Environmentally benign glycosylation of aryl pyranosides and aryl/alkyl furanosides demonstrating the versatility of thermostable CGTase from Thermoanaerobacterium sp.†
Abstract
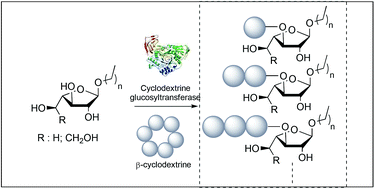
An extensive study on the specificity of transglycosylation and disproportionation of Thermoanaerobacterium sp. cyclodextrin glucosyltransferases against aryl glucopyranosides or furanosides is reported. While a mixture of maltoside and isomaltoside was obtained respectively using p-nitrophenyl glucopyranoside as an acceptor, only one regioisomer, namely p-nitrophenyl α-D-Glcp-(1,3)-α-L-Araf, was isolated using p-nitrophenyl arabinofuranoside as an acceptor. Interestingly, similar outcomes were found when using p-nitrophenyl galactofuranoside. Furthermore, activation by microwave irradiation resulted in faster reaction times and higher yields and led to glucosidic oligosaccharides with up to 70% conversion. The influence of the anomeric and C-4 configurations of the glycosidic acceptors on the transglycosylation, previously stated for the CGTase family, was not observed and unconventional substrate specificity towards alkyl furanosides was highlighted.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...