Sustainable polyacetals from isohexides†
Abstract
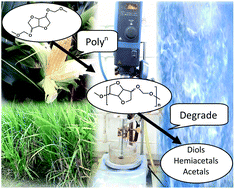
A single step synthetic protocol to access a small family of renewable diacetals was established. The resultant chiral diacetals are valuable building blocks in pharmaceuticals and materials science. To demonstrate their synthetic competence, isohexide-diacetals (2a–c) were subjected to acetal metathesis polymerization and the corresponding polymers (poly2a–c) were isolated as white solids with molecular weights in the range 3200–27 600 (g mol−1). The semi-crystalline polymers displayed glass transition temperatures between 38–65 °C and melting temperatures in the range 103–156 °C. The isohexide derived polyacetals are stable under practical washing and rinsing conditions but degrade in slightly acidic media.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...