Enhanced photocatalytic performance of direct Z-scheme BiOCl–g-C3N4 photocatalysts
Abstract
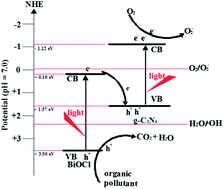
Novel BiOCl–g-C3N4 composite photocatalysts were synthesized by a one-step chemical bath method. The composites were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), high-resolution transmission microscopy (HRTEM), UV-visible light diffusion reflectance spectrometry (DRS), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL). The results indicated that BiOCl was dispersed on g-C3N4 to form heterojunction structures with high specific surface areas. BiOCl–g-C3N4 showed higher photocatalytic activity than pure g-C3N4 and BiOCl for rhodamine B (RhB) degradation. The enhanced performance was induced by the high separation efficiency of photoinduced carriers. The active species trapping and quantification experiments indicated that the photoinduced charges transfer via a direct Z-scheme.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...