Synthesis and conformational analysis of D-2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluoro-4′-dihydro-4′-thionucleosides†
Feng Zhenga, Lin Fub, Renxiao Wangb and Feng-Ling Qing*a
aKey Laboratory of Organofluorine Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 354 Fenglin Lu, Shanghai 200032, China. E-mail: flq@mail.sioc.ac.cn; Tel: 02154925185
bState Key Laboratory of Bioorganic and Natural Products, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 354 Fenglin Lu, Shanghai, 200032, China
First published on 2nd November 2009
Abstract
An efficient synthesis of D-2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluoro-4′-dihydro-4′-thionucleosides is described. The conformations of D-2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluoro-4′-dihydro-4′-thiouridine were studied by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling in an attempt to explore the roles of the two gem-difluorine atoms in the puckering preferences of the thiosugar ring. No matter which conformation (south or north) the thiosugar adopts, there is always one fluorine in a pseudoaxial position, with the other in a pseudoequitorial position and thus the strong antiperiplanar (ap) effects from C–H and C–C σ-bonds to σ*C–F are equal to each other in these two conformers. Therefore, the other weak effects, such as dipole–dipole interactions and electrostatic attractions, become more important for determining the overall conformation of the sugar ring. Based on the results of NMR spectroscopy, high-level quantum computations and molecular dynamic simulations were performed to study the preferred pucker of the thiosugar ring in solution. Our results showed that the strong antiperiplanar preference of C–H and C–C σ-bonds to σ*C–F and σ*C–O seemed to be responsible for the favored S-conformation in solution, and the weak electrostatic attractions between δ+C2–Fβδ− and δ+H6–C6δ- may stabilize the preferred structure further, and keep the base moiety in a high anti-rotamer population in solution. In contrast, the packing forces (hydrogen bond OH⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C, dipole–dipole interaction C–F⋯C
C, dipole–dipole interaction C–F⋯C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) in the solid state compensated the energetic disadvantage of the relatively less stable N-conformation, and drove the thiouridine to crystallize in the N-conformation. These results, along with the earlier empirical rules regarding proton chemical shifts in carbohydrates and nucleosides, were used to propose a method based on proton chemical shifts for the analysis of the N⇌S equilibrium of the fluorinated sugar ring.
O) in the solid state compensated the energetic disadvantage of the relatively less stable N-conformation, and drove the thiouridine to crystallize in the N-conformation. These results, along with the earlier empirical rules regarding proton chemical shifts in carbohydrates and nucleosides, were used to propose a method based on proton chemical shifts for the analysis of the N⇌S equilibrium of the fluorinated sugar ring.
Introduction
The unique role of the substituent (hydrogen or hydroxyl) on the C-2′ atom in nucleoside acids as the distinguishing feature between DNA and RNA prompted the investigation of the biological properties of nucleosides containing substituents other than hydrogen or hydroxyl at this position. Accordingly, it was interesting to study the biological properties of nucleosides containing fluorine, which could mimic both hydrogen and hydroxyl to some extent, at the C2′ position. Furthermore, the fluorine atoms at the 2′-position increase the hydrolytic stability of the nucleoside due to destabilization of the transition state (positive charge at the anomeric center) during hydrolytic cleavage of the nucleosidic bond. So far, a number of 2′-fluorinated nucleosides1–3 have been synthesized and biologically evaluated, such as 2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine (Gemcitabine), which has been approved as a drug for solid tumor treatment.4,5 Recently, it has been reported that 4′-thionucleosides,6 such as 1 and 2, and truncated nucleosides without 4′-hydroxymethyl,7,8 such as 3 and 4, possess potent antiviral and antitumor activities. In view of the above findings, we designed and synthesized our target molecules 5a–c based on bioisosteric rationale (Fig. 1).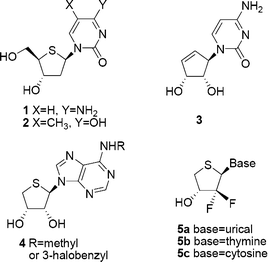 | ||
| Fig. 1 Rationale for the design of the target compounds 5a–c. | ||
The conformations of the gem-difluoromethylene-containing thiouridine 5a were studied using X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy and ab initio calculations. The conformation of the thiosugar ring was defined by the concept of pseudorotation9 (two pseudorotation parameters: the phase angle P and the maximum puckering amplitude υmax), and the conformation of the base was defined by the glycosyl rotamer angle χ.10 Altona and Sundralingham defined pseudorotational parameters and correlated them with highly populated solid-state nucleoside/nucleotide conformations.9,11 Altona et al.,12 Chattopadhyaya et al.,13 Marquez et al.,14 and others have refined and added additional parametrization to the fundamental Altona–Sundralingham approach11 for analysis of the predominant conformer populations of the nucleosides. For the sugar-fluorinated nucleosides, in 1998, a new complicated seven-parameter Karplus relationship based on JHF coupling constants was derived15 and later modified slightly by Mikhailopulo, et al.16 The 3JHF coupling constants have been widely used in the conformational analysis of fluorinated sugars and nucleosides, while chemical shifts of protons are almost ignored in the conformational or structure analysis. For the simple fluorinated nucleoside molecules, conversion of the conformation from N to S, and vice versa, would result in considerable changes in the chemical shifts of the protons, especially for those experiencing interactions with the fluorine atom in various ways, since the reoriented highly electronegative fluorine atom could profoundly alter chemical environments, as well as the stereoelectronic environments of the protons. This prompted us to propose a method dependent on the chemical shifts of the protons to analyze the N⇌S equilibrium of compound 5a. In addition, we wish to gain more insight into the weak but meaningful C–F⋯C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and C–F⋯H–C interactions,17 which may influence the overall conformation of the nucleoside.
O and C–F⋯H–C interactions,17 which may influence the overall conformation of the nucleoside.
Results and discussion
Synthesis
gem-Difluorinated synthon 6 was easily prepared according to our reported methodology.18 Compound 6 was converted to alcohol 7 by oxidation with O3 followed by reduction with NaBH4. Diol 8 was prepared in 86% overall yield by the following steps: (1) acidic hydrolysis of the isopropylidene group with TFA–THF–H2O and (2) oxidative scission of the resulting diol with sodium periodate and subsequent reduction of the resultant aldehyde with NaBH4. Mesylation of 8 followed by treatment with sodium sulfide in DMF at 90 °C for 30 min resulted in a ring closure to give thiofuranose 9 in 84% yield. Finally, oxidation of 9 with m-CPBA followed by condensation with silylated base using the Pummerer reaction afforded our desired protected nucleosides regioselectively. Subsequent removal of the protecting groups provided the target thionucleosides 5a–c (Scheme 1).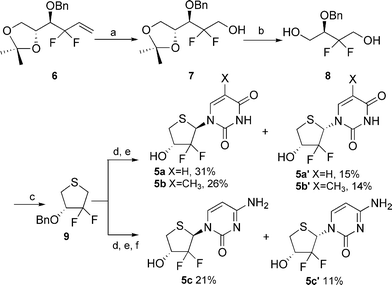 | ||
Scheme 1 Synthesis of compounds 5a–c. Reagents and conditions: (a) i. O3, CH2Cl2, −78 °C, ii. NaBH4; (b) i. TFA–H2O–THF (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), ii. NaIO4, acetone, iii. NaBH4; (c) i. MsCl, pyridine, ii. Na2S.·9H2O, DMF, 90 °C; (d) i. m-CPBA, CH2Cl2, −78 °C, ii. silylated base, TMSOTf, DCE; (e) BCl3, CH2Cl2, −70 °C; (f) NH3, CH3OH 1), ii. NaIO4, acetone, iii. NaBH4; (c) i. MsCl, pyridine, ii. Na2S.·9H2O, DMF, 90 °C; (d) i. m-CPBA, CH2Cl2, −78 °C, ii. silylated base, TMSOTf, DCE; (e) BCl3, CH2Cl2, −70 °C; (f) NH3, CH3OH | ||
Solid-state: X-ray crystallography
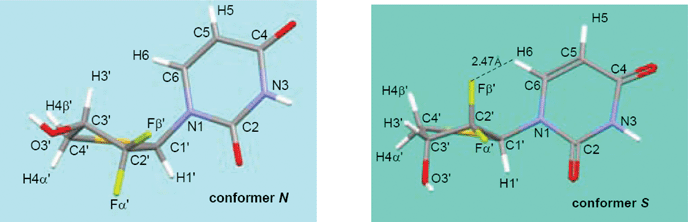
The solid state structure of 5a is shown in Fig. 2.‡ All of the structure shown represents the absolute configuration for the molecule. The structure relates to a monoclinic space group P21, and between the neighboring molecules within the same packing layer is a intermolecular hydrogen bond (C3′–OH⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C4, ∼2.002 Å). The CF2 and uracil base units form intermolecular weak C2′–Fβ′⋯C2
C4, ∼2.002 Å). The CF2 and uracil base units form intermolecular weak C2′–Fβ′⋯C2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O dipole–dipole interaction, leading to an extended layer packing. The F⋯C distance is 3.042 Å, which is about 0.13 Å shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii (3.17 Å). Similar dipole–dipole interactions have been observed between aromatic fluorine compounds and their target proteins.19,20 Herein, aliphatic C–F is also found to be involved in such interactions. In 5a (Fig. 2B), the thiosugar ring adopts a northern conformation with a pseudorotational phase angle of P = 9.4° and a maximum puckering amplitude of υmax = 45.3°, which is in contrast to its nonfluorinated parent 4′-thiothymidine21 that adopts a southern conformation in the solid state. Such a big difference may be due to the gauche relationships22,23 between OH at C3′ and both of the two gem fluorines at C2′ in 5a. The base is anti to the thiosugar ring, with a glycosyl rotamer angle of χ = −143.0°. The torsion angle of H1′–C1′–C2′–Fβ′ was the ideal 90°.
O dipole–dipole interaction, leading to an extended layer packing. The F⋯C distance is 3.042 Å, which is about 0.13 Å shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii (3.17 Å). Similar dipole–dipole interactions have been observed between aromatic fluorine compounds and their target proteins.19,20 Herein, aliphatic C–F is also found to be involved in such interactions. In 5a (Fig. 2B), the thiosugar ring adopts a northern conformation with a pseudorotational phase angle of P = 9.4° and a maximum puckering amplitude of υmax = 45.3°, which is in contrast to its nonfluorinated parent 4′-thiothymidine21 that adopts a southern conformation in the solid state. Such a big difference may be due to the gauche relationships22,23 between OH at C3′ and both of the two gem fluorines at C2′ in 5a. The base is anti to the thiosugar ring, with a glycosyl rotamer angle of χ = −143.0°. The torsion angle of H1′–C1′–C2′–Fβ′ was the ideal 90°.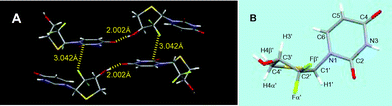 | ||
Fig. 2 Packing patterns of (A) 5a, which exhibits important intermolecular hydrogen bonding and F⋯C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O interaction; and the crystal structures of (B) 5a. O interaction; and the crystal structures of (B) 5a. | ||
Molecular modeling: quantum calculations and MD simulations
Using the experimentally determined crystal structure as a starting point, the structures of compound 5a were minimized by the CHARMm24 force field to convergence. Then, each conformation was further minimized at the B3LYP/6-311++G(2d,2p) level with the Gaussian 03 program.25 Frequency analysis was also performed to confirm that these minimized structures were true minima on the potential energy surface. In order to determine the most stable conformation in methanol, the solvation free energy of each conformation was calculated at the B3LYP/6-311++G(2d,2p) level in couple with the SCIPCM solvation model. The lowest energy conformation identified after such conformational sampling was observed to adopt a typical S-conformation with P = 177.7°, υmax = 47.6° and χ = −125.4°, whereas in the X-ray structure, the thiosugar ring pucker was basically in the pure N-conformation (P = 9.4°, Table 1).| υ0 | υ1 | υ2 | υ3 | υ4 | P | υmax | χ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-Ray | 44.75 | −38.55 | 19.26 | 5.26 | −29.67 | 9.43 | 45.36 | −142.97 |
| ab intio | −47.52 | 34.62 | −11.67 | −14.49 | 37.66 | 177.71 | 47.56 | −125.38 |
For nucleosides, the main factors which affect the chemical shift signals of the protons are the conformation of the sugar moiety and that of the nucleobase.26 Therefore, to further confirm the predominant conformation of compound 5a in solution, the 1H NMR spectra of the N- and S-conformers were predicted using the GIAO/DFT method at the B3LYP/6-311++G(2d,2p) level. The experimental data basically match with the chemical shifts predicted for the S ring pucker (Table 2).
| H6 | H5 | H1′ | H3′ | H4α′ | H4β′ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-Conformer | 7.78 | 5.80 | 6.82 | 4.50 | 3.08 | 3.13 |
| S-Conformer | 7.92 | 5.80 | 7.31 | 4.42 | 2.98 | 3.55 |
| Experimental data | 8.01 | 5.78 | 6.51 | 4.39 | 2.86 | 3.45 |
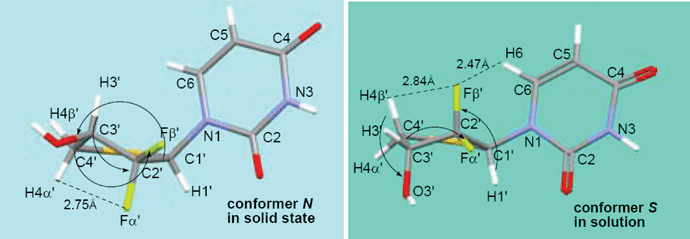
The hydrogen atoms H6, H4α′ and H4β′ on compound 5a should be paid special attention since they reveal some important structural information. In the low-energy S-conformation deduced by quantum calculations, the distance between Fβ′ and H6 is 2.47 Å, about 0.20 Å shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii (2.67 Å) of the two relevant atoms. The chemical shift of H6 on the S-conformer was shifted downfield from its counterpart on the N-conformer by 0.20 ppm. It indicates that a through-space electrostatic attraction between δ+C2′–δ−Fβ′ and δ+H6–δ−C6 exists in the S-conformer. A qualitative inspection of the experimental 13C NMR and 1H NMR also points to such interaction between δ+C2′–δ−Fβ′ and δ+H6–δ−C6: the C6 signal in 13C NMR spectra splits into a doublet (J = ∼4.2 Hz), which presumably results from through-space (ts) coupling27 with Fβ′, and a similar doublet (J = ∼1.8 Hz) for H6 signal is also observed.
The chemical shifts of H4β′ and H4α′ in chemically similar environments are largely dependent on the “neighbor anisotropy” effect arising from anisotropy in the magnetic susceptibility of nearby atoms or portions of a molecule, and the electrostatic interaction between hydrogen and strongly electronegative atoms or groups nearby.28 The pyrimidine base adopts a similar anti conformation with χ = −143.0° for solid conformer N, and χ = −125.4° for solution conformer S (Table 1), which indicates that the effect of the base moiety on the chemical-shift of H4β′ and H4α′ is alike in these two conformers. Then, we focused on the anisotropy effects of the sugar ring to rationalize the different chemical shifts of H4β′ and H4α′ between the N- and S-conformers using the earlier empirical rules, which were concluded from extensive studies on 1H NMR of carbohydrates and their derivates.26,29–34 In the S-conformer, H4β′ was strongly deshielded by the axial hydroxyl at C3′, which is at an opposing position to it,32 and was further deshielded by the spatially close axial fluorine atom because of the through space electrostatic interaction δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H4β′–C4′δ−. These deshielded effects on H4β′ in the S-conformer far outweigh the deshielded effects from the C2′(exo)–C3′(endo) bond and the relatively weak electrostatic interaction between δ+C3′–O3′δ− and δ+H4β′–C4′δ− on H4β′ in the N-conformer. Therefore, the chemical shift of H4β′ in the S-conformer is at a correspondingly lower field than that in N-conformer. A similar analysis for H4α′ was performed. The deshielding effect of the C2′(endo)–C3′(exo) bond, and electrostatic interaction between δ+C3′–O3′δ− and δ+H4α′–C4′δ− on H4α′ in the S-conformer is estimated to be weaker than that in the N-conformer, arising from the electrostatic interaction between δ+C3′–O3′δ− and δ+H4α′–C4′δ−, δ+C2′–Fα′δ− and δ+H4α′–C4′δ−, and thus H4α′ in the S-conformer is shifted upfield from its counterpart in the N-conformer. Thus, the differences in the chemical shifts (Δδ) between H4β′ and H4α′ of the S-conformer (Δδ = 0.59 ppm) are much larger than that in the N-conformer (Δδ = 0.05 ppm).35
Many of the conformational adjustments imparted by substitution of electronegative (or other) atoms into the carbohydrate ring have been rationalized based on arguments relating to the anomeric15 and gauche effects.22,36 Recent reports that studied similar difluorinated structures have invoked an alternative theory by Brunck and Weinhold,37 which suggests that, not only do vicinal electronegative atoms prefer a gauche arrangement, but the origins of this effect may be more due to an antiperiplanar (ap) σ to σ* stabilization when the donating bond is the least polar one and the acceptor orbital is at the most polarized bond. For compound 5a, in solution, three strong ap effects (σC1′–H1′ to σ*C2′–Fβ′, σC3′–C4′ to σ*C2′–Fα′ and σC4′–H4β′ to σ*C3′–O3′) appear to be responsible for keeping the ring pucker in the preferred S orientation. In addition, the small but meaningful through space electrostatic attractions (δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H6–C6δ−, ∼2.46 Å; and δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H4β′–C4δ−, ∼2.84 Å) contribute additional stabilization to the preferred structure (Table 3). The anomeric and ap effects arising from sulfur seem to be a weak contributor to the structure, since sulfur is much less electronegative in comparison to oxygen and fluorine. The 1H NMR chemical shifts of compound 5a were measured in CD3OD at six different temperatures from 213 to 313 K in 20 K increments (Table 4). The chemical shift changes in compound 5a in CD3OD showed liner dependence as a function of temperature,38 which is typical for systems where intermolecular interactions are not significant.39
| Conformer N | Conformer S | |
|---|---|---|
| a Potential antiperiplanar effects depicted by arrows.b Through space electrostatic attraction depicted by dashed line.c Intermolecular packing forces depicted by yellow hashed line in Fig. 2A. | ||
| ap σ to σ*a | σC3′–H3′ to σ*C2′–Fα′ | σC1′–H1′ to σ*C2′–Fβ′ |
| σC3′–C4′ to σ*C2′–Fβ′ | σC4′–H4β′ to σ*C3′–O3′ | |
| σC1′–C2′ to σ*C3′–O3′ | σC3′–C4′ to σ*C2′–Fα′ | |
| Electrostatic attractionb | δ+C2′–Fα′δ−⋯δ+H4α′–C4′δ− | δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H6–C6δ− |
| δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H4β′–C4′δ− | ||
| Packing forcesc | OH⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C C | |
C–F⋯C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O O | ||
| T/K | H6 | H5 | H1′ | H3′ | H4β′ | H4α′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Data were referenced to CD3OD at 3.31 ppm. | ||||||
| 213 | 8.153 | 5.800 | 6.511 | 4.413 | 3.472 | 2.850 |
| 233 | 8.116 | 5.794 | 6.509 | 4.404 | 3.465 | 2.851 |
| 253 | 8.081 | 5.789 | 6.508 | 4.402 | 3.458 | 2.853 |
| 273 | 8.048 | 5.785 | 6.506 | 4.396 | 3.451 | 2.854 |
| 293 | 8.014 | 5.778 | 6.503 | 4.391 | 3.442 | 2.858 |
| 313 | 7.977 | 5.771 | 6.496 | 4.386 | 3.436 | 2.860 |
For the N-conformer, the ap effects from C–H and C–C σ-bonds to σ*C–F are equal to that of the S-conformer (Table 3). However, the hyperconjugation coming from the more efficient C–H bond in the S-conformer rather than the C–CF2 bond in the N-conformer overlap with the σ*C–O orbital, together with the additional electrostatic attraction δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H6–C6δ− lead to an energy-favored S conformation in methanol solution. In the solid state, the packing forces (Table 3) are able to overcome the energetic disadvantage and make compound 5a crystallize as a type N-conformer.
The conformation of the uracil base is both anti in the N- and S-sugar puckers, which is confirmed by the crystal structure, quantum computation and the experimental 1H NMR, 13C NMR and NOESY spectra. The electrostatic attractions between Fβ′ and H6 in the S-conformer may be the main factor for keeping the base moiety in a high anti rotamer population in solution.10 Similar interactions have been observed in the C2′-up or C3′-up fluorinated nucleosides.40–42
Conformational equilibrium of the thiosugar ring in compound 5a
The temperature-dependent chemical shifts reflect time-averaged values of several rapidly interconverting conformers on the NMR time scale in solution. The observed chemical shifts depend not only on the geometries but also on the mole fraction of conformer N (XN) and conformer S (1 −XN) present in dynamic equilibrium, and can be writtenas δ = XNδN + (1 −XN)δS. Taking the error estimation into consideration,43 the chemical shift values of H4β′ (Table 4) are selected, which are influenced most by an interconversion from the N-conformer to the S-conformer, and XN = 0.22 is obtained at 300 K. This is only a rough estimate since there is an extremely small structural database available for compounds containing a gem-CF2 group in nucleoside templates. Our MD simulations (by using the AMBER 9 program44) of the dynamic equilibrium between the N- and S-conformers suggest that the N⇌S equilibrium in methanol is driven toward the S-conformer preferentially with a ratio of S/N = 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 at 300 K (Fig. 3), which is in good agreement with experimental observation.
1 at 300 K (Fig. 3), which is in good agreement with experimental observation.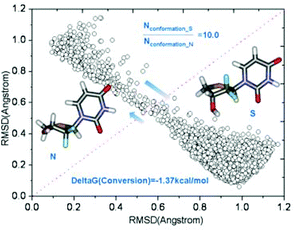 | ||
Fig. 3 MD simulations of the dynamic equilibrium between two conformers in methanol. The structure on the left is the N-conformer; while the one on the right is the S-conformer. The X axis is the RMSD values computed using the N-conformer as reference, while the Y axis is the RMSD values computed using the S-conformer as reference. Each circle represents a conformation sampled by MD simulations. Conformations close to the S-conformer are apparently more populated. The S/N ratio is computed to be 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. 1. | ||
To further evaluate the variation of the population ratios for compound 5a in a more quantitative way, van't Hoff plots were employed. A van't Hoff analysis using populations of N and S pseudorotamers based on the chemical shifts of H4β′ at six different temperatures (Table 4) enabled calculation of the enthalpy and entropy contributions that drive N⇌S equilibrium in methanol (Fig. 4). The van't Hoff analysis shows that the N⇌S equilibrium is driven by enthalpy towards S-type conformer for compound 5a, and the negative entropy (ΔS° = −0.56 J K−1) suggests a more organized S-conformer, which is consistent with the low-energy conformer from high-level ab initio calculations, in which an additional strong intramolecular δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H6–C6δ− attractive interaction was shown.
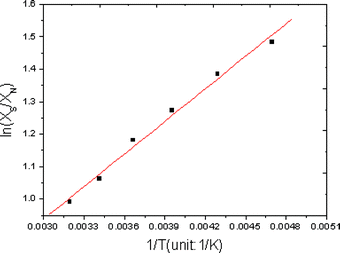 | ||
| Fig. 4 van't Hoff plots according to the relation: ln(XS/XN) = −ΔH°/RT + ΔS°/R. The values of ΔH° and ΔS° were calculated from slopes and intercepts of the van't Hoff plots. ΔH° = −2.78 kJ mol−1 and ΔS° = −0.56 J K−1 were found. | ||
Finally, the NMR data of compounds 5b and 5c were compared to that of compound 5a. The signals of the hydrogen atoms of the sugar ring in the upfield area are almost the same to that of compound 5a (Fig. 5), including chemical shifts and coupling matters, despite the different bases they had, which indicated that the predominant conformation which compound 5b and 5c adopt in solution, was type S. The doublet of C6 signals and doublet of doublets of H6 signals were also observed in the spectra of compound 5b and 5c, just like that of compound 5a, which suggested that the δ+C2′–Fβ′δ−⋯δ+H6–C6δ− interaction may also exist in compound 5b and 5c in methanol solution.
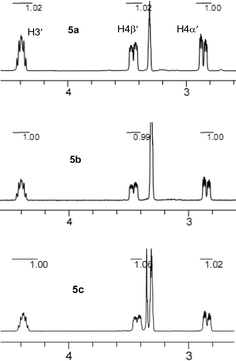 | ||
| Fig. 5 Partial 1H NMR spectra of compounds 5a, 5b and 5c in CD3OD at 300 K as referenced to CD3OD at 3.31 ppm. | ||
Conclusions
We have designed and efficiently synthesized the new gem-CF2-containing thionucleosides. The conformational analysis of compound 5a using X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy and ab initio calculations shows that compound 5a exists in the solid state as a type-N thiosugar pucker with anti conformation of the base, whereas from the NMR data and the high level calculations, it follows that the predominant conformer in methanol solution is type-S with anti conformation of the base. The strong ap effects from C–H and C–C σ-bonds to σ*C–F and σ*C–O are responsible for the favored S conformation in solution. Beside ap effects, the weak electrostatic attraction betweenδ+C2′–Fβ′δ− and δ+H6–C6δ− may also contribute additional stabilization to the preferred structure and hold the base in a high anti rotamer population in solution. However, in the solid state, the packing forces (hydrogen bond C3′–OH⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C4 and dipole–dipole interaction C2′–Fβ′⋯C2
C4 and dipole–dipole interaction C2′–Fβ′⋯C2![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) overcome the energetic disadvantage of the relatively less stable N-conformer, and drive compound 5a to crystallize in type-N-conformer. The relatively larger differences in the chemical shifts (Δδ) between H4β′ and H4α′ of the S-conformer (Δδ = 0.59 ppm) than that of the N-conformer (Δδ = 0.05 ppm) could be roughly and readily rationalized using the earliest empirical rules, which were concluded from extensive studies on 1H NMR of carbohydrates and their derivates. The conformational equilibrium between conformation N and S in methanol has been studied by MD simulations as well as chemical shift-based analyses, both of which reveal the similar preference of the N⇌S interconversion towards the S-conformer. Taking all the above into consideration, the conformational analysis for sugar pucker of the fluorinated nucleoside based on chemical-shifts sounds feasible since the chemical shifts of the protons, especially for those involved in ap effects and interaction with strong electronegative atoms (F, O), could be obviously shifted by an conversion of the conformation from N to S in fluorinated nucleosides. Moreover, the signals for the protons in NMR spectra are well dispersed due to the profound effects of the highly electronegative fluorine atom on the chemical properties as well as on the stereoelectronic properties of the modified nucleosides and could be easily assigned.
O) overcome the energetic disadvantage of the relatively less stable N-conformer, and drive compound 5a to crystallize in type-N-conformer. The relatively larger differences in the chemical shifts (Δδ) between H4β′ and H4α′ of the S-conformer (Δδ = 0.59 ppm) than that of the N-conformer (Δδ = 0.05 ppm) could be roughly and readily rationalized using the earliest empirical rules, which were concluded from extensive studies on 1H NMR of carbohydrates and their derivates. The conformational equilibrium between conformation N and S in methanol has been studied by MD simulations as well as chemical shift-based analyses, both of which reveal the similar preference of the N⇌S interconversion towards the S-conformer. Taking all the above into consideration, the conformational analysis for sugar pucker of the fluorinated nucleoside based on chemical-shifts sounds feasible since the chemical shifts of the protons, especially for those involved in ap effects and interaction with strong electronegative atoms (F, O), could be obviously shifted by an conversion of the conformation from N to S in fluorinated nucleosides. Moreover, the signals for the protons in NMR spectra are well dispersed due to the profound effects of the highly electronegative fluorine atom on the chemical properties as well as on the stereoelectronic properties of the modified nucleosides and could be easily assigned.Experimental section
(R)-3-(benzyloxy)-3-((R)-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl)-2,2-difluoropropan-1-ol (7)
A solution of compound 6 (5.12 g, 17.2 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (80 mL) was ozonized at −78 °C for 1 h. Then, a suspension of NaBH4 (1.27 g, 33.4 mmol) in C2H5OH (15 mL) was added to the reaction mixture. The reaction mixture was warmed to ambient temperature and was stirred for 30 min. Then the reaction was quenched with water (50 mL), and the organic layer was separated. The resultant aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc (25 mL × 3). The combined organic layers were washed with brine (50 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate = 7
ethyl acetate = 7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give 4.52 g (87% yield) of compound 7 as a clear oil: [α]26D = 13.7 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1 (c 1.81, CHCl3); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ 7.37–7.31 (m, 5H), 4.81 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 4.77 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H); 4.42 (m, 1H), 4.11 (m, 1H), 4.09–4.05 (m, 2H); 3.77 (m, 2H), 3.05 (br, 1H), 1.43 (s, 3H), 1.36 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100.7 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.3, 128.4, 128.1, 128.0, 121.6 (t, J = 247.6 Hz), 108.8, 76.5 (dd, J = 27.1, 23.4 Hz), 75.7, 74.4, 65.1(d, J = 4.4 Hz), 61.8 (dd, J = 32.0, 28.8 Hz), 26.2; 25.0 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3) δ−114.8 (dm, J = 258.6, 1F), −116.7 (ddd, J = 262.8, 29.3 Hz, 13.0, 1F); IR (KBr)max 3443, 2989, 1456, 1374,1136, 1029, 699 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 303.2 (M+ + H); Anal. Calcd for C15H20O4F2: C, 59.59; H, 6.67. Found: C, 59.64; H, 6.75.
1) to give 4.52 g (87% yield) of compound 7 as a clear oil: [α]26D = 13.7 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1 (c 1.81, CHCl3); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3), δ 7.37–7.31 (m, 5H), 4.81 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H), 4.77 (d, J = 11.2 Hz, 1H); 4.42 (m, 1H), 4.11 (m, 1H), 4.09–4.05 (m, 2H); 3.77 (m, 2H), 3.05 (br, 1H), 1.43 (s, 3H), 1.36 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100.7 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.3, 128.4, 128.1, 128.0, 121.6 (t, J = 247.6 Hz), 108.8, 76.5 (dd, J = 27.1, 23.4 Hz), 75.7, 74.4, 65.1(d, J = 4.4 Hz), 61.8 (dd, J = 32.0, 28.8 Hz), 26.2; 25.0 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3) δ−114.8 (dm, J = 258.6, 1F), −116.7 (ddd, J = 262.8, 29.3 Hz, 13.0, 1F); IR (KBr)max 3443, 2989, 1456, 1374,1136, 1029, 699 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 303.2 (M+ + H); Anal. Calcd for C15H20O4F2: C, 59.59; H, 6.67. Found: C, 59.64; H, 6.75.(R)-3-(benzyloxy)-2,2-difluorobutane-1,4-diol (8)
Compound 7 (4.48 g, 14.8 mmol) was dissolved in CF3COOH/H2O–THF (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 9 mL). After the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 h, the mixture was diluted with EtOAc (10 mL) and the reaction was quenched with solid NaHCO3. The resulting mixture was extracted with EtOAc (10 mL × 3). The combined organic layer was washed with brine (20 mL). After removal of the solvent in vacuo, the residue was dissolved in acetone (10 mL), followed by treatment with a solution of NaIO4 (3.49 g, 16.3 mmol) in water (10 mL) at 0 °C with stirring. After stirring for 1.5 h, the reaction was quenched with ethylene glycol (0.6 mL). The mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (10 mL × 3) and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The crude product was dissolved in CH3OH (8 mL) and then NaBH4 (680 mg, 17.9 mmol) was added at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was then warmed to room temperature and stirred for 30 min. Then the reaction was quenched with water (10 mL). The resultant mixture was extracted with Et2O (15 mL × 3). The combined organic layers were washed with brine (15 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether
1, 9 mL). After the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 h, the mixture was diluted with EtOAc (10 mL) and the reaction was quenched with solid NaHCO3. The resulting mixture was extracted with EtOAc (10 mL × 3). The combined organic layer was washed with brine (20 mL). After removal of the solvent in vacuo, the residue was dissolved in acetone (10 mL), followed by treatment with a solution of NaIO4 (3.49 g, 16.3 mmol) in water (10 mL) at 0 °C with stirring. After stirring for 1.5 h, the reaction was quenched with ethylene glycol (0.6 mL). The mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (10 mL × 3) and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The crude product was dissolved in CH3OH (8 mL) and then NaBH4 (680 mg, 17.9 mmol) was added at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was then warmed to room temperature and stirred for 30 min. Then the reaction was quenched with water (10 mL). The resultant mixture was extracted with Et2O (15 mL × 3). The combined organic layers were washed with brine (15 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate = 2
ethyl acetate = 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give 2.96 g (86% yield for three steps) of compound 8 as a clear oil: [α]25D = 17.4 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1 (c 1.05, CHCl3); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.41–7.38 (m, 5H), 4.79 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 4.67 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 3.93 (m, 1H), 3.84–3.72 (m, 4H), 2.90 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (100.7 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.1, 128.5, 128.1, 128.0, 121.4 (dd, J = 249.4, 247.1 Hz), 78.4 (dd, J = 28.3, 25.7 Hz), 73.7, 60.8 (dd, J = 32.6, 28.5 Hz), 59.6 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.7 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3) δ−111.1 (ddd, J = 267.9, 21.7, 12.1 Hz, 1F), −115.7 (dm, J = 267.5 Hz, 1F); IR (KBr)max 3383, 2945, 1456, 1101, 914, 742 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 250.2 (M+ + H2O), 255.2 (M+ + Na); Anal. Calcd for C11H14O3F2: C, 56.89; H, 6.08. Found: C, 56.70; H, 6.15. The chiral HPLC analytical data: Chiralpak AD column, detected at λ = 214 nm, eluent: n-hexane
1) to give 2.96 g (86% yield for three steps) of compound 8 as a clear oil: [α]25D = 17.4 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1 (c 1.05, CHCl3); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.41–7.38 (m, 5H), 4.79 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 4.67 (d, J = 11.4 Hz, 1H), 3.93 (m, 1H), 3.84–3.72 (m, 4H), 2.90 (s, 2H); 13C NMR (100.7 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.1, 128.5, 128.1, 128.0, 121.4 (dd, J = 249.4, 247.1 Hz), 78.4 (dd, J = 28.3, 25.7 Hz), 73.7, 60.8 (dd, J = 32.6, 28.5 Hz), 59.6 (dd, J = 6.2, 2.7 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3) δ−111.1 (ddd, J = 267.9, 21.7, 12.1 Hz, 1F), −115.7 (dm, J = 267.5 Hz, 1F); IR (KBr)max 3383, 2945, 1456, 1101, 914, 742 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 250.2 (M+ + H2O), 255.2 (M+ + Na); Anal. Calcd for C11H14O3F2: C, 56.89; H, 6.08. Found: C, 56.70; H, 6.15. The chiral HPLC analytical data: Chiralpak AD column, detected at λ = 214 nm, eluent: n-hexane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) i-PrOH (80
i-PrOH (80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20), 0.7 mL min−1, tR (minor) = 7.58 min, tR (major) = 6.94 min, 88% ee.
20), 0.7 mL min−1, tR (minor) = 7.58 min, tR (major) = 6.94 min, 88% ee.(S)-4-(benzyloxy)-3,3-difluorotetrahydrothiophene (9)
To compound 8 (2.77 g, 11.9 mmol) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (40 mL) and pyridine (8 mL) was added MsCl (3.70 mL, 47.6 mmol) slowly at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was then warmed to room temperature and stirred overnight. The reaction was quenched with water (30 mL) and the organic layer was separated. The resultant aqueous layer was extracted with Et2O (15 mL × 3). The combined organic layers were washed with 1 N HCl (20 mL × 3), saturated NaHCO3 solution (30 mL), water (30 mL) and brine (30 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in DMF (60 mL) and Na2S·9H2O (4.19 g, 17.4 mmol) was added. Then the reaction mixture was heated to 90 °C. After stirring for 30 min, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and water (70 mL) was added. The resulting mixture was extracted with diethyl ether (30 mL × 3). The combined organic layers were washed with water (50 mL) and brine (50 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate = 40
ethyl acetate = 40![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give 2.31 g (84% yield for two steps) of compound 9 as a light yellow oil: [α]28D = −16.3 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1 (c 1.95, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.28 (m, 5H), 4.77 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.66 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.04 (m, 1H), 3.26 (m, 1H), 3.11 (m, 1H), 2.98 (m, 1H), 2.87 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (100.7 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.1, 128.5, 128.1, 128.0 (dd, J = 260.5, 250.8 Hz), 127.8, 79.0 (dd, J = 31.1, 21.4 Hz), 72.6, 32.5 (t, J = 26.7 Hz), 30.5 (t, J = 3.2 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3) δ−104.4 (dm, J = 231.2 Hz, 1F), −115.0 (dm, J = 232.1 Hz, 1F); IR (KBr)max 3033, 2952, 1455, 1261, 1120, 697 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 231.2 (M+ + H), 248.2 (M++ H2O); HRMS Calcd for C11H12OF2S+ (M+): 230.0577, Found: 230.0580.
1) to give 2.31 g (84% yield for two steps) of compound 9 as a light yellow oil: [α]28D = −16.3 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1 (c 1.95, CHCl3); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.38–7.28 (m, 5H), 4.77 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.66 (d, J = 12.0 Hz, 1H), 4.04 (m, 1H), 3.26 (m, 1H), 3.11 (m, 1H), 2.98 (m, 1H), 2.87 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (100.7 MHz, CDCl3) δ 137.1, 128.5, 128.1, 128.0 (dd, J = 260.5, 250.8 Hz), 127.8, 79.0 (dd, J = 31.1, 21.4 Hz), 72.6, 32.5 (t, J = 26.7 Hz), 30.5 (t, J = 3.2 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3) δ−104.4 (dm, J = 231.2 Hz, 1F), −115.0 (dm, J = 232.1 Hz, 1F); IR (KBr)max 3033, 2952, 1455, 1261, 1120, 697 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 231.2 (M+ + H), 248.2 (M++ H2O); HRMS Calcd for C11H12OF2S+ (M+): 230.0577, Found: 230.0580.1-((2R,4S)-3,3-difluoro-4-hydroxytetrahydrothiophen–2-yl) uracil (5a)
A solution of m-CPBA (80%, 116 mg, 0.54 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of compound 9 (124 mg, 0.54 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL) at −70 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred at −40 °C for 40 min. Then, the mixture was quenched with saturated NaHCO3 solution (10 mL) and the organic layer was separated. The resultant aqueous layer was extracted with CH2Cl2 (10 mL × 3). The combined organic layers were washed with 10% aqueous Na2SO3 (10 mL) and brine (15 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo to give the sulfoxide, which was used directly in next step without purification. To a solution of silylated uracil, prepared from refluxing uracil (182 mg, 1.62 mmol) and ammonium sulfate (catalytic amount) in HMDS (4 mL), in anhydrous DCE (2 mL) was added a solution of the sulfoxide in anhydrous DCE (4 mL) followed by addition of TMSOTf (195 μL, 1.08 mmol) at 0 °C, and the mixture was stirred at the same temperature for 30 min. The mixture was quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3 solution (5 mL), filtered and poured into CH2Cl2 (10 mL). The organic layers were washed with brine (15 mL), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (petroleum ether![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ethyl acetate = 3
ethyl acetate = 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give 69 mg of the anti isomer of protected uridine and 36 mg of the syn isomer of protected uridine. To a solution of the anti isomer (69 mg, 0.20 mmol) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (10 ml) was added BCl3 (1M in CH2Cl2, 4.0 ml, 4.0 mmol) at −70 °C. After the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 h at −70 °C, the mixture was quenched with MeOH (5 ml), and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (CH2Cl2
1) to give 69 mg of the anti isomer of protected uridine and 36 mg of the syn isomer of protected uridine. To a solution of the anti isomer (69 mg, 0.20 mmol) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (10 ml) was added BCl3 (1M in CH2Cl2, 4.0 ml, 4.0 mmol) at −70 °C. After the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 h at −70 °C, the mixture was quenched with MeOH (5 ml), and the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (CH2Cl2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) MeOH = 20
MeOH = 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to give compound 5a (43 mg, 32% yield for three steps) as a white solid: [α]26D = −51.2 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1(c 2.15 MeOH); 1H NMR (300 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ 8.01 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.50 (dd, J = 12.3, 9.6 Hz, 1H), 5.78 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (m, 1H), 3.45 (m, 1H), 2.86 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ 165.6, 152.6, 143.8 (d, J = 4.2 Hz), 126.4 (dd, J = 263.1, 256.2 Hz), 103.1, 72.9 (dd, J = 30.4, 22.3 Hz), 59.7 (dd, J = 31.1, 18.9 Hz), 32.8 (t, J = 2.5 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ−110.3 (ddd, J = 236.9, 9.0, 3.9 Hz, 1F), −112.9 (ddd, J = 236.3, 20.6, 11.2 Hz, 1F); IR (KBr) max 3221, 3060, 1693, 1455, 1382, 1078 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 251.0 (M+ + H), HRMS Calcd for C8H9N2O3F2S (M+ + H): 251.0297. Found: 251.0296.
1) to give compound 5a (43 mg, 32% yield for three steps) as a white solid: [α]26D = −51.2 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1(c 2.15 MeOH); 1H NMR (300 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ 8.01 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 6.50 (dd, J = 12.3, 9.6 Hz, 1H), 5.78 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 4.39 (m, 1H), 3.45 (m, 1H), 2.86 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ 165.6, 152.6, 143.8 (d, J = 4.2 Hz), 126.4 (dd, J = 263.1, 256.2 Hz), 103.1, 72.9 (dd, J = 30.4, 22.3 Hz), 59.7 (dd, J = 31.1, 18.9 Hz), 32.8 (t, J = 2.5 Hz); 19F NMR (282 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ−110.3 (ddd, J = 236.9, 9.0, 3.9 Hz, 1F), −112.9 (ddd, J = 236.3, 20.6, 11.2 Hz, 1F); IR (KBr) max 3221, 3060, 1693, 1455, 1382, 1078 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 251.0 (M+ + H), HRMS Calcd for C8H9N2O3F2S (M+ + H): 251.0297. Found: 251.0296.The syn isomer of protected uridine was also deprotected using the similar procedure as described for the anti isomer to give 5a′ (21mg, 15% yield for three steps) as a white solid: [α]26D = 15.2 deg cm3 g−1 cm−1 (c 1.25 MeOH); 1H NMR (300 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ 8.21 (dd, J = 8.1, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 6.35 (dd, J = 14.1, 4.2 Hz, 1H), 5.73 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 4.42 (m, 1H), 3.18 (m, 1H), 3.10 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ 165.8, 152.8, 144.8, 126.6 (dd, J = 266.7, 255.3 Hz), 102.2, 73.1 (dd, J = 33.7, 22.1 Hz), 61.4 (dd, J = 38.9, 20.8 Hz), 33.6; 19F NMR (282 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ−108.7 (dd, J = 246.5, 10.1 Hz, 1F), −124.0 (d, J = 244.1 Hz, 1F); IR (KBr) max 3220, 3062, 1693, 1456, 1384, 1086 cm−1; MS (ESI) m/z 251.0 (M+ + H), HRMS Calcd for C8H9N2O3F2S (M+ + H): 251.0296. Found: 251.0296.
Acknowledgements
The National Natural Science Foundation of China and Shanghai Municipal Scientific Committee are greatly acknowledged for funding this work.Notes and references
- K. W. Pankiewicz, Carbohydr. Res., 2000, 327, 87–105 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-D. Meng and F.-L. Qing, Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 2006, 6, 1499–1528 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Liu, A. Sharon and C. K. Chu, J. Fluorine Chem., 2008, 129, 743–766 CrossRef CAS.
- L. W. Hertel, G. B. Boder, J. S. Kroin, S. M. Rinzel, G. A. Poore, G. C. Todd and G. B. Grindey, Cancer. Res., 1990, 50, 4417–4422 CAS.
- L. W. Hertel, J. S. Kroin, J. W. Misner and J. M. Tustin, J. Org. Chem., 1988, 53, 2406–2409 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yokoyama, Synthesis, 2000, 1637–1655 CrossRef CAS.
- L. S. Jeong, S. Pal, S. A. Choe, W. J. Choi, K. A. Jacobson, Z.-G. Gao, A. M. Klutz, X. Hou, H. O. Kim, H. W. Lee, S. K. Lee, D. K. Tosh and H. R. Moon, J. Med. Chem., 2008, 51, 6609–6613 CrossRef CAS.
- S. L. Mosley, B. A. Bakke, J. M. Sadler, N. K. Sunkara, K. M. Dorgan, Z. S. Zhou and K. L. Seley-Radtke, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2006, 14, 7967–7971 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Altona and M. Sundaralingam, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1972, 94, 8205–8212 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. Barchi, R. G. Karki, M. C. Nicklaus, M. A. Siddiqui, C. George, I. A. Mikhailopulo and V. E. Marquez, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 9048–9057 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Altona and M. Sundaralingam, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1973, 95, 2333–2344 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. G. Haasnoot, F. A. A. M. de Leeuw and C. Altona, Tetrahedron, 1980, 36, 2783–2792 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Thibaudeau, A. Kumar, S. Bekiroglu, A. Matsuda, V. E. Marquez and J. Chattopadhyaya, J. Org. Chem., 1998, 63, 5447–5462 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Sun, J. H. Voigt, I. Filippov, V. E. Marquez and M. C. Nicklaus, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 2004, 44, 1752–1762 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Thibaudeau, J. Plavec and J. Chattopadhyaya, J. Org. Chem., 1998, 63, 4967–4984 CrossRef CAS.
- I. A. Mikhailopulo, T. I. Pricota, G. G. Sivets and C. Altona, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 5897–5908 CrossRef CAS.
- D. O'Hagan, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008, 37, 308–319 RSC.
- X. Zhang, H. Xia, X. Dong, J. Jin, W.-D. Meng and F.-L. Qing, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 9026–9033 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Olsen, P. Seiler, B. Wagner, H. Fischer, T. Tschopp, U. Obst-Sander, D. W. Banner, M. Kansy, K. Muller and F. Diederich, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2004, 2, 1339–1352 RSC.
- J. A. Olsen, D. W. Banner, P. Seiler, B. Wagner, T. Tschopp, U. Obst-Sander, M. Kansy, K. Muller and F. Diederich, ChemBioChem, 2004, 5, 666–675 CrossRef CAS.
- L. H. Koole, J. Plavec, H. Liu, B. R. Vincent, M. R. Dyson, P. L. Coe, R. T. Walker, G. W. Hardy, S. G. Rahim and J. Chattopadhyaya, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 9936–9943 CrossRef CAS.
- R. J. Abraham, E. J. Chambers and W. A. Thomas, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1994, 949–955 RSC.
- M. Tavasli, D. O'Hagan, C. Pearson and M. C. Petty, Chem. Commun., 2002, 1226–1227 RSC.
- F. A. Momany and R. Rone, J. Comput. Chem., 1992, 13, 888–900 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, V. G. Zakrzewski, J. A. Montgomery, R. E. Stratmann, J. C. Burant, S. Dapprich, J. M. Millam, D. A. C., K. N. Kudin, M. C. Strain, O. farkas, J. Tomasi, V. Barone, M. Cossi, R. Cammi, B. Mennucci, C. Pomelli, C. Adamo, S. Clifford, J. Ochterski, G. A. Petersson, P. Y. Ayala, Q. Cui, K. Morokuma, D. K. Malick, A. D. Rabuck, K. Raghavachari, J. B. Foresman, J. Cioslowski, R. J. V, B. B. Stefanov, G. Liu, A. Liashenko, P. Piskora, I. Komaromi, R. Gomperts, R. L. Martin, D. J. Fox, T. Keith, M. A. AlLaham, C. Y. Peng, A. Nanayakkara, C. Gonzalez, M. Challacombe, M. W. Gill, B. Johnson, W. Chen, M. W. Wong, J. L. Andres, C. Gonzalez, M. H. Gordon, E. S. Replogle and J. A. Pople, Gaussian 03, Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh PA, 2003.
- B. Rayner, C. Tapiero and J.-L. Imbach, Carbohydr. Res., 1976, 47, 195–202 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Nowak and M. J. Robins, J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 8876–8883 CrossRef CAS.
- E. D. Becker, High resolution NMR, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, 2000 Search PubMed.
- L. D. Hall, Tetrahedron Lett., 1964, 5, 1457–1460 CrossRef.
- R. U. Lemieux, R. K. Kullnig, H. J. Bernstein and W. G. Schneider, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80, 6098–6105 CrossRef CAS.
- R. U. Lemieux and J. D. Stevens, Can. J. Chem., 1966, 44, 249–262 CrossRef CAS.
- R. U. L. Lemieux and J. W., Can. J. Chem., 1964, 42, 893–904 CAS.
- N. J. Oppenheimer and N. O. Kaplan, Biochemistry, 1976, 15, 3981–3989 CrossRef CAS.
- P. N. Sanderson, B. C. Sweatman, R. D. Farrant and J. C. Lindon, Carbohydr. Res., 1996, 284, 51–60 CrossRef CAS.
- Based on the earliest empirical rules, it is of interest to note that the differences of chemical shifts of the ring hydrogens in different conformers appear rationalized as a first rough approximation. The electronic attraction effect of the strong electronegative atoms (F, O) on the chemical shifts of the ring hydrogens could be simply estimated through a consideration of contact distance (just at or beyond the van der Waals distance between O or F and H) and the electronegativity, and was roughly set at 0.3 ppm and 0.4 ppm for O and F respectively. The anisotropy effect of CF2–C bond on the chemical shift of a equatorial hydrogen was set at 0.2 ppm in comparison with the axial hydrogen. Also, the effect on chemical shift of an axial hydrogen of being opposed by an axial hydroxyl was set at 0.5 ppm. On this basis, for the differences in the chemical shifts between H4β′ and H4α′ of the N conformer (ΔδN) and that of the S conformer (ΔδS), it would be anticipated that ΔδS-ΔδN=(0.5 + 0.4 + Δδbase− 0.2 − 0.3) − (0.2 + 0.3 + Δδbase− 0.3 − 0.4) = 0.6 ppm, which is in good agreement with the value derived from the ab intio calculations (δS-ΔδN = 0.54 ppm) and the observed experimental data (ΔδS−ΔδN = 0.59 ppm).
- R. D. Amos, N. C. Handy, P. G. Jones, A. J. Kirby, J. K. Parker, J. M. Percy and M. D. Su, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1992, 549–558 RSC.
- T. K. Brunck and F. Weinhold, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1979, 101, 1700–1709 CrossRef CAS.
- The chemical shift changes of H1′ and H4′ were not exactly linearly dependent as a function of temperature due to the experimental error in the measurement of the chemical shifts of H1′ and H4′. The changes of chemical shifts of H1′ and H4′ are relatively very small among six different temperatures, thus the error affects much on the calculation.
- M. Polak, K. L. Seley and J. Plavec, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 8159–8166 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. Barchi, L. S. Jeong, M. A. Siddiqui and V. E. Marquez, J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods, 1997, 34, 11–29 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. Barchi, V. E. Marquez, J. S. Driscoll, H. Ford, H. Mitsuya, T. Shirasaka, S. Aoki and J. A. Kelley, J. Med. Chem., 1991, 34, 1647–1655 CrossRef CAS.
- D. E. Bergstrom, D. J. Swartling, A. Wisor and M. R. Hoffmann, Nucleosides, Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, 1991, 10, 693–697 CAS.
- Both of the experimental and calculated chemical shift values of H4β′ were used for the analysis of the conformational equilibrium of the thiosugar ring in compound 5a. Error estimation for the calculated values was taken into consideration.
- D. A. Case, D. A. Pearlman, J. W. Caldwell, T. Cheatham, J. Wang, W. S. Ross, C. Simmerling, T. Darden, K. M. Merz, R. V. Stanton, A. Cheng, J. J. Vincent, M. Crowley, V. Tsui, H. Gohlke, Y. Duan, J. Pitera, I. Massova, G. L. Seibel, U. C. Singh, P. Weiner and P. A. Kollman, AMBER 9, University of California, San Francisco, 2002 Search PubMed.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Scans of NMR spectra, computational methods and results of MD simulations. CCDC reference number 740876. For crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/b914679b |
| ‡ Crystal data for 5a: C8H8F2N2O3S, M = 250.22, monoclinic, a = 6.1849(8), b = 18.082(2), c = 8.9343(11) Å, α = 90, β = 100.122(2), γ = 90°, V = 983.6(2) Å3, T = 293 K, space group P21, Z = 4, 5594 reflections collected, 2129 unique (Rint = 0.0244), R1 = 0.0433 [I > 2δ(I)], wR2 = 0.1110. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2010 |