Preparation and characterization of high strength and noncytotoxic bioelastomers containing isosorbide
Abstract
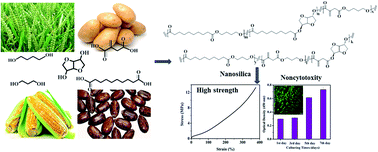
Biobased elastomers (bioelastomers) with high strength and good biocompatibility have emerged as promising biomaterials for soft tissue engineering. In the present work, we synthesized a series of biobased copolyesters, converting semicrystalline copolyesters into elastomers by introducing isosorbide, a bicyclic carbohydrate-based diol. The molecular weights, polymer structures and thermal transitions of the synthesized bioelastomers were characterized by GPC, NMR, FTIR, TGA, DSC and WAXD. The composition, melting point, and crystallinity of the bioelastomers could be tuned by changing the content of isosorbide. Furthermore, high strength composites could be prepared by compositing the synthesized bioelastomers with nanosilica. To substantiate the potential biocompatibility of the reinforced bioelastomers, the cell adhesion and proliferation were evaluated, and the results indicated that the reinforced bioelastomers were essentially noncytotoxic. The combination of sustainability, high strength and noncytotoxicity makes these bioelastomers potential candidates for high-strength biomedical materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...