Revealing the mechanism of Fructus meliae toosendan-induced liver injury in mice by integrating microRNA and mRNA-based toxicogenomics data†
Abstract
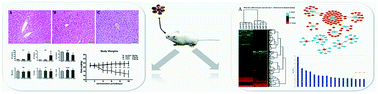
Fructus Meliae Toosendan (FMT, ChuanLianZi in Chinese) is recognized as an insecticidal and medicinal plant in China. A few previous studies demonstrated that it can induce hepatotoxicity, however, its potential toxic compositions and their mechanism of the induction of hepatotoxicity has not been completely investigated. In the present study, we performed an approach for integrating the data from microRNA (miRNA) and mRNA expression profiles combined with the general toxicological assessments method to investigate FMT-induced liver injury (FMT-ILI) in mice. Changes in the body weight, serum biochemical parameters, and histopathology were observed after 9 days exposure to FMT. A total of 37 miRNAs and 931 mRNAs were differentially expressed in the liver of FMT-treated mice. By miRNA target filter and data intersection, a total of 115 mRNA targets of the identified miRNA were obtained. Ingeniuty pathway analysis showed that lipid metabolism disorders play critical roles in FMT-ILI. Results from multi-facets of the genomic profiling provided novel insights into the mechanisms of FMT-ILI and contributed to a better understanding of liver pathobiology of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) hepatoxicity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...