Synthesis, two-photon absorption and aggregation-induced emission properties of multi-branched triphenylamine derivatives based on diketopyrrolopyrrole for bioimaging†
Abstract
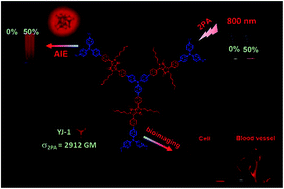
In this work, three new diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP)-based multi-branched derivatives (YJ-1, YJ-2 and YJ-3) with triphenylamine, 2,4,6-tri([1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-1,3,5-triazine and 2,2′,2′′-(nitrilotr-is([1,1′-biphenyl]-4′,4-diyl))tris(3-phenylacrylonitrile) cores have been designed and synthesized. Their one- and two-photon absorption properties have been investigated. The two-photon absorption cross sections (σ) measured by the open aperture Z-scan technique are determined to be 2912, 2016 and 2800 GM for YJ-(1–3), respectively. This result indicates that donor–acceptor–donor (D–A–D)-type molecules are benefit to improve σ and their σ data increase with the better intramolecular charge transfer (ICT). Also, all of the three DPP derivatives exhibit good aggregation-induced emission (AIE) properties which are very weakly fluorescent in DMF, but a strong red fluorescent emission in solid state and in the aggregate state. More importantly, diketopyrrolopyrrole with tri-phenylamine (YJ-1) was applied for cell imaging and two-photon excited fluorescence in vivo imaging of mouse ear.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...