Chemically exfoliated nanosilicate platelet hybridized polymer electrolytes for solid state dye sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
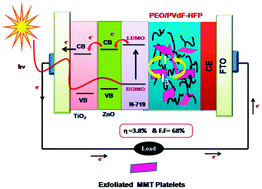
In this work, a hybrid polymer electrolyte membrane based on a poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)/poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexaflouropropylene) (PVDF–HFP) blend containing chemically exfoliated nanosilicate platelets was prepared to replace the conventionally used liquid electrolyte for dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The layered montmorillonite nanosilicates were chemically exfoliated using aminopropyltrimethoxy silane (APS). The modifications on nanosilicates by APS molecules were characterized by Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and wide angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD). The polymer composite membranes were subjected to FTIR, WAXD and Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) studies in order to understand the intercalation/exfoliation and crystallinity. The surface and porous structure of composite membranes were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis and mercury porosimetry. The porosity and weight uptake enhanced with the addition of surface modified nanoplatelets. UV-vis spectra indicated an increase in free ion concentration with the addition of exfoliated nanoplatelets, which led to an increase in the ionic conductivity up to 2.52 × 10−3 S cm−1 for 6 wt% and it decreased afterwards. On the other hand, the same amount of unmodified counterpart achieved an ionic conductivity of about 5.41 × 10−4 S cm−1. In addition to this, an increase in ion concentration, ionic mobility and ionic diffusion coefficient was found with the addition of surface modified MMT platelets. The linear steady state voltammetry indicated that the incorporation of surface modified nanoplatelets reduces the ionic diffusion length and increases the diffusion coefficient to about 4.8 × 10−9 cm2 s−1. The photovoltaic performance exhibits an enhanced open circuit voltage (Voc) of 0.73 V and a short circuit current (Jsc) of 7.7 mA cm−2 under the illumination of 100 mW cm−2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...