Design and synthesis of proton-dopable organic semiconductors†
Abstract
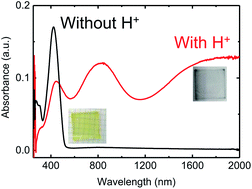
This paper shows how protonated 3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene moieties can be used as an end group to make organic conductors. An organic semiconductor 2,5-bis(5-(2,3-dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxin-5-yl)-3-dodecylthiophen-2-yl)thieno[3,2-b]thiophene is designed and synthesized. This molecule could be doped by protonic acid in both solution and solid-state, resulting in a broad absorption in the near-infrared range corresponding to polaron and bipolaron absorption. Electrical conductivity of ca. 0.1 S cm−1 was obtained at 100 °C (to avoid the water uptake by the acid). The adducts with protons bound at the end-thiophene α-position were confirmed by 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectra.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...