Insight into the substrate specificity of keratinase KerSMD from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia by site-directed mutagenesis studies in the S1 pocket†
Abstract
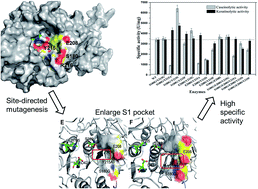
The keratinase KerSMD from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia can hydrolyze a broad range of substrates but its keratinolytic activity needs to be improved for industrial application. From sequence alignment and homologous modeling, we deduced that four residues, Ser180, Glu208, Tyr215, and Arg216, lying at the entrance or bottom of the S1 pocket, were related to the substrate specificity. The S1 pocket was enlarged by mutating a series of amino acids. We found that mutagenesis at position 215 could shift the catalytic ability of KerSMD to hydrolyze synthetic peptides and macromolecular substrates. We improved the keratinolytic activities of five mutants (Y215G, Y215S, Y215A, S180G/Y215A, and S180G/Y215S) and obtained two thermophilic keratinases (Y215S and S180G/Y215S). Compared to the wild type, the S180G/Y215S showed the highest keratinolytic activity (4755 U mg−1) and the S180G/Y215A showed the most excellent specificity to degrade feather. Our results indicate that steric hindrance and hydrophilia in the S1 pocket have a significant effect on feather keratin preference of keratinase, and the hydrogen bonds in the S1 pocket have great influence on the thermostability. These findings not only give an insight into the relationship between the S1 pocket and substrate specificity but also suggest approaches for protein engineering of keratinase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...