Uniform distribution of low content BaTiO3 nanoparticles in poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposite: toward high dielectric breakdown strength and energy storage density
Abstract
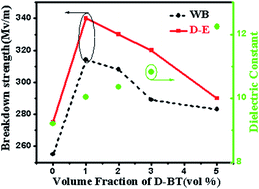
BaTiO3/poly(vinylidene fluoride) (BT/PVDF) composite material, a promising dielectric material for capacitor, has recently attracted much attention because of the promising dielectric performance and its abundant availability. Insufficient control of the hierarchal morphology of the blend has yielded a precipitous decline in breakdown strength at high BT nanoparticles volume fractions. Here, we demonstrate that breakdown strength and energy storage density can be increased up to higher value by creating uniform distribution of low content of BT nanoparticles in PVDF matrix. The dielectric properties of BT/PVDF nanocomposite were measured as a function of BT nanoparticles loading. The nanocomposite displayed a 150% increase in dielectric breakdown strength and energy density increased to more than triple that of the pure PVDF even at the 1 vol% BT nanoparticles loading. It was attributed to the uniform distribution of low content BT nanoparticles in PVDF matrix, which lead to superior dielectric breakdown strength and energy storage density than those of composites filled with high content of BT nanoparticles. Furthermore, the nanocomposites films with low content of fillers were more flexible and cost-effective. The finding based on this research provides a low-cost method to achieve high performance in capacitor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...