CO2-Assisted asymmetric hydrogenation of prochiral allylamines†
Abstract
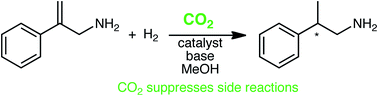
A new methodology for the asymmetric hydrogenation of allylamines takes advantage of a reversible reaction between amines and carbon dioxide (CO2) to suppress unwanted side reactions. The effects of various parameters (pressure, time, solvent, and base additives) on the enantioselectivity and conversion of the reaction were studied. The homogeneously-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of 2-arylprop-2-en-1-amine resulted in complete conversion and up to 82% enantiomeric excess (ee). Added base, if chosen carefully, improves the enantioselectivity and chemoselectivity of the overall reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...