Mechanical properties and stabilities of α-boron monolayers
Abstract
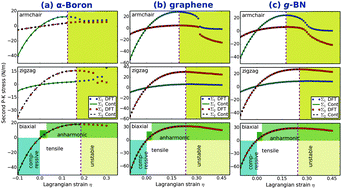
We investigate the mechanical properties and stabilities of planar α-boron monolayers under various large strains using density functional theory (DFT). α-Boron has a high in-plane stiffness, about 2/3 of that of graphene, which suggests that α-boron is four times as strong as iron. Potential profiles and stress–strain curves indicate that a free standing α-boron monolayer can sustain large tensile strains, up to 0.12, 0.16, and 0.18 for armchair, zigzag, and biaxial deformations, respectively. Third, fourth, and fifth order elastic constants are indispensable for accurate modeling of the mechanical properties under strains larger than 0.02, 0.06, and 0.08 respectively. Second order elastic constants, including in-plane stiffness, are predicted to monotonically increase with pressure, while the trend of Poisson’s ratio is reversed. The surface sound speeds of both the compressional and shear waves increase with pressure. The ratio of these two sound speeds increases with the increase of pressure and converges to a value of 2.5. Our results imply that α-boron monolayers are mechanically stable under various large strains and have advanced mechanical properties – high strength and high flexibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...