Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Asymmetric C–H functionalization of cyclopropanes using an isoleucine-NH2 bidentate directing group†
Jinhee
Kim
ab,
Mikyung
Sim
ab,
Namhoon
Kim
ab and
Sungwoo
Hong
*ba
aDepartment of Chemistry, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, 305-701, Korea
bCenter for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalization, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Daejeon, 305-701, Korea. E-mail: hongorg@kaist.ac.kr
First published on 16th April 2015
Abstract
The systematic investigation of substrate-bound α-amino acid auxiliaries has resulted in catalytic asymmetric C–H functionalization of cyclopropanes enabled by amino acid amides as chiral bidentate directing groups. The use of an Ile-NH2 auxiliary embedded in the substrate provided excellent levels of asymmetric induction (diastereomeric ratio of up to 72![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) in the Pd(II)-catalyzed β-methylene C(sp3)–H bond activation of cyclopropanes and cross-coupling with aryl iodides.
1) in the Pd(II)-catalyzed β-methylene C(sp3)–H bond activation of cyclopropanes and cross-coupling with aryl iodides.
Introduction
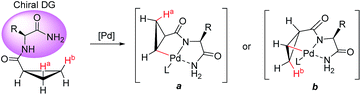
Transition-metal-catalyzed direct and regioselective C–H bond activation/functionalization is a highly efficient and straightforward tool that is useful in the field of organic synthesis and total synthesis.1 To achieve a highly selective C–H activation, the directing group embedded in the substrate must coordinate to a transition-metal center in a configuration that allows for the cleavage of a specific C–H bond, generally via the efficient formation of 5- or 6-membered metallacyclic intermediates.2 Since the novel discovery by Daugulis' group, powerful bidentate directing groups, such as 8-aminoquinoline and picolinamide auxiliaries, have been widely used in the activation of both C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds.3 Bidentate directing groups have received considerable attention by granting favorable properties to the metalated complex, thus enabling new types of catalytic transformations that are known to be difficult with conventional monodentate systems.4 For improving the convenience and efficiency, the development of new types of bidentate directing groups has been the subject of intensive research in many groups.5 Recently, Chatani's group accomplished ortho-C(sp2)–H activation using α-amino ester moieties as bidentate directing groups.6 Moreover, Yu and coworkers demonstrated that the amino acid moiety of peptides can promote the functionalization of C(sp3)–H bonds in a number of peptides.7Elegant examples of the diastereoselective functionalization of unactivated C(sp3)–H in chiral substrates were revealed by the Corey,3b Daugulis3q and Chen groups.3d,3m Moreover, remarkable achievements in catalytic asymmetric C–H activation have been demonstrated using a chiral auxiliary8 and a chiral ligand.9 We hypothesized that an appropriate chiral bidentate directing group embedded in the substrate could induce high levels of stereocontrol during C–H functionalization via a steric repulsion model. As an outgrowth of these studies, we selected α-amino acid moieties as chiral bidentate directing groups in the context of the diastereotopic β-methylene C(sp3)–H bond functionalization/arylation of cyclopropanes, enabling the stereoselective installation of an aryl group and the construction of new stereogenic centers (Scheme 1). Cyclopropanes are a privileged class of structures found in many biologically active molecules.10 In this regard, the transition-metal-catalyzed asymmetric C–H arylation of cyclopropanes has been the focus of great research interest.9,11 Moreover, functionalized cyclopropanes bearing amino acid moieties are widely used as a conformationally restricting linker in medicinal chemistry.10d,e Herein, we report the first example of chiral bidentate auxiliary-controlled diastereoselective C(sp3)–H bond activation/cross-coupling of cyclopropanes. From a conceptual viewpoint, the ability of a substrate-bound α-amino acid auxiliary to promote diastereoselective C–H functionalization is intriguing because the amino acid moiety derived from readily available chiral pools not only plays the role of a bidentate directing group, but also of a chiral auxiliary to provide efficient stereocontrol during C(sp3)–H bond functionalization. As a consequence, high levels of asymmetric induction could be expected in the C(sp3)–H functionalization of cyclopropanes controlled by a chiral bidentate directing group.
Results and discussion
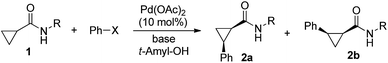
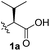
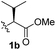
To test these hypotheses, we began our studies by investigating the direct β-methylene C(sp3)–H functionalization of a cyclopropane framework bearing a valine moiety as a potential directing group. Initially, we performed a diastereoselective C–H arylation with iodobenzene using Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%) and K2CO3 as a base in t-amyl-OH at 100 °C for 24 h (Table 1). Our early investigations were discouraging because of the lack of reactivity of the L-valine directing group (1a) (entry 1). Subsequently, several other auxiliaries, such as ester (1b), tetrazole (1c), and amino acid amide groups (1d, 1e, 1f), were investigated for feasibility as directing groups for C(sp3)–H arylation. The usage of ester or tetrazole moieties as directing groups was unsuccessful for C–H activation/C–C bond formation (entries 2 and 3). Intriguingly, the C(sp3)–H bond activation of a substrate containing a Val–NHMe auxiliary (1d) occurred effectively to afford the desired cis-substituted phenylcyclopropane product with a 26% yield and high diastereoselectivity (entry 4, d.r = 8.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). This preliminary work prompted us to scrutinize additional types of amino acid amides as stereogenic directing groups. Further investigations revealed that having the Val–NH2 group (1f) was crucial for obtaining a higher reactivity and diastereoselectivity (entry 6, 60%, d.r = 8.5
1). This preliminary work prompted us to scrutinize additional types of amino acid amides as stereogenic directing groups. Further investigations revealed that having the Val–NH2 group (1f) was crucial for obtaining a higher reactivity and diastereoselectivity (entry 6, 60%, d.r = 8.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). The Val–NMe2 group (1e) attached to the substrate led to a complete loss of reactivity (entry 5), indicating the favorable property of an NH2 motif on coordination in the active complex. We therefore decided to employ Val–NH2 (1f) as a directing group for further optimization; representative catalytic systems for the cross-coupling are listed in Table 1 (entries 6–11).12 In general, an approximate 4.3
1). The Val–NMe2 group (1e) attached to the substrate led to a complete loss of reactivity (entry 5), indicating the favorable property of an NH2 motif on coordination in the active complex. We therefore decided to employ Val–NH2 (1f) as a directing group for further optimization; representative catalytic systems for the cross-coupling are listed in Table 1 (entries 6–11).12 In general, an approximate 4.3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of mono- and diarylated products were obtained with substrate 1f, containing Val–NH2, at 100 °C. Attempts to improve the conversion at a higher temperature (120 °C, entry 7) resulted in an increased proportion of the diarylated product (81%, mono/di = 2.5
1 mixture of mono- and diarylated products were obtained with substrate 1f, containing Val–NH2, at 100 °C. Attempts to improve the conversion at a higher temperature (120 °C, entry 7) resulted in an increased proportion of the diarylated product (81%, mono/di = 2.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, d.r = 6.3
1, d.r = 6.3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) with mixtures of polyarylated by-products13 (∼10%). Several solvents were also evaluated and the use of t-amyl-OH as the solvent was necessary to achieve a higher conversion. The use of AgOAc (entry 9), which was employed previously in arylation reactions,10d,e provided a lower product yield (20%) along with the recovery of the remaining starting material (58%). Alternative arylating coupling partners, such as diphenyliodonium salt3o failed to improve the reaction efficiency (entry 10). With the use of 1.5 equiv. of iodobenzene, the reaction reached full conversion to provide the mono- and diarylated products in yields of 71 and 16%, respectively, with only a negligible amount of the undesired by-products. Thus, the best results were obtained with the substrate (1 equiv.) with iodobenzene (1.5 equiv.), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), and K2CO3 (2 equiv.) in t-amyl-OH (0.5 M) at 100 °C to give the monoarylation product (71%) with high diastereoselectivity (d.r = 8.6
1) with mixtures of polyarylated by-products13 (∼10%). Several solvents were also evaluated and the use of t-amyl-OH as the solvent was necessary to achieve a higher conversion. The use of AgOAc (entry 9), which was employed previously in arylation reactions,10d,e provided a lower product yield (20%) along with the recovery of the remaining starting material (58%). Alternative arylating coupling partners, such as diphenyliodonium salt3o failed to improve the reaction efficiency (entry 10). With the use of 1.5 equiv. of iodobenzene, the reaction reached full conversion to provide the mono- and diarylated products in yields of 71 and 16%, respectively, with only a negligible amount of the undesired by-products. Thus, the best results were obtained with the substrate (1 equiv.) with iodobenzene (1.5 equiv.), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), and K2CO3 (2 equiv.) in t-amyl-OH (0.5 M) at 100 °C to give the monoarylation product (71%) with high diastereoselectivity (d.r = 8.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
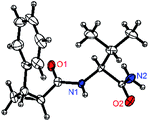
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) (entry 11). The structure of the major diastereomer 2a (Val–NH2 derivative) was unambiguously verified by H NMR and X-ray crystallographic analyses (Fig. 1).
1) (entry 11). The structure of the major diastereomer 2a (Val–NH2 derivative) was unambiguously verified by H NMR and X-ray crystallographic analyses (Fig. 1).
| Entry | R | PhX (equiv.) | Base (equiv.) | Temp. (°C) | Yieldb (d.r)c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a Substrate (1.0 equiv.), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), K2CO3 (2.5 equiv.), and ArX in t-amyl-OH (0.5 M).
b Isolated yields of monoarylation products.
c The d.r was determined by HPLC analysis.
d Mono- and diarylation products (4.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) were observed by NMR analysis. 1) were observed by NMR analysis.
|
|||||
| 1 |
|
PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 100 | Trace |
| 2 |
|
PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 100 | NR |
| 3 |
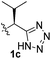
|
PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 100 | NR |
| 4 |
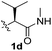
|
PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 100 | 26% (8.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
| 5 |
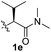
|
PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 100 | NR |
| 6 |
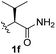
|
PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 100 | 60% (8.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
| 7 | PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 120 | 58% (6.3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
|
| 8 | PhI (3) | K2CO3 (2.5) | 80 | 12% | |
| 9 | PhI (4) | AgOAc (2.5) | 100 | 20% | |
| 10 | Ph2IOTf (2) | K2CO3 (3) | 100 | 33% | |
| 11d | PhI (1.5) | K2CO3 (2) | 100 | 71% (8.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
|
Having identified that the N-nonsubstituted –CONH2 moiety was crucial for achieving both high reactivity and diastereoselectivity, we further explored the effect of steric bulk at the α-position of amino acid amides on the selectivity. For this purpose, substrates bearing a range of R substituents were examined and chiral auxiliaries featuring sterically bulky side chains appear to be essential for achieving high levels of stereoselectivity (Scheme 2). Importantly, the replacement of an isopropyl group (d.r = 8.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) at the α-position of the amino acid amide with sterically demanding isobutyl and t-butyl groups produced the corresponding products 3a and 3b with higher diastereoselectivity (d.r = 10.2
1) at the α-position of the amino acid amide with sterically demanding isobutyl and t-butyl groups produced the corresponding products 3a and 3b with higher diastereoselectivity (d.r = 10.2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 for 3a, d.r = 13.7
1 for 3a, d.r = 13.7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 for 3b). Further studies revealed that the isobutyl and t-butyl groups present on the substrates gave superior results to those with benzyloxy ethyl (3c), phenyl (3d), cyclohexyl (3e), or benzyl (3f) groups. Of the various chiral auxiliaries that were tested, the Ile-NH2 moiety (3a) was selected as a bidentate directing group after considering both yield and diastereoselectivity. In order to gain insight into the influence of the diarylation process on the diastereoselectivity, a reaction profile was performed by monitoring the conversion to 3a under standard conditions (see Table S4 in the ESI† for more details). An increase of d.r from 7.2
1 for 3b). Further studies revealed that the isobutyl and t-butyl groups present on the substrates gave superior results to those with benzyloxy ethyl (3c), phenyl (3d), cyclohexyl (3e), or benzyl (3f) groups. Of the various chiral auxiliaries that were tested, the Ile-NH2 moiety (3a) was selected as a bidentate directing group after considering both yield and diastereoselectivity. In order to gain insight into the influence of the diarylation process on the diastereoselectivity, a reaction profile was performed by monitoring the conversion to 3a under standard conditions (see Table S4 in the ESI† for more details). An increase of d.r from 7.2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (after 1 h) to 10.2
1 (after 1 h) to 10.2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (after 24 h) was observed, which suggests that the favorable second arylation of the minor stereoisomer may contribute, in part, to the overall diastereoselectivity observed.
1 (after 24 h) was observed, which suggests that the favorable second arylation of the minor stereoisomer may contribute, in part, to the overall diastereoselectivity observed.
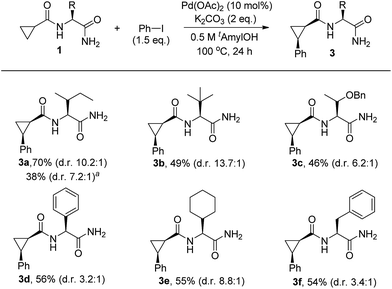 | ||
Scheme 2 Influence of the side chain on C–H arylation. Substrate (1.0 equiv.), Pd(OAc)2 (10 mol%), K2CO3 (2.0 equiv.), and PhI (1.5 equiv.) in t-amyl-OH (0.5 M) at 100 °C for 24 h: isolated yields of monoarylation products after purification by silica gel chromatography. The d.r was determined by HPLC analysis. In general, mixtures of mono- and diarylation products (4.0–4.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) were observed by NMR analysis. aAfter 1 h: NMR yield of monoarylation products (see Table S4 in the ESI† for more details). 1) were observed by NMR analysis. aAfter 1 h: NMR yield of monoarylation products (see Table S4 in the ESI† for more details). | ||
The directing group is removable and the hydrolysis of the amino acid amide group of 3a occurred smoothly under acidic conditions to afford arylated cyclopropanecarboxylic acid (81%) with the conservation of the stereogenic centers (eqn (1)).14,15
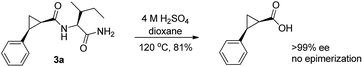 | (1) |
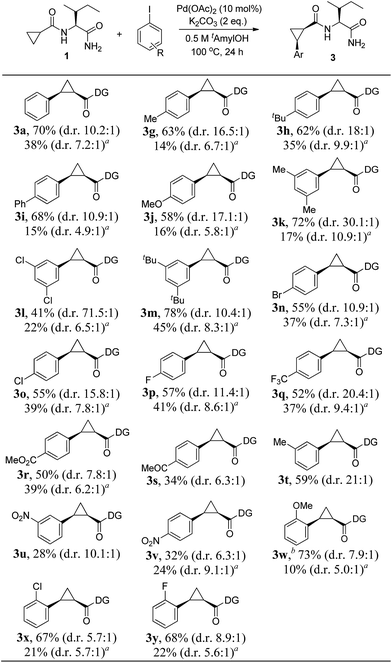
Having established that the Pd(II)-catalyzed highly diastereoselective C–H arylation of cyclopropanes was enabled by the Ile-NH2 directing group, the scope of aryl iodides was studied with a range of functional groups such as phenyl, methoxy, ketone, ester, alkyl, halides, and trifluoromethyl, which could be used as a useful synthetic handle for the further transformations. We were delighted to observe that substitution with both electron-donating (Me–, tBu–, and OMe–) and electron-withdrawing groups (F–, Cl–, Br–, CF3–, CO2Me–, and COMe–) on the aryl iodides were viable under the reaction conditions to afford the corresponding products with high levels of diastereoselectivity, summarized in Scheme 3. In addition, the major isomer could be easily isolated by silica gel chromatography. Outstanding diastereoselectivities could be achieved in the reactions of 3,5-disubstituted iodobenzenes (d.r = 30.1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 for 3k, d.r = 71.5
1 for 3k, d.r = 71.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 for 3l). The chemoselective coupling with bromo iodobenzene afforded the synthetically important 3n, of use for further synthetic elaboration. The position of the substituents in the iodobenzene did not show much change to the reactivity. Notably, aryl iodides with ortho-substituents, such as OMe, Cl, and F were also compatible with the reaction conditions to afford the corresponding products (3w–y) with good yields (67–73%). Expanding the scope to nitro-substituted iodobenzenes was also possible, but the products were obtained in only around 30% yields (3u and 3v).
1 for 3l). The chemoselective coupling with bromo iodobenzene afforded the synthetically important 3n, of use for further synthetic elaboration. The position of the substituents in the iodobenzene did not show much change to the reactivity. Notably, aryl iodides with ortho-substituents, such as OMe, Cl, and F were also compatible with the reaction conditions to afford the corresponding products (3w–y) with good yields (67–73%). Expanding the scope to nitro-substituted iodobenzenes was also possible, but the products were obtained in only around 30% yields (3u and 3v).
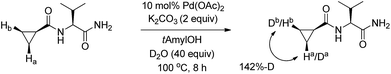
Although severe peak overlap occurs in the NMR spectra of two diastereotopic hydrogens, a significant level of the di-deuterated product (>40%) was observed when the reaction mixture was treated with D2O under the optimized conditions and in the absence of aryl iodide (Scheme 4).12 This controlled H/D exchange study implies a facile C–H activation process for both diastereotopic hydrogens of the cyclopropanes.
We proposed one of the possible reaction mechanisms involving Ile-NH2 auxiliary-controlled asymmetric C–H functionalization in which a Pd(II)/Pd(IV)16 catalytic cycle is invoked (Scheme 5). The coordination of two nitrogen atoms to the Pd catalyst generates a palladium amide I. Subsequently, the cleavage of the C(sp3)–H bond on the cyclopropane through a concerted metalation deprotonation (CMD) process produces the palladacycle complexes II and III, which may exist in equilibrium.17 The diastereoselectivity of the arylation could occur either at the C–H activation step or at the oxidative addition step. At this stage, the diastereoselectivity can be assumed to be established at the oxidative addition step under Curtin–Hammett control18 because the C–H activation process of both diastereotopic hydrogens is relatively facile (Scheme 4). The oxidative addition of the aryl iodide to II affords Pd(IV) intermediate IV,19 which then undergoes reductive elimination followed by protonation leading to the formation of the arylated product. On the other hand, the oxidative addition process for the insertion of an aryl iodide into Pd complex III appears to be less feasible because the R substituent and the methylene group of cyclopropane cause blocking of the top and bottom faces.
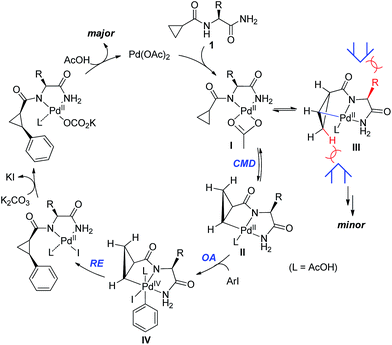 | ||
| Scheme 5 Mechanistic considerations for Pd-catalyzed diastereoselective C–H activation of cyclopropanes. | ||
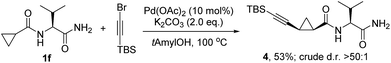
Furthermore, we preliminarily investigated the diastereoselective C–H alkynylation and observed that 1f reacted with bromoalkyne under the same reaction conditions,20 resulting in the single diastereomer 4 in a 53% yield along with 44% of unreacted starting material (Scheme 6).
Conclusions
In summary, we have developed the Pd(II)-catalyzed highly diastereoselective β-methylene C(sp3)–H bond activation/C–H arylation of cyclopropanes enabled by the Ile-NH2 directing group. This study represents the first systematic investigation of substrate-bound α-amino acid amides as chiral bidentate directing groups in the asymmetric C(sp3)–H functionalization of cyclopropanes. The present reactions demonstrated a broad range of substrate scope and allowed for the selective installation of a variety of substituents on cyclopropanes. Further developments to extend this methodology to other substrates and detailed mechanistic studies are underway.Acknowledgements
This research was supported financially by the Institute for Basic Science (IBS-R010-G1).Notes and references
- For selected recent reviews on C–H activation, see: (a) J. Wencel-Delord, T. Dröge, F. Liu and F. Glorius, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 4740 RSC; (b) W. Shi, C. Liu and A. Lei, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 2761 RSC; (c) L. McMurray, F. O'Hara and M. J. Gaunt, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 1885 RSC; (d) D. A. Colby, R. G. Bergman and J. A. Ellman, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 624 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) L.-M. Xu, B.-J. Li, Z. Yang and Z.-J. Shi, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 712 RSC; (f) C.-J. Li, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, 335 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) X. Chen, K. M. Engle, D.-H. Wang and J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 5094 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) R. Giri, B.-F. Shi, K. M. Engle, N. Maugel and J.-Q. Yu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 3242 RSC; (i) C. S. Yeung and V. M. Dong, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 1215 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) S.-H. Cho, J. Y. Kim, J. Kwak and S. Chang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 5068 RSC; (k) L. Ackermann, R. Vicente and A. R. Kapdi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 9792 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) J. A. Ashenhurst, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 540 RSC; (m) P. B. Arockiam, C. Bruneau and P. H. Dixneuf, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 5879 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (n) G. Song, F. Wang and X. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 3651 RSC; (o) D. Alberico, M. E. Scott and M. Lautens, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 174 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (p) H. M. L. Davies and Y. Lian, Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45, 923 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (q) J. Mousseau and A. B. Charette, Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46, 412 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (r) S. I. Kozhushkov and L. Ackermann, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 886 RSC.
- For recent reviews on chelation-assisted C–H functionalization, see: (a) T. W. Lyons and M. S. Sanford, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 1147 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. M. Engle, T.-S. Mei, M. Wasa and J.-Q. Yu, Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45, 788 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) D. A. Colby, A. S. Tsai, R. G. Bergman and J. A. Ellman, Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45, 814 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Selected recent examples: (a) V. G. Zaitsev, D. Shabashov and O. Daugulis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 13154 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) B. V. S. Reddy, L. R. Reddy and E. J. Corey, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 3391 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) D. Shabashov and O. Daugulis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 3965 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Y. Feng and G. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 958 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) G. He and G. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 5192 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) S.-Y. Zhang, G. He, W. A. Nack, Y. Zhao, Q. Li and G. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 2124 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) Y. Aihara and N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 5308 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) M. Nishino, K. Hirano, T. Satoh and M. Miura, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 4457 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) R. Shang, L. Ilies, A. Matsumoto and E. Nakamura, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 6030 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) T. Truong, K. Klimovica and O. Daugulis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 9342 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) L. D. Tran, J. Roane and O. Daugulis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 6043 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) S. Asako, L. Ilies and E. Nakamura, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 6030 CrossRef PubMed; (m) S.-Y. Zhang, Q. Li, G. He, W. A. Nack and G. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 12135 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (n) T. Matsubara, S. Asako, L. Ilies and E. Nakamura, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 646 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (o) Y. Aihara and N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 898 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (p) F. Pan, P.-X. Shen, L.-S. Zhang, X. Wang and Z.-J. Shi, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 4758 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (q) L. D. Tran and O. Daugulis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 5188 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. Rouquet and N. Chatani, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 11726 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. Corbet and F. De Campo, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 9896 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Shang, S.-Z. Sun, H.-X. Dai and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 3354 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. Shang, H.-L. Wang, S.-Z. Sun, H.-X. Dai and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 11590 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) R. K. Rit, M. R. Yadav and A. K. Sahoo, Org. Lett., 2012, 14, 3724 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) N. Hasegawa, V. Charra, S. Inoue, Y. Fukumoto and N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 8070 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) H. Shiota, Y. Ano, Y. Aihara, Y. Fukumoto and N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 14952 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) S. Inoue, H. Shiota, Y. Fukumoto and N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 6898 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. C. Misal Castro and N. Chatani, Chem.–Eur. J., 2014, 20, 4548 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Gong, G. Zhang, T. Liu, R. Giri and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 16940 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) R. Giri, X. Chen and J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 2112 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) R. Giri, J. Liang, J.-G. Lei, J.-J. Li, D.-H. Wang, X. Chen, I. C. Naggar, C. Guo, B. M. Foxman and J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 7420 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) R. Giri, Y. Lan, P. Liu, K. N. Houk and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 14118 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) J. A. Johnson, N. Li and D. Sames, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 6900 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) A. Wangweerawong, R. G. Bergman and J. A. Ellman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 8520 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) C. K. Hazra, Q. Dherbassy, J. Wencel-Delord and F. Colobert, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 13871 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) E. E. Stache, C. A. Seizert and E. M. Ferreira, Chem. Sci., 2012, 3, 1623 RSC.
- (a) M. Wasa, K. M. Engle, D. W. Lin, E. J. Yoo and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 19598 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) T. Saget and N. Cramer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 12842 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. L. Kelvin, H.-Y. Fu and J.-Q. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2042 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) S. F. Martin, M. P. Dwyer, B. Hartmann and K. S. Knight, J. Org. Chem., 2000, 65, 1305 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. Gagnon, M. Duplessis and L. Fader, Org. Prep. Proced. Int., 2010, 42, 1 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. Cheng, Y. S. Lee, R. B. Rothman, C. M. Dersh, R. W. Bittman, A. E. Jacobson and K. Rice, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 957 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) S. Yonezawa, T. Yamamoto, H. Yamakawa, C. Muto, M. Hosono, K. Hattori, K. Higashino, T. Yutsudo, H. Iwamoto, Y. Kondo, M. Sakagami, H. Togame, Y. Tanaka, T. Nakano, H. Takemoto, M. Arisawa and S. Shuto, J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55, 8838 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) P. B. Sampson, Y. Liu, N. K. Patel, M. Feher, B. Forrest, S.-W. Li, L. Edwards, R. Laufer, Y. Lang, F. Ban, D. E. Awrey, G. Mao, O. Plotnikova, G. Leung, R. Hodgson, J. Mason, X. Wei, R. Kiarash, E. Green, W. Qiu, N. Y. Chirgadze, T. W. Mak, G. Pan and H. W. Pauls, J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55, 8838 CrossRef PubMed; (f) A. Reichelt and S. F. Martin, Acc. Chem. Res., 2006, 39, 433 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) R. Parella, B. Gopalakrishnan and S. A. Babu, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 3238 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) N. Hoshiya, T. Kobayashi, M. Arisawa and S. Shuto, Org. Lett., 2013, 15, 6202 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. Miyamura, M. Araki, T. Suzuki, J. Yamaguchi and K. Itami, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 846 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- ESI.†.
- Mixture of unidentified polyarylated by-products.
- The conservation of the stereogenic centers was verified by HPLC analysis: G. R. Elling, R. C. Hahn and G. Schwab, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1973, 95, 5659 CrossRef CAS.
- Authentic sample was prepared using known procedures: (a) K. Cheng, Y. S. Lee, R. B. Rothman, C. M. Dersch, R. W. Bittman, A. E. Jacobson and K. C. Rice, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 957 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. J. Johansson, D. J. Gorin, S. T. Staben and F. D. Toste, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 18002 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) L.-M. Xu, B.-J. Li, Z. Yang and Z.-J. Shi, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 712 RSC; (b) P. Sehnal, R. J. K. Taylor and I. J. S. Fairlamb, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 824 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) K. M. Engle, T.-S. Mei, X. Wang and J.-Q. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 1478 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) A. J. Hickman and M. S. Sanford, Nature, 2012, 484, 177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) R. K. Rit, M. R. Yadav and A. K. Sahoo, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 968 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. Shabashov and O. Daugulis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 3965 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. I. Seeman, Chem. Rev., 1983, 83, 83 CrossRef CAS.
- Complex IV could be the other geometric isomer in which the iodide ligand and the phenyl group switch places.
- Unoptimized conditions.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 1053232. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c5sc01137j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |