Investigation on the quality diversity and quality-FTIR characteristic relationship of sunflower seed oils
Abstract
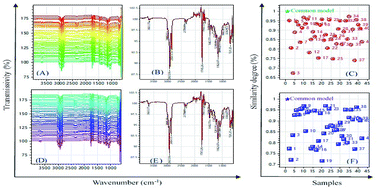
Forty-one sunflower seed oil (SSO) products were collected to investigate their quality parameters before and after high-temperature and short-time (HTST) cooking, including peroxide value (PV), acid value (AV) and fatty acid (FA) composition. Their Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were then scanned to explore the parameter-FTIR characteristic relationship using chemometrics with multiple linear regression (MLR) analysis. The PV and AV of uncooked products were in the range of 1.49–6.29 mmol kg−1 and 0.04–0.31 mg g−1, with the variation coefficient of 36.47% and 146.82%, respectively. They were mainly composed of palmitic acid (2.39–3.33%), stearic acid (1.76–2.54%), oleic acid (10.02–24.77%) and linoleic acid (66.42–83.62%). The parameter changes caused by HTST cooking were slight. SSO products from different countries might have significantly different FA composition, especially linoleic acid content (P < 0.05), and those with different shelf times might differ in PV (P < 0.05). In addition, the FTIR spectra of cooked and uncooked SSO showed the similarity degree values ranging from 0.67 to 0.97 and 0.72 to 0.97, respectively. All the spectra exhibited the characteristic bands of –C–H, –C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, –C–O– and
O, –C–O– and ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2, in which 11 common bands as independent variables were selected to establish various FTIR characteristic–quality relationship models. The models of palmitic acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid were acceptable for their content predictions. Moreover, the cooked oils and uncooked oils could be completely distinguished by orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis due to the cooking-caused changes in FTIR spectrum. Production place and shelf time were the important factors related to the quality diversity of SSO, and FTIR spectroscopy combined with chemometrics was feasible for the simultaneous determination of various quality parameters.
CH2, in which 11 common bands as independent variables were selected to establish various FTIR characteristic–quality relationship models. The models of palmitic acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid were acceptable for their content predictions. Moreover, the cooked oils and uncooked oils could be completely distinguished by orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis due to the cooking-caused changes in FTIR spectrum. Production place and shelf time were the important factors related to the quality diversity of SSO, and FTIR spectroscopy combined with chemometrics was feasible for the simultaneous determination of various quality parameters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...