Pyrite nanoparticles: an Earth-abundant mineral catalyst for activation of molecular hydrogen and hydrogenation of nitroaromatics†
Abstract
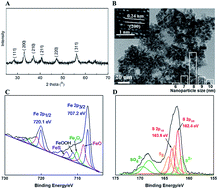
Pyrite (FeS2) nanoparticles, a kind of Earth-abundant mineral, can efficiently activate molecular hydrogen under mild conditions. At ambient pressure, H2 can be dissociatively adsorbed by FeS2 nanoparticles, react with nitrobenzene, and selectively produce aniline. The catalytic activity for hydrogenation of nitrobenzene is comparable to most non-precious metal catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...