Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads and their recognition for baicalein
Abstract
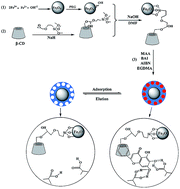
Magnetite–β-cyclodextrin@poly(ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) core–shell microspheres imprinted with baicalein (Fe3O4–β-CD@MIPs) were synthesized by ultrasonic assisted precipitation polymerization (UAPP) using methacrylic acid (MAA) as a functional monomer and EGDMA as a crosslinker in the presence of Fe3O4–β-CD nanoparticles as the template and baicalein (BAI) as the imprinting molecule. The structure, morphology and magnetic properties of the resultant Fe3O4–β-CD@MIPs have been systematically characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The unique recognition ability of Fe3O4–β-CD@MIPs for BAI was evaluated by the adsorption experiments via comparing those of Fe3O4@MIPs and Fe3O4–β-CD@NIPs non-imprinted nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...