Open Access Article
Open Access ArticlePreparation and enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen-evolution activity of ZnGa2O4/N-rGO heterostructures†
X. P. Baia,
X. Zhaob and
W. L. Fan *a
*a
aKey Laboratory for Colloid and Interface Chemistry of State Educating Ministry, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China. E-mail: fwl@sdu.edu.cn; Fax: +86-531-88364864; Tel: +86-531-88366330
bState Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
First published on 17th November 2017
Abstract
Semiconductor–graphene composites have been widely reported as photocatalysts for hydrogen generation. The structure of the semiconductor, intimate interfacial contact between the components, and high electrical conductivity of the catalyst support can affect the performance of semiconductor–graphene composite photocatalysts. We successfully synthesized size-controlled ZnGa2O4 nanospheres by adjusting the amount of surfactant trisodium citrate, and assembled size-controlled ZnGa2O4 nanospheres on the two-dimensional platform of an N-doped reduced graphene oxide (N-rGO) sheet through the conventional and efficient hydrothermal method, during which the intimate interfacial contact between ZnGa2O4 nanospheres and the N-rGO sheet are achieved. The obtained photocatalysts were characterized by X-ray powder diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and ultraviolet visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. The photocatalytic activity of the prepared samples for H2 evolution was tested using sodium sulfite as the sacrificial agent. The effects of the crystallinity, morphology, and specific surface area of the ZnGa2O4 samples on the rate of photocatalytic hydrogen production were studied. Considering the above three factors, the rate of H2 production was highest when the diameter of the ZnGa2O4 spheres reached 230 nm. The rate of H2 evolution of the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites dramatically improved when compared with that of pure ZnGa2O4. ZnGa2O4/N-rGO had higher photocatalytic activity than ZnGa2O4/rGO because the nitrogen atoms in N-rGO could anchor the metal nanoparticles to form an intimate interfacial contact between N-rGO and ZnGa2O4, and N-rGO had higher electrical conductivity than rGO, resulting in more effective charge separation and transfer in the ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites. This study offers a promising method to design more efficient graphene-based nanocomposite photocatalysts for enhancing photocatalytic activity.
Introduction
Hydrogen has attracted increased attention in recent years as a renewable and clean energy carrier.1–10 One of the best ways to produce hydrogen is photocatalytic water splitting under light irradiation, which offers a viable strategy to solve the energy crisis and environmental problems resulting from the burning of fossil fuels.11 So far, much effort has been dedicated to the development of photocatalysts, and numerous active photocatalysts such as various oxide, sulfide, and oxynitride semiconductors have been reported.12–17 Among them, metal oxides and their composites that contain metal cations with d0 and d10 electronic configurations at the highest oxidation states are regarded as good photocatalysts for water splitting.18,19 Zinc gallate (ZnGa2O4), a ternary metal-oxide-based spinel, has been widely used as a catalyst in air-pollution control,20 wastewater treatment,21 and water splitting.22–24 However, the fast recombination of photogenerated charge carriers remains a major problem. Modulating the structure of the semiconductor, such as its crystallinity and morphology, and constructing semiconductor-matrix systems have proved to be efficient ways to retard the recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs.25–33Graphene, a two-dimensional (2D) sheet of sp2-hybridized carbon atoms, has been considered as an excellent catalyst support and electron-transport matrix because of its high surface area, electrical conductivity, and mobility of charge carriers.34–40 So far, various semiconductor–graphene composite photocatalysts for hydrogen generation have been reported.41–44 The hydrophilicity of GO can be used as a binder, which is necessary for the development of graphene-based composites for various applications.45 However, reduced graphene oxide (rGO) does not exhibit high electronic conductivity because of damages to the sp2-hybridized network. Generally speaking, heteroatom doping can dramatically alter the electrical properties of graphene,46,47 and both theoretical and experiment studies have revealed that N doping can effectively modulate the chemical reactivity and electronic properties of graphene.48,49 Since N doping can increase the electronic conductivity because nitrogen has stronger electronegativity than carbon and because of the conjugation between the graphene π-system and the nitrogen lone-pair electrons,50 N-doped graphene has been used in lithium–ion batteries,51 biosensors or chemical sensors,52 and catalytic reactions including oxygen reduction53 and degradation of organic contaminants.54
In this study, we successfully synthesized size-controlled ZnGa2O4 nanospheres composed of ZnGa2O4 particles by adjusting the amount of surfactant trisodium citrate. We assembled the size-controlled ZnGa2O4 nanospheres on the 2D platforms of N-doped reduced graphene oxide (N-rGO) sheets and rGO sheets through the conventional and efficient hydrothermal method. We then investigated the effects of the crystallinity and morphology of the semiconductor and the electrical conductivity of the catalyst support on the photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. In addition, a possible photocatalytic mechanism of ZnGa2O4/N-rGO was explored.
Experimental
Preparation
The starting materials were Ga(NO3)3·xH2O (99.9%, Alfa Aesar Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China), graphene oxide powder (XFNANO Materials Tech. Co., China), and other reagents (Shanghai Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China). All chemicals were analytical grade and used without further purification.Synthesis of ZnGa2O4 nanospheres
ZnGa2O4 nanospheres were synthesized by the conventional hydrothermal method. First, 0.298 g Zn(NO3)2·6H2O was added 40 mL deionized water and 0.512 g Ga(NO3)3·xH2O was added 40 mL deionized water to obtained Zn2+ and Ga3+ solutions by stirring. The Ga3+ and Zn2+ solutions were mixed and stirred for 15 min, and then a certain amount of trisodium citrate (C6H5Na3O7·2H2O) was added, together with an ammonia solution (25.0 wt% NH3) used to control the pH was 8.5. After stirring for an additional 20 min, the solution was transferred to a 100 mL Teflon autoclave, sealed, and heated at 200 °C for 24 h. The precipitated solid product was collected by centrifuging, washed, dried at 60 °C in air, and then calcined at 400 °C in air. Hereafter, the obtained samples are denoted as ZnGa2O4-x, where x represents the amount of trisodium citrate in grams.Synthesis of N doped graphene oxide
Nitrogen-doped graphene oxide (NGO) was synthesized by a moderate refluxing process in an ammonia solution.55 The ammonia solution (25.0 wt%, 0.3 mL) was mixed with an aqueous GO solution (0.2 wt%, 20.0 mL) by magnetic stirring at 80 °C for 8 h to obtain partly reduced NGO.Synthesis of ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites
First, ZnGa2O4 nanospheres (0.120 g) were added to deionized water (30 mL) and sonicated for 30 min to obtain a homogeneous suspension. Next, 3 mL GO solution (1 mg mL−1) or the NGO suspension (1 mg mL−1) was added under magnetic stirring for 30 min. The suspension was then transferred to a 50 mL Teflon autoclave, sealed, and heated at 200 °C for 6 h. The precipitated solid product was collected by centrifuging, washed, and then dried at 60 °C in air. Hereafter, the obtained sample is denoted as ZnGa2O4/rGO (if prepared with the aqueous GO solution) or ZnGa2O4/N-rGO (if prepared with the NGO suspension). The synthesis parameters of the samples are listed in the Table S1.†For comparison, the ZnGa2O4 nanospheres in deionized water and the ZnGa2O4 nanospheres in an ammonia solution (without the aqueous GO solution or the NGO suspension) were also transferred to a 50 mL Teflon-autoclave, sealed, and heated at 200 °C for 6 h. And the sample of ZnGa2O4 and N-rGO composites by stirred mixing 6 h was prepared, which based on the same weight ratio with the above ZnGa2O4/N-rGO.
Characterization
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) measurements were performed on an X-ray diffractometer (D8 Advance, Bruker, Germany) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was carried out with a field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM; S-4800, Hitachi, Japan) at an accelerating voltage of 5 kV. The transmission electron microscope (TEM) images and high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) images were obtained with an electron microscope (JEM 2100. JEOL, Japan) operating at an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. Raman spectroscopy was performed at room temperature by a Raman spectrometer (Nicolet 67000/NXR, ThermoFisher, USA) with a 532 nm Nd:YAG excitation source. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements and valence-band X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (VB XPS) measurements were performed on an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (ESCALAB 250, ThermoFisher, USA) equipped with an Al Kα source. Photoluminescence (PL) spectra were obtained with a fluorescence spectrophotometer (F-4500, Hitachi High-Technologies, Japan) at the emission wavelength of 310 nm. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) diffuse-reflectance spectra (DRS) were recorded on a UV-vis spectrophotometer (UV-2550, Shimadzu, Japan), with BaSO4 used as the reference sample. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area of each sample was obtained on a surface area analyzer (ASAP 2020, Micromeritics, USA) at the liquid-nitrogen temperature. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were obtained with an infrared spectrometer (NEXUS 670, Thermo Nicolet, USA).Photoelectrochemical characteristics
The photoelectrochemical characteristics of the samples were measured with an electrochemistry potentiostat (CHI 660D, Shanghai Chenhua Limited, China) using a homemade three-electrode cell with Ag/AgCl as the reference electrode and a Pt wire as the counter electrode. An aqueous Na2SO4 (0.5 M) solution was used as the electrolyte under UV light irradiation from a 300 W xenon lamp (PLS-SXE300CUV, Beijing Perfect Light Co., Ltd., China). For the fabrication of the photoanode, 10 mg of each sample was added to a certain amount of dimethyl formamide (DMF) and ground for 15 min to obtain slurry. The slurry was then spread on a 15 mm × 20 mm indium–tin oxide (ITO) conducting glass and then dried under ambient conditions.Photocatalytic activity evaluation
Hydrogen production reactions were carried out at 5 °C in a closed-circulation gas system. First, 0.05 g of sample was dispersed in 100 mL of an aqueous 0.05 M Na2SO3 solution as the sacrificial reagent in a borosilicate glass reactor equipped with a quartz lid for light penetration. A suitable amount of H2PtCl6 (Pt content: 1 wt%) was then added to the solution as the co-catalyst. The photoreactor containing the cocatalyst, sacrificial reagent, and photocatalyst was then sonicated for several minutes to allow the suspension to mix uniformly. Before illumination, nitrogen gas was purged through the suspension for 0.5 h. A 300 W xenon lamp (λ ≥ 250 nm, PLS-SXE300CUV, Beijing Perfect Light Co., Ltd., China) was used as UV light source (15 cm far away from the photocatalytic reactor). The focused intensity on the flask was detected to be 89.68 mW cm−2 by UV radiometer (UV-A 141108). The amount of hydrogen produced was analyzed by a gas chromatograph (GC-7806 TCD) using 5 Å molecular sieve columns and N2 as the carrier gas. The apparent quantum efficiency (QE) was measured under the similar photocatalytic reaction conditions using four low power UV-LEDs (3 W, 365 nm, Shenzhen LAMPLIC Science Co. Ltd. China) and an UV radiometer (UV-A 141108). The four low power UV-LEDs were used as light sources (1 cm away from the reactor in four different directions). The focused intensity and areas on the flask for each UV-LED was detected to be 75.61 mW cm−2 and 1 cm,2 respectively. According to eqn (1),43 the QE was measured and calculated:
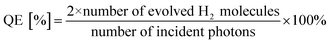 | (1) |
Results and discussion
Structure and morphology of the ZnGa2O4, ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites
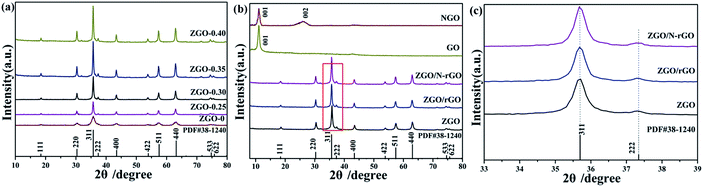
The phase crystallinity and purity of the precursor and as-prepared samples were determined by analyzing the XRD measurements. Fig. 1a shows the XRD patterns of the as-prepared ZnGa2O4 samples with different amounts of the surfactant trisodium citrate, which match the powder diffraction pattern of cubic ZnGa2O4 (JCPDS card no. 38-1240). The absence of other XRD features indicates the high purity of the as-prepared ZnGa2O4 samples. The diffraction patterns are weak for the sample prepared without added surfactant, indicating that the crystallinity of ZnGa2O4-0 was low. Furthermore, the diffraction patterns of the samples with increasing amount of surfactant are stronger, indicating that the crystallinity of ZnGa2O4-x increases with increasing surfactant content.56 This phenomenon may be ascribed to the structure-directing reagent trisodium citrate, that could form Zn2+–Cit3−–Ga3+ complexes to control the nucleation and growth of the crystals, resulting in the ZnGa2O4 particles assembling into nanospheres57 and increased crystallinity. The formation of ZnGa2O4 nanospheres was confirmed by SEM and TEM observations. The crystallinity of the ZnGa2O4 nanospheres did not exhibit obvious changes when the amount of trisodium citrate was above 0.35 g. Fig. 1b shows the XRD patterns of GO, NGO, ZnGa2O4-0.30 (ZGO), ZnGa2O4-0.30/rGO (ZGO/rGO), and ZnGa2O4-0.30/N-rGO (ZGO/N-rGO). The GO plates showed a sharp diffraction peak at 2θ = 10.8°, which is indexed to the (001) crystal plane. However, NGO exhibited an XRD peak corresponding to the (002) plane at 26.3°, indicating that part of GO was mildly reduced during the moderate refluxing process in the ammonia solution.55 Obviously, the diffraction peaks of the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites are in good agreement with those of cubic ZnGa2O4 (JCPDS card no. 38-1240), which has the same composition as pure ZnGa2O4. No shift in the diffraction peaks of the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites were observed when compared with of the peaks of pure ZnGa2O4 (Fig. 1c), indicating that there were no changes in the lattice structure of ZnGa2O4 in the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites.58 This result suggests that rGO and N-rGO were not inserted in the lattice of ZnGa2O4, which means that ZnGa2O4 was deposited on the surface of rGO and N-rGO. The absence of the rGO and N-rGO diffraction peaks in the patterns of the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites can be ascribed to the low content (2%) of rGO and N-rGO.59The morphology of the as-prepared ZnGa2O4 samples (ZnGa2O4-x) prepared with different amounts of trisodium citrate (x in grams) was investigated with TEM and SEM, and the results are shown in Fig. 2 and S1,† respectively. It can be seen that with the increase in the amount of trisodium citrate amount, the diameter of ZnGa2O4 spheres increased. The morphology of the ZnGa2O4 samples was characterized by irregular particles when the amount of trisodium citrate used was below 0.25 g (Fig. 2a–d). Further increase in the amount of trisodium citrate used (0.30 g) led to the assembling of ZnGa2O4 particles into nanospheres with diameters of about 80 nm (Fig. 2e and f). The diameter of the ZnGa2O4 nanospheres was about 230 and 260 nm when the amount of trisodium citrate used was 0.35 g (Fig. 2g and h) and 0.40 g (Fig. 2i and j), respectively. These results indicate that we successfully synthesized size-controlled ZnGa2O4 nanospheres by adjusting the amount of trisodium citrate.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 TEM images of ZnGa2O4 samples with different amount of surfactant trisodium citrate: (a, b) ZnGa2O4-0; (c, d) ZnGa2O4-0.25; (e, f) ZnGa2O4-0.30; (g, h) ZnGa2O4-0.35 and (i, j) ZnGa2O4-0.40. | ||
The morphology of the ZnGa2O4/N-rGO and ZnGa2O4/rGO composites are shown in Fig. 3 and S2.† Fig. 3 shows typical TEM and HRTEM images of the ZnGa2O4-0.25/N-rGO, ZnGa2O4-0.30/N-rGO, and ZnGa2O4-0.35/N-rGO samples, in which we can clearly see that ZnGa2O4 was deposited on the surface of the N-rGO sheet. The lattice fringe of d = 0.34 nm corresponds to the (002) plane of N-rGO,59 and the lattice spacing of d = 0.25 nm matches well with the (311) plane of ZnGa2O4.57 The ZnGa2O4 aggregated on the surface of the N-rGO sheet when ZnGa2O4 consisted of irregular particles (Fig. 3a), which was an adverse effect on charge separation and charge transfer. Fig. 3c and e show ZnGa2O4 uniformly dispersed on the N-rGO sheet when the ZnGa2O4 particles assembled to form nanospheres, which could promote charge separation and thus enhance the catalytic activity. These results indicate that we successfully assembled ZnGa2O4 on the 2D platform of the N-rGO sheet.
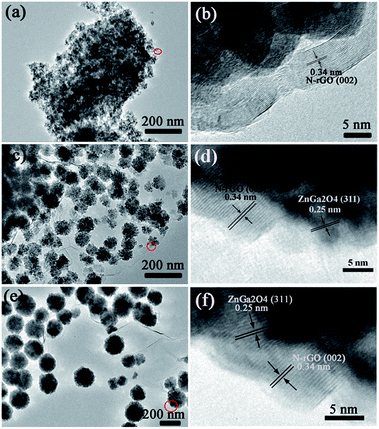 | ||
| Fig. 3 TEM and HRTEM images of the samples: (a, b) ZnGa2O4-0.25/N-rGO; (c, d) ZnGa2O4-0.30/N-rGO; (e, f) ZnGa2O4-0.35/N-rGO. | ||
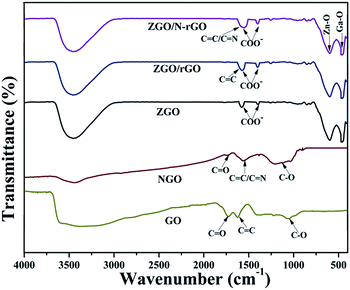
Fig. 4 shows the FT-IR spectra of GO, NGO, ZGO, ZGO/rGO, and ZGO/N-rGO. In the FT-IR spectra of the GO and NGO, the bands at 1726, 1623, 1560 and 1052 cm−1 are ascribed to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O in COOH stretching, aromatic C
O in COOH stretching, aromatic C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C skeletal vibration, and alkoxy C–O stretching, respectively.54 In the FT-IR spectrum of NGO, the broad band centered at 1000–1240 cm−1 includes alkoxy C–O (1052 cm−1) and epoxy C–O (1226 cm−1) stretching vibrations, and the peak of C
C skeletal vibration, and alkoxy C–O stretching, respectively.54 In the FT-IR spectrum of NGO, the broad band centered at 1000–1240 cm−1 includes alkoxy C–O (1052 cm−1) and epoxy C–O (1226 cm−1) stretching vibrations, and the peak of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O at 1726 cm−1 stretching is significantly diminished, implying that GO was mildly reduced. Owing to the overlapping C
O at 1726 cm−1 stretching is significantly diminished, implying that GO was mildly reduced. Owing to the overlapping C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N (1572 cm−1) and C
N (1572 cm−1) and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C peaks and the relatively low ratio of N to C atoms, it was difficult to identify the C
C peaks and the relatively low ratio of N to C atoms, it was difficult to identify the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N signal by FT-IR.60 In the FT-IR spectra of ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites, the peaks of C
N signal by FT-IR.60 In the FT-IR spectra of ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites, the peaks of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching at 1726 cm−1 and alkoxy C–O stretching at 1052 cm−1 are absent, indicating that there was reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites. These results were further confirmed by Raman and XPS observations.
O stretching at 1726 cm−1 and alkoxy C–O stretching at 1052 cm−1 are absent, indicating that there was reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites. These results were further confirmed by Raman and XPS observations.
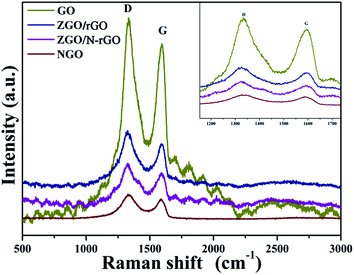
In order to confirm that there was reduced graphene oxide in the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites, Raman spectra of GO, ZGO/rGO, ZGO/N-rGO, and NGO were obtained. It can be seen in Fig. 5 that all samples exhibited two typical peaks (D band and G band). In Raman spectroscopy, the D band is related to structural disorder and defects in graphene, and the G band is due to stretching of sp2-hybridized C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C.61–63 Both bands can be modified by doping, with the D and G bands shifting toward lower frequencies upon N-doping,50 which has also been observed in N-doped graphene oxide derived from a moderate refluxing treatment in an ammonia solution of graphene oxide. It has been reported that the Raman shifts of the D and G bands are slightly blue-shifted when GO is reduced to rGO.64,65 Similar trends were observed in this study: as GO transformed to ZGO/rGO, the D band shifted from 1332 to 1325 cm−1, whereas the G band shifted from 1595 to 1593 cm−1; for the transformation from NGO to ZGO/N-rGO, the D band shifted from 1330 to 1326 cm−1, whereas the G band shifted from 1588 to 1584 cm−1. Compared with the Raman spectra of GO and NGO, an increase in the ratio between the intensities of D and G bands (ID/IG) was observed in the spectra of the composites. The values of ID/IG for GO and NGO was 1.15 and 1.19, respectively, while it increased to 1.28 and 1.29 for ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO, thus confirming the existence of reduced graphene oxide sheets in the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites43,66 and indicating the reduction of the exfoliated GO.67 In addition, the values of ID/IG of NGO and ZGO/N-rGO were higher than those of GO and ZGO/rGO, thereby implying that nitrogen was successfully introduced into GO.68 This result was further confirmed by XPS analysis.
C.61–63 Both bands can be modified by doping, with the D and G bands shifting toward lower frequencies upon N-doping,50 which has also been observed in N-doped graphene oxide derived from a moderate refluxing treatment in an ammonia solution of graphene oxide. It has been reported that the Raman shifts of the D and G bands are slightly blue-shifted when GO is reduced to rGO.64,65 Similar trends were observed in this study: as GO transformed to ZGO/rGO, the D band shifted from 1332 to 1325 cm−1, whereas the G band shifted from 1595 to 1593 cm−1; for the transformation from NGO to ZGO/N-rGO, the D band shifted from 1330 to 1326 cm−1, whereas the G band shifted from 1588 to 1584 cm−1. Compared with the Raman spectra of GO and NGO, an increase in the ratio between the intensities of D and G bands (ID/IG) was observed in the spectra of the composites. The values of ID/IG for GO and NGO was 1.15 and 1.19, respectively, while it increased to 1.28 and 1.29 for ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO, thus confirming the existence of reduced graphene oxide sheets in the ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO composites43,66 and indicating the reduction of the exfoliated GO.67 In addition, the values of ID/IG of NGO and ZGO/N-rGO were higher than those of GO and ZGO/rGO, thereby implying that nitrogen was successfully introduced into GO.68 This result was further confirmed by XPS analysis.
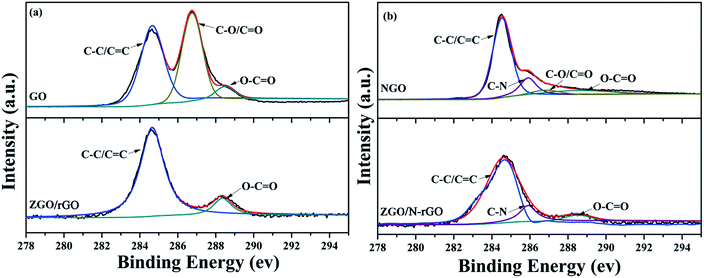
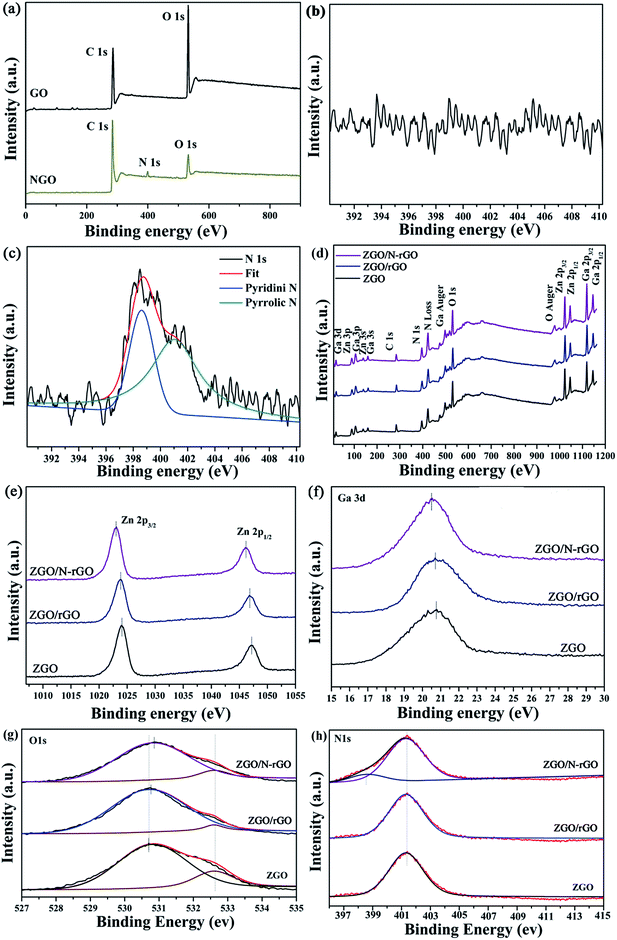
XPS was conducted to characterize the chemical composition and surface chemical states of the as-prepared samples. As shown in Fig. 6, the C 1s XPS peaks of GO centered at 284.5, 286.7 and 288.5 eV are assigned to the C–C bond, C–O/C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond (epoxy, hydroxyl, and carbonyl) and O–C
O bond (epoxy, hydroxyl, and carbonyl) and O–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond (carboxyl), respectively,69,70 which clearly indicate a high degree of oxidation. In the C 1s XPS spectrum of ZGO/rGO, the intensity of the peak for the O–C
O bond (carboxyl), respectively,69,70 which clearly indicate a high degree of oxidation. In the C 1s XPS spectrum of ZGO/rGO, the intensity of the peak for the O–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond is much lower than that in the spectrum of GO, and the peak for the C–O/C
O bond is much lower than that in the spectrum of GO, and the peak for the C–O/C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond is almost absent. Compared with the spectrum of NGO, the peak of the C–O/C
O bond is almost absent. Compared with the spectrum of NGO, the peak of the C–O/C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond is also almost absent in the C 1s XPS spectrum of ZGO/N-rGO, which indicates that the hydrothermal synthesis significantly removed most oxygen-containing functional groups, thereby converting GO and NGO to rGO and N-rGO. In addition, the appearance of a peak at 286.20 eV in the respective C 1s XPS spectra of NGO and ZGO/N-rGO can be attributed to the C–N bond,71 which indicates that nitrogen was successfully introduced into GO.
O bond is also almost absent in the C 1s XPS spectrum of ZGO/N-rGO, which indicates that the hydrothermal synthesis significantly removed most oxygen-containing functional groups, thereby converting GO and NGO to rGO and N-rGO. In addition, the appearance of a peak at 286.20 eV in the respective C 1s XPS spectra of NGO and ZGO/N-rGO can be attributed to the C–N bond,71 which indicates that nitrogen was successfully introduced into GO.
Fig. 7a shows that the XPS spectrum of the as-prepared NGO has a N peak (∼400.0 eV),55 whereas this peak does not appear in the XPS spectrum of GO (Fig. 7b), providing convincing evidence that nitrogen was successfully introduced into GO. The N 1s spectrum of NGO (Fig. 7c) comprises peaks corresponding to pyridine (398.45 eV) and pyrrole (400.68 eV).55 Fig. 7d shows typical XPS survey spectra of ZnGa2O4, ZnGa2O4/N-rGO, and ZnGa2O4/rGO composites. The high-resolution spectra of the Zn 2p, Ga 3d, O 1s, and N 1s states of ZGO, ZGO/rGO, and ZGO/N-rGO are shown in Fig. 7e–h. The two peaks of pure ZnGa2O4 at 1024 and 1046.2 eV are attributed to Zn 2p3/2 and Zn 2p1/2, respectively, which are assigned to Zn2+ oxidation (Fig. 7e). The peaks with binding energies of 20.75 and 401.3 eV correspond to the Ga 3d state and the N 1s state of NO3−, respectively, in ZnGa2O4 (Fig. 7f and h).72 The O 1s spectrum of pure ZnGa2O4 consists of two components: the peak with lower bind energy at 530.7 eV is ascribed to the lattice oxygen; the peak with higher bind energy at 532.6 eV is ascribed to the chemisorbed H2O molecules or OH− groups on the surface (Fig. 7g).73 For the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites, the peak corresponding to the Zn 2p state is blue shifted by 0.2 and 0.9 eV, respectively, while the Ga 3d peak is blue shifted by 0.05 and 0.2 eV, respectively, compared with the peak in the spectrum of pure ZnGa2O4. The O 1s peak of the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites is shifted by 0.07 and 0.2 eV toward higher energy when compared with the peak in the spectrum of pure ZnGa2O4. The N 1s peak remains at the same binding energy for pure ZnGa2O4 and the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites. Finally, a peak at 398.5 eV corresponding to pyridine from the C–N bond appears in the spectrum of the ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composite, which further confirms that nitrogen was successfully introduced into GO. These XPS spectra reveal the existence of chemical bonds between ZnGa2O4 and rGO or N-rGO in the composites, and the interfacial interaction between ZnGa2O4 and N-rGO was stronger than that in the ZnGa2O4/rGO composite.
The optical properties and band structures of the as-prepared samples were measured by UV-vis diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy and valence-band X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (VB XPS). As shown in Fig. S4,† the absorption edge of the as-prepared ZnGa2O4 samples with ZnGa2O4 spheres of different sizes remained the same, indicating that the band gap (4.40 eV) estimated using Tauc plots of (αhν)n versus photon energy (hν) following the Kubelka–Munk method74 did not change. The absorption edge of the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites also remained the same as that of bare ZnGa2O4 (Fig. 8a and b). However, when compared with the spectrum of pure ZnGa2O4, a wide absorption feature in the visible-light region appears in the spectra of the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites. This can be attributed to the presence of carbon in the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites, which reduced the reflection of light.75 As shown in Fig. 8c, the position of the VB maxima of pure ZnGa2O4 and the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites are same and located at about 3.36 eV, which means that the band gap and valance band did not change with the addition of rGO and N-rGO.
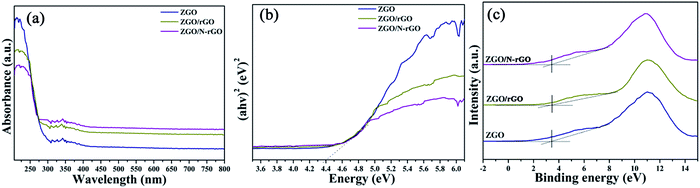 | ||
| Fig. 8 (a) UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectra and (b) the plot of transformed Kubelka–Munk function versus the energy and (c) valence-band XPS spectra of ZGO, ZGO/rGO and ZGO/N-rGO. | ||
Photocatalytic activity of the ZnGa2O4, ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites
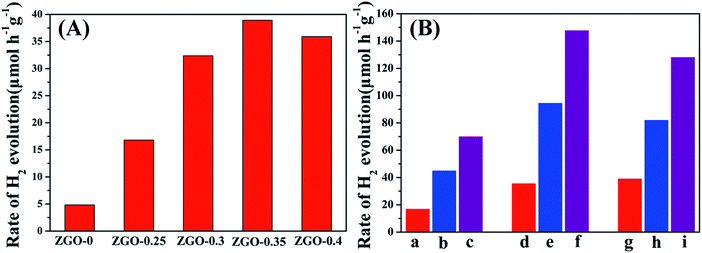
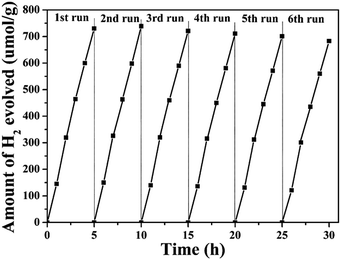
The photocatalytic activities of the samples for H2 production were evaluated under irradiation by a 300 W xenon lamp and using sodium sulfite as a sacrificial agent. Fig. 9A shows a comparison of the photocatalytic activities of ZnGa2O4 with different sizes: ZnGa2O4-0, ZnGa2O4-0.25, ZnGa2O4-0.30, ZnGa2O4-0.35, and ZnGa2O4-0.40. The rate of H2 production was poor when the ZnGa2O4-0 and ZnGa2O4-0.25 samples were made up of irregular particles. The photocatalytic activity for H2 production was significantly enhanced when the ZnGa2O4 particles assembled to form nanospheres. As the diameter of the ZnGa2O4 spheres increased, the rate of H2 production first increased, with a highest value of 38.94 μmol h−1 g−1 when the diameter of the ZnGa2O4 spheres reached 230 nm. Further increase in the diameter of the ZnGa2O4 spheres led to a decrease in the rate of H2 evolution, which can be ascribed to the crystallinity, morphology, and BET surface area of the samples. The BET surface area of each sample is listed in the ESI Table S2.† It can be seen that ZnGa2O4-0 and ZnGa2O4-0.25 had large BET surface areas, but the two samples were made up of irregular particles and the crystallinity was low, resulting in low rates of H2 evolution. When the amount of trisodium citrate used during synthesis was increased, the BET surface area of the samples decreased, but the morphology of ZnGa2O4-0.30, ZnGa2O4-0.35, and ZnGa2O4-0.40 was characterized by ZnGa2O4 particles assembling into nanospheres and the crystallinity was high, resulting in improved rates of H2 evolution. Taking into account the above three factors, ZnGa2O4-0.35 showed the highest photocatalytic activity. Fig. 9B shows the photocatalytic activities for H2 evolution of ZnGa2O4-0.25, ZnGa2O4-0.30, and ZnGa2O4-0.35 and their corresponding composites with rGO and N-rGO. The rates of H2 evolution of the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites dramatically improved when compared with that of ZnGa2O4, and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO had higher photocatalytic activity than ZnGa2O4/rGO. To investigate the effect of surface area on the photocatalytic activity for H2 production, the rate of H2 production as a function of the BET surface area was examined (Fig. S5†). It can be seen that the BET surface area was not the cause of the dramatic improvement in the rate of H2 evolution of the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites when compared with that of ZnGa2O4. Thus, it can be concluded that because N-rGO possessed better electrical conductivity than rGO, it improved charge-carrier separation and transfer, resulting in the enhanced photocatalytic activities for H2 production. Unlike pure ZnGa2O4, the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites showed the highest photocatalytic activity for H2 production when the diameter of ZnGa2O4 spheres reached 80 nm, which was due to the intimate interfacial contact between the ZnGa2O4 spheres with suitable size and rGO or N-rGO. The results showed that using rGO or N-rGO as a catalyst support led to much higher ability for H2 evolution. Moreover, a suitable size of ZnGa2O4 spheres was crucial to the optimization of interfacial contact and photocatalytic activity.The stability of the composites is an important factor in their practical application as photocatalysts. To assess their suitability for practical use, we measured the photostability of the ZnGa2O4-0.30/N-rGO composites, and the result is shown in Fig. 10. The photocatalytic activity did not significantly diminish after six cycles of photocatalytic water splitting, which indicates that the composite exhibited excellent stability in photocatalytic H2 generation from water splitting.
Mechanism accounting for the photocatalytic activity enhancement in ZnGa2O4, ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites
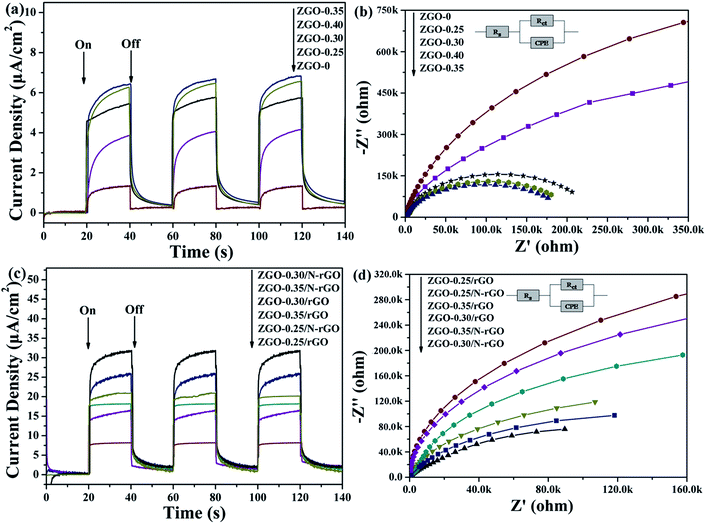
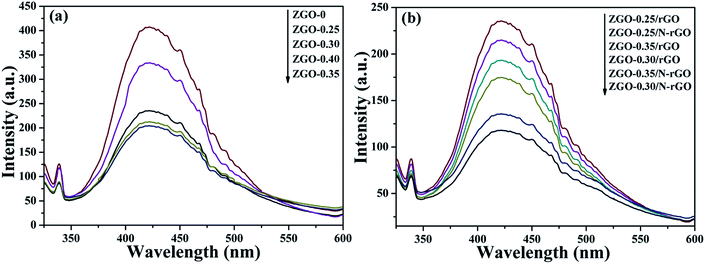
To investigate the charge-carrier separation and transfer in the samples, the photocurrent transient response (PCTR) and electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) were measured. In the EIS, the semicircles in the Nyquist plots can be simulated well by an electrical equivalent circuits model. A smaller semicircle radius, corresponding to a lower charge-carrier transfer resistance value (Rct), suggests a higher charge-carrier separation and transfer rate. Table S3† show Rct value, which are calculated based on electrical equivalent circuits model. Fig. 11a and b show the PCTR and EIS of as-prepared ZnGa2O4 samples with different sizes. For ZnGa2O4-0 and ZnGa2O4-0.25, which consisted of irregular particles, the photocurrent densities were about 1.32 and 3.87 μA cm−2, respectively. The photocurrent density of ZnGa2O4-0.30, ZnGa2O4-0.35, and ZnGa2O4-0.40 spheres were about 5.45, 6.4, and 6.27 μA cm−2, respectively. The higher photocurrent in ZnGa2O4-0.35 and ZnGa2O4-0.40 suggests a higher charge-transfer rate, which promotes efficient separation of photogenerated electron–hole pairs and retards recombination of charge carriers. As shown in Fig. 11b, the Nyquist plots of ZnGa2O4-0.30, ZnGa2O4-0.35, and ZnGa2O4-0.40 show lower Rct value when compared to those in the Nyquist plots of ZnGa2O4-0 and ZnGa2O4-0.25, indicating that the ZnGa2O4-0.30, ZnGa2O4-0.35 and ZnGa2O4-0.40 spheres had faster charge-transport rates. These results suggest that ZnGa2O4-0.35 and ZnGa2O4-0.4 had similar capability of charge-carrier separation and transfer because they had similar crystallinity. The PCTR and EIS results of ZnGa2O4 with different sizes are consistent with the results of photocatalytic water splitting activity. As shown in Fig. 11c, the ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites showed increased current when compared to the ZnGa2O4/rGO composites, indicating that doping nitrogen into reduced graphene oxide increased the transfer rate of electrons from the conduction band of the semiconductor.76 In addition, the photocurrent density of the ZnGa2O4-0.30/N-rGO composite was the highest, with a value of about 31.65 μA cm−2, which can be attributed to the catalyst support N-rGO and the intimate interfacial contact between the ZnGa2O4 spheres with suitable size and N-rGO. Fig. 11d shows the EIS Nyquist plots of ZnGa2O4, ZnGa2O4/rGO, and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO. The Rct value of the ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites was lower, which further proved that nitrogen doping of reduced graphene oxide could enhance the charge-carrier separation and transfer for improved photocatalytic activity. The PCTR and EIS results of the ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites are consistent with the results of photocatalytic water splitting activity. This is because that rGO possessed high surface area and superior electrical conductivity, and N-rGO had better electrical conductivity than rGO. It is beneficial for the separation and transfer of photoinduced charge carriers.In general, the PL spectrum is used to investigate the separation efficiency of photogenerated charge carriers in a photocatalyst. Fig. 12 shows PL spectra of as-prepared ZnGa2O4 samples with different size and ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites, obtained with an excitation wavelength of 310 nm. The spectra show a strong emission band in the 375–500 nm range, with the peak position at 421 nm, and it originated from the self-activation center of the octahedral Ga–O.77 The weak band at 338 nm can be ascribed to absorption by ZnGa2O4.57 As shown in Fig. 12a, both ZnGa2O4-0.35 and ZnGa2O4-0.40 exhibited a similar and weaker emission peak at the same position, indicating that high crystallinity was beneficial to suppressing the recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. In the PL spectrum of ZnGa2O4/N-rGO, a weaker emission peak appears at the same position, indicating that the addition of N-rGO significantly suppressed the recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. The PL results further confirmed that N-rGO possessed higher electrical conductivity than rGO and was beneficial for the separation and transfer of photoinduced charge carriers.
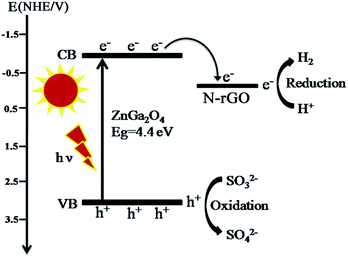
Based on the above results and discussion, we propose the mechanism for the photocatalytic reaction over ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites as shown in Fig. 13. ZnGa2O4 can excite the electrons and produce photogenerated electron–hole pairs under ultraviolet light irradiation. Then the excited electrons on the conduction band (−1.04 V vs. NHE) of ZnGa2O4 could be easily transferred to the N-rGO sheets due to the lower Fermi level (−0.08 V vs. NHE)54 of N-rGO compared to ZnGa2O4, which could inhibit electron–hole pairs recombination, leading to the enhanced photocatalytic activity. As a result, the photogenerated electrons gathered on the N-rGO sheets could effectively reduce H+ to produce H2 whereas the photogenerated holes could be sacrificed by oxidizing sulfite ions to sulfuric ions (Fig. 13). The N-rGO catalyst support possessed high electrical conductivity and the intimate interfacial contact between the ZnGa2O4 spheres with suitable size (80 nm) and N-rGO, which were beneficial for the separation of photoinduced charge carriers, resulting in enhanced photocatalytic H2 generation from water splitting. For the ZnGa2O4 samples with different sizes, their crystallinity, morphology, and BET surface area were determining factors of their photocatalytic activities for H2 production. Since a semiconductor with high crystallinity is beneficial for the transfer of photoinduced charge carriers.56 As the crystallinity of ZnGa2O4 nanospheres increased with increasing diameter of the ZnGa2O4 spheres, the rate of H2 production increased. When the crystallinity of ZnGa2O4-0.35 and ZnGa2O4-0.40 nanospheres were the similar, the BET surface area was the factor that resulted in a decrease of the rate of H2 evolution for the ZnGa2O4-0.40 nanospheres. Thus, based on the combined effect of the crystallinity, morphology and BET surface area ZnGa2O4-0.35 showed the highest photocatalytic activity for H2 production when the diameter of ZnGa2O4 spheres reached 230 nm.
Conclusion
In summary, we successfully synthesized size-controlled ZnGa2O4 nanospheres by adjusting the amount of surfactant trisodium citrate, and assembled ZnGa2O4 on the 2D platform of N-doped reduced graphene oxide (N-rGO) sheet through conventional and efficient hydrothermal method, during which the intimate interfacial contact between ZnGa2O4 and the N-rGO sheet are achieved. The ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites showed remarkably improved photocatalytic performance under ultraviolet light irradiation. The highest H2 evolution rate reached 147.61 μmol h−1 g−1 with an apparent quantum efficiency of 3.2% at 365 nm. The H2-production rate is almost 4.2 times of that of pure ZnGa2O4 measured at the same conditions. The excellent photocatalytic H2-evolution activity of the ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites can be attributed to the presence of N-rGO and the intimate interfacial contact between ZnGa2O4 nanospheres with suitable size (80 nm) and N-rGO. N-rGO acted as a catalyst support and electron sink for promoting charge separation and transfer. The size of ZnGa2O4 nanospheres was related to the strong interfacial contact between ZnGa2O4 and N-rGO. This work provides a new strategy to improve the photocatalytic activity of ZnGa2O4 and offers new insight into the design and development of graphene-based composites for various applications.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21173131 and 21771119) and the Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province.Notes and references
- J. O. M. Bockris, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2002, 27, 731–740 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Ravelli, D. Dondi, M. Fagnoni and A. Albini, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 1999–2011 RSC.
- J. A. Turner, Science, 1999, 285, 687–689 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Li, X. Wang, D. Xiong and L. Liu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41, 9344–9354 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, W. Li, D. Xiong, D. Y. Petrovykh and L. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 4067–4077 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Xiong, W. Li, X. Wang and L. Liu, Nanotechnology, 2016, 27, 375401 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Li, X. Gao, X. Wang, D. Xiong, P.-P. Huang, W.-G. Song, X. Bao and L. Liu, J. Power Sources, 2016, 330, 156–166 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Li, X. Gao, D. Xiong, F. Xia, J. Liu, W.-G. Song, J. Xu, S. M. Thalluri, M. F. Cerqueira, X. Fu and L. Liu, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 2952–2958 RSC.
- W. Li, X. Gao, D. Xiong, F. Wei, W.-G. Song, J. Xu and L. Liu, Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7, 1602579 CrossRef.
- W. Li, D. Xiong, X. Gao, W.-G. Song, F. Xia and L. Liu, Catal. Today, 2017, 287, 122–129 CrossRef CAS.
- F. E. Osterloh, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 2294–2320 RSC.
- A. Kudo and Y. Miseki, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 253–278 RSC.
- R. M. Navarro, M. C. Alvarez-Galván, J. A. Villoria de la Mano, S. M. Al-Zahrani and J. L. G. Fierro, Energy Environ. Sci., 2010, 3, 1865–1882 CAS.
- L. Qi, J. Yu and M. Jaroniec, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13, 8915–8923 RSC.
- J. Zhang, J. Yu, M. Jaroniec and J. R. Gong, Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 4584–4589 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Cao, D. Chen, W. Li and R. A. Caruso, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 13129–13137 CAS.
- Y. Yu, C. Cao, W. Li, P. Li, J. Qu and W. Song, Nano Res., 2012, 5, 434–442 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Hisatomi, J. Kubota and K. Domen, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 7520–7535 RSC.
- Y. Inoue, Energy Environ. Sci., 2009, 2, 364–386 CAS.
- S. C. Yan, S. X. Ouyang, J. Gao, M. Yang, J. Y. Feng, X. X. Fan, L. J. Wan, Z. S. Li, J. H. Ye, Y. Zhou and Z. G. Zou, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 6400–6404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Liu, J. Huang, L. Cao, J. Wu, J. Fei, H. Ouyang, F. Ma and C. Zhou, Mater. Lett., 2013, 95, 160–163 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Kumagai, L. Ni and H. Irie, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 1884–1886 RSC.
- X. Xu, A. K. Azad and J. T. S. Irvine, Catal. Today, 2013, 199, 22–26 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zeng, T. Hu, N. Hou, S. Liu, W. Gao, R. Cong and T. Yang, Mater. Res. Bull., 2015, 61, 481–485 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Marschall, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24, 2421–2440 CrossRef CAS.
- L. J. Zhang, R. Zheng, S. Li, B. K. Liu, D. J. Wang, L. L. Wang and T. F. Xie, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 13406–13412 CAS.
- X. Li, Y. Feng, M. Li, W. Li, H. Wei and D. Song, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25, 6858–6866 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Trzciński, M. Szkoda, M. Sawczak, J. Karczewski and A. Lisowska-Oleksiak, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 385, 199–208 CrossRef.
- D. Lang, F. Cheng and Q. Xiang, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6, 6207–6216 CAS.
- H. Yu, P. Xiao, P. Wang and J. Yu, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 193, 217–225 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, T. Li, R. Yu, H. Yu and J. Yu, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 8682–8689 CAS.
- F. Cheng, H. Yin and Q. Xiang, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 391, 432–439 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wen, J. Xie, X. Chen and X. Li, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 391, 72–123 CrossRef CAS.
- A. K. Geim and K. S. Novoselov, Nat. Mater., 2007, 6, 183–191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M.-Q. Yang, N. Zhang, M. Pagliaro and Y.-J. Xu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 8240–8254 RSC.
- N. Zhang, M.-Q. Yang, S. Liu, Y. Sun and Y.-J. Xu, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 10307–10377 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Perreault, A. Fonseca de Faria and M. Elimelech, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 5861–5896 RSC.
- X. Li, J. Yu, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi and J. Xie, Small, 2016, 12, 6640–6696 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xu, Y. Mo, J. Tian, P. Wang, H. Yu and J. Yu, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 181, 810–817 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Xiang, F. Cheng and D. Lang, ChemSusChem, 2016, 9, 996–1002 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Liu, F. Li, Z. Sun, L. Xu, Y. Song and A. Munventwali, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 47314–47318 RSC.
- G. P. Singh, K. M. Shrestha, A. Nepal, K. J. Klabunde and C. M. Sorensen, Nanotechnology, 2014, 25, 265701 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Xiang, J. Yu and M. Jaroniec, Nanoscale, 2011, 3, 3670–3678 RSC.
- X. Tang, W. Chen, Z. Zu, Z. Zang, M. Deng, T. Zhu, K. Sun, L. Sun and J. Xue, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 18498–18503 RSC.
- Y. Zhu, S. Murali, W. Cai, X. Li, J. W. Suk, J. R. Potts and R. S. Ruoff, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 3906–3924 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Ci, L. Song, C. Jin, D. Jariwala, D. Wu, Y. Li, A. Srivastava, Z. F. Wang, K. Storr, L. Balicas, F. Liu and P. M. Ajayan, Nat. Mater., 2010, 9, 430–435 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, X. Li, L. Zhang, Y. Yoon, P. K. Weber, H. Wang, J. Guo and H. Dai, Science, 2009, 324, 768–771 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Deifallah, P. F. McMillan and F. Corà, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 5447–5453 CAS.
- Y. Li, Z. Zhou, P. Shen and Z. Chen, ACS Nano, 2009, 3, 1952–1958 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Deng, X. Pan, L. Yu, Y. Cui, Y. Jiang, J. Qi, W.-X. Li, Q. Fu, X. Ma, Q. Xue, G. Sun and X. Bao, Chem. Mater., 2011, 23, 1188–1193 CrossRef CAS.
- A. L. M. Reddy, A. Srivastava, S. R. Gowda, H. Gullapalli, M. Dubey and P. M. Ajayan, ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 6337–6342 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Xu, J. Xiao, B. Liu, S. Griveau and F. Bedioui, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 66, 438–444 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wu, L. Liao, Q. Zhang, Y. Nie, J. Xiao, S. Wang, S. Dai, Q. Gao, Y. Zhang, X. Sun, B. Liu and Y. Tang, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 158, 42–48 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Liu, L. Zhang, R. Liu, Z. Gao, X. Yang, Z. Tu, F. Yang, Z. Ye, L. Cui, C. Xu and Y. Li, Journal, 2016, 656, 24–32 CAS.
- Z.-L. Wang, J.-M. Yan, Y.-F. Zhang, Y. Ping, H.-L. Wang and Q. Jiang, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 3073–3077 RSC.
- K. Lin, B. Ma, W. Su and W. Liu, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 286, 61–65 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, Z. Wu, D. Geng, X. Kang, M. Shang, X. Li, H. Lian, Z. Cheng and J. Lin, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24, 6581–6593 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Liu, C. Dong, K.-L. Wu, Y. Ye and X.-W. Wei, Mater. Lett., 2014, 129, 170–173 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Mou, Y. Wu, J. Sun, P. Yang, Y. Du and C. Lu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 13798–13806 CAS.
- Q. Mi, D. Chen, J. Hu, Z. Huang and J. Li, Chin. J. Catal., 2013, 34, 2138–2145 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Rao, R. Podila, R. Tsuchikawa, J. Katoch, D. Tishler, A. M. Rao and M. Ishigami, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 1594–1599 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Le-Sheng, L. Wei, C. Zhi-Min and S. Wei-Guo, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 20594–20598 Search PubMed.
- W. Li, L.-S. Zhang, Q. Wang, Y. Yu, Z. Chen, C.-Y. Cao and W.-G. Song, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 15342 RSC.
- T. N. Lambert, C. A. Chavez, B. Hernandez-Sanchez, P. Lu, N. S. Bell, A. Ambrosini, T. Friedman, T. J. Boyle, D. R. Wheeler and D. L. Huber, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 19812–19823 CAS.
- S. Stankovich, D. A. Dikin, R. D. Piner, K. A. Kohlhaas, A. Kleinhammes, Y. Jia, Y. Wu, S. T. Nguyen and R. S. Ruoff, Carbon, 2007, 45, 1558–1565 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, J. Yu, W. Xiao and Q. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 3847–3855 CAS.
- P.-G. Ren, D.-X. Yan, X. Ji, T. Chen and Z.-M. Li, Nanotechnology, 2011, 22, 055705 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Zheng, Y. Jiao, L. Ge, M. Jaroniec and S. Z. Qiao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 3110–3116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. S. Dey, S. Hajra, R. K. Sahu, C. R. Raj and M. K. Panigrahi, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 1787–1789 RSC.
- W. Tu, Y. Zhou, Q. Liu, S. Yan, S. Bao, X. Wang, M. Xiao and Z. Zou, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2013, 23, 1743–1749 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Che, L. Shen and Y. Xiao, J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 1722–1727 RSC.
- T. Zheng, Y. Xia, X. Jiao, T. Wang and D. Chen, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 3206–3211 RSC.
- L. Armelao, G. Bottaro, C. Maccato and E. Tondello, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 5480–5485 RSC.
- N. M. Nursam, J. Z. Y. Tan, X. Wang, W. Li, F. Xia and R. A. Caruso, ChemistrySelect, 2016, 1, 4868–4878 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-Y. Zhang, H.-P. Li, X.-L. Cui and Y. Lin, J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 2801–2806 RSC.
- B. Appavu, K. Kannan and S. Thiripuranthagan, J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2016, 36, 184–193 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Y. Bae, J. Lee, H. Jung, J. Park and J.-P. Ahn, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 10802–10803 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: The SEM images, FT-IR spectra and UV-vis spectra of the ZnGa2O4 with different size, the TEM and HRTEM images of the ZnGa2O4/rGO samples, the BET surface area of all samples, photocatalytic water splitting activity normalized by the BET surface areas of ZnGa2O4/rGO and ZnGa2O4/N-rGO composites. See DOI: 10.1039/c7ra09981a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |