Changes in the SNAr reaction mechanism brought about by preferential solvation†
Jazmín Alarcón-Espósito*a,
Ricardo A. Tapiab,
Renato Contrerasa and
Paola R. Campodónico*c
aDepartamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Chile, Casilla 653-Santiago, Chile. E-mail: jazminalarcon@ug.uchile.cl
bFacultad de Química, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Código Postal 7820436, Santiago, Chile
cCentro de Química Médica, Facultad de Medicina, Clínica Alemana, Universidad del Desarrollo, Código postal 771-0162, Santiago, Chile
First published on 11th November 2015
Abstract
We herein report an experimental and theoretical study on preferential solvation effects for the reactions of 1-fluoro and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene towards morpholine in acetonitrile, water and mixtures of them of varying compositions. A detailed kinetic study opens the possibility of analyzing preferential solvation and reaction rates. The kinetic study was complemented with an exploration of the potential energy surface in order to analyze the nature of the molecular interactions. For the fluorine derivative, this analysis reveals that the solvation of the TS in the mode TS1F-water/MeCN clearly outweighs the solvation of TS1F-MeCN/water, thereby suggesting that there is preferential solvation in favor of the aqueous phase.
Introduction
It is well known that chemical reactivity may often be determined by solute–solvent interactions. These solvation effects are generally expressed beyond the simple stabilization of species present in the reaction channel, as for instance specific interactions that can elicit catalytic effects by the solvent or one component of the reaction media in mixtures of solvents. Of special relevance is the relative stabilization of all stationary points on the potential energy surface (PES) including the ground and activated intermediates and the transition state (TS) structures.1,2Experimentally, the most common way to measure the polarity of a solvent is through its (bulk) dielectric constant (ε). The concept of polarity has been defined as the sum of all possible intermolecular interactions between the solvent and the solute, including specific interactions as for instance hydrogen bonding effects, dipole–dipole, dipole–induced dipole, electron pair acceptor–electron pair donor and acid–base interactions.3 Solute–solvent interactions are much more complexes in mixtures than pure solvents; yet the study in mixtures opens the possibility of addressing preferential solvation issues.4 Preferential solvation has been defined as the difference between the local and bulk composition of the solutes with respect to the composition of the solvents in a binary mixture.5–8 Previous studies have shown that in mixtures of conventional organic solvents such as acetonitrile (MeCN), the formation of micro-domains may become a determinant on the reaction path.9 MeCN is completely soluble in water in a broad mole fraction range. It exhibits three critical regions respect to MeCN: (a) a water rich region (0 ≤ XMeCN ≤ 0.3) which is characterized by a dramatic decreasing in acidity of the mixture upon addition of MeCN. The net response is the increase of basicity and the decrease of polarity of the mixture. The MeCN molecules loss translational degrees of freedom into the cavities of the 3D network formed by water molecules, induced by effective hydrogen bond (HB) MeCN–H2O interactions, thereby diminishing the HB interactions towards the electrophile/nucleophile pair; (b) intermediate region (XMeCN = 0.5). In this regime, the polarity is uniform, with an increase in basicity of the mixture, and finally (c) a MeCN rich region (0.8 ≤ XMeCN ≤ 1.0), where the polarity of the mixture remains constant while the basicity of the mixture is increased and its acidity decreases with respect to pure MeCN.9 A series of studies suggest that the reactivity in nucleophilic aromatic substitutions (SNAr) reactions are significantly affected by the reaction media.10,11 Widespread series of solvatochromic studies based on kinetic response have been reported by Mancini et al.4,10,23 and other authors12–14 for SNAr processes in mixtures of solvents to derive solvent polarity parameters. A SNAr is a polar process characterized by activated substrates and good leaving groups (LG). This type of reactions proceed via stepwise mechanism15–19 involving the nucleophilic attack to the activated substrates at the ipso carbon of the electrophile, normally consisting in electron-deficient aromatic systems to yield an anionic σ-bonded adduct, commonly known as Meisenheimer complex (MC).20 In the second step, the LG is eliminated to regenerate the aromatic ring through catalyzed or non-catalyzed pathways (k3 or k2, respectively in Scheme 1).15–22
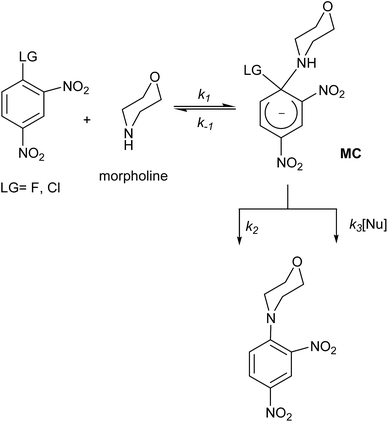 | ||
| Scheme 1 General mechanism for a SNAr reaction between morpholine as nucleophile towards 1-halo-2,4-dinitrobenzene as an electrophile. | ||
The solvents considered in this study are MeCN and water. MeCN exhibits significant HB acceptor ability, while water is a protic polar solvent with strong HB donor/acceptor properties.23 The main focus in this study was put on bulk and specific solute–solvent interactions that determine the reaction rates and the rate-determining step (RDS) in the reaction mechanism. The reacting electrophile/nucleophile pair is considered as “solute” (or a single molecule). The kinetic measurements were complemented with the determination of activation thermodynamic parameters (ATP) and the full exploration of the PES. From the relevant stationary points located on the PES, it is useful to perform further studies using population analysis complemented with second order perturbation theory studies in order to quantify and define a hierarchy in the specific electronic effects that determine solvation effects and reactivity.24–26 Recently, it has been proposed that intramolecular interactions at the TS structure may determine the selectivity and even catalysis in SNAr processes.27 This background prompted us to perform a comparative study of solvation effects in pure conventional solvents and its mixtures with the aim of understanding how the solvent influences the reaction mechanism in a SNAr reaction. This benchmark system involves the substrates 1-fluoro and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (FDNB and ClDNB, respectively) towards morpholine as nucleophile in MeCN, aqueous media and several mixtures of them.
Results and discussion
Kinetic study
Under the experimental conditions used, the formation of a single product was spectrophotometrically observed (see synthetic details in Experimental section). Therefore, the possibility of nucleophilic attack at the unsubstituted ring positions may safely be discarded.17,22,28 The rate law obtained for the reactions studied is given by eqn (1), where Nu represents morpholine and kobs is the pseudo first order rate constant:
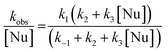 | (1) |
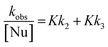 | (2) |
Previous kinetic studies for the title reactions in pure MeCN and water have been reported.17,18,22 In this work, we shall revisit these systems but allowing this time both solvents to be present in order to gain insight about the microscopic solute–solvent interactions in a wide range of composition. Of course, the limiting cases are expected to converge towards the previous studies performed in pure solvents. An additional interest is the possibility that some situation of preferential solvation could be operative.
Table 1 shows the kN values measured in pure MeCN and water, together with its different mixtures for the reactions of FDNB and ClDNB towards morpholine. The corresponding Kk2 and Kk3 values for the reaction of FDNB with morpholine in pure MeCN are also included. The detailed kinetic data are given in ESI.† We shall first relay on the data at room temperature (25 °C). The remaining data at different temperature will be used afterwards to deduce the activation parameters and to include a short discussion about the effect of these parameters on preferential solvation, if any.
| 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition MeCN | Type | 12 °C Kk3/M−2 s−1 | 20 °C Kk3/M−2 s−1 | 25 °C Kk3/M−2 s−1 | 30 °C Kk3/M−2 s−1 | 45 °C Kk3/M−2 s−1 | 55 °C Kk3/M−2 s−1 |
| 100% | C | 92.7 ± 3.9 | 116.2 ± 7.4 | 123.2 ± 6.9 | 237.7 ± 15.5 | 394.5 ± 44.1 | 527.3 ± 28.3 |
| 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition MeCN | Type | Kk2/M−1 s−1 | Kk2/M−1 s−1 | Kk2/M−1 s−1 | Kk2/M−1 s−1 | Kk2/M−1 s−1 | Kk2/M−1 s−1 |
| 100% | C | 0.47 ± 0.09 | 0.94 ± 0.18 | 0.71 ± 0.17 | 1.21 ± 0.22 | 2.67 ± 0.32 | 1.96 ± 0.22 |
| 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition MeCN | Type | 102kN/M−1 s−1 | 102kN/M−1 s−1 | 102kN/M−1 s−1 | 102kN/M−1 s−1 | 102kN/M−1 s−1 | 102kN/M−1 s−1 |
| 90% | NC | 171 ± 4 | 215 ± 3 | 249 ± 5 | 279 ± 10 | 416 ± 12 | 461 ± 8 |
| 75% | NC | 129 ± 4 | 169 ± 4 | 201 ± 3 | 240 ± 3 | 384 ± 7 | 482 ± 10 |
| 50% | NC | 106 ± 4 | 188 ± 8 | 222 ± 4 | 268 ± 5 | 396 ± 6 | 558 ± 20 |
| 10% | NC | 64 ± 1 | 120 ± 5 | 142 ± 3 | 183 ± 6 | 371 ± 6 | 492 ± 16 |
| 0% | NC | 18 ± 2 | 28 ± 2 | 35 ± 1 | 54 ± 4 | 113 ± 10 | 146 ± 5 |
| 1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition MeCN | Type | 103kN/M−1 s−1 | 103kN/M−1 s−1 | 103kN/M−1 s−1 | 103kN/M−1 s−1 | 103kN/M−1 s−1 | 103kN/M−1 s−1 |
| 100% | NC | 19.8 ± 1.0 | 32.8 ± 1.0 | 42.7 ± 1.0 | 52.1 ± 1.0 | 78.2 ± 3.0 | 108.1 ± 3.0 |
| 90% | NC | 6.2 ± 0.3 | 12.1 ± 0.4 | 14.4 ± 0.2 | 20.3 ± 0.8 | 36.2 ± 1.0 | 52.7 ± 1.0 |
| 50% | NC | 2.7 ± 0.01 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 7.6 ± 0.1 | 14.3 ± 0.2 | 24.3 ± 0.2 |
| 25% | NC | 1.8 ± 0.01 | 2.9 ± 0.01 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 7.3 ± 0.01 | 15.3 ± 0.2 | 38.7 ± 2.0 |
| 10% | NC | 1.7 ± 0.01 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.01 | 6.7 ± 10−4 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 20.8 ± 1.0 |
| 0% | NC | 0.7 ± 0.01 | 0.9 ± 0.01 | 1.6 ± 0.01 | 2.1 ± 0.01 | 5.7 ± 0.01 | 10.5 ± 0.01 |
For FDNB the results show that: (i) the composition of 10% vol. H2O is sufficient to destabilize the MC leading to a change in the RDS from a catalyzed by a second amine molecule to a non-catalyzed route (left branch in Scheme 1), where the MC formation is the RDS and (ii) only at 12 °C the kN values are increased with an increasing proportion of MeCN in the mixture. These results can be explained by the changes on the reactivity patterns from pure solvents to their mixtures of varying composition.
For instance, the reactivity and the reaction mechanism in water can be explained based on a previous report showing that the determining TS structure for FDNB in the presence of water can acts as “a bridge” for the relay of the electron density from amine moiety towards the electrophilic center (i.e. the ipso carbon atom on the ring). This TS structure can establish two kind of HB: the first one between the acidic hydrogen atom of the amine and the oxygen atom of water; and a second one between the hydrogen atom of water and the o-NO2 group in the substrate. These HB interactions can activate both the electrophilic and the nucleophilic centers, thereby diminishing the activation barrier along the PES (vide infra). While in water the reaction media is highly structured, in MeCN it is relatively disordered.17 The HB pattern expected for water, suggests that the net result is the activation of both reaction centers, thereby reinforcing the idea that the intramolecular HB formation at the TS structure facilitates the nucleophilic attack. According to Table 1 at 25 °C, the nucleophilic micro-constant is about 22![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 in favor of FDNB in water respect to ClDNB.
1 in favor of FDNB in water respect to ClDNB.
For MeCN with water in significant minor composition (10% vol.), the results suggest that water molecules added to MeCN in both substrates will contribute to the formation of another kind of dative bridges within the TS structure.9 Note that for FDNB, the reaction rate is increased ca. 7 times respect to the same reaction in pure water, whereas for ClDNB, the ratio is reduced to 9 times. These results may probably be traced to an enhancement of the basicity of the mixture; a result previously advanced by Barbosa et al., where the basicity of mixtures were evaluated using Kamlet–Taft parameters.29 The minor composition of water seems to mainly affect the reactivity via preferential solvation.
For instance, they reported that probes in solvatochromic measurements of acidity/basicity and polarization parameters show preferential solvation phenomena at compositions close to 0.75 mole fraction respects to MeCN. In the present case, it seems that for FDNB, in the regime of 90% vol. MeCN (X = 0.76), preferential solvation in the aqueous phase may be at the origin of the observation that the rate coefficient displays a maximum value within the range 12–45 °C respect others mixtures (see Table 1).
Up to this point, we have qualitatively described the fundamental kinetic responses for the reactions studied at room temperature. Now we would like to take a look at the thermodynamic activation parameters in order to shed some light on the observed reactivity and solvent effects. Using the data of Table 1, compiling the kinetics of the SNAr reactions studied herein within the range of (12–55) °C we can build the data compiled in Table 2, using two well-known equations, namely Arrhenius eqn (3) and Eyring eqn (4):
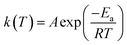 | (3) |
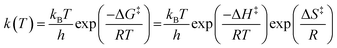 | (4) |
| Composition MeCN | ΔH‡ (kcal mol−1) | ΔS‡ (cal mol−1 K−1) | ΔG‡ (kcal mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| a Mixtures expressed in % vol. to respect MeCN. The complete set of activation parameters is given in ESI. | |||
| 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene | |||
| 90% | 3.8 ± 0.3 | −43.9 ± 0.7 | 16.9 ± 0.00 |
| 75% | 5.1 ± 0.3 | −40.0 ± 1.1 | 17.0 ± 0.01 |
| 50% | 6.0 ± 0.3 | −37.0 ± 1.8 | 17.0 ± 0.01 |
| 10% | 8.1 ± 0.2 | −30.9 ± 1.6 | 17.3 ± 0.01 |
| 0% | 8.8 ± 0.3 | −30.7 ± 1.9 | 18.0 ± 0.01 |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) |
|||
| 1-Chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene | |||
| 100% | 6.4 ± 0.3 | −43.7 ± 1.8 | 19.4 ± 0.01 |
| 90% | 8.3 ± 0.3 | −39.3 ± 1.8 | 20.0 ± 0.01 |
| 50% | 8.6 ± 0.3 | −40.0 ± 0.8 | 20.5 ± 0.00 |
| 25% | 12.3 ± 0.5 | −27.9 ± 2.6 | 20.6 ± 0.01 |
| 10% | 10.4 ± 0.3 | −34.5 ± 2.1 | 20.7 ± 0.01 |
| 0% | 11.5 ± 0.4 | −32.9 ± 2.1 | 21.3 ± 0.01 |
In eqn (3) k(T) is the rate coefficient; A is the collision frequency describing the successful collisions that have a high probability to evolve to products; Ea is the activation energy, R the universal constant of gases and T the absolute temperature. This equation (Arrhenius) provides a quite crude picture relating the rate coefficient with the reaction rate. In eqn (4) kB and h are the Boltzmann and Plank constants; ΔG‡, ΔH‡ and ΔS‡ are the activation free energy, enthalpy and entropy, respectively.
A first look at Table 2 reveals that, even at the very crude approximation using Arrhenius equation, the condition in composition for the reaction of FDNB and morpholine is that containing 90% vol. MeCN for it predicts that in this condition the reaction will be faster.
For ClDNB on the other hand the same is true, in agreement with the experimental results reported herein. Note that for the FDNB case in MeCN no further comparisons can be made because there is a change in the reaction mechanism. However, using the more sophisticated Eyring equation, useful additional information can be deduced. For instance, on the basis of the global ΔG‡ values the composition 90% vol. in MeCN seem to be again the more favorable composition for both FDNB and ClDNB, even though the figures are not too much well resolved, yet the differences are beyond of the error range and therefore significant. The thermal contribution given by ΔH‡ is also in line with the experimental result for it reveals that the activation enthalpy for ClDNB is about twice that for FDNB in the mixture 90% vol. in MeCN.
The analysis on the basis of ΔS‡ values for FDNB reveals that at the 90% composition the water molecule closest to the TS structure may produce more ordered TS with a probable nucleophilic activation at the NH group in morpholine. We will discuss this point in the light of second order perturbation theory afterwards. The analysis of ΔS‡ for ClDNB is less clear.
Computational study
Potential energy surface analysis
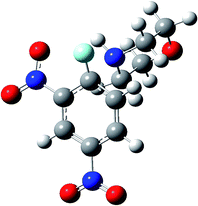
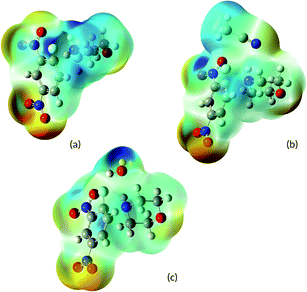
In order to give an additional rationale to the preferential solvation hypothesis, we performed a complete analysis of the PES, involving the rate determining TS and specific solvation effects, using the M06-2X/6-31+G(d,p) level of theory. For the sake of clarity, we will perform the theoretical analysis on the PES involving FDNB firstly and then we will discuss the ClDNB case. The PES analysis considers the experimental result showing that the nucleophilic attack is rate determining in the 90% MeCN composition. Because the solvation model from electron density (SMD) algorithm used to mimic dielectric solvation effects is based on the Born's reaction field theory30 we will discard the electrostatic dielectric contribution because the reaction field response factor g(ε) = (1 − 1/ε) quickly saturates for values ε > 10. Because the dielectric constant for water and MeCN are 78 and 36, respectively, the corresponding reaction field factors g(ε) are essentially the same, and as a result the bulk dielectric solvation energies are very close to each other and almost cancel out. The same is true for the average weighted by composition dielectric constants. Therefore, preferential solvation is considered here only via hydrogen bond and second order electronic polarization effects. For calculational purpose, the TS structures were located in the gas phase and then corrected by dielectric solvation by single point calculations in order to assess second order orbital contributions to TS stabilization.Fig. 1 shows the TS structure (TS1F) for the nucleophilic attack of morpholine towards FDNB. From this structure, the electrophilic and nucleophilic regions of this complex were identified by performing the calculation of the molecular electrostatic potential (MEP). The MEP output helps in identifying those regions available for the electrophilic and nucleophilic specific solvation by water and MeCN. The MEPs obtained are depicted Fig. 2. Fig. 2a shows the electrophilic and nucleophilic regions of TS1F available for electrophilic and nucleophilic solvation.
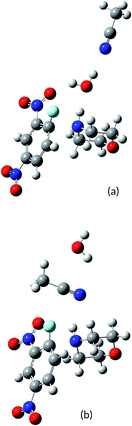
Note that the electrophilic region in Fig. 2a is located at the amine acidic hydrogen atom (blue region). Water can solvate the TS1F structure via hydrogen bonding between the oxygen atom of water and the amine hydrogen atom. The other configuration with water bridged by any of its hydrogen atoms is less favorable. MeCN can solvate the TS1F structure only via nucleophilic solvation through the nitrogen center (see Fig. 2b). Finally, Fig. 2c shows the available sites for the MeCN coordination to the TS1F structure already solvated by water. In summary, the significant structures to discuss preferential solvation are TS1F-water/MeCN and TS1F-MeCN/water, describing the micro solvation shells with water and MeCN in the first shells, respectively. These structures are depicted in Fig. 3.
With the relative energies of the solvated structures TS1F-water/MeCN and TS1F-MeCN/water at hand, we can build a relative energy profile, shown in Fig. 4.
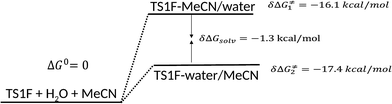 | ||
| Fig. 4 Comparison of solvation energy between TS1F-MeCN/water and TS1F-water/MeCN respect to the separated molecules. | ||
Fig. 4 shows that at the total energy level, preferential solvation in the aqueous phase is favorable to within 1.3 kcal mol−1 with respect to the MeCN phase. For the ClDNB case, the comparison in free energy of solvation in the modes similar to that shown in Fig. 4, slightly rises to 1.4 kcal mol−1 in favor of the aqueous phase. A reviewer asked for an additional calculation of solvation energy using a triple zeta basis set (6-311+G(d,p)) with the geometry optimized at the double zeta level. With this more extended basis set we obtain a value very close to that obtained by using the double zeta basis (6-31+G(d,p)): 1.0 kcal mol−1 for FDNB. Therefore, the correction to the energy profile in Fig. 4 is marginal.
Natural Bond Orbital (NBO) and second order perturbation analysis
In order to have a closer view into the molecular interactions that drives preferential solvation, we performed a NBO population analysis. Table 3 summarizes the results for the aminolysis of FDNB in the gas phase. Scheme 2 shows the micro-environment of the TS of FDNB and atom numbering for Tables 3 and 4.| Structure | Donor | Acceptor | E(2) | Interaction type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Energies are in kcal mol−1. w: water; an: acetonitrile. LP: lone pair; BD*: anti-bonding state. | ||||
| TS1Fw/an | LP(O4) | BD*(N2–H3) | 2.1 | |
| LP(O4) | BD*(O5–H6) | 2.5 | ||
| LP(N2) | LP*(C1) | 119.5 | Bond forming | |
| LP(O5) | BD*(N2–H3) | 11.1 | Specific solvation | |
| LP(N8) | BD*(O5–H7) | 9.8 | ||
| TS1Fan/w | LP(O4) | BD*(N2–H3) | 2.9 | |
| LP(O4) | BD*(C9–N8) | 1.1 | ||
| LP(N2) | LP*(C1) | 127.9 | Bond forming | |
| LP(N8) | BD*(N2–H3) | 2.0 | Specific solvation | |
| LP(N8) | BD*(O5–H7) | <0.5 | ||
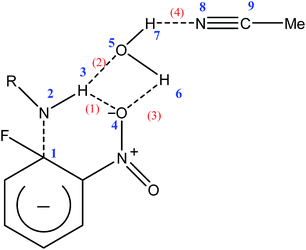 | ||
| Scheme 2 Possible interaction between the TS and the preferred solvation pattern by water and atom numbering. Irrelevant atoms were omitted. | ||
| Structure | Donor | Acceptor | E(2) | Interaction type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Energies are in kcal mol−1. LP: lone pair; BD*: anti-bonding state. | ||||
| TS1Fw/an | LP(O4) | BD*(N2–H3) | 2.1 | |
| LP(O4) | BD*(O5–H6) | 2.5 | ||
| LP(N2) | LP*(C1) | 126.8 | Bond forming | |
| LP(O5) | BD*(N2–H3) | 10.7 | Specific solvation | |
| LP(N8) | BD*(O5–H7) | 10.4 | ||
| TS1Fan/w | LP(O4) | BD*(N2–H3) | 2.8 | |
| LP(O4) | BD*(C9–N8) | 1.1 | ||
| LP(N2) | LP*(C1) | 135.6 | Bond forming | |
| LP(N8) | BD*(N2–H3) | 1.9 | Specific solvation | |
| LP(N8) | BD*(O5–H7) | <0.5 | ||
Inspection of Table 3 reveals that the solvation of the transition state in the mode TS1F-water/MeCN clearly outweighs the solvation of TS1F-MeCN/water, thereby suggesting that there is preferential solvation in favor of the aqueous phase. Note that this result is more resolved than the conclusions obtained from the total energy analysis. In fact, specific solvation in favor of aqueous phase is around 6 times that observed for the arrangement with acetonitrile in the first solvation shell. A reviewer called our attention about including the interaction of the departing fluorine atom and the solvent. We performed such calculation and the resulting second order interaction energies are too low: 0.48 kcal mol−1 and 0.16 kcal mol−1 for fluorine with water, and fluorine with acetonitrile, respectively.
Table 4 summarizes the results for the aminolysis of FDNB including continuum dielectric corrections. This table shows the orbital interaction analysis similar to that presented in Table 3, but corrected by dielectric solvation effects using the SMD model.31
Note that in general, and as expected, a similar response is obtained with respect to the gas phase analysis. As previously stated, the reaction field shape factor g(ε) = (1 − 1/ε) quickly saturates for water and MeCN, and therefore the reaction field factor g(ε) are essentially the same. As a result, the bulk dielectric solvation free energies become very close to each other and almost cancel out.
Conclusions
We have performed and integrated experimental and theoretical study on preferential solvation effects for the reactions of FDNB and ClDNB towards morpholine in acetonitrile, water and mixtures of them of varying compositions. The kinetic study opened the possibility for the analysis of preferential solvation for FDNB. The results show that 10% vol. H2O is sufficient to destabilize the MC leading to a change in the RDS. The HB pattern expected for water suggests that the net result is the activation of both reaction centers, thereby reinforcing the idea that the intramolecular HB formation at the TS structure facilitates the nucleophilic attack. In the binary mixtures, both substrates in the regimen of 90% vol. MeCN display the maximum value of the rate constant. The kinetic study was complemented with an exploration of the PES. This analysis reveals that the solvation of the TS in the mode TS1F-water/MeCN clearly outweighs the solvation of TS1F-MeCN/water, thereby suggesting that there is preferential solvation in favor of the aqueous phase. This result is more resolved than the conclusions obtained from the total energy analysis. In fact, solvation in favor of aqueous phase is around six time that observed for the arrangement with MeCN in the first solvation shell. The orbital interaction analysis corrected by dielectric solvation effects using the SMD model gives, as expected, a similar response.Experimental
Kinetic measurements
Were carried out spectrophotometrically (330–500 nm range) by means of a diode array spectrophotometer in aqueous solution, acetonitrile (MeCN) and different water/MeCN mixtures. The reactions, studied under excess of the amine over the substrate were started by injection of a substrate stock solution in MeCN into the amine solution in the spectrophotometric cell. Under these conditions pseudo first order rate coefficients (kobs) were found. Rate coefficient values for morpholine (kN) were obtained from plots of kobs vs. [amine], for the reaction of FDNB the rate constant Kk2 and Kk3 should be obtained from the intercept and slope of the linear plots of kobs/[amine] vs. [amine], respectively. The thermodynamic activation parameters were obtained using Arrhenius and Earing equations (eqn (1) and (2) below) at different temperatures (12 to 55.0 ± 0.1 °C). The experimental conditions of the reaction and the kobs values are listed in Tables S73–S96 in ESI.†Product analysis
The presence of N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl) morpholine as products of the reactions were determined spectrophotometrically by comparison of the UV-visible spectra at the end of the reactions with those of authentic samples under the same conditions.Computational details
Cartesian coordinates, energies and the number of imaginary frequencies for stationary points are compiled in ESI.† The transition-state structures were fully optimized at the M06-2X/6-31+G(d,p) level of theory. All the calculations were performed using the Gaussian 09 package.32Synthetized product
To a stirred solution of 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (1.0 g, 5.4 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL), containing potassium carbonate (1.49 g, 10.8 mmol), was added morpholine (468 mg, 5.4 mmol) and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 30 min. The ethanol was evaporated, the residue was extracted with ethyl acetate (25 mL) and the organic layer was dried and concentrated. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography on silica gel (ethyl acetate–hexane 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)morpholine (1.2 g, 88%), mp 120–121 °C (Lit. 117–118 °C). 1H-NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3) d: 3.28 (t, J = 4.7 Hz, 4H), 3.87 (t, J = 4.7 Hz, 4H), 7.13 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 8.28 (dd, J = 9.3, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 8.69 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H); 13C-NMR (50.4 MHz, CDCl3) d: 50.9, 66.1, 119.2, 123.9, 128.4, 138.4, 138.9, 149.3. FT-IR (Nujol) 3115, 1610, 1590, 1530, 1330 cm−1.33
1) to give N-(2,4-dinitrophenyl)morpholine (1.2 g, 88%), mp 120–121 °C (Lit. 117–118 °C). 1H-NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3) d: 3.28 (t, J = 4.7 Hz, 4H), 3.87 (t, J = 4.7 Hz, 4H), 7.13 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 8.28 (dd, J = 9.3, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 8.69 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H); 13C-NMR (50.4 MHz, CDCl3) d: 50.9, 66.1, 119.2, 123.9, 128.4, 138.4, 138.9, 149.3. FT-IR (Nujol) 3115, 1610, 1590, 1530, 1330 cm−1.33
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by project RC-130006 CILIS, granted by fondo de Innovacion para la competitividad Del Ministerio de Economia, Fomento y Turismo, Chile and Fondecyt Grants 1150759. J. A.-E. thanks CONICYT of Chile for a doctoral fellowship.Notes and references
- I. Newintong, J. Pérez-Arlandis and T. Welton, Org. Lett., 2007, 9, 5247 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. D'Anna, S. Marullo and R. Noto, J. Org. Chem., 2010, 75, 767 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. P. Hallet and T. Welton, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 3508 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. M. E. Mancini, A. Terenzani, A. Adam, A. Pérez and L. R. Vottero, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 1999, 12, 207 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ben-Naim, Pure Appl. Chem., 1990, 62, 25 CrossRef CAS.
- J. G. Kirkwood, J. Chem. Phys., 1934, 2, 351 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Onsager, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1936, 58, 1486 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ormazábal-Toledo, J. G. Santos, P. Ríos, E. Castro, P. R. Campodónico and R. Contreras, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117, 5908 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Catalán, C. Díaz and F. García-Blanco, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2003, 1, 575 Search PubMed.
- P. M. Mancini, G. Fortunato, C. Adam, L. R. Vottero and A. J. Terenzani, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2002, 15, 258 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Gazitúa, R. A. Tapia, R. Contreras and P. R. Campodónico, New J. Chem., 2014, 38, 2611 RSC.
- F. Terrier, in Nucleophilic Aromatic Displacement, VCH, Weinheim, 1991 Search PubMed.
- N. S. Nudelman, in The Chemistry of Amino, Nitroso, Nitro and Related Groups, ed. S. Patai, Wiley, Chichester, 1996, ch. 26 Search PubMed.
- M. Crampton, in Organic Reaction Mechanism, ed. A. C. Knipe and W. E. Watts, Wiley, Chichester, 1996, ch. 5 Search PubMed.
- (a) J. F. Bunnett and R. E. Zahler, Chem. Rev., 1951, 49, 273 CrossRef CAS; (b) J.-H. Choi, B.-C. Lee, H.-W. Lee and I. Lee, J. Org. Chem., 2002, 67, 1277 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) I.-H. Um, J.-Y. Hong, J.-J. Kim, O.-M. Chae and S.-K. Bae, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 5180 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) I.-H. Um, S.-M. Chun, O.-M. Chae, M. Fujio and Y. Tsuno, J. Org. Chem., 2004, 69, 3166 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) I.-H. Um, J.-Y. Hong and J.-A. Seok, J. Org. Chem., 2005, 70, 1438 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) I.-H. Um, L.-R. Im, J.-S. Kang, S.-S. Bursey and J. M. Dust, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77, 9738 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Banjoko and I. A. Babatunde, Tetrahedron, 2004, 60, 4645 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. Ormazábal-Toledo, R. Contreras, R. A. Tapia and P. R. Campodónico, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 2302 RSC; (b) R. Ormazábal-Toledo, R. Contreras and P. R. Campodónico, J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 1091 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Contreras, R. Ormazábal-Toledo and P. R. Campodónico, in Arene Chemistry: Reaction Mechanisms and Methods for Aromatic Compounds, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2015 Search PubMed.
- F. Terrier, in Modern Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution, Wiley-VHC, Weinheim, Germany, 2013 Search PubMed.
- A. Williams, in Concerted Organic and Bio-organic Mechanisms, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2000, ch. 4, pp. 43–46 Search PubMed.
- C. F. Bernasconi, MTP Int. Rev. Sci.: Org. Chem., Ser. One, 1973, 3, 33 CAS.
- I.-H. Um, S.-W. Min and J.-M. Dust, J. Org. Chem., 2007, 72, 8797 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. M. E. Mancini, A. Adam, A. Perez and L. R. Vottero, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2000, 13, 221 CrossRef CAS.
- H. J. Eyring, Chem. Phys., 1935, 3, 107 CAS.
- (a) S. S. Shaik, H. B. Schlegel and S. S. Wolfe, in Theoretical Aspects of Physical Organic Chemistry: the SN2 Mechanism, Wiley, New York, 1992 Search PubMed; (b) P. G. Mezey, in Potential Energy Hypersurfaces, Elsevier, New York, 1987 Search PubMed; (c) J. I. Steinfeld, J. S. Francisco and W. L. Hase, in Chemical Kinetics and Dynamics, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New York, 2nd edn, 1999 Search PubMed.
- S. Gallardo-Fuentes, R. A. Tapia, R. Contreras and P. R. Campodónico, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 30638 RSC.
- (a) F. D'Anna, V. Frenna, S. La Marca, R. Noto, V. Pace and D. Spinelli, Tetrahedron, 2008, 64, 672 CrossRef; (b) F. D'Anna, S. Marullo, P. Vitale and R. Noto, Chem. Phys. Chem., 2012, 13, 1877 CrossRef PubMed; (c) F. D'Anna, V. Frenna, R. Noto, V. Pace and D. Spenelli, J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 9637 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Buncel, J. M. Dust and F. Terrier, Chem. Rev., 1995, 95, 2261 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Barbosa and V. Sanz-Nebot, J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 1994, 90, 3287 RSC.
- M. Born, Z. Phys., 1920, 1, 45 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. Tomasi, Chem. Rev., 1994, 94, 2027 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. J. Cramer and D. G. Truhlar, in Review in Computational Chemistry, ed. K. B. Lipkowitz and D. B. Boyd, VCH, New York, 1995, vol. 6, pp. 1–72 Search PubMed.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, et al., Gaussian 09, Revision B.01, Wallingford, CT, 2009 Search PubMed.
- A. V. Gulevskaya, S. Verbeeck, O. N. Burov, C. Meyers, I. N. Korbukova, W. Herrebout and B. U. W. Maes, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2009, 23, 564 CrossRef.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Kinetic results (Tables S73–S96), plots of kobs versus [Nu]T for all the reactions (Fig. S1–S72), H1 and C13 NMR spectra for final product; complete ref. 27; Cartesian coordinates, energies and the number of imaginary frequencies of the stationary states considered in the computational study. See DOI: 10.1039/c5ra20779g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |