Synthesis, characterization and in vitro validation of a magnetic zeolite nanocomposite with T2-MRI properties towards theranostic applications†
Abstract
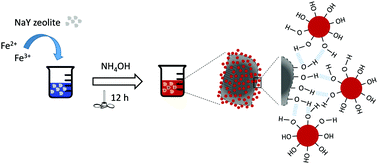
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have been gaining significant importance as building blocks to form more complex nanostructures due to the multifunctional performance enabled by their magnetic character, i.e. in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic hyperthermia (MH). This study focusses on the development of a magnetic zeolite nanocomposite (MZNC) as a suitable platform towards the design of a theranostic system. In addition to the well-known drug encapsulation properties of zeolite structures, in this work we explored their ability to act as T2-MRI contrast enhancers in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) when magnetic nanoparticles are incorporated in their structure. The MZNC was prepared by a simple one-pot colloidal chemistry route based on the co-precipitation of Fe(II) and Fe(III) salts in an aqueous solution containing a NaY zeolite. The as-synthesized samples were carefully characterized in terms of morphological, structural and magnetic properties. The results confirm the formation of magnetic assemblies with microporous structure and superparamagnetic behavior, based on the combination of the structural properties from the zeolite and the magnetic performance of the magnetite nanoparticles. TEM analysis evidenced the cell internalization of MZNC particles by human breast cancer cells and their accumulation in the cytoplasm, whereas cytotoxicity assays in both tumoral breast and non-tumoral mammary cell lines showed that the MZNC was non-toxic at the highest concentration tested. Finally, the capability of the MZNC to act as an imaging probe in MRI was confirmed and validated in vitro at a clinical field of 3T, resulting in an enhanced dark contrast compared to control cells. The combination of the well-known high load encapsulation efficiency of the NaY zeolite and the additional MRI contrast enhancement provided by its innovative assembly with biocompatible magnetite nanoparticles constitutes a step forward towards the design of inorganic hybrids as image-drug delivery systems combining thermo- and chemotherapeutic effects.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...