Dual effect of chitosan-based nanoparticles on the inhibition of β-amyloid peptide aggregation and disintegration of the preformed fibrils†
Abstract
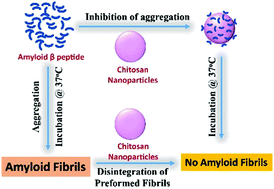
Deposition of amyloid β (1–42), i.e. (Aβ1–42), peptide aggregates in the brain is the hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, therapeutic strategies specifically targeted towards inhibition of early toxic oligomers and disruption of amyloid aggregates to treat AD remain elusive. Recently, nanoparticle-based therapies for CNS disorders have emerged as an area of considerable interest because of their reach across the blood–brain barrier. Here we study the anti-amyloidogenic activity of two types of chitosan-based nanoparticles, bare chitosan and chitosan copolymerized with PLGA. We show that the chitosan-based nanoparticles strongly inhibit the Aβ1–42 peptide aggregation process and cause substantial disintegration of the pre-formed soluble and insoluble aggregates in vitro. Furthermore, these nanoparticles appear to stabilize the peptides in an α-helical conformation and inhibit the formation of β-sheet structure, which is more prone to form aggregates. The inhibitory effect of chitosan nanoparticles was seen to alleviate the cytotoxicity elicited by Aβ1–42. Interestingly, the observed anti-amyloid activity of bare chitosan nanoparticles is ∼200-fold more potent than polymeric (bulk) chitosan. Moreover, our results also demonstrate that the amyloid inhibition efficiency varies according to the nanoparticle type and the inhibitory activity of the nanoparticles declines considerably when chitosan is copolymerized with PLGA. The observed phenomena could be attributed to the different surface charge present on the two types of nanoparticles. Collectively, our results suggest that chitosan nanoparticles could provide a promising alternative to the curative strategies being developed for treating amyloid-related neurodegenerative disorders.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...