to −0.0006 mA and the receptor R gets saturated at one equivalent of H2S (Fig. 9a). The reduction peak for H2S becomes sharper towards the end of the addition and ultimately linearity is observed (Fig. 9b). Hence, the reduction of the nitro group in receptor by H2S is evident.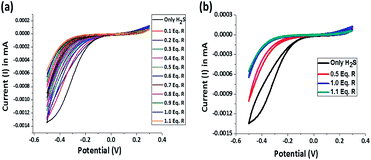 | ||
| Fig. 9 (a) Potentiometric titration of receptor R and H2S and (b) a correlative plot of potential for only H2S, after 0.5 equivalent of R, after 1.0 equivalent of R and after 1.1 equivalent of R. | ||
Sensing mechanism
From UV, PL spectroscopy, 1H-NMR titration, potentiometric titration and theoretical calculations, it is ascertained that deprotonation of [–NH] proton by cyanide ions is the driving force for the sensing action of the receptor. From the sequential titration plot, it is confirmed that the saturation limit of the R is 1 equivalent of cyanide. The molecular framework of the receptor facilitates an ESIPT mechanism between the adjacent carbonyl oxygen and the [–NH] group on excitation rendering the receptor non-emissive. Upon deprotonation, there is a formation of a negatively charged species in which a delocalization of negative charge through resonance is curtailed. Therefore, the only tool available for charge dissipation is amide–imine tautomerism which results in the attenuation of ESIPT and switches on the ICT mechanism. The result is the appearance of an intense orange emission at 563 nm. The introduction of Fe3+ to the emissive system results in the protonation of the receptor, thereby effectively inhibiting ICT due to the absence of free cyanide in the solution (Fig. 10). The sensing of H2S in purely chemodosimetric and does not affect ESIPT. The only discernible change was the reduction of the nitro group on the receptor. As a result, there is only a color change from colorless to red but no emission.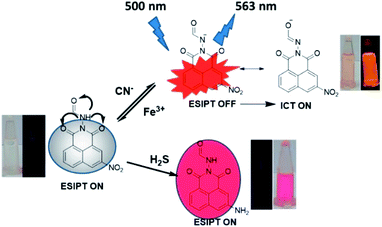 | ||
| Fig. 10 The probable sensing mechanism for relay recognition of CN−/Fe3+ and chemodosimetric sensing of H2S. | ||
Application
To ascertain the employability of the receptor R for real-world applications, three different tests were considered. The pH effect studies showed that the receptor is effective within the biological pH range. Subsequently, a strip-test was performed to assess the relay recognition of CN−/Fe3+. H2S etching was used for real-sample analysis. A cytotoxicity (MTT) assay of R was also performed to test the viability of the molecule for biological applications. And finally, the receptor was used for confocal fluorescence imaging of RAW264.7 cells and zebrafish for relay recognition of CN−/Fe3+.Real sample
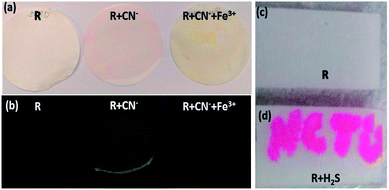
Since the receptor R showed selectivity and specificity for CN−/Fe3+ ions and H2S in semi-aqueous media without any interference, R was applied for colorimetric and fluorometric naked eye observable strip-test analysis. A 15 μM solution was prepared in 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 acetone–DMSO solvent. The filter papers were coated with the receptor solution and dried in a hot-air oven at 70 °C for about 2 hours. On the dry paper strips, cyanide was added and immediately an intense red colour was observed (Fig. 11a) along with an orange emission which was instantly quenched by Fe3+. The addition of Fe3+ produced a feeble yellowish colour on the paper strips. This was attributed to the presence of FeCl3 (Fig. 11b). For the H2S strip test, a solution of H2S is used as ink and then the letters ‘NCTU’ were inscribed on the dried strip using a paintbrush (Fig. 11c and d). The strip test for CN−/H2S was validated using various concentration of CN−/H2S ranging from (0.1–10) μM (Fig. S14†).
1 acetone–DMSO solvent. The filter papers were coated with the receptor solution and dried in a hot-air oven at 70 °C for about 2 hours. On the dry paper strips, cyanide was added and immediately an intense red colour was observed (Fig. 11a) along with an orange emission which was instantly quenched by Fe3+. The addition of Fe3+ produced a feeble yellowish colour on the paper strips. This was attributed to the presence of FeCl3 (Fig. 11b). For the H2S strip test, a solution of H2S is used as ink and then the letters ‘NCTU’ were inscribed on the dried strip using a paintbrush (Fig. 11c and d). The strip test for CN−/H2S was validated using various concentration of CN−/H2S ranging from (0.1–10) μM (Fig. S14†).
Cell imaging
The cell line RAW264.7 were cultured on 18 mm glass-cover slips in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with fetal bovine serum (10% FBS) at 37 °C under 5% CO2 atmosphere and allowed to adhere for 24 h. After washing with PBS, the setup was incubated for another 30 min with R (20 μM) in DMEM. After washing the excess R using PBS, R + RAW264.7 cells were incubated with CN− (10 μM) for 30 min. To assess CN− ion uptake, the cells were treated with CN− (10 μM in 2 mL) dissolved in sterilized PBS at pH 7.4 and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C and 5% CO2 atmosphere. The treated cells were washed using PBS (2–3 mL) to remove remaining CN− ions. 2 mL of culture media was added to the cell culture, which was treated with a 10 mM solution of R (10 mM, 2 mL) dissolved in DMSO. The samples were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. After removing the culture media and followed by washing with PBS, confocal images were recorded. From the images, it could be inferred that R has very good permeability through the RAW264.7 cell membrane and the receptor does not possess any emission. Whereas R sensed CN− selectively with ‘turn-on’ orange fluorescence which again gets quenched on introduction of Fe3+ (Fig. 12).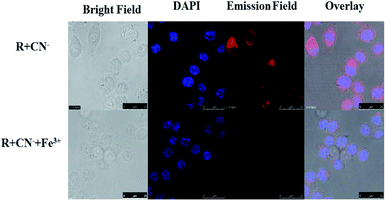 | ||
| Fig. 12 The confocal fluorescence RAW264.7 cell imaging for sequential recognition of CN− and Fe3+ via ‘on–off’ emission response. | ||
Zebrafish imaging
The eggs of zebrafish were subjected to a 3 day maturation period and subsequently used for confocal fluorescence imaging experiment. Firstly, the zebrafish were placed in 2 mL of 15 μM solution of receptor to allow for a smooth intake and then rested for 30 min at room temperature. After the standby period, the fishes were washed 2–5 times with deionized water and fluorescence images were recorded. It is obvious that the receptor is not inherently emissive in the fish. The cleaned fishes were treated with 2 mL of 15 μM solution of cyanide and allowed for another 30 min. Then again after cleaning the fishes, the fluorescence images were recorded. The fish show red emission and the intensity of the emission is maximum in the stomach region. After this, the fish were again treated with 2 mL of 15 μM Fe3+ (FeCl3 solution) and fluorescence images were recorded. The intense red emission is quenched completely upon the introduction of Fe3+. These tests show that the receptor can be used as a cyanide marker for in vivo applications and can precisely indicate the presence of Fe3+ ions (Fig. 13). | ||
| Fig. 13 The confocal fluorescence zebrafish imaging for sequential recognition of CN− and Fe3+ via ‘off–on–off’ emission response. | ||
Experimental
Materials and instrumentations
3-nitro-1,8-napthalimide and formic hydrazide were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used as received. The solvents used for synthesis and photophysical studies were of spectroscopic grade. For photophysical studies double-distilled water was used and pH of water was 6.7 and conductivity was 30 dS m−1. For stock solution of all anions tetrabutylammonium salts were purchased and for all cations, chloride salts were used. Bruker DRX-300, Agilent Unity INOVA-500 and Bruker Ascend 500 NMR spectrometer were used for NMR spectral characterization. UV-Vis spectra were obtained using Agilent 8453 UV-Vis spectrometer and Shimadzu UV-2600 spectrophotometer. Fluorescence spectra measurements were obtained from Hitachi F-7000 fluorescence spectrophotometer and Shimadzu RF5301pc spectrofluorophotometer. The potentiometric titration was measured using Bio-logic SP-150 cyclic-voltammeter (CV). Lifetime measurement studies were done at Horiba Delta time instrument coupled with TCSPC. Fluorescent images were taken on a Leica TCS SP5 X AOBS and Leica TCS SP5 II Confocal fluorescence microscope. The cells RAW264.7 were provided by the Food Industry Research and Development Institute (Taiwan). The cell imaging and zebrafish imaging experiments were conducted in strict accordance with the guidelines provided by Govt. of Taiwan and was approved by Institutional committee (NCTU, Taiwan).Spectroscopic procedures
The stock solution of receptor R (1.0 × 10−3 M in DMSO) was prepared and kept at room temperature. Then the stock solution was diluted with 5% (H2O + DMSO) to a final concentration of 2.5 × 10−5 M for spectral analysis. All anion, cations and RSS stock solutions were prepared in the concentration of 5 × 10−3 M in water. ROS and RSS were prepared freshly and used.Synthesis of R
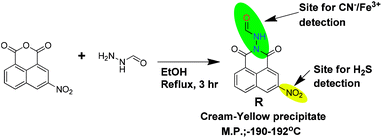
In a hot-dry 100 mL round bottom flask, 15 mL ethanol solution of 3-nitro-1,8-napthalimide (486 mg, 2 mM) was prepared and stirred vigorously at 78 °C for 15 min. To the resultant clear solution, 10 mL ethanolic solution of formic hydrazide (130 mg, 2.1 mM) was added dropwise over a time period of 10 min. The resultant mixture was set for reflux for 3 h. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature followed by 20 mL of diethylether was added and kept in room temperature for 12 h. A cream-yellow precipitate was obtained which was separated through filtration and washed with hot water, hot ethanol, then product was dried in vacuum oven. The compound was further purified using ethyl acetate wash followed by re-crystallization in methanol–acetonitrile (9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) medium (Scheme 1). Yield of the reaction is 530 mg (92%).
1) medium (Scheme 1). Yield of the reaction is 530 mg (92%).
Melting point: (190–192) °C.
FT-IR (cm−1): 3421 (absorbed water, KBr), 3198 (Ar–C–H), 3076 and 2922 (![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NH), 1735 (C
NH), 1735 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, amide), 1700 and 1664 (C–N, amide) (Fig. S1†).
O, amide), 1700 and 1664 (C–N, amide) (Fig. S1†).
1H δ (500 MHz; DMSO-d6; TMS): 11.025 (s, 1H), 9.578 (s, 1H), 9.015 (s, 1H), 8.879–8.863 (d, 1H, J = 8), 8.759–8.746 (d, 1H, J = 7), 8.436 (s, 1H) and 8.13–8.099 (t, 1H, J = 8).
13C ppm (125 MHz; DMSO-d6; TMS): 161.16, 160.79, 160.28, 146.38, 137.70, 135.23, 131.62, 131.06, 129.90, 129.82, 124.30, 123.91 and 122.53 (Fig. S3a and b†).
135-DEPT ppm (125 MHz; DMSO-d6; TMS): 137.69, 135.22, 131.04, 129.89 and 124.29 (Fig. S3c†).
LCMS (HR-MS) m/z: calcd for C13H7N3O5, 285.0386, found: 284.0313 [M − H] (Fig. S4†).
Conclusions
In summary, we have successfully developed a triple action smart receptor which can detect quantitatively and qualitatively CN− and Fe3+ via a relay recognition pathway and H2S through a reductive chemodosimetric mechanism without any interference from other analytes in 5% H2O–DMSO media. The receptor senses the analytes effectively and efficiently within permissible limits. The CN−/Fe3+ and H2S sensing mechanisms are supported by 1H-NMR and cyclic voltammetric titrations. Quantum mechanical calculations using DFT support the experimental findings. The receptor is employed in strip-tests for the detection of CN−/Fe3+ via both naked eye colorimetric and fluorometric response along with writing ink for H2S. Since the receptor is bio-compatible and non-toxic, it is capable in detecting CN−/Fe3+ in RAW264.7 cells and zebrafish via confocal fluorescence imaging.Conflicts of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.Acknowledgements
Author Sanay Naha is highly thankful to Department of Science and Technology, India (DST-India) for providing financial support through INSPIRE Fellowship (IF150881), TEEP internship program and NCTU, Taiwan for research infrastructure.References
- V. Kumar, H. Rana and M. P. Kaushik, Analyst, 2011, 136, 1873 RSC.
- X. Wu, B. Xu, H. Tong and L. Wang, Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 4241 CrossRef CAS.
- C. O. Ng, S. W. Lai, H. Feng, S. M. Yiu and C. C. Ko, Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 10020 RSC.
- M. D. Holaday, G. Tarafdar, B. Adinarayana, M. L. P. Reddy and A. Srinivasan, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 10834 RSC.
- S. Wang, H. Xu, Q. Yang, Y. Song and Y. Li, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 47990 RSC.
- C. Aebersold, B. Amstutz, A. E. Steuer, T. Kraemer and F. Zelder, Anal. Methods, 2015, 7, 9707 RSC.
- G. Balamurugan and S. Velmathi, Anal. Methods, 2016, 8, 1705 RSC.
- S. Suganya, J. S. Park and S. Velmathi, J. Fluoresc., 2016, 26, 207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Bhalla, H. Singh and M. Kumar, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 11413 RSC.
- C. Männel-Croisé and F. Zelder, Anal. Methods, 2012, 4, 2632 RSC.
- J. Isaad, F. Malek and A. El Achari, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 22168 RSC.
- Y. Singh and T. Ghosh, Talanta, 2016, 148, 257 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. H. Organization, Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 3rd edn, 2004, vol. 1, p. 339 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yue, F. Huo, C. Yin, J. Chao and Y. Zhang, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, 212, 451 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Mardanya, S. Karmakar, D. Mondal and S. Baitalik, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 15994 RSC.
- N. Thirumalaivasan, P. Venkatesan and S. P. Wu, New J. Chem., 2017, 41, 13510 RSC.
- B. Zhao, Y. Yang, Y. Wu, B. Yang, J. Chai, X. Hu and B. Liu, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 256, 79 CrossRef CAS.
- C. B. da Silva, E. S. Gil, F. d. S. Santos, A. M. Moras, L. Steffens, P. F. B. Goncalves, D. J. Moura, D. S. Ludtke and F. S. Rodembusch, J. Org. Chem., 2018, 83, 15210 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Mardanya, S. Karmakar, M. Bar and S. Baitalik, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 21053 RSC.
- Z. Q. Hu, X. M. Wang, Y. C. Feng, L. Ding, M. Li and C. S. Lin, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 1622 RSC.
- A. Balamurugan and H. Lee, Macromolecules, 2015, 48, 3934 CrossRef CAS.
- J. B. Chae, H. J. Jang and C. Kim, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017, 16, 1812 RSC.
- H. J. Jang, H. M. Ahn, M. S. Kim and C. Kim, Tetrahedron, 2017, 73, 6624 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Zhao, T. Liu, Y. Fang, L. Wang, W. Kan, Q. Deng and B. Song, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 246, 370 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Lin, F. Zheng, T. T. Lu, J. Liu, H. Li, T. B. Wei, H. Yao and Y. M. Zhang, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 251, 250 CrossRef CAS.
- P. S. Nayab and M. Shkir, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 245, 395 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Zhou, X. Chen, Q. Hua, W. Lei, Q. Hao, B. Zhou, C. Su and X. Bao, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 253, 292 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Narayanaswamy and T. Govindaraju, Sens. Actuators, B, 2012, 161, 304 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Fu, G. Chen, Y. Liu, Z. Cao, X. Zhao, G. Li, F. Yu, L. Chen, H. Wang and J. You, Analyst, 2017, 142, 1619 RSC.
- P. Zhang, X. Nie, M. Gao, F. Zeng, A. Qin, S. Wu and B. Z. Tang, Mater. Chem. Front., 2017, 1, 838 RSC.
- Y. Singh and T. Ghosh, Talanta, 2016, 148, 257–263 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Suganya, S. Naha and S. Velmathi, ChemistrySelect, 2018, 3, 7231 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Yun, J. M. Jung and C. Kim, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2018, 479, 154 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Wang, J. Wu, Q. Liu, Y. Gao and B. Zhao, Tetrahedron Lett., 2018, 59, 1860 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Mohammadi and S. Yaghoubi, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 241, 1069 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Kumar, V. Bhalla and M. Kumar, Dalton Trans., 2013, 42, 8808 RSC.
- L. Wang, W. T. Li, W. J. Qu, J. X. Su, Q. Lin and M. Zhang, Supramol. Chem., 2017, 7, 489 CrossRef.
- G. Punithakumari and S. Velmathi, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2019, 373, 94 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Vijay, G. Balamurugan, P. Venkatesan, S. P. Wu and S. Velmathi, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017, 16, 1441 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c9ra07998j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |