Core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized with well-dispersed hydrophilic Fe3O4 seeds
Chao
Hui
a,
Chengmin
Shen
a,
Jifa
Tian
a,
Lihong
Bao
a,
Hao
Ding
a,
Chen
Li
a,
Yuan
Tian
a,
Xuezhao
Shi
ab and
Hong-Jun
Gao
*a
aBeijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190, People's Republic of China. E-mail: hjgao@aphy.iphy.ac.cn; Tel: +86 10 82648035
bDepartment of Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, 730000, People's Republic of China
First published on 19th November 2010
Abstract
Silica coated magnetite (Fe3O4@SiO2) core-shell nanoparticles (NPs) with controlled silica shell thicknesses were prepared by a modified Stöber method using 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs as seeds. The core-shell NPs were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-resolution TEM (HRTEM), selected area electron diffraction (SAED), and UV-Vis adsorption spectra (UV-Vis). The results imply that NPs consist of a crystalline magnetite core and an amorphous silica shell. The silica shell thickness can be controlled from 12.5 nm to 45 nm by varying the experimental parameters. The reaction time, the ratio of TEOS/Fe3O4, and the concentration of hydrophilic Fe3O4 seeds were found to be very influential in the control of silica shell thickness. These well-dispersed core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs show superparamagnetic properties at room temperature.
Introduction
The fabrication of transition metals and their oxide nanomaterials is of great importance in the development of modern nanotechnology due to their numerous applications.1 Among all the currently studied nanomaterials, magnetite (Fe3O4) is one of the most popular ones, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles have been found highly applicable in ferrofluids,2 high-density information storage,3 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),4 the role of catalyst or support of catalysts,5 tissue-specific releasing of therapeutic agents,6labeling and sorting of cells,7 as well as separation of biochemical products.8 In recent years, Fe3O4 NPs have raised much interest in the fields of biomedicine and biosensing.9 Such applications typically require Fe3O4 NPs to be water-soluble, chemically stable in vivo, highly dispersible in various pH liquid media and magnetically resonant efficient with regard to magnetic resonance. Although strategies for synthesizing Fe3O4 NPs have been fully developed, none of them, unfortunately, is capable of producing Fe3O4 NPs that meet all the requirements above right after synthesis. In particular, a high local concentration of metal cations resulting from the dissolution of surface Fe cations is toxic to organisms and the aggregation of Fe3O4 NPs resulting from incompatible surface chemistry in liquid media weakens the specific targeting. Therefore, it is necessary to add a coating to Fe3O4 NPs that is expected to offer an inert surface layer with compatible surface chemistry to help magnetic NPs survive in vivo and work well in specific targeting.10 Many kinds of materials have been discovered in recent years for use as the coating, including noble metals,11 metal oxides12 and inorganic silica.13 Among these coating materials, silica is very promising since the dense silica shell may prevent Fe3O4 cores from chemical contact with corrosive liquid media and, most importantly, the surface chemistry of a silica shell is compatible with various chemicals and molecules for bio-conjugations.14 By taking these two advantages of silica, it has been proved experimentally that the silica surface works well with various coupling agents to covalently attach to specific ligands and to deliver ligands to target organs viaantibody-antigen recognition.15Currently, the major approaches for coating silica onto Fe3O4 NPs include the microemulsion method16 and the alkaline hydrolysis of tetraethyl orthosilicate (known as the Stöber method).17 The microemulsion method employs micelles to confine and control the coating. It produces the core-shell NPs with a surfactant layer on the silica surface, which somewhat blocks the advantage of easy bio-conjugations of silica surface. In contrast, the alkaline hydrolysis of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) is promising for producing core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with no surfactant, but is still stable and easily dispersed. The core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with a pure silica surface are definitely ideal model NPs for the discovery of bio-applications.
In this paper, we report on a modified Stöber method to synthesize water-soluble core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with no surfactant. Well-dispersed 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs18 were used as core materials. By changing the hydrolysis conditions of TEOS in the presence of Fe3O4 NPs, the thickness of the silica shell was controlled from 12.5 to 45 nm. This control leads to a further manipulation of the composition, morphology and magnetic properties of the core-shell NPs.
Experimental
Materials
Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS, 98%), and citric acid, trisodium salt dehydrate (C6H5Na3O7·2H2O, 99%) were purchased from ACROS, and ferrous sulfate (FeSO4·4H2O, 99%), ammonia hydroxide (25 wt%) and ethanol (99.9%) were purchased from Beijing Chemistry Reagent Company. All reagents were used without further purification.Preparation of 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs
Hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs with a mean diameter of ∼20 nm were synthesized by a simple alkaline deposition method we have reported before.18 The Fe3O4 NPs were synthesized by injecting Fe2+ into an alkaline solution at 100 °C, in the presence of citrate and sodium nitrate. The obtained black precipitate of Fe3O4 NPs was washed with water several times and then dried at 50 °C. The as-prepared hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs can easily be dispersed in water and used as seeds in the next step.Synthesis of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs
The synthesis of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs was performed by modifying the Stöber method via the hydrolysis of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) in the presence of Fe3O4 NPs.17,19 In a typical synthesis of 60 nm core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs (with a silica shell thickness of 20 nm), 45 mg as-prepared 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs were dispersed in 16 mL of water by using an ultrasonic water bath, then mixing with 2 mL of aqueous ammonia solution (25 wt%) and 80 mL of ethanol. Next, 0.8 mL of TEOS was added dropwise into the Fe3O4 nanoparticle solution under violent stirring at room temperature. The stirring continued at room temperature for 24 h. The products were separated by an external magnet and washed with water several times. The final product was collected and dried at 50 °C. The thickness of the silica shell was controlled in the range of 12.5 nm to 45 nm (equivalent to NPs of 45 nm and 110 nm, respectively) by varying the hydrolysis conditions.Characterizations
The structure of hydrophilic NPs was characterized by using a Mac Science M18AHF X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (1.5418 Å) generated at 40 kV and 30 mA. In order to investigate the composition and morphology of the product, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of the NPs were obtained by a JEOL 200CX microscope operated at an accelerating voltage of 120 kV. The nanoparticle powder samples were dispersed in anhydrous ethanol by an ultrasonic water bath and then dropped onto a copper grid for TEM observation. UV-Vis absorption spectra were also measured by a Varian Cary 5000 UV-Vis-NIR spectrophotometer. Magnetic properties of powder samples were characterized with a Quantum Design PPMS 6000 by measuring the applied-field dependence of magnetization between −14 and 14 kOe at 300 K.Results and discussion
Fig. 1 shows the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of 20 nm Fe3O4 NPs and core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with different SiO2 shell thickness. In Fig. 1, A is the XRD pattern of as-prepared 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs, and B and C are the patterns of Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with silica shell thicknesses of 12.5 nm and 20 nm (equivalent to NP diameters of 45 nm and 60 nm), respectively. From Fig. 1, it is seen clearly that the core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs exhibit diffraction patterns similar to that of Fe3O4 NPs. The diffraction peaks at 30, 35.4, 43, 53.4, 56.9, and 62.5° refer to [220], [311], [400], [422], [511], and [440] planes of cubic inverse spinel Fe3O4, respectively. The results are in good agreement with the XRD patterns of Fe3O4 NPs reported previously.20 The average crystal size of the Fe3O4 cores, obtained by calculation of Sherrer's formula, is about 20 nm, which is consistent with the average size of the Fe3O4 NPs used. This indicates that the particles are single-crystalline and the crystallinity of Fe3O4 cores persists after SiO2 coating.21 | ||
| Fig. 1 XRD patterns for 2θ in the range of 20° to 70° of sample (A) 20 nm as-prepared hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs, sample (B) 45 nm Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell NPs (with a 12.5 nm silica shell), and sample (C) 60 nm Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell NPs (with a silica shell thickness of 20 nm). | ||
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to observe core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs. Fig. 2 shows typical TEM images of core-shell NPs with different silica shell thicknesses of 12.5 nm, 15 nm, 20 nm, and 45 nm (equivalent to NP diameters of 45 nm, 50 nm, 60 nm, and 110 nm). The TEM images demonstrate that the NPs have a core-shell structure with light contrast silica shells and dark contrast cores of Fe3O4, implying that the hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs were successfully coated by a silica shell. The average size of Fe3O4 cores is about 20 nm, consistent with the XRD results. The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs exhibits a typical cubic inverse spinel structure (Fig. 2e). The lattice spacing, measured based on the diffraction rings (Fig. 2e), is in accordance with the standard lattice spacing of Fe3O4 from the PDF database.9b, 21a The diffraction of crystalline SiO2 was not observed in the SAED pattern, which is probably because the silica shell is amorphous, as observed in XRD. In addition, Fig. 2f is a TEM image of 60 nm SiO2 hollow spheres, which were easily obtained by removing the Fe3O4 cores with acid treatment, for example by using 3 M of hydrochloric acid overnight.
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Typical TEM images of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with silica shell thicknesses of (a) 12.5, (b) 15, (c) 20, and (d) 45 nm. (e) SAED patterns of Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with a silica shell thickness of 20 nm. (f) TEM image of 60 nm SiO2 hollow spheres. | ||
In order to observe the detailed structure of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs, HRTEM was used. Fig. 3 shows HRTEM images of 60 nm silica coated Fe3O4 NPs. Fig. 3a and b were made by focusing on the silica shell and the magnetite core, respectively. The images clearly show the single-crystallinity of the Fe3O4 core and the amorphous nature of the silica shell. The interplanar distance measured from the adjacent lattice fringes in Fig. 3b is about 0.49 nm, corresponding to [111] planes of the Fe3O4 single crystal with cubic inverse spinel structure. The results are consistent with the inferences from the XRD patterns in Fig. 1 and the SAED patterns in Fig. 2.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 HRTEM images of 60 nm Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell NPs focusing on the silica shell (a), and the Fe3O4 core (b). The images clearly show the single crystallinity of the Fe3O4 core and the amorphous nature of the silica shell. | ||
The UV-Vis absorption spectra of different samples in water are illustrated in Fig. 4. No obvious peaks appear in the spectra of 20 nm Fe3O4 seeds and 200 nm SiO2 spheres, but a broad featureless peak can be seen at a wavelength of about 380 nm in the spectrum of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs. We also measured the UV-Vis spectrum of the SiO2 hollow spheres, which also showed no significant peaks. The broad peak indicated the core-shell structure of the NPs, and may come from the changes of band gap caused by the quantum size effect and surface effect of nanostructures,22 and the Fe–O–Si bonds of the core-shell NPs.23
 | ||
| Fig. 4 UV-Vis adsorption spectra of different samples: (a) 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs, (b) 200 nm SiO2 spheres, (c) 60 nm Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell NPs, and (d) 60 nm SiO2 hollow spheres. | ||
The magnetic properties of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with different silica shell thicknesses were measured using a physical property measurement system (PPMS) at room temperature. The hysteresis loops of 20 nm Fe3O4 NPs and Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with silica shell thicknesses of 12.5 nm, 15 nm, and 20 nm (equivalent to the NP diameters of 45 nm, 50 nm, and 60 nm, respectively) are shown in Fig. 5. Curve 5a shows the superparamagnetic property of the 20 nm NPs, and the Ms (saturation magnetization) is about 57.5 emu g−1. Compared with the hysteresis loop of the 20 nm NPs, the silica coated NPs with different shell thicknesses show similar magnetic properties. Curves 5b, c, and d show the hysteresis loops of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with silica shell thicknesses of 12.5, 15, and 20 nm, respectively. The core-shell NPs show superparamagnetic properties, as do the 20 nm Fe3O4 NPs. The Ms of Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with silica shell thicknesses of 12.5, 15, and 20 nm are 44, 37.5, and 26 emu g−1, respectively. The decrease of Ms results from the increase of the silica component.
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Room temperature hysteresis loops of 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs (a), and core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with silica shell thickness of 12.5 (b), 15 (c), and 20 nm (d). The core-shell NPs exhibit superparamagnetic properties. The Ms of the 20 nm Fe3O4 NPs is about 57.5 emu g−1 and the Ms of the core-shell NPs are about 44, 37.5, and 26 emu g−1, respectively. | ||
The core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs in dispersion responded quickly under an external magnetic field. Fig. 6 shows photographs of the core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticle dispersion and the response of these core-shell NPs under an external magnetic force. The 60 nm core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs were dispersed in ethanol with a concentration of 0.5 mg mL−1 by sonicating for several minutes. The photograph of the dispersion in Fig. 6a shows a light brown nanoparticle solution. As an external magnetic field was applied, the core-shell NPs were attracted by the magnet, leaving the ethanol solution clear and transparent (shown in Fig. 6b). Removing the external magnetic field and sonicating the solution redispersed the core-shell NPs into the solution, and the dispersion could be stable for more than 20 min. The attraction and redispersion processes can be readily altered by applying and removing an external magnetic field, showing great potential for bio-separation.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Photographs of the separation and redispersion processes of magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs: (a) without external magnetic field, and (b) with external magnetic field. | ||
For years, a means has been sought to prepare various kinds of silica materials by the Stöber method. The formation of silica was concluded as the hydrolysis and condensation of alkoxysilanes in a mixture of ethanol, water, and ammonia.24 The chemical reaction can be briefly summarized as follows:
| Si(OC2H5)4 + 4H2O → Si(OH)4 + 4C2H5OH | (1) |
| Si(OH)4 → SiO2 + 2H2O | (2) |
In order to coat silica onto Fe3O4 NPs rather than forming silica spheres, it is necessary to vary the experimental parameters to optimize the synthesis. The selectivity depends strongly on the Ostwald ripening process, and the key is to tune the competition between the nucleation (hydrolysis) and growth (condensation) of silica. The silica tends to coat onto the Fe3O4 NPs as the condensation rate is much higher than the hydrolysis rate. It was previously found that lower temperature, lower pH value, lower TEOS concentration, and less H2O are predominant in facilitating the condensation process.24b, 25 In this coating experiment we found that a better performance of coating can be achieved using the mixture of 16 mL H2O, 80 mL ethanol, and 2 mL 25% ammonia solution.
The silica shell thickness of core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs was controlled in the range of 12.5 nm to 45 nm by varying the experimental parameters. Under the constant dosage of H2O, ethanol, and ammonia, it was found that three experimental parameters influence silica shell thickness: (1) the reaction time; (2) the ratio of TEOS to Fe3O4 NPs; and (3) the concentration of Fe3O4 NPs. Fig. 7 shows the size-time variation curve of the formation process of 75 nm core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs. The relation between the particle size and reaction time is consistent with the results reported before.24,26 The curve indicates that the reaction was almost saturated after 12 h.
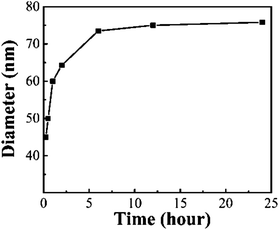 | ||
| Fig. 7 Size-time variation curve of the formation process of 75 nm Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell NPs, indicating that the reaction was almost saturated after 12 h. | ||
It was also found that the ratio of TEOS to Fe3O4 NPs is a key factor for controlling the thickness of silica shells. A higher TEOS/Fe3O4 molar ratio will lead to a thicker silica shell. For example, core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with a silica shell thickness of 15 nm were prepared by using a TEOS/Fe3O4 molar ratio of about 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. When the TEOS/Fe3O4 molar ratio was increased to 18
1. When the TEOS/Fe3O4 molar ratio was increased to 18![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and 27.5
1 and 27.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, the core-shell NPs with a silica shell thickness of 20 nm and 45 nm were obtained.
1, the core-shell NPs with a silica shell thickness of 20 nm and 45 nm were obtained.
We also investigated the influence of Fe3O4 nanoparticle concentration and found that the concentration of Fe3O4 NPs does not affect the thickness of silica shells. Thus, under a constant dosage of H2O, ethanol, and ammonia, the thickness of silica shells relies mainly on the ratio of TEOS to Fe3O4 NPs. The concentration of Fe3O4 NPs only affects the dispersity of the core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs, and the number of Fe3O4 cores in each nanoparticle. Aggregation of magnetite NPs during the coating process sometimes leads to the trapping of multiple nuclei in a single silica shell. The hydrophilic citrate-capped Fe3O4 NPs used here dispersed well in water,18,27 which can prevent the NPs from aggregation during the coating process. Mononuclear core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs were obtained at the critical Fe3O4 NP concentration of 0.30 mg mL−1 or 0.45 mg mL−1. As the concentration of Fe3O4 NPs is increased to 1.0 mg mL−1, core-shell NPs with multiple Fe3O4 cores are produced.
Conclusions
Core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with controlled silica shell thickness were prepared by a modified Stöber method using 20 nm hydrophilic Fe3O4 NPs. The Fe3O4 cores are single-crystalline and the silica shell is amorphous. The silica shell thickness could be controlled in the range of 12.5 nm to 45 nm by varying the ratio of TEOS/Fe3O4 or reaction time. The core-shell NPs show superparamagnetic properties at room temperature. These core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 NPs with controlled silica shell thicknesses are very promising for much needed bio-conjugation applications.Acknowledgements
The project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National “863” project (2007AA03Z305), and the Key Technologies Research and Development Program of China.Notes and references
- (a) S. H. Sun, C. B. Murray, D. Weller, L. Folks and A. Moser, Science, 2000, 287, 1989–1992 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. M. Shen, Y. K. Su, H. T. Yang, T. Z. Yang and H. J. Gao, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 373, 39–45 CrossRef CAS; (c) B. K. Johnson and R. K. Prud'homme, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 91, 118302 CrossRef; (d) H. T. Yang, C. M. Shen, Y. K. Su, T. Z. Yang, H. J. Gao and Y. G. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 82, 4729–4731 CrossRef CAS; (e) C. M. Shen, C. Hui, T. Z. Yang, C. W. Xiao, J. F. Tian, L. H. Bao, S. T. Chen, H. Ding and H. J. Gao, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 6939–6944 CrossRef CAS; (f) C. W. Xiao, H. Ding, C. M. Shen, T. Z. Yang, C. Hui and H. J. Gao, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 13466–13469 CrossRef CAS; (g) Z. C. Xu, C. M. Shen, Y. A. Tian, X. Z. Shi and H. J. Gao, Nanoscale, 2010, 2, 1027–1032 RSC.
- R. Rosensweig, Ferrohydrodynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1985 Search PubMed.
- M. Ozaki, in MRS Bulletin, 1989, p. 41 Search PubMed.
- (a) L. Babes, B. Denizot, G. Tanguy, J. J. Le Jeune and P. Jallet, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1999, 212, 474–482 CrossRef CAS; (b) T. Neuberger, B. Schopf, H. Hofmann, M. Hofmann and B. von Rechenberg, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2005, 293, 483–496 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) X. J. Wang, J. F. Tian, T. Z. Yang, L. H. Bao, C. Hui, F. Liu, C. M. Shen, C. Z. Gu, N. S. Xu and H. J. Gao, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 4480 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. F. Yin, C. Wang, H. G. Zhu, S. H. Overbury, S. H. Sun and S. Dai, Chem. Commun., 2008, 4357–4359 RSC; (c) J. F. Tian, J. M. Cai, C. Hui, C. D. Zhang, L. H. Bao, M. Gao, C. M. Shen and H. J. Gao, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 93, 122105 CrossRef; (d) J. Tian, C. Hui, L. Bao, C. Li, Y. A. Tian, H. Ding, C. M. Shen and H. J. Gao, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 94, 083101 CrossRef.
- T. Fukushima, K. Sekizawa, Y. Jin, M. Yamaya, H. Sasaki and T. Takishima, Am. J. Physiol., 1993, 265, L67–L72 CAS.
- Y. R. Chemla, H. L. Crossman, Y. Poon, R. McDermott, R. Stevens, M. D. Alper and J. Clarke, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2000, 97, 14268–14272 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Ugelstad, A. Berge, T. Ellingsen, R. Schmid, T. N. Nilsen, P. C. Mork, P. Stenstad, E. Hornes and O. Olsvik, Prog. Polym. Sci., 1992, 17, 87–161 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) S. H. Sun, Adv. Mater., 2006, 18, 393–403 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. H. Sun and H. Zeng, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 8204–8205 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Lu, Y. D. Yin, B. T. Mayers and Y. N. Xia, Nano Lett., 2002, 2, 183–186 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. L. Lyon, D. A. Fleming, M. B. Stone, P. Schiffer and M. E. Williams, Nano Lett., 2004, 4, 719–723 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. O. Obare, N. R. Jana and C. J. Murphy, Nano Lett., 2001, 1, 601–603 CrossRef CAS; (c) Z. C. Xu, Y. L. Hou and S. H. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 8698–8699 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) Y. J. Chen, P. Gao, R. X. Wang, C. L. Zhu, L. J. Wang, M. S. Cao and H. B. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 10061–10064 CrossRef CAS; (b) J. Q. Wan, H. Li and K. Z. Chen, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2009, 114, 30–32 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) Y. H. Deng, C. H. Deng, D. W. Qi, C. Liu, J. Liu, X. M. Zhang and D. Y. Zhao, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 1377–1382 CrossRef CAS; (b) J. P. Ge, Q. Zhang, T. R. Zhang and Y. D. Yin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 8924–8928 CrossRef CAS.
- A. L. Morel, S. I. Nikitenko, K. Gionnet, A. Wattiaux, J. Lai-Kee-Him, C. Labrugere, B. Chevalier, G. Deleris, C. Petibois, A. Brisson and M. Simonoff, ACS Nano, 2008, 2, 847–856 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. Ulman, Chem. Rev., 1996, 96, 1533–1554 CrossRef CAS; (b) F. Gritti and G. Guiochon, J. Chromatogr., A, 2006, 1132, 51–66 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. M. Sieburth and L. Fensterbank, J. Org. Chem., 1993, 58, 6314–6318 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Santra, R. Tapec, N. Theodoropoulou, J. Dobson, A. Hebard and W. H. Tan, Langmuir, 2001, 17, 2900–2906 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Stober, A. Fink and E. Bohn, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1968, 26, 62 CrossRef.
- C. Hui, C. M. Shen, T. Z. Yang, L. H. Bao, J. F. Tian, H. Ding, C. Li and H. J. Gao, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 11336–11339 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Y. Liu, X. L. Yang and Y. M. Wang, Langmuir, 2008, 24, 5485–5491 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) R. Maoz, E. Frydman, S. R. Cohen and J. Sagiv, Adv. Mater., 2000, 12, 424 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. H. Sun, H. Zeng, D. B. Robinson, S. Raoux, P. M. Rice, S. X. Wang and G. X. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 273–279 CrossRef CAS; (c) Z. C. Xu, C. M. Shen, Y. L. Hou, H. J. Gao and S. S. Sun, Chem. Mater., 2009, 21, 1778–1780 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) T. Z. Yang, C. M. Shen, Z. Li, H. R. Zhang, C. W. Xiao, S. T. Chen, Z. C. Xu, D. X. Shi, J. Q. Li and H. J. Gao, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 23233–23236 CrossRef CAS; (b) T. Z. Yang, C. M. Shen, H. T. Yang, C. W. Xiao, Z. C. Xu, S. T. Chen, D. X. Shi and H. J. Gao, Surf. Interface Anal., 2006, 38, 1063–1067 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) P. Ball and L. Garwin, Nature, 1992, 355, 761–766 CrossRef; (b) H. Takagi, H. Ogawa, Y. Yamazaki, A. Ishizaki and T. Nakagiri, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1990, 56, 2379–2380 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Ribera, I. Arends, S. de Vries, J. Perez-Ramirez and R. A. Sheldon, J. Catal., 2000, 195, 287–297 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) I. Artaki, M. Bradley, T. W. Zerda and J. Jonas, J. Phys. Chem., 1985, 89, 4399–4404 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. J. Brinker and G. W. Scherer, Sol–Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol–Gel Processing, Academic Press, San Diego, 1990 Search PubMed.
- (a) A. P. Katsoulidis, D. E. Petrakis, G. S. Armatas and P. J. Pomonis, J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17, 1518–1528 RSC; (b) B. Tan and S. E. Rankin, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 22353–22364 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) G. H. Bogush and C. F. Zukoski, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1991, 142, 1–18 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. L. Chen, P. Dong, G. H. Yang and J. J. Yang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 1996, 35, 4487–4493 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. Filankembo, S. Giorgio, I. Lisiecki and M. P. Pileni, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107, 7492–7500 CrossRef; (b) M. P. Pileni, Nat. Mater., 2003, 2, 145–150 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 |
