Efficient localization of a native metal ion within a protein by Cu2+-based EPR distance measurements†
Abstract
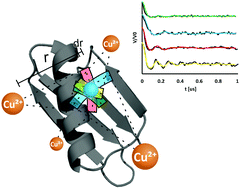
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) based distance measurements have been exploited to measure protein–protein docking, protein–DNA interactions, substrate binding and metal coordination sites. Here, we use EPR to locate a native paramagnetic metal binding site in a protein with less than 2 Å resolution. We employ a rigid Cu2+ binding motif, the double histidine (dHis) motif, in conjunction with double electron electron resonance (DEER) spectroscopy. Specifically, we utilize a multilateration approach to elucidate the native Cu2+ binding site in the immunoglobulin binding domain of protein G. Notably, multilateration performed with the dHis motif required only the minimum number of four distance constraints, whereas comparable studies using flexible nitroxide-based spin labels require many more for similar precision. This methodology demonstrates a significant increase in the efficiency of structural determinations via EPR distance measurements using the dHis motif.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
