3-Propionyl-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid ethyl esters: a family of antiproliferative thiazolidines†
F. Esra Önen-Bayram *a, Kerem Buran a, Irem Durmaz b, Barkin Berk c and Rengul Cetin-Atalay b
aDepartment of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Yeditepe University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Istanbul, Turkey. E-mail: esra.bayram@yeditepe.edu.tr; filizesraonen@gmail.com
bDepartment of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Faculty of Science, Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey
cDepartment of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Medipol University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Istanbul, Turkey
First published on 15th September 2014
Abstract
Cancer results from unregulated cell growth. Reactivating the process of the programmed cell death, i.e. apoptosis, is a classical anticancer therapeutic strategy. The apoptosis-inducing property of the (2RS,4R)-2-phenyl-3-propionyl-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (ALC 67) molecule has recently been discovered. We analyzed in this study the impact of the phenyl moiety of this molecule on its biological activity by synthesizing and evaluating analogues where this substituent was replaced by a series of aromatic and aliphatic groups. The results demonstrated that the molecule's antiproliferative property resisted such modifications. Thus, in addition to developing a family of thiazolidine compounds with promising anticancer properties; our investigation revealed that the second position of the thiazolidine ring can be used either to tune the physicochemical properties of ALC67 or to introduce a fluorescent tag to the structure in order to track it in cells and determine its exact molecular mechanism of action.
Introduction
Cancer is a disease that results from the abnormal proliferation of normal cells. Cancer cells present mutations that allow them to multiply rapidly, not only by escaping growth suppressors but also by resisting apoptosis, the natural cell death mechanism.1–3 Reactivating apoptosis either by developing anti-apoptotic protein inhibitors or pro-apoptotic protein agonists has constituted a considerable anticancer strategy for two decades.4Thiazolidines are five-membered heterocycles containing a sulfur and a nitrogen atom at their first and third positions respectively. They were first described by Miller et al. for their anticancer property in 2005.5,6 The authors, who first generated serine phosphate amides as lysophosphatidic acid analogues to treat prostate cancer, noted their poor selectivity due to the possible hydrolysis of the phosphate group present in their structures.7 To circumvent this issue, they chose to work with 4-thiazolidinone derivatives8 because this cycle is described as a phosphate biomimetic.9 To optimize their cytotoxicity results the authors then developed thiazolidine compounds, and subsequently discovered their promising apoptotic property.10–12
In a previous study based on these findings, we prepared a library of small molecules around a thiazolidine scaffold and demonstrated the relevant cytotoxicity of a propargylic compound, the ALC 67 molecule (Fig. 1A), on liver, colon, breast and endometrial cancer cell lines,13 which was also proven to induce apoptosis by activating caspase-9. However, the exact mechanism of action of this compound remains unknown. As 2-phenylthiazolidine carboxylic acid (Fig. 1B) and the corresponding ethyl ester (Fig. 1C) from which ALC 67 was synthesized did not exhibit any biological activity, we assigned the antiproliferative property of the molecule to its propargylic group.
 | ||
| Fig. 1 (A) The molecular structure of the cytotoxic ALC67. (B) The carboxylic acid precursor of ALC67, which exhibits no cytotoxicity. (C) The ethyl ester precursor of ALC67, with no cytotoxic activity. | ||
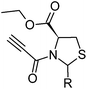
To analyze the impact of the phenyl moiety present at the second position of the heterocycle on the bioactivity of ALC67, we generated in this study 3-propionyl-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid ethyl esters presenting a series of aromatic and aliphatic moieties at this very position (Fig. 2). We then tested the synthesized compounds for their biological activity to check if the cytotoxicity resisted such modifications.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Examination of the effect of phenyl moiety on the cytotoxicity of ALC67. | ||
Results and discussion
Compounds were synthesized according to pathways previously described.13,14 Briefly, first an acetylation was carried out using L-cysteine and a series of commercially available aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes. Then, the resulting thiazolidine carboxylic acids (1a–1m) were converted into their corresponding ethyl esters (2a–2m) in ethanol in the presence of thionyl chloride. Finally, the secondary amine of the heterocycle was acylated by propiolic acid, which was previously activated by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) to provide the terminal alkyne compounds (3a–3m) (Scheme 1). | ||
| Scheme 1 Preparation of 3-propionyl-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid ethyl esters from a series of aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes. Reagents: (a) NaOH in ethanol–H2O (1/1); (b) thionyl chloride in absolute ethanol; (c) DCC in dry dichloromethane. | ||
The first step, which consisted of generating the thiazolidine ring from the nucleophilic addition reaction of L-cysteine (aminothiol) with a series of aliphatic and aromatic aldehydes, was conducted under basic conditions.15 As the ring-closure generates a new chiral center in an uncontrolled manner, thiazolidine compounds were obtained as diastereomeric mixtures with satisfactory yields (59–92%).
The synthesized carboxylic acid molecules were analyzed by FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR and mass spectrometry. The generation of the heterocyclic structure was confirmed by 1H NMR since the spectra exhibited the expected characteristic signals of a thiazolidine cycle. Indeed, in addition to the singlets at around 5.2 ppm and 5.6 ppm that correspond to the signals of C2–H of each diastereomer, a pair of doublet of doublets (dd) at around 4.2 ppm and 3.80 ppm for the C4-H and a set of four dd around 3.3 ppm for the unequivalent C5-Hs were also recorded in the spectra (Fig. 3A). The successful formation of the thiazolidine ring was also confirmed by 13C NMR as the spectra displayed the typical signals of C2, C4 and C5 at around 71 ppm, 65 ppm and 38 ppm respectively (Fig. 3B). The 2R, 4R and 2S, 4R diastereomers were obtained in general in a 40 : 60 ratio. This ratio was easily determined using the C2-H singlet signals of 1H NMR. Interestingly the thiazolidines derived from o-fluorobenzaldehyde and trimethylacetaldehyde (1d and 1m respectively) gave diastereomers in 15 : 85 and 5 : 95 ratios, probably due to the steric hindrance caused by the proximity of the fluorine atom or the tert-butyl group to the carboxylic acid moiety in the 2R, 4R configuration. Moreover, 1k and 1l were prepared from racemic mixtures of 3,5,5-trimethylhexanal and 2-methylpentanal respectively. For these reasons, each aldehyde led to four different thiazolidines: the 1H NMR spectra of these compounds exhibited four different doublets for the C2-H and the 13C NMR showed sets of four peaks for each signal. Given the difficulty of separation, the isomers were not isolated, neither when proceeding to the esterification or acylation steps, nor when biologically evaluated.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 (A) Typical 1H NMR signals of C2, C4 and C5 hydrogens of a diastereomeric mixture of thiazolidines. (B) Typical 13C NMR signals of C2, C4 and C5 carbons of a diastereomeric mixture of thiazolidines. | ||
The conversion of carboxylic acid derivatives into ethyl ester moieties was achieved in the presence of thionyl chloride in absolute ethanol. The generation of the ethyl ester function was readily confirmed by FT-IR since the typical large band at around 3300 cm−1 corresponding to the hydroxyl of the carboxylic acid function was no longer detected (data not shown). NMR analyses were not performed on these molecules because of their instability: though pure compounds were obtained (checked on TLC), we noticed that they tended to decompose when stored. This is why all obtained ester derivatives were directly acylated without further analyses.
To obtain ALC67 analogues, a propionyl group was introduced to the secondary amine of the thiazolidine ring of the 2a–2m molecules. The peptidic coupling reaction was carried out by classically activating the carboxylic acid function of propiolic acid by DCC. The presence of the terminal alkyne was analyzed by FT-IR, 1H NMR and 13C NMR. In fact in addition to the band at 2100 cm−1 that corresponds to the stretching band of the C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C bond, the IR spectra gave a strong and narrow band at 3200 cm−1 for the H–C
C bond, the IR spectra gave a strong and narrow band at 3200 cm−1 for the H–C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C stretching. The presence of two singlets around 3.25 ppm, which are typical of terminal alkyne protons in 1H NMR, and the peaks of sp hybridized carbons observed around 75 ppm and 81 ppm in 13C NMR also confirmed the successful synthesis of the 3a–3m molecules (except for 3e and 3f for which we could not isolate pure products). Yields of the obtained compounds are given in Table 1.
C stretching. The presence of two singlets around 3.25 ppm, which are typical of terminal alkyne protons in 1H NMR, and the peaks of sp hybridized carbons observed around 75 ppm and 81 ppm in 13C NMR also confirmed the successful synthesis of the 3a–3m molecules (except for 3e and 3f for which we could not isolate pure products). Yields of the obtained compounds are given in Table 1.
| R | Yield (%) | HUH7 IC50 ± SEM (μM) | MV IC50 ± SEM (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a CPT: camptothecin; 5FU: 5-fluorouracil. | |||||
 | |||||
| Ph | ALC67 | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | ||
| p-OCH3–Ph– | (3a) | 89 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | |
| p-F–Ph– | (3b) | 37 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | |
| m-F–Ph– | (3c) | 58 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 2.0 | |
| o-F–Ph– | (3d) | 30 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | |
| p-CN–Ph– | (3g) | 24 | 2.6 ± 0.6 | 2.4 ± 2.3 | |
| –(CH2)4CH3 | (3h) | 55 | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 1.4 | |
| –(CH2)3CH3 | (3i) | 87 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | |
| –CH(CH2–CH3)–CH2CH2CH2CH3 | (3j) | 30 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | |
| –CH2–CH(CH3)–CH2–C(CH3)3 | (3k) | 55 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.6 | |
| –CH(CH3)–CH2–CH2CH3 | (3l) | 63 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | |
| –C(CH3)3 | (3m) | 52 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | |
| CPT | 0.1 | <1 | |||
| 5FU | 30.7 | 10.0 | |||
The antiproliferative activity of the synthesized alkyne compounds (3a–3m) was examined on two different hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HUH7 and Mahlavu cells) using the sulforhodamine B assay.16 The derivatives were evaluated as diastereomeric mixtures since we could not separate the isomers and also because thiazolidine compounds are commonly analyzed as diastereomeric mixtures in the literature.5,6,10–13 The obtained cytotoxicity was compared to the activity of ALC67, camptothecin and 5-fluorouracil, two marketed anticancer agents frequently used as positive controls in cytotoxicity assays.17–21
All obtained IC50 values were similar to ALC67's values (Table 1): the bioactivity of the terminal alkyne molecule remained when the phenyl moiety was replaced either by aliphatic or aromatic groups suggesting that this position is not essential for the molecule to be cytotoxic. Hence, a novel class of antiproliferative thiazolidines was developed.
The effect of substituting the phenyl moiety was analyzed through the 3a–3g compounds. The cytotoxic activity did not vary, regardless of the electron donor or acceptor property of the pending group: with the para-substituted molecules (3a, 3b and 3g), the best activity was observed for the para-fluorophenyl substituted derivative (smallest IC50 value) while the electron-donating methoxy and the electron-attracting cyano substitutions led to greater IC50 values (1.4 and 2.6 respectively). We also investigated the effect of the substitution position, preparing the ortho- (3d), meta- (3c) and para-fluorophenyl (3b) thiazolidines. The results revealed better activity for the para-fluorophenyl compound, indicating a possible impact of the substitution position on the biological activity due to the generated steric hindrance.
Regarding the thiazolidines derived from alkyl aldehydes, the determined IC50 values showed that biological activity is also maintained with both linear (3h, 3i) and branched chains (3j–3m), with the highest activity observed for the 3i molecule.
Conclusion
All these results demonstrated that the phenyl moiety present on the second position of the thiazolidine ring of the ALC67 molecule is not crucial for its biological activity. This observation allowed us to generate similarly cytotoxic novel molecules using a rapid and easy methodology. This investigation also suggested that the second position of the heterocycle can be used to tune the physicochemical properties of the cytotoxic molecule or to further introduce a fluorescent tag on this position to elucidate its molecular mechanism of action.22Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms R. Nelson for copyediting the final version of the manuscript.Notes and references
- D. Hanahan and R. A. Weinberg, Cell, 2000, 100, 57–70 CrossRef CAS
.
- D. Hanahan and R. A. Weinberg, Cell, 2011, 144, 646–674 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. F. R. Kerr, C. M. Winterford and B. V. Harmon, Cancer, 1994, 73, 2013–2026 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Storey, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2008, 7, 971–972 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- V. Gududuru, E. Hurh, J. T. Dalton and D. D. Miller, J. Med. Chem., 2005, 48, 2584–2588 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- V. Gududuru, E. Hurh, J. Sullivan, J. T. Dalton and D. D. Miller, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2005, 15, 4010–4013 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- V. Gududuru, E. Hurh, G. G. Durgam, S. S. Hong, V. M. Sardar, H. P. Xu, J. T. Dalton and D. D. Miller, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2004, 14, 4919–4923 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- V. Gududuru, E. Hurh, J. T. Dalton and D. D. Miller, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2004, 14, 5289–5293 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C. J. Andres, J. J. Bronson, S. V. D'Andrea, M. S. Deshpande, P. J. Falk, K. A. Grant-Young, W. E. Harte, H. T. Ho, P. F. Misco, J. G. Robertson, D. Stock, Y. X. Sun and A. W. Walsh, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2000, 10, 715–717 CrossRef CAS
.
- W. Li, Z. Wang, V. Gududuru, B. Zbytek, A. T. Slominski, J. T. Dalton and D. D. Miller, Anticancer Res., 2007, 27, 883–888 CAS
.
- W. Li, Y. Lu, Z. Wang, J. T. Dalton and D. D. Miller, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2007, 17, 4113–4117 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Lu, Z. Wang, C. M. Li, J. J. Chen, J. T. Dalton, W. Li and D. D. Miller, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2010, 18, 477–495 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- F. E. Onen-Bayram, I. Durmaz, D. Scherman, J. Herscovici and R. Cetin-Atalay, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2012, 20, 5094–5102 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- F. E. Onen, Y. Boum, C. Jacquement, M. V. Spanedda, N. Jaber, D. Scherman, H. Myllykallio and J. Herscovici, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2008, 18, 3628–3631 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Kallen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1971, 93, 6236–6248 CrossRef CAS
.
- V. Vichai and K. Kirtikara, Nat. Protoc., 2006, 1, 1112–1116 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Blois, A. Smith and L. Josephson, Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 2011, 68, 795–803 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X.-C. Huang, M. Wang, Y.-M. Pan, G.-Y. Yao, H.-S. Wang, X.-Y. Tian, J.-K. Qin and Y. Zhang, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2013, 69, 508–520 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X.-C. Huang, M. Wang, H.-S. Wang, Z.-F. Chen, Y. Zhang and Y.-M. Pan, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2014, 24, 1511–1518 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- R. Thierbach and P. Steinberg, Anal. Biochem., 2009, 387, 318–320 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Yuenyongsawad, K. Bunluepuech, C. Wattanapiromsakul and S. Tewtrakul, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2013, 150, 765–769 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Y. Yue, Y. Guo, J. A. Xu and S. J. Shao, New J. Chem., 2011, 35, 61–64 RSC
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c4md00306c |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 |
