Super-base-derived hypergolic ionic fuels with remarkably improved thermal stability†
Abstract
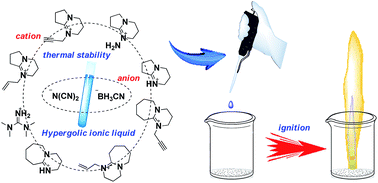
Two series of super-base-derived hypergolic ionic liquid materials were synthesized and fully characterized by 1H and 13C NMR, IR spectroscopy, and high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). Their physicochemical properties such as thermal properties, density, viscosity, heats of formation, specific impulse, and ignition delay time were intensively characterized or calculated. Among fourteen new organic ionic materials, eleven salts are liquids at room temperature, which all exhibit good stability to heat and expected hypergolic properties upon contact with WFNA. The densities of these ionic compounds range from 1.00 to 1.22 g cm−3, and their heats of formation vary between −38.0 and 478.6 kJ mol−1. Surprisingly, most of these new ionic liquids exhibited an unexpected thermal stability of >280 °C, in which salt 1 gave the Td value of 310 °C, which is superior to those of any known hypergolic ionic liquids. As a new class of hypergolic fuels, these novel ionic liquid materials have some unique advantages compared to traditional propellant fuels like hydrazine and its derivatives, including extremely low vapour pressure, short ID time, high thermal stability, etc., thereby demonstrating their potential applications as green fuels in liquid bipropellant formulations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...