Thermoreversible photocyclization of a pyrazolotriazole to a triazasemibullvalene: a novel electrocyclic reaction†
Claudio
Carra
a,
Thomas
Bally
*a,
Titus A.
Jenny
a and
Angelo
Albini
b
aDepartment of Chemistry, University of Fribourg, Perolles, CH-1700, Fribourg, Switzerland
bDepartment of Organic Chemistry, University of Pavia, I-27100 Pavia, Italy
First published on 2nd January 2002
Abstract
The photochemistry of the pyrazolo[1,2-a]benzotriazole 1b and its dimethyl derivative 1c was studied in argon matrices at 12 K and in solution at 190 K. On irradiation at 365 nm, 1b and 1c undergo ring closure to yield the triazasemibullvalenes 2b and 2c, respectively, which were identified unambiguously by NMR and IR spectroscopy. This novel type of cyclization is reversed on warming or by irradiation at 313 nm. Quantum chemical calculations serve to model the observed IR and UV spectra and to rationalize the mechanism of the photocyclization and its thermal back-reaction.
1 Introduction
4-Electron electrocyclic rearrangements of three-membered heterocycles to betaines have been studied for a number of systems, in particular for oxiranes and aziridines.1,2 The appropriate choice of the substituents (usually aryl groups) allows tuning of the thermal reversibility of such photochromic equilibria and in some cases to have a two wavelength photochemistry which may be useful for micro-reproduction.2–4 However, only few related reactions have been reported for other three-membered heterocycles. In particular, the synthetically appealing conversion of readily accessible and functionalizable diaziridines to azomethine imines has not been extensively documented.5,6 On heating, a number of diaziridines, generally ring-fused or substituted by electron-withdrawing groups, were found to give adducts that may result from the trapping of azomethine imines.5–7 Photochemical ring closure of azomethine imines to diazirines has been reported for a few cyclic acylated derivatives.8–11In the course of our studies on the chemistry of o-pyrazolylphenylnitrenes we have discovered by coincidence a clean example of a photochemically and thermally reversible photorearrangement of the azomethine imine–diaziridine type, where the heterocyclic moiety is part of an aromatic pyrazolotriazole structure of type 1a (Scheme 1) and the photoproduct is a triazasemibullvalene 2a. These experiments and the corresponding model calculations are reported in this paper.
 | ||
| Scheme 1 | ||
The stability (and the aromaticity) of heteropentalenes such as 1a with respect to monocyclic or bicyclic isomers and the possible thermal or photochemical rearrangement to such isomers have been long debated.12 These compounds easily undergo 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions,13 while, as mentioned above, the generation of diaziridines from azomethine imines is restricted to a few special cases. This experimental and computational study thus also aimed to assess the aromaticity of such heteropentalenes and more generally to quantitatively characterize the azomethine imine–diaziridine interconversion and the corresponding structure dependence. This is significant in view of the role of azomethine imines for the preparation of pyrazol(id)ines, a synthetic path that has been developed to some degree14 following the original suggestion by Huisgen.15
2 Experimental and theoretical methods
The pyrazolo[1,2-a]benzotriazoles 1b and 1c16 were synthesized according to the method described previously.17,18 They were deposited in cryogenic matrices by placing them in a U-shaped tube kept at −10 °C from where they were carried along by a stream of Ar, mixed with 15% N2 to improve the optical quality of the matrix. After deposition of the matrix at about 20 K it was cooled to 12 K. UV/VIS spectra were measured on a Perkin-Elmer Lambda 19 instrument, while the IR spectra were measured at 0.5 cm−1 resolution on a Bomem DA3 FT-IR spectrometer.The photoproducts were produced by 365 nm photolysis (Hg/Xe lamp, interference filter) of 1b and 1c. The reverse reaction was effected by irradiation with the 313 nm line of the same lamp. The same photolyses were carried out on thoroughly degassed ca. 10−2 M solutions of the samples in CD2Cl2. Due to the low thermal stability of the photoproduct of 1b the solution must be kept below 190 K during the experiment. After we verified by optical spectroscopy that the photocyclization is also reversible (either by 313 nm irradiation or by warming above 210 K) in solution, we proceeded to measure NMR spectra on a Bruker Avance DRX 500 spectrometer.
The geometries of all the ground-state stationary points were optimized by the B3LYP/6-31G* hybrid density functional method19,20 using the Gaussian 98 program package.21 Excited state geometry optimizations were carried out by the CI singles (CIS) method,22 while conical intersections23 were located by the state-averaged complete active space (CAS) SCF procedure24,25 as implemented also in Gaussian 98.21 The pathway leading to the open-shell singlet vinlylnitrene that arises by cleavage of the N+–N− bond in 1a required also a treatment by the CASSCF method. For the sake of consistency the ground-state stationary point energies of 1a–2a were therefore reoptimized at the CASSCF level for the construction of Fig. 6.
Excitation energies and transition moments of 1b were computed by the recently introduced DFT-multireference CI (MRCI) method26 which gave predictions in excellent agreement with the experimentally observed spectrum of this compound.27
3 Results and discussion
3.1 UV/VIS and IR spectra in Ar matrices
Fig. 1a (solid line) shows the UV spectrum of the pyrazolo[1,2-a]benzotriazole 1b. It contains three vibronically structured band systems peaking at 367, 300, and 235 nm in addition to a weak shoulder at ca. 260 nm. According to the results of the DFT-MRCI calculations listed in Table 1, which are in excellent accord with the observed spectrum (see bars in Fig. 1), these bands comprise five electronic excitations involving the π-MOs of 1b shown in Fig. 2. The first transition is predominantly HOMO(π4)→LUMO(π5*) electron promotion, a fact that is very important in view of the photochemistry of 1b which stands at the focus of this paper. The 300 nm peak and the associated vibrational progressions are due to a transition which is best represented as the negative combination of π4→π6* and π3→π5* excitation, the positive counterpart of which is the intense band peaking at 235 nm. Between the above two lie two transitions that are described to over 50% by π4→π7* and π4→π8* excitation, respectively, with about 10% of the other one mixed in. The first of them is assigned to the shoulder at 260 nm, whereas the predicted oscillator strength for the second transition is so small that it is probably obscured by the former.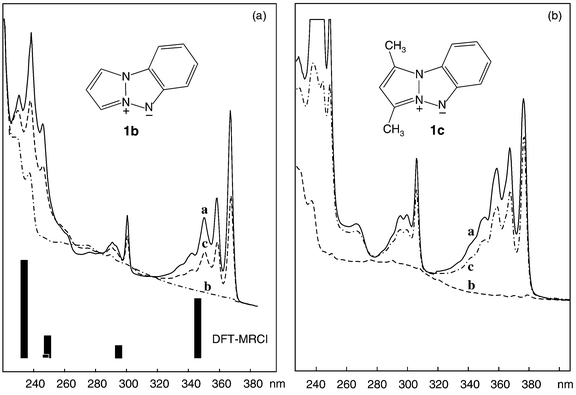 | ||
| Fig. 1 UV spectra documenting the bleaching of the heteropentalene 1b and the dimethyl derivative 1c, respectively, in an Ar matrix, by irradiation at 365 nm (a→b) and their partial re-formation on subsequent 313 nm irradiation (b→c). The broad shoulder at ≈300 nm in spectrum b is due to the photoproduct. The bars at the bottom of the left hand figure represent the results of the excited state DFT-MRCI calculations on 1a listed in Table 1. | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 2 Hartree–Fock π molecular orbitals of the heteropentalene 1b that are involved in the excitations listed in Table 1. | ||
| States | EASb | DFT-MRCI (f)c | MRCI config. compositiond |
|---|---|---|---|
| a Energies relative to ground state in eV. b Data from UV/VIS spectra in Fig. 1a. c Oscillator strength for electronic transitions. d Composition of states in terms of configurations that arise by excitation among the MOs in Fig. 2. | |||
| 1A′ | — | (0) | 95% (π4)2 |
| 2A′ | 3.38 | 3.58 (0.350) | 84% π4 → π5* |
| (367 nm) | 2% π3 → π5* | ||
| 1% π4 → π6* | |||
| 3A′ | 4.13 | 4.21 (0.073) | 51% π4 → π6* |
| (300 nm) | −29% π3 → π5* | ||
| 3% π4 → π5* | |||
| 4A′ | 4.77 | 4.97 (0.130) | 52% π4 → π7* |
| (260 nm) | 9% π4 → π8* | ||
| 6% π4 → π6* | |||
| 4% 2π4 → 2π5* | |||
| 4% π2 → π5* | |||
| 5A′ | ? | 5.00 (0.021) | 51% π4 → π8* |
| 11% π4 → π7* | |||
| 9% π1 → π5* | |||
| 6A′ | 5.27 | 5.31 (0.575) | 42% π3 → π5* |
| (235 nm) | +23% π4 → π6* | ||
| 5% π2 → π6* | |||
| 5% π4 → π7* | |||
The spectrum of the dimethyl derivative, 1c (solid line in Fig. 1b), is very similar in appearance to that of the parent species 1b, apart from some slight bathochromic shifts and some changes in the relative intensities of the four observed band systems. Most notable is the fact that the 260 nm shoulder in the spectrum of 1b has now evolved into a full band peaking at 266 nm which lends additional support to the above assignment. We did not run separate calculations for the excited states of 1c because we did not expect additional insight into the electronic structure of the pyrazolobenzotriazole chromophore of 1 from this undertaking.
On irradiation at 365 nm the spectrum of 1b can be fully bleached (spectrum b in Fig. 1a), whereby a nondescript, flat absorption arises at ca. 300 nm with some small humps at higher energy. On changing the wavelength of irradiation to 313 nm, the spectrum of 1b can be reconstituted to about 65% (spectrum c) i.e. the reaction is partially photoreversible. In 1c which can also be bleached completely in Ar matrices the degree of photoreversibility attains nearly 90% (see spectrum c in Fig. 1b).
In Fig. 3a, the IR spectra which correspond to the bleaching of 1b and 1c, respectively, at 365 nm are shown in the form of difference spectra (on subsequent irradiation at 313 nm, near-mirror images of these spectra are obtained). The traces above the experimental spectra are simulated ones based on B3LYP/6-31G* calculations of the vibrational structure of the triazasemibullvalenes, 2b and 3b, respectively.28 The two IR spectra, and in particular the shifts introduced by methyl substitution, are in suffficiently good accord with the IR bands of the photoproducts to allow their tentative assignent to structures 2 which will be confirmed by the NMR measurements described below. Note that, although the bands of the precursors 1 are not fully re-formed on 313 nm bleaching, no significant new IR bands arise in this process in either case. Therefore the fact that the reactants are only partially recovered is not due to a side-reaction, but to the formation of a photostationary equilibrium between structures 1 and 2 under 313 nm irradiation. Apparently, this equilibrium lies more on the side of structure 1 in the case of the dimethyl derivatives.
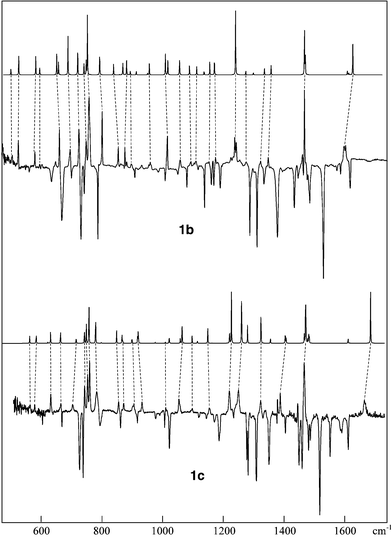 | ||
| Fig. 3 IR difference spectra for the 365 nm bleaching of the heteropentalene 1b (top) and its dimethyl derivative 1c (bottom), respectively, in an Ar matrix. The bands of 1b and 1c, respectively, point down, those of the photoproducts point up. The simulated spectra of the triazasemibullvalenes 2b and 2c, respectively, based on B3LYP/6-31G* calculations of their vibrational structure, are plotted above the experimental spectra. Note the excellent accord between the experimental spectra of the photoproducts and these simulations. | ||
3.2 Photochemical behavior of 1b and 1c in solution
In view of the planned NMR experiments described below, we repeated the above experiments in solution. In a degassed EPA (ether–pentane–ethanol) glass at 77 K the behavior of 1b and 1c paralleled that observed in Ar matrices, i.e. pyrazolotriazoles 1 could be completely bleached by short 365 nm photolysis and recovered partially by subsequent 313 nm irradiation. However, on melting of the glass and warming the EPA solution to room temperature, the recovery of 1b or 1c was complete (spectrum superimposable on that obtained before freezing). This proves that the photoreaction of compounds 1 is thermally reversible, and it confirms that the partial recovery by 313 nm irradiation of the photoproducts is not due to irreversible losses in side or secondary reactions, but to the formation of a photostationary equilibrium.Compound 1b could still be bleached and recovered (partially by 313 nm irradiation, fully by warming to room temperature) when an EPA or CH2Cl2 solution was kept at −78 °C. In contrast, 1c appeared comparatively stable to 365 nm light under these conditions, but faded slowly and irreversibly upon prolongued irradiation, even if the temperature was lowered to −100 °C (attempts to regenerate 1c by 313 nm irradiation led to even more rapid photodegradation). Experiments at intermediary temperatures showed that the thermal recovery of 1b sets in at ca. −60 °C where the half life of the metastable photoproduct is in the minute range and becomes too rapid to be followed by conventional spectroscopy above −50 °C.
At room temperature both heteropentalenes are degraded irreversibly by photolysis, in agreement with previous reports29 where preparative photochemical runs resulted in products (amines, azo compounds) that are derived from the nitrenes that are obtained by cleavage of the lateral N8–N8a (see Fig. 4 for atom numbering) bond in compounds 1. Since the corresponding triplet nitrenes, which can easily be distinguished by their sharp absorptions in the visible,30 were not detected in the Ar matrix experiments, we conclude that their formation at higher temperature involves an activated process. When room temperature photolyses were conducted in CH2Cl2 the solutions turned colored (green in the case of 1b, pink for 1c).
The above-described experiments were all conducted with degassed solutions. However, it turned out that admitting air had no profound influence on the reactivity: at −78 °C the behavior was the same with or without air, whereas at room temperature, the degradation of 1b was even slightly retarded by the presence of O2. Thus, no intermediates that are susceptible to degradation by oxygen seem to be involved in the reversible photochemical cycle. On the other hand, we cannot say anything about the fate of the side (or secondary) product(s) of the irreversible bleaching of the pyrazolotriazoles at room temperature in the presence or absence of O2.
3.3 NMR spectra: confirmation of the structure of 2b
Because a matching of measured and calculated vibrational spectra is not generally regarded as conclusive evidence for a structural assignment, we proceeded to repeat the above experiments in solution with the aim of obtaining NMR evidence to confirm the structure of the photoproduct. A typical spectrum obtained after partial 365 nm photolysis of 1b in CH2Cl2 solution at −80 °C is shown in Fig. 4.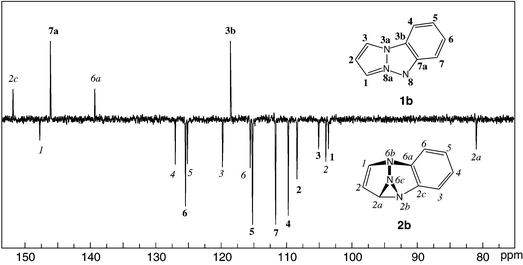 | ||
| Fig. 4 13C NMR spectrum of a mixture of pyrazolotriazole 1b and triazasemibullvalene 2b (obtained from the former by 365 nm photolysis) in CD2Cl2 at −80 °C. Bold labels refer to C-atoms of 1b, italic labels to those of 2b (atom numbering indicated on inset structures). Assignments were made on the basis of 2D-HETCOR, NOE and undecoupled 13C spectra (not shown). | ||
Among the new signals that are obtained upon 365 nm irradiation of 1b, the most notable are those for the three former pyrazolo carbons and their attached hydrogen atoms which are listed in Table 2. Most indicative is the high-field shifted signal at ca. 81 ppm. This resonance lies well below the range for an olefinic or aromatic carbon atom. However, the observed 1JCH coupling constant of 197 Hz with its directly attached proton largely exceeds the normal range of aliphatic carbons. The proposed triazasemibullvalene structure 2b (Scheme 2) not only explains this large coupling constant by ring strain, combined with double heteroatom substitution (cf.1JCH in N-methylphenyloxaziridine: 183 Hz31) but provides at the same time a rationale for the observed spread in JHH coupling constants: the 3.8 Hz coupling between the signals at 6.34 and 5.39 ppm matches the expected value for an olefinic Z-coupling in a strained 5-membered ring, whereas the small 1.7 Hz vicinal coupling between the signals at 5.39 and 4.86 ppm is difficult to explain in view of the dihedral angle of only ∼30° between protons at C(2) and C(2a) in the B3LYP structure. No measurable coupling is observed between H–C(1) and H–C(2a), presumably because the dihedral angle between the H–C(2a) bond and the π-orbitals of the double bond (∼60° according to B3LYP) lies close to the sign inversion point of the allylic coupling constant.32
| δ 13C (ppm) | J CH/Hz | δ 1H (ppm) | J HH/Hz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(1) | 147.73 | 192.4, 6.6, 4.3 | 6.34 | 3.8 |
| C(2) | 103.90 | 181.5, 6.9, 5.7 | 5.39 | 3.8, 1.7 |
| C(2a) | 80.84 | 197.3, 9.4, 9.4 | 4.86 | 1.7 |
 | ||
| Scheme 2 Structure of 2b from B3LYP/6-31G* calculation. | ||
Final support of the proposed structure comes from NOE experiments: irradiation at 6.34 ppm produces enhancements both at 5.39 ppm (8.5%) and 7.04 ppm (2.0%), the latter signal being one of the two aromatic o-protons (the corresponding calculated H–H distances are 2.7 and 3.2 Å, respectively, cf.Scheme 2). Irradiation at 5.39 ppm leads to large effects both at 6.34 ppm (12.9%) and at 4.86 ppm (12.6%) (both distances are about 2.7 Å), whereas irradiation at 4.85 ppm only enhances the signal at 5.39 ppm (7.9%). The lack of any response of an aromatic signal in the latter case points to a fairly remote location of H–C(2a) from the remainder of the molecule, in agreement with the fact that the distance to the closest o-hydrogen is nearly 4.6 Å in the above B3LYP structure (cf.Scheme 2).
In contrast to 1b, where very sharp NMR spectra were obtained, photolysis of the dimethyl derivative 1c led to a strong broadening of all lines. On standing overnight at −80 °C the lines narrowed a bit, but not to the point where spectral assignments would have become possible. Since all lines were affected, including those of the precursor, the broadening must be caused by an external perturber that acts indiscriminately on all species present in the solution. Based on the conclusions from the calculations presented below we propose that the triplet phenylnitrene which is formed as a side product by cleavage of the N+–N− bond in 1c acts as this external perturber.
3.4 Quantum chemical calculations
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Ground-state potential energy surfaces for the ring opening process of the triazasemibullvalenes 2a, 2b, and 2c, respectively, from B3LYP/6-31G* calculations (relative energies, corrected for zero point energy differences. For thermochemical activation parameters, see Table 3. | ||
Most importantly, these calculations show that the ring opening of the triazasemibullvalenes 2 to the heteropentalenes 1 proceeds directly, in an adiabatic process, with the thermodynamic parameters listed in Table 3. The rates at lower temperatures which can be deduced from the activation parameters are in good accord with the experimental observation of a decay of 2b over minutes at −60 °C (k = 0.034 s−1), whereas 2c reverts within seconds to 1c, even at 173 K (k = 25 s−1).
| Reaction | ΔH | ΔS | ΔH‡ | ΔS‡ | E a | log (A/s−1) | k/s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a → 1a | −59.64 | 1.04 | 12.31 | 2.64 | 12.90 | 13.81 | 22135 |
| 2b → 1b | −50.71 | 1.13 | 13.95 | 0.94 | 14.54 | 13.43 | 582 |
| 2c → 1c | −48.23 | 3.04 | 10.52 | 1.84 | 11.12 | 13.63 | ca. 300000 |
It is interesting to note that the ring opening of compounds 2 is very strongly exothermic. In view of the fact that the ring opening of parent diazirine 3a to azomethine imine 3b is endothermic (by 7.7 kcal mol−1 according to B3LYP/6-31G*), the question arises what causes this strong change in the thermochemistry. We carried out a series of calculations on the model compounds shown in Scheme 3 which demonstrate that introduction of an amino group at the central nitrogen atom of the azomethine imine (compound 4b) makes the ring opening process of aminodiazirine 4a almost thermoneutral, presumably due to stabilization of the formal positive charge on that nitrogen atom. Introduction of four alkyl substituents in the form of two dimethylene bridges (compounds 5a–5b) already creates a small degree of exothermicity.
 | ||
| Scheme 3 B3LYP/6-31G* energy differences for the ring-opening of model compounds 3–8. | ||
A more pronounced effect is obtained by dehydrogenation of 5b to give 6b or 7b which both contain a 6π aromatic ring (ΔH for ring opening of the corresponding diazirines 6a and 7a grows from −5 to about −20 kcal mol−1). Surprisingly, further dehydrogenation to give the heteropentalene 8b (=1a) which now contains a cyclic array of 10 π-electrons leads to a tripling of the exothermicity to over 60 kcal mol−1, which testifies to the pronounced aromatic character of the pyrazolotriazole moiety. The same feature is also illustrated by the hydrogenation enthalpies which are positive (8b → 7b: 0.5 kcal mol−1) or only slightly negative (8b → 6b: −5.7 kcal mol−1) for 8b, whereas they are in the normal negative range for hydrogenation of 7b and 6b, respectively, to 5b (−26.7 and −20.1 kcal mol−1, respectively). Benzannelation appears to stabilize the semibullvalene 2 more than the heteropentalene 1 because it decreases the exothermicity of the ring-opening by about 10 kcal mol−1.
(a) On S0→S1 excitation of pyrazolotriazoles 1, an electron is promoted from the HOMO which is strongly antibonding between C(1) and the N(6) to the LUMO which is bonding between these two atoms (cf.Table 1 and MOs in Fig. 2 and 6). As a result, the bond order between these two atoms increases strongly, thus promoting the cyclization to the triazasemibullvalene photoproducts, 2. Indeed, geometry optimizations of 1a or 1b in their S1 excited states by the CIS method leads to a pronounced shortening of the transannular C–N bond accompanied by spontaneous out-of-plane deformation, i.e. movement towards 2a and 2b.
This process is reminiscent of the out of plane deformation found e.g. in the benzene excited state–benzvalene conversion, where it is also related to a decrease of the bonding between neighboring atoms and an increase between non-neighboring atoms.33
(b) Conversely, S0→S1 excitation of triazasemibullvalenes 2 involves electron promotion from a Walsh-type MO that is bonding between C(2a) and N(2b) to its antibonding counterpart (see MOs in Fig. 6) which leads to a weakening of that bond. Indeed, CIS geometry optimizations of these compounds in their first excited states invariably lead to spontaneous ring-opening towards pyrazolotriazoles 1.
(c) Both photoreactions lead through a common conical intersection (CI) whose structure, calculated by the CASSCF state averaging procedure, is shown in Fig. 7(a) together with that of the transition state TSa for the thermal ring opening of the model compound 2a (calculated by the same method, structure b). The two structures show great similarities, but the most notable feature of the conical intersection (a) is the suprisingly long lateral N–N bond.
(d) The above indicates a possible bifurcation of the reaction path after passage through the conical intersection into two valleys, one leading to structure 1a, the other to full cleavage of the lateral N–N bond to yield eventually vinylnitrene, 9a.‡ If the same feature prevails also in the benzannelated compounds (which could not be subjected to CASSCF geometry optimizations to locate conical intersections), it could explain the formation of products derived from the corresponding phenylnitrenes, 9b/9c on prolonged irradiation of heteropentalenes 1b or 1c.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Energies of selected points on the excited-state potential energy surfaces for the interconversion of 1a and 2a, calculated at the CASSCF level with S0/S1 state averaging (the geometries of 1a, 1b, and TSa were optimized by ground-state CASSCF, whereas that of the conical intersection, CI, requires S0/S1 state averaging). Inserted drawings show the singly occupied MOs in the two S1 excited states which meet at CI. Also indicated is the transition state, TSd, leading from 1a to the singlet state of vinylnitrene, 9a, all calculated by ground-state CASSCF.34 | ||
 | ||
| Fig. 7 Structures of CI, TSa, and TSd calculated by (10,8)CASSCF. | ||
In an effort to shed more light on the possible formation of nitrenes in the course of the photochemical reactions involving compounds 1 and 2, we also located the transition state, TSd, for the opening of 1a to 1[9a]. As the latter species is of open-shell nature, this calculation had to be done again by the CASSCF method, which led to the structure shown in Fig. 7(c) which lies 35.8 kcal mol−1 above 1a, but significantly below the conical intersection and TSa.34 Nevertheless, considerable structural changes are required to get from CI to TSd and we could find no activationless path connecting the two structures on the CASSCF potential energy surface.
We also considered whether the photoinduced conversion of heteropentalenes 1 to nitrenes 9, which have in fact triplet ground states, might occur on the triplet potential energy surfaces. Intersystem crossing to the triplet may occur either from the S1 state of 1, or in the course of the reaction that leads to 2. To explore this possibility, we carried out calculations on the triplet potential surfaces, this time by the B3LYP method. Thereby we found that relaxation of 1a in its T1 state leads to a bis-allylic structure 3[10a] (Scheme 4) which may also be attained from 3[2a] or from the T1 state of TS1 which lies actually below the corresponding singlet state! However, 3[10a] resides in a rather deep potential energy well, hence it appears unlikely that ring opening of 1b–1c to the corresponding phenylnitrenes occurs on the triplet surface.
 | ||
| Scheme 4 | ||
Conclusions
We have found that 365 nm irradiation of pyrazolo[1,2-a]benzotriazoles 1 results in cyclization to the triazabenzosemibullvalenes 2, which constitutes a novel chemical rearrangement of the azomethine ylide–diazirine type. Similarly to other 4π electrocyclic processes this is a thermally and photochemically reversible reaction, but in contrast to most related processes the more stable form in this case is by far the open chain mesomeric zwitterion. This novel photorearrangement and its electronic origin have been thoroughly characterized through a combination of experimental and theoretical approaches. On the basis of these results it may be possible to modulate the properties of such systems through appropriate structural variations in order to devise systems useful either as photochromic materials or as reagents for organic synthesis.The electronic structures of reactants and products and the mechanism of the above interconversion were studied by different kinds of excited state calculations. By these we were able to show that the S1 states of the reactants and products undergo activationless decay to a conical intersection whose lower cone connects to the respective ground state surfaces. The spontaneous distortions of the S1 excited states of 1a towards 2a and vice versa can be explained by the nodal properties of the MOs involved in these excitations. A notable feature of the conical intersection structure is a surprisingly long N–N bond which suggests the possibility of a reaction path that involves cleavage of that bond, i.e. decay to the corresponding phenylnitrenes. This would explain the formation of products derived from phenylnitrenes on prolonged irradiation of pyrazolo[1,2-a]benzotriazoles 1 in solution at room temperature.
Acknowledgements
This work is part of project No 2000–061560.00 of the Swiss National Science Foundation. We are indebted to Felix Fehr (University of Fribourg) for the measuring of the low-temperature NMR spectra and to Professor Elisa Fasani (University of Pavia) for experimental help. A. A. acknowledges partial support from the M.U. R. S. T. Rome. Special thanks go to Professor Stefan Grimme for the results of the DFT-MRCI calculations shown in Table 1.References
- G. W. Griffin, K. Nishiyama and K. Ishikawa, J. Org. Chem., 1977, 42, 180 CrossRef CAS.
- A. M. Trozzolo, T. M. Leslie, A. S. Sarpotdar, A. D. Small, G. J. Ferraudi, T. D. Minh and R. L. Hartless, Pure Appl. Chem., 1979, 51, 261 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Schulz and H. Dürr, in Photochromism, H. Dürr and H. Bouas-Laurent (Ed.), Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1990, p. 193 Search PubMed.
- H. Dürr, in CRC Handbook of Organic Photochemistry and Photobiology, W. H. Horspool and P. S. Song (Ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1995, p. 1121 Search PubMed.
- H. W. Heine, in Small Rings, Part 2, A. Hassner (Ed.), Wiley, New York, 1983, p. 547 Search PubMed.
- E. Schmitz, Houben-Weyl Meth. Org. Chem., D. Klaman (Ed.), Thieme, Stuttgart, 1992, vol. E16C, p. 678 Search PubMed.
- (a) H. W. Heine, R. Henrie, L. Heitz and S. R. Kovvali, J. Org. Chem., 1974, 39, 3192 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. G. Pleiss and J. A. Moore, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1968, 90, 4738 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Schulz and G. West, J. Prakt. Chem., 1970, 312, 161 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Maki, M. Suzuki, T. Furuta, M. Kawamura and M. Kuzuye, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1979, 1199 RSC.
- G. Tomaschewski, G. Geissler and G. Schauer, J. Prakt. Chem., 1980, 322, 623 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) M. Nastasi and J. Streith, in Rearrangements in Ground and Excited States, vol. 3, P. de Mayo (Ed.), Academic Press, New York, 1980, p. 445 and references cited therein Search PubMed; (b) T. Tsuchiya, in CRC Handbook of Organic Photochemistry and Photobiology, W. H. Horspool and P. S. Song (Ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1995, p. 892 Search PubMed.
- Benzodiazirines have been postulated as intermediates in the photochemical rearrangement of N-iminopyridinium ylides, but no direct evidence has been found for such compounds10a.
- C. Ramsden, Tetrahedron, 1977, 33, 3203 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Albini, G. Bettinetti and G. Minoli, J. Org. Chem., 1984, 49, 2670 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Grashey, in 1,3 Dipolar Cycloadditions, A. Padwa (Ed.), Wiley, New York, 1984, vol. 1, p. 733 Search PubMed.
- R. Huisgen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1963, 2, 565 CrossRef.
- The systematic name of compound 1b is 8H-3a,8,8a-triazacyclopent[a]indene. 1c is the corresponding 1,3-dimethyl derivative.
- J. M. Lidley, I. M. McRobbie, O. Meth-Cohn and H. Suschitzky, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1980, 982 RSC.
- A. Albini, G. Bettinetti and G. Minoli, J. Org. Chem., 1983, 48, 1080 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 5648 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Lee, W. Yang and R. G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B, 1988, 37, 785 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, V. G. Zakrzewski, J. A. Montgomery, R. E. Stratmann, J. C. Burant, S. Dapprich, J. M. Millam, A. D. Daniels, K. N. Kudin, M. C. Strain, O. Farkas, J. Tomasi, V. Barone, M. Cossi, R. Cammi, B. Mennucci, C. Pommelli, C. Adamo, S. Clifford, J. Ochterski, G. A. Petersson, P. Y. Ayala, Q. Cui, K. Morokuma, D. K. Malick, A. D. Rabuck, K. Raghavachari, J. B. Foresman, J. Cioslowski, J. V. Ortiz, B. B. Stefanov, G. Liu, A. Liashenko, P. Piskorz, I. Komaromi, R. Gomperts, R. L. Martin, D. J. Fox, T. Keith, M. A. Al-Laham, C. Y. Peng, A. Nanayakkara, M. Challacombe, P. M. W. Gill, B. G. Johnson, W. Chen, M. W. Wong, J. L. Andres, C. Gonzalez, M. Head-Gordon, E. S. Replogle and J. A. Pople, Gaussian 98, Rev. A7Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, 1998 Search PubMed.
- J. B. Foresman, M. Head-Gordon, J. A. Pople and M. J. Frisch, J. Phys. Chem., 1992, 96, 135 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Bernardi, M. A. Robb and M. Olivucci, Chem. Soc. Rev., 1996, 25, 321 RSC.
- I. N. Ragazos, M. A. Robb, F. Bernardi and M. Olivucci, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1992, 197, 217 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Bearpark, M. A. Robb and H. B. Schlegel, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1994, 223, 269 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Grimme and M. Waletzke, J. Chem. Phys., 1999, 111, 5645 CrossRef CAS.
- We also attempted to calculate the excited-state electronic structure of compounds 1 by the CASPT2 method. However, this turned out to be difficult because on inclusion of higher roots in the state-averaging CASSCF procedure the nature of the first excited state changed completely from that which is obtained on averaging only the lowest two roots. Normal CASPT2 perturbation theory proved incapable of rectifying this and consequently the corresponding predictions were unsatisfactory. Note, however, that this particular difficulty with CASSCF has no bearing on the application of this procedure in the remainder of the present work.
- The systematic name of compound 2b is: 2aH-2b,6b,6c-triazabenzo[a]cyclopropa[cd]pentalene. Compound 2c is the corresponding 1,2a-dimethyl derivative.
- A. Albini, G. Bettinetti and G. Minoli, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113, 6928 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Carra, T. Bally and A. Albini, manuscript in preparation.
- H.-O. Kalinowski, S. Berger and S. Braun, C-NMR-Spektroskopie, Thieme, Stuttgart, 1984 Search PubMed.
- S. Sternhell, Q. Rev. Chem. Soc., 1969, 23, 236 RSC.
- J. Malkin, Photophysical and Photochemical Properties of Aromatic Compounds, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1992 Search PubMed.
- Note that the energies of CI and TSa on the one hand, and TSd–9a on the other hand cannot be directly compared because the former were calculated by S0/S1 state averaging, whereas the latter were calculated with CASSCF wavefunctions optimized for the ground states only.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: structures and energies of all stationary points located in the course of the study, in the form of Gaussian input files, followed by energies and, where available, thermal corrections from frequency calculations. See http://www.rsc.org/suppdata/pp/b1/b106231j/ |
| ‡ This would have some analogy with the photodecomposition of N-iminopyridinium ylides which yield, next to 1,2-diazepines that may be thought to arise from intermediary diazirines, nitrenes that are formed as a consequence of N–N cleavage.10a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry and Owner Societies 2002 |
