Selective electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO with a cobalt chlorin complex adsorbed on multi-walled carbon nanotubes in water†
Abstract
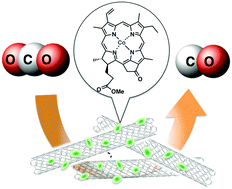
Electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 occurred efficiently using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a cobalt(II) chlorin complex adsorbed on multi-walled carbon nanotubes at an applied potential of −1.1 V vs. NHE to yield CO with a Faradaic efficiency of 89% with hydrogen production accounting for the remaining 11% at pH 4.6.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...