Carbon dots-based ratiometric nanosensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) ions and glutathione†
Shuaimin Lua,
Di Wub,
Guoliang Li*ac,
Zhengxian Lva,
Zilin Chena,
Lu Chena,
Guang Chena,
Lian Xiaa,
Jinmao You*a and
Yongning Wu*c
aKey Laboratory of Life-Organic Analysis of Shandong Province, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, People's Republic of China. E-mail: 61254368@163.com; jmyou6304@163.com; Tel: +86-537-4456305
bSchool of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
cKey Laboratories of Chemical Safety and Health, China National Center for Food Safety Risk Assessment, Beijing 100050, People's Republic of China. E-mail: wuyongning@cfsa.net.cn
First published on 21st October 2016
Abstract
Glutathione (GSH) plays a crucial role in many cellular processes. Recently, great efforts have been made to develop efficient methods for GSH sensing in organisms. Herein, we reported the design and application of a specific ratiometric fluorescent probe, which contained carbon quantum dots (CDs) as sensing signal and Rhodamine B (RhB) as reference, for highly sensitive detection of mercury ions (Hg2+) and glutathione (GSH). The obtained nanosensor showed characteristic fluorescence emissions of CDs and RhB under a single excitation wavelength. The functional CDs were first synthesized in our laboratory according to a one-pot pyrolysis process of sodium citrate with histidine. In the presence of Hg2+, only the fluorescence of CDs was quenched due to electron transfer between Hg2+ and functional groups on the surface of CDs. Subsequently, the fluorescence of CDs–Hg2+ system was recovered gradually with the addition of GSH due to their stronger affinity with Hg2+, which could effectively exclude numerous background interferences. This method has been successfully applied to oxidative stress model investigation. The proposed ratiometric sensing strategy was proven to be facile, reliable, sensitive and selective, showing great potential for Hg2+ and GSH detection in environmental monitoring and biological detection.
Introduction
Glutathione (GSH), a thiol-containing tripeptide, is endogenously formed through L-glutamic acid, L-cysteine and glycine. As the most abundant intracellular nonprotein thiol (90% thiol in the cells), GSH is often involved in maintaining the normal functions of the immune system and a number of cellular processes including the maintenance of intracellular redox homeostasis, metabolism and detoxification.1–3 Meanwhile, many biomedical researchers have indicated that the altered levels of intracellular GSH concentration are closely associated with many diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV),4 liver damage,5 diabetes,6 Parkinson7 and so on. With growing concern over its importance for human health, there is an immediate demand for the development of sensitive, simple, and accurate method for GSH determination.So far, a variety of analytical techniques have been employed for the monitoring of GSH level, including capillary electrophoresis (CE),8 high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),9 surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS),10 electrochemical analysis,11 and colorimetric analysis.12 However, there are many intrinsic limitations for these conventional methods that include the need for heavy instrumentation and technical expertise, as well as complicated assay procedures and long operation time. With the aim of developing alternative approaches that overcome these limitations, increasing attentions have focused on fluorescence-based sensor, owing to their high selectivity, excellent sensitivity, easy to operation, economy and real-time detection.13,14 And a number of advanced fluorescent materials, especially upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs),15 fluorescent semiconductor quantum dots (QDs),16 and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs),17 have been actually designed for the determination of various substances over the years. However, these available materials suffer from various drawbacks, for instance the UCNPs, their limitations including special equipment and cutting-edge technology which might limit their application in the routine determination. Moreover, the synthesis of the QDs requires heavy metals, and not only that, the methods are often complex and extraordinarily time consuming. And the AuNPs, despite the excellent properties containing high sensitivity, convenient readout and so on, the disadvantages such as low quantum yield, and costly material, are obvious. Therefore, searching for a kind of benign nanomaterial is highly desirable.
Carbon quantum dots (so-called CDs), a new kind of fluorescent nanoparticles, have recently aroused explosive attention because of their superior optical properties and a wide variety of potential applications.18–20 Compared with traditional fluorescent probes, CDs are superior in terms of highly stable fluorescence intensity, low toxicity, easily synthesized, favorable biocompatibility, and excellent aqueous solubility.21–23 To date, various CDs-based methods for GSH detection have been well-developed. For instance, Ran et al. reported a fluorescence turn-off detection mode for GSH sensing, which could increase the considerably likelihood of false positive signals due to the presence of external quenchers or other environmental conditions.24 Efforts with this focus have brought a series of new turn-on fluorescence sensors based on CDs to detect GSH. For example, Gu et al. recently described an “off–on” fluorescence sensor by the complex of Au(III) and GSH with the limit of detection of 2.02 μM.25 However, these nanosensors only have a sole emission peak and the change of single emission peak intensity can be easily compromised by some other factors such as excitation and emission efficiency, concentration change of sensors, and complex environmental conditions.26 In order to overcome these problems, ratiometric fluorescence technique has caught increasing attention attributed to the advantage to eliminate environmental effects and offer more precise measurement.27,28 Such a system is often composed of two individual materials with different fluorescence emission wavelengths, in which one as the reference provides an invariable background signal and another is used as the sensing signal.29,30 By measuring the ratio of two fluorescent peaks instead of the absolute intensity of one peak, the strategy not only excludes numerous background interferences, but also improves the sensitivity and accuracy.31
In this paper, we reported a novel, turn-on ratiometric fluorescence assay containing CDs and Rhodamine B (RhB) for GSH detection based on the recovered fluorescent intensity of the CDs–Hg(II) system. This nanohybrid system possessed dual emission peaks at 440 and 570 nm upon one excitation wavelength of 350 nm. Owning to the electron transfer between the functional CDs and Hg2+, the fluorescence from CDs would be quenched efficiently.32 With the addition of GSH, the fluorescence of the CDs–Hg(II) system was recovered gradually because of their selective bond to Hg2+ through Hg–S bonding interactions, while the fluorescence of RhB remained constant.33 By taking advantage of the ratiometric fluorescence sensor, the satisfactory selectivity and sensitivity for GSH detection were carefully investigated. Furthermore, an oxidative stress model in rats was also constructed to explore the practicability of the proposed method, showing great potential in biosensing related applications.
Results and discussion
Characterization of CDs
The UV-vis absorption and emission spectra of the CDs are shown in Fig. 1a. It is can be seen that the maximum absorption peak and emission wavelength of CDs are confirmed to be 300 nm and 440 nm, respectively. Very bright blue luminescence under 365 nm UV light of the CDs solution can be clearly seen in the inset of Fig. 1a. Moreover, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was utilized to characterize the morphology and size of the CDs. As seen from Fig. 1b, the CDs are nearly spherical with the average diameter of 1.5 nm. The surface chemistry of the as-prepared CDs was identified by FT-IR spectrum (Fig. 1c). Accordingly, the absorption band at 3429 cm−1 is attributed to the stretching vibration of O–H and N–H. The peaks at 2923 and 815 cm−1 belong to the C–H stretching vibration mode and C–H out-of-plane bending mode. The strong absorption band at 1583 cm−1 indicates the existence of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O. The high intensity of the peak at 1388 cm−1 is assigned to C–N stretching vibrations. These characterization results confirm that abundant of hydroxyl and amino groups present on the surface of the as-prepared CDs, which significantly improves the water solubility of CDs. The XRD pattern of CDs in Fig. 1d reveals a broader peak at about 2θ = 24.6–25.8°, which is also attributed to highly disordered carbon atoms.34
O. The high intensity of the peak at 1388 cm−1 is assigned to C–N stretching vibrations. These characterization results confirm that abundant of hydroxyl and amino groups present on the surface of the as-prepared CDs, which significantly improves the water solubility of CDs. The XRD pattern of CDs in Fig. 1d reveals a broader peak at about 2θ = 24.6–25.8°, which is also attributed to highly disordered carbon atoms.34
Design principle study
As depicted in Scheme 1, the original fluorescence of CDs can be quenched in the presence of Hg2+. Upon the addition of GSH in the above CDs–Hg(II) system, Hg2+ can be removed from CDs surfaces through the formation of Hg–S bonds and the fluorescence of the CDs is dramatically recovered, while the fluorescence of RhB remains constant, thereby realizing the ratiometric fluorescence response to GSH. Fig. S1A† presents that Hg2+ can strongly quench the fluorescence of CDs. The selective quenching has been elucidated to be presumably via electron or energy transfer process resulting from the strong electrostatic interaction and metal–ligand coordination between CDs and Hg2+ as described in the literature reports.32 With the addition of GSH, the fluorescence of CDs–Hg2+ system is recovered gradually (Fig. S1B†). Hg2+ as a thiophilic metal ion has a high affinity preference to GSH.2,33 Therefore, Hg2+ can be competitively captured by GSH and the fluorescence intensity of CDs is restored readily. Herein, RhB is served as the reference signal in the sensor owning to its chemical inertness with Hg2+ and GSH. It is observed that the emission spectrum of RhB remains unchanged with the addition of Hg2+ and GSH, respectively (Fig. S1C and D†). As mentioned above, a novel, facile, sensitive, selective and accurate turn-on ratiometric fluorescence assay was established for determination of GSH. | ||
| Scheme 1 Schematic illustration of the application of ratiometric fluorescent probe based on a CDs–RhB nanohybrid system for detection of Hg2+ and GSH. | ||
Optimization of experimental conditions
To get the best sensing response, we systematically optimized the analytical conditions for the developed method. Therefore, prior to application of the CDs–Hg(II) system in the sensing assay for GSH, the effect of various factors containing pH, Hg2+ concentration, incubation time of quenching and restoration were investigated.Fig. 2a displays the fluorescent intensity of CDs at different pH values of solution. It is can be seen that the fluorescent intensity of CDs remains stable in an alkaline pH range of 7.0–9.0 and is influenced by a certain under the conditions of excess acidic or basic. Such a phenomenon implies that the fluorescence intensity of CDs is pH dependent and closely associated with the protonation state.35
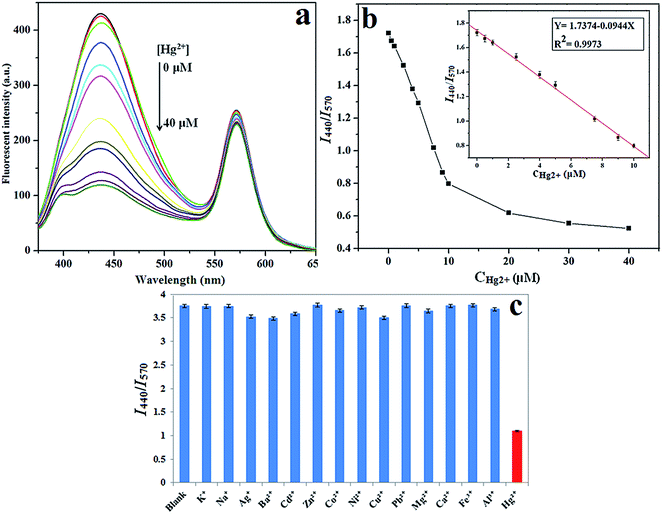
In order to achieve the best sensing response for GSH, the dosage of Hg2+ added to the assay solution needed to be optimized. Different concentrations of Hg2+ were added into 1 mL CDs solution, followed by the addition of 5 μM GSH and then the fluorescence recovery value ΔF was recorded. As shown in Fig. 2b, the ΔF value rapidly enhances with the increased Hg2+ concentration from 7 μM to 10 μM, reaches a maximum value at 10 μM, and then has a declined change with the further increase of Hg2+ concentration. The reason for this phenomenon is mainly because that the excess Hg2+ results in the binding between GSH with free Hg2+ in assay solution instead of Hg2+ on the surface of CDs. Therefore, based on the above results, 10 μM of Hg2+ was selected as the best candidate in the ratiometric fluorescence sensor.
The effect of pH on the restoration performance of GSH was also explored in the range of 5.0–11.0. As shown in Fig. 2c, GSH shows stronger affinity with Hg2+ in alkaline solutions than in acidic solution, which is in agreement with reported literature.36 In addition, Fig. 2a presents that the CDs have strongest fluorescent intensity in the pH of 8.0. Taking the two factors into account, pH 8.0 was chosen as the optimum reaction pH for further detection.
The quenching and restoration time of the sensing system was eventually optimized as shown in Fig. 2d and e. The assay was performed in 0.1 M PBS buffer (pH 8.0) with 10 μM Hg2+. As demonstrated in Fig. 2d, after the addition of Hg2+ into CDs solution, the fluorescence signal decreases rapidly with the extension of incubation time and then reaches to a stable stage after 8 min. Meanwhile, it is found from Fig. 2e that the fluorescence intensity keeps unchanged after 3 min with the addition of GSH. Therefore, 8 min and 3 min were recommended as the optimal quenching time and restoration time in the following ratiometric fluorescence assay.
Analytical performance
| Y = 1.7374 − 0.0944X, μM, (R2 = 0.9973) |
To investigate the specificity of fluorescence quenching by Hg2+, the fluorescence intensity ratio (I440/I570) of the nanohybrid system in the presence of a variety of metal ions including Hg2+, K+, Na+, Ag+, Ba2+, Cd2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Fe3+ and Al3+ is evaluated under the same conditions. As illustrated in Fig. 3c, the I440/I570 ratio exhibits obvious decrease with the addition of Hg2+, while the other metal ions show negligible effect, indicating the high specificity of the ratiometric nanosensor for Hg2+ detection over other metal ions.
| Y = 0.051X + 0.7379, μM, (R2 = 0.9979) |
| Assay method | Detection model | Linear range | Detect limit (nM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical | Current | 0–5 mM | 90 | 41 |
| CdSe–ZnS quantum dots | Fluorescent | 5–250 μM | 600 | 42 |
| CdTe quantum dots | Fluorescence | 0.6–20 μM | 100 | 34 |
| CDs–Hg2+ | Fluorescence | 0.1–20 μM | 30 | 43 |
| Ratiometric CDs–RhB–Hg2+ | Fluorescence | 0–10 μM | 20 | Proposed method |
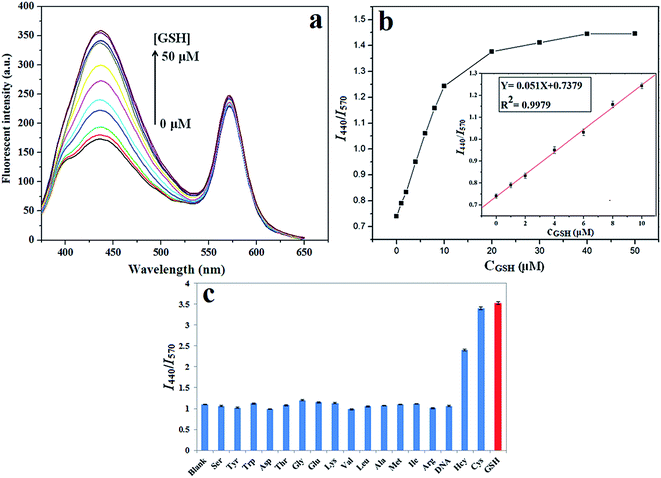
Besides sensitivity, selectivity is another important factor to verify the performance of our sensor system in practical applications. The complexity of serum systems presents great challenges to GSH detection because there are many kinds of amino acids and DNA in living systems. To investigate the selectivity of the proposed assay strategy for GSH, the fluorescence response to a series of relevant interfering substances was tested at the concentration of 10 μM, such as Ser, Tyr, Trp, Asp, Thr, Gly, Glu, Lys, Val, Leu, Ala, Met, Ile, Arg, Hcy, Cys, GSH and DNA. It can be observed that only thiol-containing compounds (Cys, Hcy and GSH) exhibit a significant enhancing influence on the I440/I570 ratio of the sensor system, while the other amino acids and DNA do not induce any noticeable fluorescence recovery (Fig. 4c). Although Cys and Hcy can also cause fluorescence response to this system, their concentrations (μM levels) are much lower than that of GSH (mM levels) in biological systems.37 Furthermore, due to the high sensitive of our proposed method, the serum sample needed to be diluted before the measurement. Under such conditions, Cys and Hcy would be at very low concentrations, and thus would not interfere with the assay. Thus, the new sensing method is highly selective toward the target GSH detection without any significant interference, which making it promising as a candidate for GSH detection in the practical bio-analysis.
Determination of GSH in rat serum samples
GSH is an essential endogenous antioxidant in mammals, and plays important roles in maintenance of intracellular redox states and several detoxification reactions. The liver represents the major site of GSH metabolism, in which GSH and its related enzymes constitute an antioxidant defense system to protect against oxidative stress.38 Herein we applied this method to an oxidative stress model, which could cause the liver injury in rats by the gavage of bromobenzene. And we could explore the practicability of the proposed method by studying the relationship between the acute liver injury degrees with the GSH concentrations in rat serum.Since our assay is relative sensitive, appropriate pretreatment and dilution of serum (100-fold) are necessary to ensure the concentration of GSH in the standard calibration curve of this method. As illustrated in Fig. 5, the GSH concentration of the liver injury group exhibits a sharp decrease, and reaches the lowest value at 4 hours, and then has no obvious change in the next six hours. Compared with the liver injury group, the concentration of GSH remains nearly unchanged in the control group. It is can be seen that GSH concentration is effectively influenced by liver injury, which is probably because that GSH firstly appears to defense against oxidative stress, so that the GSH concentration occurs significant reduction. As a result, the phenomenon is in good agreement with the previously reported studies.39 Furthermore, the recovery of known spiked amounts of GSH in serum samples is ranging from 97.46 to 102.13%, indicating the good reliability of the proposed method (Table 2). Meanwhile, to further verify the accuracy of the developed method, the sample was also measured by DTNB colorimetric method,40 and consistent results were obtained (Table S1†). Although DTNB had been selected as the most commonly used UV probe, the disadvantages such as high toxicity and easy oxidation limited its practical applications in vivo assay. In our study, the nanohybrid-based probe not only possessed low toxicity and easy to get, but also provided ultrasensitive and accurate results in samples assay, making it promising as a candidate for GSH detection in biological detection.
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Changes in the GSH concentration with time of the control group (black line) and liver injury group (red line). | ||
Conclusion
In conclusion, by employing a nanohybrid system containing CDs and RhB as the probe, a turn-on ratiometric fluorescence nanosensor has been designed for the determination of GSH, which was demonstrated to be facile, less-cost, low sample consumption, accurate and sensitive. Such a typical CDs–RhB nanohybrid-based assay displays several advantages as follow: (1) the ratiometric fluorescence nanosensor could effectively eliminate the background interference and realized the selective analysis of GSH more accurately; (2) a fluorescence “turn-on” assay could greatly reduce the possibility of false positive signals compared with the “turn-off” mode; (3) in addition to the satisfactory analytical performances, the synthesis of CDs was simple and no further surface modification of CDs was demanded, which would greatly simplify the processes; (4) more importantly, the method had been successfully employed to assay of GSH in rat serum samples and satisfactory results were obtained; (5) all the available materials in the experiment were inexpensive and environment friendly. Considering the outstanding specialty of the proposed approach, our new sensing strategy would provide a powerful platform for GSH detection in biological applications.Experimental section
Materials
Rhodamine B, sodium citrate, glutathione (GSH), heparin sodium, quinine sulfate and all amino acids containing histidine (His), glycine (Gly), serine (Ser), alanine (Ala), threonine (Thr), valine (Val), aspartic acid (Asp), asparagine (Asn), leucine (Leu), isoleucine (Ile), glutamic acid (Glu), glutamine (Gln), tyrosine (Tyr), phenylalanine (Phe), proline (Pro), methionine (Met), tryptophane (Trp), lysine (Lys), cysteine (Cys) and arginine (Arg) were purchased from Aladdin Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Metal salts (HgCl2, KCl, NaCl, Zn(NO3)2·6H2O, CaCl2, MgSO4, Cu(NO3)2·5H2O, CoCl2·6H2O and FeCl3) were supplied by Fuyu Chemical Reagent Co. (Tianjin, China). Bromobenzene, sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4), disodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4), acetic acid (HAc), sodium acetate (NaAc), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) were purchased from Beijing Chemical Factory (Beijing, China). All reagents of analytical grade were used as received without further purification. Ultrapure water purified by a Milli-Q system (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA) was used throughout all of the experiments.Apparatus
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were obtained by a Tecnai G2 F20 electron microscope. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were recorded with a WQF-520A FTIR spectrophotometer using KBr pellets. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra were measured by a Cary 300 Bio UV-vis spectrophotometer. The crystal phase and structure of the sample were identified by the X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD, D/MAX 2500, Rigaku, Japan) using a Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å) and a fixed power source (40.0 kV, 200.0 mA). All fluorescence spectra were collected by a Hitachi F-7000 fluorescence spectrophotometer with an voltage of 400 V and slit width of 5 nm for both excitation and emission.Synthesis of the CDs
The functional CDs were first obtained in our laboratory using a one-pot pyrolysis process. Sodium citrate (0.5 g) and histidine (0.12 g) were dissolved in 20 mL ultrapure water to form a transparent solution. Then the mixture was transferred to a 50 mL Teflon equipped stainless steel autoclave and heated at 200 °C for 6 h. After the autoclave was cooled down to room temperature, the light brown solution was dialyzed with a cut-off dialysis bag (1000 Da) for 2 days to remove the unreacted small molecules. Finally, the CDs solution with a quantum yield (QY) of 29.7% was obtained (the details on QY measurements were described in ESI†) and stored at 4 °C for further detection and characterization.Fluorescence experiments
The fluorescence detection was performed in PBS buffer solution (10 mM, pH 8.0) at room temperature. In a typical process, 0.1 mL of diluted CDs dispersion solution (15.5 μg mL−1) was mixed with 1.9 mL PBS buffer solution in the presence of 1 μM RhB, followed by the addition of a series of concentrations of Hg2+ ranging from 0.5 to 40 μM. After incubating at room temperature for 8 min, the fluorescence measurements were carried out.Then, to investigate the effect of GSH on the fluorescent recovery of the CDs–Hg(II) system, different amounts of GSH were added into above mentioned CDs–RhB nanohybrid solution (the Hg2+ concentration was 10 μM). Subsequently, the mixture was fully blended for 3 min and monitored for fluorescent measurements. All experiments were performed at room temperature and conducted in triplicate.
Oxidative stress model construction and serum sample preparation
The present experiment was performed in compliance with the Guidelines of the Committee for Animal Experimentation of Jining Medical University. Healthy seven-week-old male mice (20 g to 30 g) were purchased from the Animal Center of Jining Medical University (Jining, China) and housed individually under a 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 12 h light–dark cycle at 22 ± 2 °C. After acclimatizing for 5 d, these mice were randomly divided into two groups: the control group (n = 6) and the liver injury group (n = 6). On the day of the experiment, these mice were starved for 12 h. To the liver injury group, a dose of 470 mg of bromobenzene per kg of body weight (300 μL) was administered by oral gavage. Olive oil (300 μL) was orally administered to the control group. Blood samples were obtained by docking every hour after bromobenzene or olive oil administration.
12 h light–dark cycle at 22 ± 2 °C. After acclimatizing for 5 d, these mice were randomly divided into two groups: the control group (n = 6) and the liver injury group (n = 6). On the day of the experiment, these mice were starved for 12 h. To the liver injury group, a dose of 470 mg of bromobenzene per kg of body weight (300 μL) was administered by oral gavage. Olive oil (300 μL) was orally administered to the control group. Blood samples were obtained by docking every hour after bromobenzene or olive oil administration.
Blood samples were mixed with heparin sodium to prevent from blood clotting. Serum was prepared by centrifuging at 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm for 15 min and stored at −80 °C until needed for analysis.
000 rpm for 15 min and stored at −80 °C until needed for analysis.
Compliance with ethical standards
Kunming mice were obtained from animal house, China Biologic Products, Inc. This study was performed strictly according to the standards described in the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” (National Research Council Commission on Life Sciences, 1996 edition). All animal treatment procedures were approved by the Animal Care Committee of Qufu Normal University, and all efforts were made to minimize suffering.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21537001, 21677085, 81472986, 31301595, 21475074 and 21505084), the Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M590071) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Grant ZR2013BQ019).References
- J. Yin, Y. Kwon, D. Kim, D. Lee, G. Kim, Y. Hu, J.-H. Ryu and J. Yoon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 5351–5358 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. S. Park, M. I. Kim, M.-A. Woo and H. G. Park, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2013, 45, 65–69 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Huang, X. Yang, T. R. Xu, Q. H. Kong, Y. P. Zhang, Y. H. Shen, Y. L. Wei, G. L. Wang and K. J. Chang, Int. J. Oncol., 2016, 49, 153–163 Search PubMed.
- P. S. Samiec, C. Drews-Botsch, E. W. Flagg, J. C. Kurtz, P. Sternberg, R. L. Reed and D. P. Jones, Free Radical Biol. Med., 1998, 24, 699–704 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. C. Lu, Mol. Aspects Med., 2009, 30, 42–59 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. A. Herzenberg, S. C. De Rosa, J. G. Dubs, M. Roederer, M. T. Anderson, S. W. Ela, S. C. Deresinski and L. A. Herzenberg, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1997, 94, 1967–1972 CrossRef CAS.
- D. M. Townsend, K. D. Tew and H. Tapiero, Biomed. Pharmacother., 2003, 57, 145–155 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Zinellu, S. Sotgia, A. M. Posadino, V. Pasciu, M. G. Perino, B. Tadolini, L. Deiana and C. Carru, Electrophoresis, 2005, 26, 1063–1070 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. N. Cao, J. H. Li, H. H. Xu, L. Lin, Y. Z. Xian, K. Yamamoto and L. T. Jin, Biomed. Chromatogr., 2004, 18, 564–569 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Chen, S. Pang, L. He and S. R. Nugen, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 85, 726–733 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Hua, H. Han and X. Zhang, Talanta, 2009, 77, 1654–1659 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhou and J. Yoon, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 52–67 RSC.
- L.-Y. Niu, Y.-S. Guan, Y.-Z. Chen, L.-Z. Wu, C.-H. Tung and Q.-Z. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 18928–18931 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Xu and M. Hepel, Anal. Chem., 2011, 83, 813–819 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-L. Zhang, C. Zheng, S.-S. Guo, J. Li, H.-H. Yang and G. Chen, Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 3426–3434 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, H. Chen, Z. Lin and J.-M. Lin, Anal. Chem., 2010, 82, 7380–7386 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Tian, Z. Qian, Y. Xia and C. Zhu, Langmuir, 2012, 28, 3945–3951 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Barati, M. Shamsipur and H. Abdollahi, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2016, 931, 25–33 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Cayuela, M. L. Soriano and M. Valcárcel, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2015, 872, 70–76 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. C. G. E. da Silva and H. M. R. Gonçalves, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2011, 30, 1327–1336 CrossRef.
- G. Li, W. Kong, M. Zhao, S. Lu, P. Gong, G. Chen, L. Xia, H. Wang, J. You and Y. Wu, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 79, 728–735 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Li, H. Fu, X. Chen, P. Gong, G. Chen, L. Xia, H. Wang, J. You and Y. Wu, Anal. Chem., 2016, 88, 2720–2726 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Dong, J. Cai, X. You and Y. Chi, Analyst, 2015, 140, 7468–7486 RSC.
- X. Ran, H. Sun, F. Pu, J. Ren and X. Qu, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 1079–1081 RSC.
- J. Gu, D. Hu, W. Wang, Q. Zhang, Z. Meng, X. Jia and K. Xi, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 68, 27–33 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Lan, J. Zhang, Y.-S. Chui, P. Wang, X. Chen, C.-S. Lee, H.-L. Kwong and W. Zhang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 21270–21278 CAS.
- X. Liu, N. Zhang, T. Bing and D. Shangguan, Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 2289–2296 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Li, H. Zhu, M. Sun, Y. Yan, K. Zhang, D. Huang and S. Wang, Langmuir, 2015, 31, 8667–8671 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Zhang, H. Zhou, Q. Mei, S. Wang, G. Guan, R. Liu, J. Zhang and Z. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 8424–8427 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Ai, B. Zhang and L. Lu, Angew. Chem., 2009, 121, 310–314 CrossRef.
- D. W. Domaille, L. Zeng and C. J. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 1194–1195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Lu, X. Qin, S. Liu, G. Chang, Y. Zhang, Y. Luo, A. M. Asiri, A. O. Al-Youbi and X. Sun, Anal. Chem., 2012, 84, 5351–5357 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Han, J. Yuan and E. Wang, Anal. Chem., 2009, 81, 5569–5573 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhu, Q. Meng, L. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Song, H. Jin, K. Zhang, H. Sun, H. Wang and B. Yang, Angew. Chem., 2013, 125, 4045–4049 CrossRef.
- X. Jia, J. Li and E. Wang, Nanoscale, 2012, 4, 5572–5575 RSC.
- V. Mah and F. Jalilehvand, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2008, 13, 541–553 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q.-Y. Cai, J. Li, J. Ge, L. Zhang, Y.-L. Hu, Z.-H. Li and L.-B. Qu, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 72, 31–36 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Yang, J.-H. Chen, T. Xu, A.-S. Zhou and H.-K. Yang, Life Sci., 2012, 91, 389–394 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wu, W. Li, J. Chen and C. Yu, Talanta, 2014, 119, 538–543 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Luthman, S. Eriksson, A. Holmgren and L. Thelander, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1979, 76, 2158–2162 CrossRef CAS.
- J. C. Ndamanisha, J. Bai, B. Qi and L. Guo, Anal. Biochem., 2009, 386, 79–84 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, C. Bao, X. Zhong, C. Zhao and L. Zhu, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 2971–2973 RSC.
- J. Hou, F. Zhang, X. Yan, L. Wang, J. Yan, H. Ding and L. Ding, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2015, 859, 72–78 CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c6ra21309j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |