DOI:
10.1039/C3RA47760F
(Paper)
RSC Adv., 2014,
4, 11360-11366
The long persistent luminescence properties of phosphors: Li2ZnGeO4 and Li2ZnGeO4:Mn2+
Received
18th December 2013
, Accepted 11th February 2014
First published on 12th February 2014
Abstract
The blue emitting long persistent phosphor (LPP) Li2ZnGeO4 and green emitting LPP Li2ZnGeO4:Mn2+ were newly prepared by a high temperature solid-state reaction method. The blue and green afterglow with duration of 5 and 8 h were confirmed to originate from host emission and d–d transitions of Mn2+ ions, respectively. The density of traps with suitable depth was significantly increased with the incorporation of Mn2+ ions. The energy transfer from host emission to Mn2+ ions was observed. The motion of charge carriers and a possible LAG mechanism based on a tentative model were illuminated and discussed in detail.
Introduction
Long persistent phosphors are a kind of energy absorbing, storing and releasing material. Under the excitation by sunlight or other artificial light source, it can absorb and store energy and then release the energy gradually for several seconds to hours in the form of visible light after the stoppage of the excitation source at room temperature.1–3 LPPs can find applications in many fields such as security illumination, decoration, storage media, detection of high energy rays and fiber-optic thermometers and in vivo bio-imaging4 due to the environmentally friendly nature, economical sustainability and unique properties.
Since the report of SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ by Matsuzawa et al. in 1996,5 many researchers have paid much attention on the development of divalent europium doped LPPs and a large number of LPPs that Eu2+-doped in various matrices have been discovered.6 During the past decades, the number of publications on non-Eu2+-doped (mainly includes trivalent rare-earth ions and transition metal ions) LPPs have also seen a steady increase. However, compared to the Eu2+-doped LPPs, the luminance and duration of the present non-Eu2+-doped LPPs are still poor. The lack of excellent non-Eu2+-doped LPPs is striking. Furthermore, to explain the occurrence of long afterglow (LAG) and solve the unrevealed problems, several different kinds of models on LAG mechanism have been proposed such as Hölsä7 and Dorenbos.8 Unfortunately, there are still many unknown details such as the nature of traps and the interaction between traps which are critical to explore and design the desired LPPs though most authors have reached an agreement on the general idea that charge carriers are trapped by long-lived traps inside the band gap. In order to better understand the LAG generation process and pave the way for the further development of LPPs avoiding some unnecessary detours, it is urgent to unravel these mysteries. Thus, it is necessary to in search for various new kinds of LPPs with different lattice host and activators to unravel and complete the mechanism behind the LAG.
Recently, Mn2+-doped germanates such as Zn2GeO4 and Li2ZnGeO4 have attracted much more interest due to the excellent performance and potential practical application in field-emission displays.9,10 Divalent manganese ion has a d5 electron configuration with a broad emission band varying from deep green to far red depending on the strong ligand of the 4T1(4G) state and the emission is ascribed to the parity-forbidden d–d transition from the lowest excited level 4T1(4G) to the ground state 6A1(6S).11 As an important activator, Mn2+ ion has been extensively employed in a large number of important phosphors. But, up to now, few studies about Mn2+ solely doped LPPs have been reported, for examples, CaZnGe2O6:Mn2+ (red),12 CdSiO3:Mn2+ (orange)13 and Zn2GeO4:Mn2+ (green).14 These motivated us to predict that Li2ZnGeO4 may have the potential to serve as a new host material for Mn2+ with LAG emission.
Therefore, in our present work, Li2ZnGeO4 and Mn2+ were selected as host and activator, respectively. Phosphors of un-doped Li2ZnGeO4 and Mn2+-doped Li2ZnGeO4 were synthesized successfully by high temperature solid state method. Accordingly, a green emitting LPP Li2ZnGeO4:Mn2+ with excellent LAG properties was obtained, just as we anticipated. To our surprise, the phenomenon of blue LAG originating from un-doped Li2ZnGeO4 was also observed. According to the photoluminescence, afterglow, decay curves and TL glow curves, the traps in lattice and the generation mechanism of LAG were discussed in detail on basis of a schematic.
Experiments
Sample synthesis
Powder samples of Mn2+-doped Li2ZnGeO4 (LZGO) phosphors were prepared via a conventional high temperature solid state reaction method. The starting materials used in the preparation were Li2CO3 (AR), ZnO (AR), MnCO3 (AR) and GeO2 (99.99%). The stoichiometric amounts of raw materials were weighed out according to the nominal compositions of Li2Zn1−tGeO4:tMn2+ (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, 0.015, and 0.02). Then the powders were mixed and homogenized thoroughly for 40 min in an agate mortar. Next, the mixtures were transferred into alumina crucibles and calcined at 1200 °C for 4 h in a tube furnace in air atmosphere. After cooling down to room temperature naturally, all as-synthesized samples were ground again to fine powders in an agate mortar.
Measurements and characterization
The phase identification of samples LZGO:tMn (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.01 and 0.02) were carried out by a XD-2 powder diffractometer (Beijing PGeneral) using Cu Kα irradiation (λ = 1.5406 Å) at 36 kV tube voltage and 20 mA tube current with a scanning step of 0.02° in the 2θ range from 10° to 70°. In order to carry out a whole-powder-pattern profile fitting, the XRD data of all as-prepared samples were also collected in the 2θ range from 10° to 110° with intervals of 0.02° and a pace time of 2 s per step. These data diffraction data were collected on a Rigaku X-ray diffractometer D/Max-2400 with a power of 40 kV at 140 mA, employing Cu Ka radiation by using a graphite monochromator. The divergence, scattering, and receiving slit were set at 18, 18 and 0.3 mm, respectively. Structure refinements of all obtained samples were performed by a Fullprof program15 using a whole-powder-pattern profile fitting procedure. The excitation and emission spectra were measured using a Hitachi F-7000 Fluorescence Spectrophotometer equipped with a Xe lamp (150 W) as excitation source. Both the slits of excitation and emission were set to be 2.5 nm. The scanning rate was 1200 nm min−1 under 400 V working voltage. Suitable filters were used to avoid the appearance of diffraction peaks. The afterglow spectra were also obtained by the same Hitachi F-7000 Fluorescence Spectrophotometer. The UV excitation source was switching off after the samples were irradiated by 254 nm for 3 min and the afterglow spectra were recorded immediately. Afterglow decay curves were recorded immediately after the samples being irradiated by 254 nm for 2 min with a GFZF-2A single-photon counter system. A FJ427A1 thermoluminescent dosimeter (CNNC Beijing Nuclear Instrument Factory) was utilized to collect the TL curves from room temperature to 250 °C with a heating rate of 1 °C s−1. Prior to the TL measurements, each sample was first exposed to a 254 nm UV radiation lamp (60 W) for 1 min and then put in dark waiting for 2 min. To ensure the validity of comparison, the amount of each sample for afterglow decay and TL measurements was kept as a constant. All the measurements were performed at room temperature except for the TL curves.
Results and discussion
Phase identification
Fig. 1 shows X-ray powder diffraction patterns of some selective samples LZGO:tMn2+ (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.01 and 0.02) and standard card of compound Li2ZnGeO4. It can be clearly seen that all diffraction peaks are matched well with the standard data of Li2ZnGeO4 (JCPDS no. 38-1082) indicating the high purity and crystalline of the samples in this work. Fig. 2(a)–(f) exhibit the experimental, fitted and difference results of the XRD refinements using Rietveld refinement for powder XRD data of LZGO:tMn (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, 0.015 and 0.02 respectively) at room temperature. The corresponding structure parameters are listed in Table 1(a). Based on it, the structure of Li2ZnGeO4 can be assigned to the monoclinic crystal system with space group P21/n. The reliability parameters of refinements for all as-obtained samples are listed in Table 1(b). The LZGO host lattice is built up by GeO4 tetrahedra, which are linked together by LiO4 and Zn(Mn)O4 tetrahedra.16,17 No extra phase can be observed inferring that Mn2+ ions have been completely dissolved into the LZGO host lattice by substitution for Zn sites and such a small amount of Mn2+ ions doping does not have significant influence on the crystal structure of host.
 |
| | Fig. 1 XRD patterns of some representative samples LZGO:tMn (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.01 and 0.02). | |
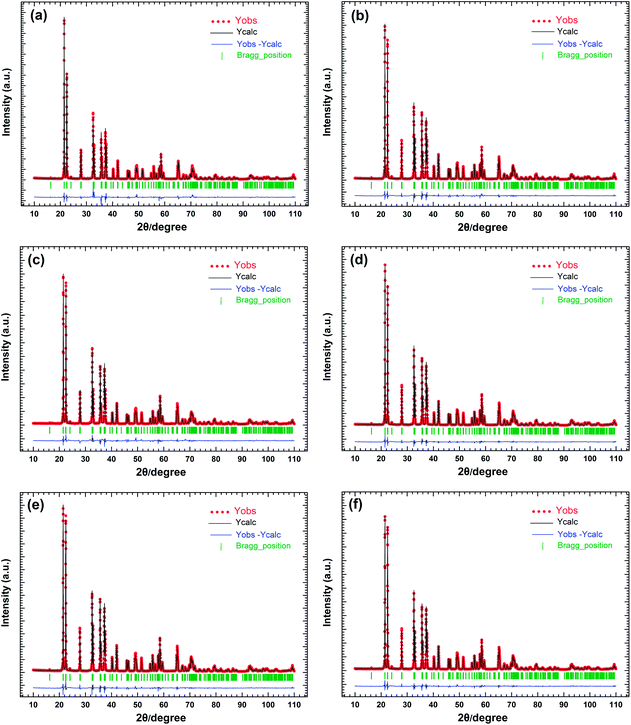 |
| | Fig. 2 Rietveld refinement of powder XRD profiles of all obtained samples LZGO:tMn ((a)–(f) correspond to t = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, 0.015 and 0.02, respectively). | |
Table 1 (a) Crystallographic data and structure parameters of samples LZGO:tMn2+ (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, 0.015 and 0.02) and (b) the goodness of fitting parameters
| (a) |
| Parameters |
Samples |
Zn |
Ge |
Li1 |
Li2 |
O1 |
O2 |
O3 |
O4 |
Mn |
| x |
t = 0 |
0.251 |
0 |
0.493 |
0.724 |
0.469 |
0.271 |
0.997 |
0.250 |
— |
| t = 0.0025 |
0.251 |
0 |
0.460 |
0.729 |
0.467 |
0.271 |
0.997 |
0.242 |
0.251 |
| t = 0.005 |
0.253 |
0 |
0.504 |
0.729 |
0.473 |
0.285 |
0.997 |
0.245 |
0.253 |
| t = 0.01 |
0.252 |
0 |
0.480 |
0.737 |
0.467 |
0.271 |
0.997 |
0.244 |
0.252 |
| t = 0.015 |
0.252 |
0 |
0.449 |
0.739 |
0.450 |
0.268 |
0.997 |
0.246 |
0.252 |
| t = 0.02 |
0.252 |
0 |
0.479 |
0.731 |
0.469 |
0.268 |
0.997 |
0.243 |
0.252 |
| y |
t = 0 |
0.333 |
0.165 |
0.190 |
0.364 |
0.160 |
0.669 |
0.161 |
0.313 |
— |
| t = 0.0025 |
0.332 |
0.168 |
0.188 |
0.349 |
0.151 |
0.668 |
0.160 |
0.312 |
0.332 |
| t = 0.005 |
0.330 |
0.170 |
0.192 |
0.365 |
0.125 |
0.651 |
0.158 |
0.310 |
0.330 |
| t = 0.01 |
0.331 |
0.167 |
0.200 |
0.358 |
0.143 |
0.672 |
0.170 |
0.310 |
0.331 |
| t = 0.015 |
0.331 |
0.168 |
0.202 |
0.345 |
0.135 |
0.672 |
0.164 |
0.319 |
0.331 |
| t = 0.02 |
0.332 |
0.167 |
0.202 |
0.345 |
0.144 |
0.662 |
0.153 |
0.310 |
0.332 |
| z |
t = 0 |
0.541 |
0.039 |
0.005 |
0.520 |
0.381 |
0.447 |
0.381 |
0.903 |
— |
| t = 0.0025 |
0.542 |
0.039 |
0.005 |
0.505 |
0.410 |
0.448 |
0.390 |
0.915 |
0.542 |
| t = 0.005 |
0.541 |
0.039 |
0.005 |
0.511 |
0.396 |
0.456 |
0.404 |
0.894 |
0.541 |
| t = 0.01 |
0.541 |
0.039 |
0.005 |
0.517 |
0.413 |
0.444 |
0.390 |
0.912 |
0.541 |
| t = 0.015 |
0.542 |
0.039 |
0.005 |
0.512 |
0.415 |
0.440 |
0.393 |
0.913 |
0.542 |
| t = 0.02 |
0.543 |
0.039 |
0.005 |
0.518 |
0.413 |
0.445 |
0.393 |
0.911 |
0.543 |
| Occupancy factor |
t = 0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
— |
| t = 0.0025 |
0.998 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
0.002 |
| t = 0.005 |
0.995 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
0.005 |
| t = 0.01 |
0.99 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
0.01 |
| t = 0.015 |
0.985 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
0.015 |
| t = 0.02 |
0.98 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
0.02 |
| Unit cell parameters and the errors |
t = 0 |
a = 6.363(2) Å, b = 5.434(1) Å, c = 5.033(1) Å, β = 90.204 (2)° |
| t = 0.0025 |
a = 6.363(1) Å, b = 5.435(1) Å, c = 5.033(1) Å, β = 90.209(1)° |
| t = 0.005 |
a = 6.364(1) Å, b = 5.435(2) Å, c = 5.033(2) Å, β = 90.207(2)° |
| t = 0.01 |
a = 6.364(1) Å, b = 5.436(1) Å, c = 5.033(1) Å, β = 90.207(1)° |
| t = 0.015 |
a = 6.365(1) Å, b = 5.435(1) Å, c = 5.034(1) Å, β = 90.204 (1)° |
| t = 0.02 |
a = 6.366(1) Å, b = 5.435(1) Å, c = 5.034(1) Å, β = 90.205(2)° |
| (b) |
| |
t = 0 |
t = 0.0025 |
t = 0.005 |
t = 0.01 |
t = 0.015 |
t = 0.02 |
| RP (%) |
10.1 |
8.53 |
9.37 |
7.25 |
6.72 |
7.03 |
| RWP (%) |
12.0 |
10.3 |
11.6 |
9.08 |
8.16 |
8.40 |
| χ2 |
2.58 |
1.75 |
2.09 |
1.57 |
1.21 |
1.16 |
Photoluminescence properties
The excitation and emission spectra of LZGO and LZGO:Mn2+ in UV-vis range are shown in Fig. 3. For non-doped sample LZGO, a broad excitation band from 200 to 280 nm with a maximum at 245 nm can be observed when monitoring emission at 396 nm. Under excitation by 245 nm, it shows a broad emission band between 300 and 600 nm with a peak at ∼396 nm. The blue emission can be attributed to the recombination of donors (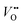 and
and  ) and acceptors (
) and acceptors (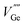 and
and 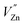 ) which are associated with native defects.18,19 Compared to the results by Shang et al.,10 there is slight wavelength shift of excitation and emission. In this paper, some more details of photoluminescence are observed. For Mn2+ doped LZGO samples, when monitoring emission at 530 nm, a broad strong excitation band with a maximum at 266 nm which is assigned to the charge-transfer transition in Mn2+ ions20 and several weak sharp peaks which are attributed to the transitions of 6A1(6S) to 4E(4D), 4T2 (4D), 4T2 (4G) and 4T1 (4G) (seen in Fig. 3(b)) can be observed. Upon excitation by 266 nm, two broad separated corresponding emission bands are observed. One emission band in the range from 300 to 500 nm with a peak at ∼367 nm (seen in Fig. 3(c)) is related to the emission of LZGO host. Compared to the emission of un-doped LZGO, it shows significant blue shift, which may be resulted from the distortion distribution of donors and acceptors as the incorporation of Mn2+ ions. Another emission band between 480 and 600 nm is attributed to 4T1–6A1 forbidden transition of the Mn2+ ions. Moreover, it is notable that the emission spectrum of LZGO host covers the excitation of Mn2+. So it is reasonable to conclude that the energy transfers from host to Mn2+ ions.
) which are associated with native defects.18,19 Compared to the results by Shang et al.,10 there is slight wavelength shift of excitation and emission. In this paper, some more details of photoluminescence are observed. For Mn2+ doped LZGO samples, when monitoring emission at 530 nm, a broad strong excitation band with a maximum at 266 nm which is assigned to the charge-transfer transition in Mn2+ ions20 and several weak sharp peaks which are attributed to the transitions of 6A1(6S) to 4E(4D), 4T2 (4D), 4T2 (4G) and 4T1 (4G) (seen in Fig. 3(b)) can be observed. Upon excitation by 266 nm, two broad separated corresponding emission bands are observed. One emission band in the range from 300 to 500 nm with a peak at ∼367 nm (seen in Fig. 3(c)) is related to the emission of LZGO host. Compared to the emission of un-doped LZGO, it shows significant blue shift, which may be resulted from the distortion distribution of donors and acceptors as the incorporation of Mn2+ ions. Another emission band between 480 and 600 nm is attributed to 4T1–6A1 forbidden transition of the Mn2+ ions. Moreover, it is notable that the emission spectrum of LZGO host covers the excitation of Mn2+. So it is reasonable to conclude that the energy transfers from host to Mn2+ ions.
 |
| | Fig. 3 (a) Excitation spectra of LZGO (λem = 393 nm) and LZGO:Mn2+ (λem = 530 nm) along with the emission spectra of LZGO (λex = 245 nm) and LZGO:Mn2+ (λex = 266 nm); (b) the amplified excitation spectrum of LZGO in the wavelength range from 350 to 500 nm; (c) the amplified emission spectrum of LZGO:Mn2+ between 300 and 450 nm. | |
After the excitation of 254 nm UV lamp is switched off, an unexpected result of the present work is that the blue and green LAG in un-doped and Mn2+ doped LZGO can be clearly observed for more than 5 and 8 h by the naked eyes in the dark room, respectively. The photos of non-doped and Mn2+ doped LZGO before, under and after irradiation by UV light can be seen in the inset of Fig. 4. The afterglow spectra of all obtained samples were recorded as shown in Fig. 4. The shape and position of spectra are almost the same as emission spectra (in Fig. 3). The un-doped LZGO only shows blue LAG emission. The Mn2+ doped LZGO mainly shows green LAG emission and the intensity decrease with the rising of Mn2+ contents. The optimal Mn2+ concentration for afterglow is not observed though the content of Mn2+ is already as small as t = 0.0025. In addition, the extremely weak LAG emission of LZGO:Mn2+ in the range of 300–450 nm which is related to the host emission is also observed. The emissions decrease and disappear with the increase of Mn2+ contents, which confirms the ET from host to Mn2+. The significant blue shift of emission band is attributed to the influence of donors and acceptors by the incorporation of Mn2+ ions.
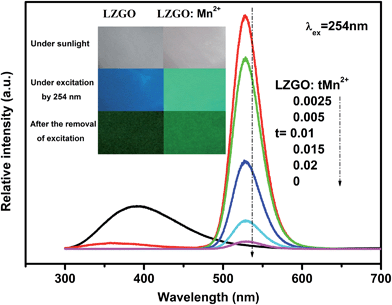 |
| | Fig. 4 The afterglow spectra of all obtained samples after the removal of 254 nm excitation. Insets: the photos of LZGO and LZGO:tMn samples under sunlight, under the irradiation by 254 nm and after the removal of excitation in dark, respectively. | |
Decay of afterglow
In order to study the afterglow decay behavior in more detail and compare the decay rates between LZGO samples with different Mn2+ doping contents, the decay curves in the time range of 0–1000 s of all as-obtained samples are collected and shown in Fig. 5. They can be well fitted and analyzed with a bi-exponential eqn (1) as follows:| |
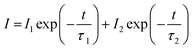 | (1) |
where I represents intensity; I1 and I2 are constants; τ1 and τ2 are decay times for the exponential component, they determine the rapid and slow decay processes, respectively; t is time. The fitting results of all decay curves are listed in Table 2. Apparently, the fitting results indicate that there are two decay processes are involved in LAG decay process including a rapid decay process at first and then a slow decay process. For Mn2+-doped LZGO samples, the values of τ1 and τ2 present continuous decreasing trends along with the increase of Mn2+ ions concentration. Thus, it can be concluded that LZGO: 0.0025Mn shows the best LAG performance in our work.
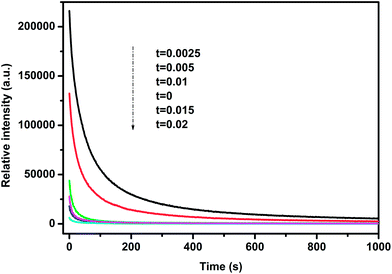 |
| | Fig. 5 Afterglow decay curves of samples LZGO:tMn (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, 0.015 and 0.02) from 0 to 1000 s. | |
Table 2 Decay times for two exponential components of LZGO:tMn2+ (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, 0.015 and 0.02) with different concentrations of Mn2+
| Contents of Mn2+ (t) |
τ1 (s) |
I1 |
τ2 (s) |
I2 |
| 0 |
13 |
21![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 321 321 |
257 |
3213 |
| 0.0025 |
46 |
149![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 683 683 |
386 |
45![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 954 954 |
| 0.005 |
34 |
94![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 571 571 |
328 |
26![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 584 584 |
| 0.01 |
18 |
34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 719 719 |
326 |
3739 |
| 0.015 |
18 |
13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 568 568 |
273 |
1737 |
| 0.02 |
14 |
4450 |
171 |
1165 |
Thermoluminescence analysis
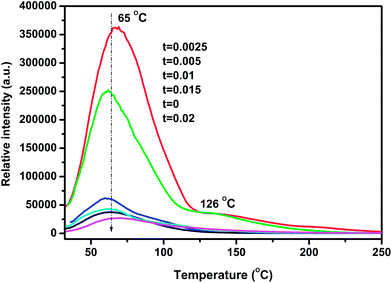
It is well known that LAG is primarily attributed to trapping and de-trapping of charge carriers which are captured by various traps. The suitable trap depth and high trap density play crucial roles in the generation of super LAG performance. Generally, TL curve studies can provide vital information about nature of the traps and the trap levels.21,22 In order to characterize the traps, TL measurements were carried out on each sample. As exhibited in Fig. 6, un-doped LZGO shows an asymmetry broad TL band between 32 and 150 °C with the peak predominating at ∼65 °C. For Mn2+ doped LZGO samples, a predominate band centered at ∼65 °C and a relatively weak band at ∼126 °C are observed. It is commonly considered that the lower and higher temperature of the TL bands is related to the shallower and deeper traps, respectively.23 The suitable TL peak is situated slightly above room temperature (50–120 °C) for the excellent LAG performance.24,25 Therefore, the TL band centered at ∼65 °C may be responsible for the blue and green LAG. Evidently, the incorporation of a slight amount of Mn2+ ions largely promotes the generation of traps at ∼65 °C as well as the creation of new deeper traps at ∼126 °C. The equivalent substitution of Zn2+ by Mn2+ creates isoelectronic traps such as 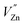 . The TL intensities for Mn2+-doped samples corresponding to 65 °C decrease continuously with the rising of Mn2+ doping concentration. Since that the trap density is approximately proportional to the integral intensity of TL band, the traps of sample LZGO:0.0025Mn2+ possess the biggest capacity to capture carriers. Undoubtedly, Mn2+-doped LZGO LPP shows the best LAG performance in the case of very small Mn2+ doping concentration.
. The TL intensities for Mn2+-doped samples corresponding to 65 °C decrease continuously with the rising of Mn2+ doping concentration. Since that the trap density is approximately proportional to the integral intensity of TL band, the traps of sample LZGO:0.0025Mn2+ possess the biggest capacity to capture carriers. Undoubtedly, Mn2+-doped LZGO LPP shows the best LAG performance in the case of very small Mn2+ doping concentration.
 |
| | Fig. 6 TL curves of samples LZGO:tMn (t = 0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, 0.015 and 0.02). | |
The mechanism of the persistent luminescence
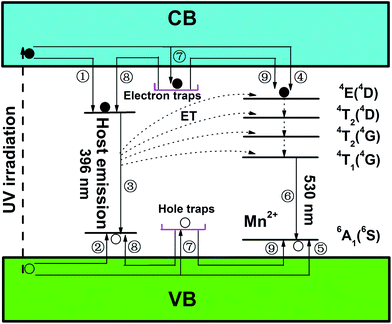
In order to explore the motion of charge carriers and interpret the generation process of LAG emission in LZGO and LZGO:Mn clearly, a schematic of phosphorescence mechanism based on the above analyses is illustrated as Fig. 7. Under UV excitation, electrons are excited to conduction band (CB) and holes are generated in valence band (VB) in un-doped LZGO host. Some excited electrons move through CB (1) and some holes move through VB freely (2) to the native defects. Then the recombination of electrons and holes (3) resulting in the generation of host emission. However, other excited electrons and holes also can be captured by the electron and hole traps, respectively (7). Under the activation of thermal motion, these trapped charge carriers (electrons and holes) can escape from their respective traps to CB and VB with a slow rate and move to the native defects (8) leading to the process (3), which creates the blue LAG from the host. When Mn2+ ion is doped into the host lattice, on the one hand, those unbound excited electrons mentioned above will move around in VB jumping to the excited energy level 4E(4D) of Mn2+ (4) and holes have the motion via VB to the ground state of Mn2+ (5). These excited electrons in higher energy level will transfer to the lower levels and finally to 4T1(4G) with non-radiative transitions. Afterwards, they will jump to ground state and combines with holes accompanying with the emission from Mn2+ (6). Meanwhile, the energy from host emission (3) will transfer to the excited energy levels of Mn2+. On the other hand, those gradually released electrons and holes from traps also can transfer to the excited energy level and ground state of Mn2+, respectively (9). The same process of charge carriers motion as the intrinsic emission of Mn2+ (6) occurs with a delay time, which causes the blue LAG phenomenon from Mn2+ ion. Similarly, there is a great chance of energy transfer from the LAG emission to Mn2+ ions at the same time. Thus, the emission and LAG are largely weakened by the incorporation of Mn2+ ions.
 |
| | Fig. 7 The schematic model of phosphorescence mechanism in long afterglow phosphors of LZGO and LZGO:Mn. | |
Conclusions
The un-doped blue emitting long persistent phosphor Li2ZnGeO4 and green emitting long persistent phosphor Li2ZnGeO4:Mn2+ with excellent afterglow performance were designed, prepared and characterized. The blue and green afterglow emissions originate from the host and Mn2+ emission. The duration of them can persist 5 and 8 h, respectively. The energy transfer from host to Mn2+ ions was confirmed. A possible afterglow mechanism was proposed and the generation processes of LAG were illustrated in detail. The two brand new LPPs may have great potential for application in many important fields.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21271049).
References
- W. Zeng, Y. H. Wang, S. C. Han, W. B. Chen, G. Li, Y. Z. Wang and Y. Wen, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013, 1, 3004 RSC.
- Y. Q. Li, Y. H. Wang, Y. Gong, X. H. Xu and M. J. Zhou, Opt. Express, 2010, 18, 24853 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. H. Jin, Y. H. Hu, L. Chen, X. J. Wang, G. F. Ju and Z. F. Mou, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2013, 96, 3821 CrossRef CAS.
- S. X. Lian, Y. Qi, C. Y. Rong, L. P. Yu, A. L. Zhu, D. L. Yin and S. B. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 7196 CAS.
- T. Matsuzawa, Y. Aoki, N. Takeuchi and Y. Murayama, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1996, 143, 2670 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Van den Eeckhout, P. F. Smet and D. Poelman, Materials, 2010, 3, 2536 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Aitasalo, J. Hölsä, H. Jungner, M. Lastusaari and J. Niittykoski, J. Lumin., 2001, 94–95, 59 CrossRef.
- P. Dorenbos, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2005, 152, H107 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. H. Zhang and J. Wang, Appl. Phys. A, 2012, 108, 943 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Shang, G. G. Li, D. M. Yang, X. J. Kang, C. Peng and J. Lin, Dalton Trans., 2012, 8861 RSC.
- C. Bertail, S. Maron, V. Buissette, T. L. Mercier, T. Gacoin and J.-P. Boilot, Chem. Mater., 2011, 23, 2961 CrossRef CAS.
- G. B. Che, C. B. Liu, X. Y. Li, Z. L. Xu, Y. Liu and H. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2008, 69, 2091 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Y. Kuang, Y. L. Liu and B. F. Lei, J. Lumin., 2006, 118, 33 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. D. Partlow and D. W. Feldman, J. Lumin., 1973, 6, 11 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Rodriguez-Carvajal, Reference Guide for the Computer Program FullProf, Laboratoire LeÂon Brillouin, CEA-CNRS, Saclay, France, 1996 Search PubMed.
- E. Plattner, H. Völlenke and A. Wittmann, Monatsh. Chem., 1976, 107, 921 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Sebastian, R. S. Jayashree and J. Gopalakrishnan, J. Mater. Chem., 2003, 13, 1400 RSC.
- Z. S. Liu, X. P. Jing and L. X. Wang, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, 154, H500 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. M. Shang, G. G. Li, D. M. Yang, X. J. Kang, C. Peng, Z. Y. Cheng and J. Lin, Dalton Trans., 2011, 9379 RSC.
- K. Uheda, T. Maruyama, H. Takizawa and T. Endo, J. Alloys Compd., 1997, 262–263, 60 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Thomast, M. Banerjeet, P. B. Vidyasagart and A. D. Shaligramz, Meas. Sci. Technol., 1995, 6, 554 CrossRef.
- Y. H. Jin, Y. H. Hu, L. Chen, X. J. Wang, Z. F. Mou, G. F. Ju and F. Liang, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2013, 178, 1205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. H. Xu, Y. H. Wang, W. Zeng, Y. Gong and B. T. Liu, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 94, 3632 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. L. Liu, B. F. Lei and C. S. Shi, Chem. Mater., 2005, 17, 2108 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Van den Eeckhout, A. J. J. Bos, D. Poelman and P. F. Smet, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2013, 87, 045126 CrossRef.
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here. 
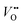 and
and  ) and acceptors (
) and acceptors (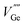 and
and 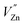 ) which are associated with native defects.18,19 Compared to the results by Shang et al.,10 there is slight wavelength shift of excitation and emission. In this paper, some more details of photoluminescence are observed. For Mn2+ doped LZGO samples, when monitoring emission at 530 nm, a broad strong excitation band with a maximum at 266 nm which is assigned to the charge-transfer transition in Mn2+ ions20 and several weak sharp peaks which are attributed to the transitions of 6A1(6S) to 4E(4D), 4T2 (4D), 4T2 (4G) and 4T1 (4G) (seen in Fig. 3(b)) can be observed. Upon excitation by 266 nm, two broad separated corresponding emission bands are observed. One emission band in the range from 300 to 500 nm with a peak at ∼367 nm (seen in Fig. 3(c)) is related to the emission of LZGO host. Compared to the emission of un-doped LZGO, it shows significant blue shift, which may be resulted from the distortion distribution of donors and acceptors as the incorporation of Mn2+ ions. Another emission band between 480 and 600 nm is attributed to 4T1–6A1 forbidden transition of the Mn2+ ions. Moreover, it is notable that the emission spectrum of LZGO host covers the excitation of Mn2+. So it is reasonable to conclude that the energy transfers from host to Mn2+ ions.
) which are associated with native defects.18,19 Compared to the results by Shang et al.,10 there is slight wavelength shift of excitation and emission. In this paper, some more details of photoluminescence are observed. For Mn2+ doped LZGO samples, when monitoring emission at 530 nm, a broad strong excitation band with a maximum at 266 nm which is assigned to the charge-transfer transition in Mn2+ ions20 and several weak sharp peaks which are attributed to the transitions of 6A1(6S) to 4E(4D), 4T2 (4D), 4T2 (4G) and 4T1 (4G) (seen in Fig. 3(b)) can be observed. Upon excitation by 266 nm, two broad separated corresponding emission bands are observed. One emission band in the range from 300 to 500 nm with a peak at ∼367 nm (seen in Fig. 3(c)) is related to the emission of LZGO host. Compared to the emission of un-doped LZGO, it shows significant blue shift, which may be resulted from the distortion distribution of donors and acceptors as the incorporation of Mn2+ ions. Another emission band between 480 and 600 nm is attributed to 4T1–6A1 forbidden transition of the Mn2+ ions. Moreover, it is notable that the emission spectrum of LZGO host covers the excitation of Mn2+. So it is reasonable to conclude that the energy transfers from host to Mn2+ ions.
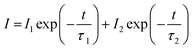

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 321
321![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 683
683![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 954
954![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 571
571![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 584
584![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 719
719![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 568
568 . The TL intensities for Mn2+-doped samples corresponding to 65 °C decrease continuously with the rising of Mn2+ doping concentration. Since that the trap density is approximately proportional to the integral intensity of TL band, the traps of sample LZGO:0.0025Mn2+ possess the biggest capacity to capture carriers. Undoubtedly, Mn2+-doped LZGO LPP shows the best LAG performance in the case of very small Mn2+ doping concentration.
. The TL intensities for Mn2+-doped samples corresponding to 65 °C decrease continuously with the rising of Mn2+ doping concentration. Since that the trap density is approximately proportional to the integral intensity of TL band, the traps of sample LZGO:0.0025Mn2+ possess the biggest capacity to capture carriers. Undoubtedly, Mn2+-doped LZGO LPP shows the best LAG performance in the case of very small Mn2+ doping concentration.





