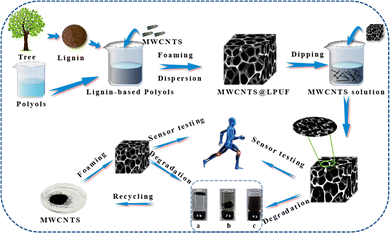
Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleFlexible, recyclable and sensitive piezoresistive sensors enabled by lignin polyurethane-based conductive foam†
Fan
Wang
ab,
Xiaozhen
Ma
bc,
Jialong
Wu
b,
Yeyan
Chao
b,
Peng
Xiao
 *b,
Jin
Zhu
b and
Jing
Chen
*b,
Jin
Zhu
b and
Jing
Chen
 *b
*b
aZhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, 310014, Zhejiang, China
bKey Laboratory of Bio-based Polymeric Materials Technology and Application of Zhejiang Province, Laboratory of Polymers and Composites, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo 315201, China. E-mail: chenjing@nimte.ac.cn
cUniversity of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100039, China
First published on 12th December 2022
Abstract
Flexible sensors are of great significance in wearable electronic devices. Herein, this work solves the problems of unfriendly and high cost materials and not easy to recycle conductive parts. Multi-functional conductive polyurethane (PU) foam has been constructed based on lignin, PU, and MWCNTs. Lignin is widely available and environmentally friendly, which endows polyurethane foam with degradable properties. The sensor exhibited excellent resistance change performance in the ultra-wide compression range from 0 to 90%. After 2000 cycles of compression test, the resistance change curve was still stable, and then the resistance returned to the initial value. The detection pressure was as high as 275.95 kPa. This sensor can detect a minimum deformation of 0.23%. The gauge factor 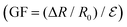 value is as high as 2.75 in the strain range of 30% to 60% of compression deformation. It does not change shape under 90% cyclic compression strain, and does not change micro surface morphology after washing in distilled water for 12 hours. The sensor can not only detect large-scale movements of human limbs and joints but also detect weak physiological activities such as mouth opening, swallowing, breathing, and pulse. At the same time, it has good repeatability and reproducibility for throat vibration caused by human pronunciation and for some non-contact movements (such as blowing and vibration). Finally, because MWCNTs@LPUF is degradable in an alkaline environment, MWCNTs can also be recycled and used. MWCNTs@LPUF sensors are environmentally friendly, recyclable, sensitive and have excellent environmental stability, enabling them to have great potential for future application in the fields of flexible wearable electronics and healthcare.
value is as high as 2.75 in the strain range of 30% to 60% of compression deformation. It does not change shape under 90% cyclic compression strain, and does not change micro surface morphology after washing in distilled water for 12 hours. The sensor can not only detect large-scale movements of human limbs and joints but also detect weak physiological activities such as mouth opening, swallowing, breathing, and pulse. At the same time, it has good repeatability and reproducibility for throat vibration caused by human pronunciation and for some non-contact movements (such as blowing and vibration). Finally, because MWCNTs@LPUF is degradable in an alkaline environment, MWCNTs can also be recycled and used. MWCNTs@LPUF sensors are environmentally friendly, recyclable, sensitive and have excellent environmental stability, enabling them to have great potential for future application in the fields of flexible wearable electronics and healthcare.
Introduction
The demand for wearable electronic products has increased, promoting the rapid development of flexible strain sensors over recent years.1–5 Flexible sensors can transform physical signals into measurable electrical signals. At present, the sensing mechanism of flexible sensors includes transistor sensing,6–8 capacitance sensing,9,10 piezoelectric sensing,11,12 and piezoresistive sensing mechanisms.13–15 A piezoresistance stress sensor works by measuring the resistance change16 of conductive materials, and as one of the most widely used strain sensors, piezoresistive strain sensors have attracted extensive attention due to the advantages of low cost and simple manufacturing.17–21 So far, the conductive materials of the piezoresistance stress sensor mainly include silicon metal oxides and semiconductors,22 thin films, colloids, foam and sponge. Traditional sensors based on silicon metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) have high sensitivity, but their rigidity is too strong to be suitable for flexible devices.23Recently, PU foams have been employed for nearly 60% of the production of PU products.24 Compared with thin films and colloids, PU foam has high compressibility, flexibility and a better elastic response rate. It is more suitable for the human body and microstructure colloid sensors that require good nanostructure design.25,26 With the exploration and development of compressible, flexible, biocompatible organic materials, they could be widely used in biomedical devices, such as flexible pressure array insoles, which can detect foot pressure during walking, and flexible dynamic pressure sensors on the wrist which can monitor the heartbeat and pulse information in real-time. Since piezoresistive stress sensors work by measuring the resistance change of conductive materials, it is necessary to combine foam with conductive components to make them have high conductivity. So far conductive components have mainly included multi-walled carbon nanotubes,27–30 graphene,31,32 conductive metals,33,34 carbon black,35,36 and MXenes37–40. There are three main ways to combine foam and conductive components to endow foam conductivity.
Zhang41et al., prepared a CA @ PU pressure resistance stress sensor through a simple dip-coating process. It exhibited excellent stability, repeatability, and durability even at high compression strains of up to 80%, and the sensor possessed a detection limit of as low as 0.2%. Zhao42et al., fabricated high-performance pressure sensors via constructing a unique conductive/insulating/conductive sandwich-like porous structure (SPS) and the interpenetration of the conductive graphene network throughout the porous insulating interlayer produces a highly efficient transition from the non-conductive to the conductive state; the SPS sensors exhibited an extreme resistance-switching behavior (resistance change of >105 at 30 kPa). Such SPS pressure sensors are applicable for detecting various mechanical deformation modes (pressing, bending and torsion). Guo43et al. embedded three-dimensional electrodes in a self-healing foam material; the foam material is mixed with conductive metal particles to improve the conductivity and can operate in both piezo-resistive and piezo-capacitive sensing modes to effectively resolve various proximity and mechanical interactions.
To summarize the above methods, we found that the conductive components prepared by impregnation or coating methods are unstable and vulnerable to environmental impact, resulting in the falling off of the conductive elements on the surface and exposing the internal non-conductive parts. Although the sensors obtained by the assembly method are acute, the assembly process is often complex, involving many cumbersome steps and materials. The sensors prepared by the embedding or mixing method are stable and sensitive, but the mechanical properties of the materials may become nonadjustable during the embedding or mixing process. Therefore, we hope to prepare a low-cost, high-sensitivity, stable, and environmentally friendly flexible pressure-sensitive conductive material to meet the needs of flexible sensors.
Lignin is a kind of nongrain biomass, which has attracted extensive attention due to its universal availability and low cost. And it is the second most abundant biopolymer resource in nature, next only to cellulose. The paper and pulp industry produces about 50 million tons of industrial lignin annually.44 However, the vast majority of lignin is not utilized and is just burned as a cheap fuel or stored in the form of waste residue, causing a great deal of energy wastage and a potential pollution threat to the environment. Because of the molecular structure with abundant hydroxyl groups, lignin can be a promising alternative to polyols in the synthesis of PU materials.45,46 Polyurethane foams are block copolymers obtained by the combination of di- or polyisocyanates and oligomeric hydroxy polyol components. Currently, most diisocyanates and polyols come from fossil resources and are nonrenewable. Lignin grafted with polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG-400) can replace some petroleum-based polyols, and can also enhance the compression modulus and elasticity of the polyurethane foam47 (this is because increasing the lignin content with the same amount of isocyanate leads to more polyurethane bonds and thus increases the compression modulus of the foam, and lignin itself contains a large number of aromatic structures which also act as stiff segments in the foam and play a reinforcing role (filler–matrix interactions also affect the mechanical properties of lignin-containing polyurethane foams).48 Meanwhile, more lignin would improve the dispersion of carbon nanotubes due to hydrogen bonding and π–π stacking between the carbon nanotubes and lignin.49
This work solves the problems of unfriendly and high cost materials and not easy to recycle conductive parts. Lignin from biomass was used to replace petroleum-based polyols to liquefy into lignin-based polyols, and subsequently, MWCNTs were introduced into the lignin-based polyols as conductive components because of their conductivity, large surface area and environmental stability,50,51 then the lignin-based polyols containing MWCNTs were ultrasonically dispersed for 30 min and mixed with HDI for foaming. MWCNTs were dip-coated in MWCNT solution to further enhance the electrical conductivity, and then washed in ethanol for 3 minutes after dip-coating and dried in an oven at 80 °C. The sensor made of this foam has high sensitivity, excellent mechanical properties, and outstanding environmental stability. It exhibits excellent resistance change performance in the ultra-wide compression range from 0 to 90%, the detection limit is as low as 3.64 Pa, and the gauge factor 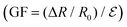 value is as high as 2.75 in the strain range of 30% to 60% of compression deformation. The MWCNTs@LPUF sensor is capable of detecting not only the large-scale movements of human limbs and joints, but also weak physiological activities such as mouth opening, swallowing, pulse and breathing. In addition, it has excellent repeatability and reproducibility for throat vibration caused by human pronunciation and also for some non-contact movements such as blowing and vibration. Finally, because lignin-based polyurethanes prepared using bio-based lignin, such as MWCNTs@LPUF, are degradable in alkaline environments, MWCNTs can also be recycled and used. The performance of the re-prepared sensor after recovery of MWCNTs is the same as that of the previous sensor. MWCNTs@LPUF sensors possess excellent cycling stability and environmental stability, and are simple to prepare, environmentally friendly, recyclable, and sensitive, exhibiting great potential for the future in the fields of flexible wearable electronics and healthcare.
value is as high as 2.75 in the strain range of 30% to 60% of compression deformation. The MWCNTs@LPUF sensor is capable of detecting not only the large-scale movements of human limbs and joints, but also weak physiological activities such as mouth opening, swallowing, pulse and breathing. In addition, it has excellent repeatability and reproducibility for throat vibration caused by human pronunciation and also for some non-contact movements such as blowing and vibration. Finally, because lignin-based polyurethanes prepared using bio-based lignin, such as MWCNTs@LPUF, are degradable in alkaline environments, MWCNTs can also be recycled and used. The performance of the re-prepared sensor after recovery of MWCNTs is the same as that of the previous sensor. MWCNTs@LPUF sensors possess excellent cycling stability and environmental stability, and are simple to prepare, environmentally friendly, recyclable, and sensitive, exhibiting great potential for the future in the fields of flexible wearable electronics and healthcare.
Experimental
Materials
Enzymatic lignin (EHL) extracted from corn cob was provided by Shandong Longli Biotechnology Co., Ltd, China, without further purification or chemical modification, and MWCNTs were obtained from Turing Evolution Technology Co., Shenzhen, China. Polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG-400), glycerol, concentrated sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide were purchased from China Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd, and hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and dibutyltin dilaurate (DBTDL) were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd, China.Fabrication of lignin-based polyols
In a three-port flask with a capacity of 500 mL, 160 g PEG-400 and 40 g glycerol were mixed evenly. Then 30% EHL (60 g) of mass (160 g PEG-400 + 40 g glycerol) and 15% (9 g) concentrated sulfuric acid were added, and finally heated in an oil bath to 140 °C and fed with nitrogen at constant speed of stirring for 1 h. After liquefaction, the three flasks were removed and the mixture was poured into a beaker to cool it to room temperature, and then the mixture was neutralized with an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of about 7. After liquefaction, water was removed from the rotary evaporator for 2 h to obtain brown lignin-based polyols.Fabrication of lignin-based polyurethane foam containing MWCNTs
One-step preparation of MWCNTs@LPUF using the polyurethane foam foaming method, 5% and 10% (mass of lignin-based polyols) MWCNTs were added to the mixture of lignin-based polyols, and ultrasonic treatment was carried out for 30 minutes to obtain a uniform mixture of lignin-based polyols containing MWCNTs. DBTDL (2 g) was added to the polyols as a catalyst and 0.3% (0.6 g) polyols as a foaming agent, and mixed for 10 minutes. HDI was added and stirred in a high-speed mixer (pay attention to the amount of MWCNTs introduced. MWCNTs have high thermal conductivity, and the temperature peak may lead to the failure of foam foaming), and when the mixture temperature was about 70 °C it was poured into the mold. It was found that the viscosity of polyols increased with the addition of more MWNTs, resulting in an incomplete reaction. When the content of MWCNTs exceeds 10%, the viscosity of polyols is too high, and the mechanical properties of the foam are poor, so it is not suitable for the preparation of sensors.Assembling the MWCNTs@LPUF sensor
1 g of MWCNTs dispersed in 200 ml ethanol solution was taken, the foam was soaked in the ethanol solution containing MWCNTs for three minutes, washed with ethanol solution and placed in the oven to dry. Then, the dried foam was taken out, the silver paste was applied on its upper surface, and placed in the oven at 80 °C to soften the silver paste for 5 minutes. After softening, two sheets of copper foil were used as parallel electrodes and placed on the softened silver paste on the foam surface, next the cured copper foil was stably fixed on the silver surface of the foam as the electrode. Finally two copper wires soldered on the copper foil were used to make the sensor.Characterization
Results and discussion
Chemical structure characterization
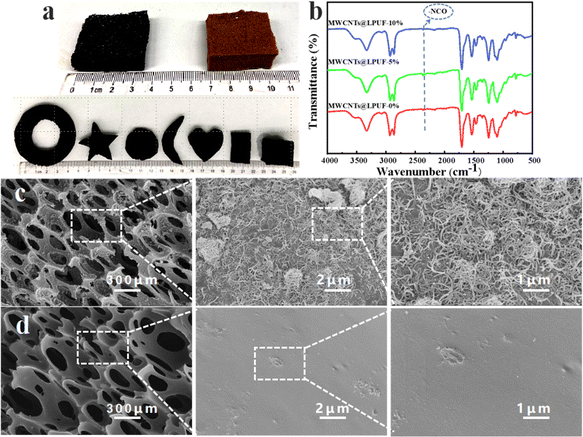
Preparation of the lignin-based polyurethane foam and the sensor is shown in Fig. 1. First, we start from the synthesis of foam and adopt the traditional polyurethane foam foaming method, 5% and 10% (mass of lignin-based polyols) MWCNTs were introduced in foam to build the conductive network. The MWCNTs in the foam continuously contact each other to form high conductivity. Then, a layer of MWCNT solution (5 mg mL−1) is dip-coated on the surface of the foam, further improving the electrical conductivity of the foam.We can see that after the introduction of MWCNTs, the lignin based polyurethane foam changes from brown without MWCNTs to black. At the same time, the foam can be easily cut into various shapes, such as rings, stars, hearts, moons, circles, rectangles and squares to meet different scenarios (Fig. 2a), MWCNTs@LPUF will change the contact spacing of MWCNTs because of its stretching, bending, or compression, thus changing the conductivity of MWCNTs@LPUF. Therefore, MWCNTs@LPUF can be used as a piezoresistive strain sensor.
In FT-IR spectroscopy (Fig. 2b), the spectra of different contents of MWCNTs foam were almost the same, because MWCNTs have almost no peaks or are very weak in the FT-IR spectra. The peaks at 2928 cm−1 and 2860 cm−1 are due to the tensile vibration of C–H. The tensile vibration of C–O–C at the 1102 cm−1 peak is because of PEG-400. The broad peak at 3525 cm−1 is due to the tensile vibration of the –OH group here. The peak at 3330 cm−1 is the extended vibration of N–H because of the polyurethane bond. The peak at 1700 cm−1 is due to the stretching of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O in the amide. While the peaks at 1530 cm−1 and 1240 cm−1 are due to the stretching of C
O in the amide. While the peaks at 1530 cm−1 and 1240 cm−1 are due to the stretching of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O in the amide, urea, and ether groups, –NCO is an asymmetric scaling vibration peak at 2260–2280 cm−1. The peak of –NCO has disappeared, indicating that the reaction has been completed.
O in the amide, urea, and ether groups, –NCO is an asymmetric scaling vibration peak at 2260–2280 cm−1. The peak of –NCO has disappeared, indicating that the reaction has been completed.
Microstructures and compressive properties
A scanning electron microscope was used to watch the microscopic surface morphology of the foam we prepared, the higher the content of MWCNTs introduced during the foaming process, the higher the amount of MWCNTs adsorbed by the foam wall and the foam skeleton, the higher the content of MWCNTs and the higher the electrical conductivity and the more sensitive the sensor. Based on the dipping under the same conditions, the lignin-based polyurethane foam without MWCNTs in the foaming process found only a small amount of MWCNTs. The 10% MWCNTs@LPUF containing higher MWCNTs than the 5% MWCNTs@LPUF is shown in Fig. 2c and Fig. S1 (ESI†), so it was chosen as the sensitive element of the sensor. The introduced lignin can improve the compression modulus of foam, 10% MWCNTs@LPUF showed no change in shape at 50 compression cycles with a strain of 90%, indicating that the foam had good compression properties (Fig. S2, ESI†).Resistance properties
Then we conducted the conductivity experiment (Fig. S3, ESI†) by placing MWCNTs@LPUF in a small light bulb circuit and slowly pressing MWCNTs@LPUF with a laboratory glass rod. As the pressure increased, the blue glowing area increased indicating that the small light bulb gradually became brighter, so we guessed from this small experiment that when the deformation of MWCNTs@LPUF would change, the foam inside the MWCNTs will be arranged more closely as shown in the Fig. 3a–c, the circuit will be connected, and the resistance will decrease. To verify this experiment, MWCNTs@LPUF was tested for resistance change. The machine adjusted the compression shape of the foam to 90%, and as the pressure slowly increased, the compression deformation increased from 0% to 90%, so that the resistance change curve could be obtained. As shown in Fig. 3d, the resistance decreases with the increase of compressive deformation. Therefore, MWCNTs@LPUF foam has better advantages over thin-film sensors to detect various simulated compressional deformations, which are difficult to achieve with thin-film piezoresistive strain sensors. | ||
Fig. 3 Conductivity testing of MWCNTs@LPUF undergoing different deformations. (a) Region “I” (compression strain 0–30%), (b) Region “II” (compression strain 30–60%), (c) Region “III”(compression strain 60–90%), (d) the change of resistance and gauage factor (GF), (e) current curves under different compression deformation, (f) comparison with GF values of other foams at 0% to 30% compressional deformation (the region“I”), (g) comparison with GF values of other foams at 30% to 60% compressional deformation (the region“II”),52–57 and (h) reproducibility test of a MWCNTs@LPUF for 2000 cycles at 40% compression strain, resistance change at time from 2000 s to 2200 s, 8000 s to 8200 s, 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800 s to 16 800 s to 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 s. 000 s. | ||
The GF of the device is defined as the gauge factor (GF)
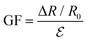 | (1) |
 represents the instantaneous resistance change, original resistance, and compression strain, respectively), the strain sensor showed different GF at different strains.
represents the instantaneous resistance change, original resistance, and compression strain, respectively), the strain sensor showed different GF at different strains.
In Fig. 3d, we can see that there are three regions of GF, 0.60 for 0–30%, 2.75 for 30–60%, and 0.54 for 60–90%. Here we propose a conjecture as shown in Fig. 3a–c, in region “I” as shown in Fig. 3a, compression strain under 0–30% is a “point to point” contact (mutual contact between few MWCNTs and few MWCNTs), so the change of resistance is not particularly obvious and thus the GF value is low. Region “II” is shown in Fig. 3b, 30–60% compression strain, from the “point to point” contact in the “I” region to “surface to surface” contact (between the skeleton surface of the foam and the foam wall surface), the change of GF also verifies our conjecture from 0.60 in region “I” to 2.75 in region “II”. A comparison of the GF value in region “I” and “II” with other foams shows a particularly good performance of our material, as shown in Fig. 3f and g, due to the introduction of MWCNTs by the foaming method. Because MWCNTs have an excellent dispersion inside the foam, it makes the GF value high, and then the GF drops to 0.54 after compressive strain increases from 60% to 90%, probably because the “surface to surface” contact is complete so the change in resistance tends to be stable, resulting in a smoother GF. Then, we tested the current change of foam under compression deformations, as shown in Fig. 3e. The ratio of current is relatively stable under the same compression deformation, and the ratio of current also increases with the increase of compression deformation, which indicates that our foam can detect the compression deformation of foam caused by objects with different masses. The conductive stability and reproducibility of the MWCNTs@LPUF were tested further. As shown in Fig. 3h, we selected the resistance response curves from the 2000 s to 2200 s, 8000 s to 8200 s, and 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 s to 15
000 s to 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 s in 2000 loading and unloading cycles at 40% compression strain, and the comparison shows that the resistance response curves in different periods are almost the same, and the resistance change increases with the increase of compressive strain and decreases with the decrease of compressive strain, then the resistance returns to the initial value. This is attributed to our foam possessing excellent compression stability performance.
200 s in 2000 loading and unloading cycles at 40% compression strain, and the comparison shows that the resistance response curves in different periods are almost the same, and the resistance change increases with the increase of compressive strain and decreases with the decrease of compressive strain, then the resistance returns to the initial value. This is attributed to our foam possessing excellent compression stability performance.
Properties of the MWCNTs@LPUF sensor
The MWCNTs@LPUF were made into wearable piezoresistive strain sensors and connected to the electrochemical workstation, using the MWCNTs@LPUF sensors to pre-detect the mass size of different objects, placing the plastic sample bottle cap on the sensor and then picking up (Fig. S4a, ESI†) because the 4 g plastic sample bottle causes a small compressive deformation of the foam, thus decreasing the resistance, when the plastic sample bottle cap is picked up, the compression deformation recover and the contact spacing of MWCNTs increases thus the resistance increases, the electrochemical workstation is set to a constant voltage, the resistance increases so the current decreases, as shown in the current curve in Fig. S4 (ESI†). Our sensor can also detect smaller masses as shown in (Fig. S4b, ESI†). Four sheets of filter paper of length and width 1.7 cm × 1.7 cm are placed on the MWCNTs@LPUF sensor, and the change in the current curve is recorded for the sensor detecting a 1 g mass of the object. From Fig. S4b (ESI†), we found that the change in the current generated by 1 g of paper is recorded, sensor detects a weak compression deformation, a weak decrease in contact spacing of the MWCNTs, thereby decreasing the resistance and increasing the current.According to the pressure formula:
| P = F/S | (2) |
| F = G = m g | (3) |
We put a leaf on the sensor to calculate the response time of the sensor, and the calculated response time is 0.036 s (Fig. S5a, ESI†). The pressure sensitivity “S” can be defined as the slope of curves in Fig. S5b, ESI† (S = (ΔI/I0)/δP, where P denotes the applied pressure),41 which also shows that our sensors have excellent response and sensing performance. Meanwhile, we test the frequency of loading/unloading at 0.2 Hz, 0.5 Hz, 1 Hz, and 2 Hz (Fig. S6, ESI†). The stability of the curve in the graph shows good repeatability of our sensors at different rate frequencies.
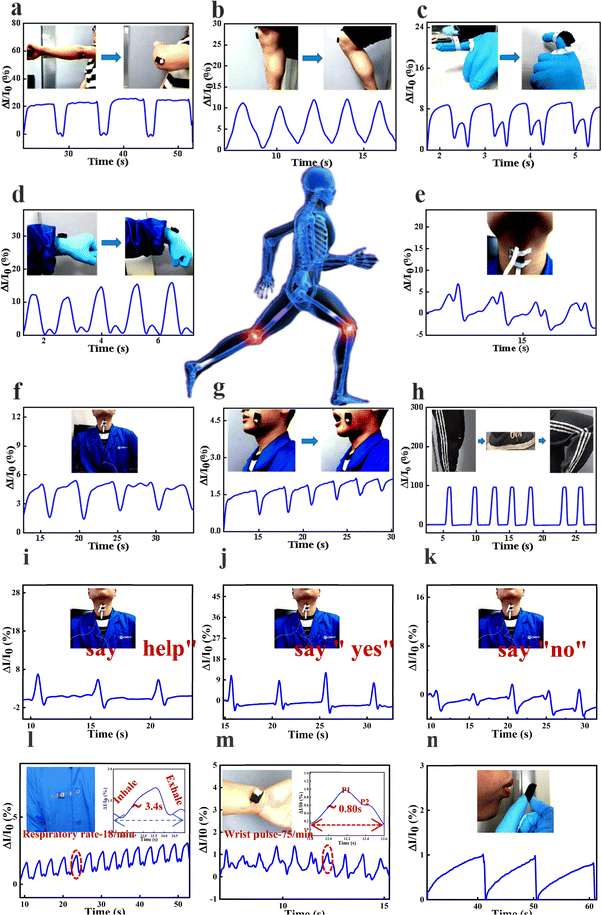
The MWCNTs@LPUF sensors were attached to the body to detect the physiological movements of the human body. First, we test the large range of limb movements of the human body (Fig. 4a and b), and we connect the elbow and knee of the human body in turn. The images reveal that the MWCNTs@LPUF sensor detects physical changes in the elbow and knee flexion. The elbow and knee possess different current curves from each other but are almost the same relative to themselves, so the MWCNTs@LPUF sensor has excellent responsiveness and repeatability to physical changes in the limbs. At the same time, if we attach the sensor to the bottom of the foot it can also monitor the walking movement (Fig. 4h). The MWCNTs@LPUF sensor then connects to the fingers and wrists (Fig. 4c and d), and like the limbs, the MWCNTs@LPUF sensor also picks up the changes in the current profile due to physical changes in the finger and wrist flexion. The MWCNTs@LPUF sensor can not only detect a wide range of limb and joint movements but also some small physiological signals (Fig. 4e–g). We connect the sensor to the throat knot, cheek, and abdomen to detect the physiological movement of coughing, swallowing, mouth opening, and breathing. When coughing, swallowing, mouth opening, and breathing, the mouth, cheek, laryngeal node, and abdomen can slightly squeeze the sensor and soles of the feet, resulting in slight compression deformation of the foam and the change of resistance. Therefore, it can be seen from the figure that our sensor can record these small physiological activities and have good repeatability and reproducibility of these small physiological activities.
When the sensor was placed on the throat for testing, the experimenter says “help”, “yes”, or “no”, and the sensor can record the vibrations of the vocal folds. indicating that our sensor can record the vibrations of human vocal folds and has excellent responsiveness and reproducibility to them as shown in Fig. 4i–k. The MWCNTs@LPUF sensor can also monitor some pivotal and weak signals of human physiological activity (Fig. 4l and m). With the change of time, our sensor can record the current variation of respiration and pulse well, where the respiration curve can be divided into inhaling and exhaling, with a time interval of about 3.4 s, about 18 times per minute, and the current curve of the pulse can be divided into systolic and diastolic peaks, noted as P1 and P2, with a time interval of about 0.80 s, 75 times per minute. Together, these tests show that our sensors have excellent reproducibility and repeatability for the weak physiological activities of the human body, suggesting that our sensor could have potential for medical health applications. Our sensors can also detect motion that is not in direct physical contact as shown in Fig. 4n and Fig. S7 (ESI†), this also shows that our sensors can also be used for some specific applications, such as detecting the size of the wind, the frequency of object vibration, etc.
Stability, recycling, and degradation properties of the MWCNTs@LPUF sensor
Since MWCNTs@LPUF was prepared by introducing MWCNTs into the polyurethane foam by the foaming method, it has excellent environmental stability. We washed MWCNTs@LPUF with distilled water for 12 hours and then analyzed their micro-surface morphology before and after 12 hours by SEM comparison. As shown in (Fig. 5a and b), the distilled water solution in the sample bottle was still limpid after 12 hours of washing, and the foam hardly changed its morphology and micro-surface morphology, indicating excellent environmental stability of the foam. The foam dried after 12 hours of rinsing was again assembled into the sensor for a simple wrist test as shown in Fig. 5d and e, and the current curve was almost the same, indicating that our sensor also has excellent environmental stability.We also prepared polyurethane foam MWCNTs@LPUF without the introduction of lignin, and compared the human wrist test for MWCNTs@PUF and MWCNTs@LPUF sensors. The comparison results showed that the changes of current curves were approximately the same (Fig. 5c and d), and the introduction of lignin did not significantly change the sensing performance of the sensors, but MWCNTs@LPUF could be degraded, and MWCNTS could be recycled and reused. The schematic diagram of degradation, recycling and reuse is shown in Fig. 5f. Since the lignin-based polyurethane foam was prepared using biomass lignin, MWCNTs@LPUF is degradable under an alkaline environment, as shown in Fig. S8 (ESI†). Moreover, MWCNTs@LPUF with high content of MWCNTs has the ability to be recycled. We used methanol mixed with 0.5 mol L−1 sodium hydroxide solution to degrade MWCNTs@LPUF. A piece of foam with a mass of 0.075 g was placed in a sample bottle and then dried in an oven at 60 °C, and showed complete degradation after 6 hours. The degradation efficiency was 88.98%, and the residue after degradation was identified as MWCNTs by SEM as shown in Fig. 5g.
The recycled MWCNTs were reused to make MWCNTs@LPUF, and the MWCNTs@LPUF sensors were tested for knee flexion (Fig. 5h), vocal cord vibration (Fig. 5i), and pulse rate (Fig. 5j) in turn. The knee joint flexion and vocal cord vibration tests are almost the same as the previous curves, and the current pulse curve is slightly different, but the occurrence of systolic and diastolic peaks (P1, P2) when the current curve is amplified indicated the same pulse beat curve as before. It is worth noting that, possibly because the experimenter is in a different physical state, the time interval of this peak is 0.83 compared with the previous time interval S (about 72 times per minute), but it is also consistent with the heart rate of normal adult males. Therefore, from the results, our foam has excellent degradation properties so that MWCNTs can be recycled and reused.
Conclusions
In conclusion, MWCNTs@LPUF foam was easily prepared using a combination of traditional polyurethane foam foaming and dip-coating methods, which show excellent resistance to changes in compressive strain from 0% to 90% and remains stable for 2000 repetitive cycles, with GF up to 2.75 in the range of 30–60% compressive strain. The sensor can detect pressure as low as 3.64 Pa, and a minimum deformation of 0.23%, and can be worn on the human body to detect not only a wide range of movements of limbs and joints, but also some weak physiological signals such as mouth opening, swallowing, breathing, pulse, and also some non-contact movements such as blowing and vibration. After 12 hours of washing, the microscopic surface morphology remains unchanged, and the lignin of biomass endows the foam with degradable properties so that MWCNTs can be recycled. The performance of the re-prepared sensor after recovery of MWCNTs is the same as that of the previous sensor. This kind of sensor with a simple fabrication process, stable cycling performance, high sensitivity, environmentally friendly nature, low-cost materials and recyclability may have great potential in the fields of flexible electronics and medical health.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFE0102300), the S&T Innovation 2025 Major Special Program of Ningbo (2022Z139), the STS Project of Fujian-CAS (2021T3050, 2022T3049) and the Open Research Projects of Zhejiang Lab (No. 2022MG0AB01) is gratefully acknowledged.Notes and references
- X. Liu, Science, 2020, 370, 910 CrossRef.
- C. Tan, Z. Dong, Y. Li, H. Zhao, X. Huang, Z. Zhou, W. Jiang, Y. Z. Long, P. Jiang, T. Y. Zhang and B. Sun, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 3530 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Gao, L. Chao and M. Hou, npj Flex. Electron., 2019, 1, 1 Search PubMed.
- C. Zhu, A. Chortos, Y. Wang, R. Pfattner, T. Lei, A. C. Hinckley, I. Pochorovski, X. Yan, J. W. F. To, J. Y. Oh, J. B. H. Tok, Z. Bao and B. Murmann, Nat. Electron., 2018, 1, 183 CrossRef.
- Z. F. Liu, S. Fang, F. A. Moura, J. N. Ding, N. Jiang, J. Di, M. Zhang, X. Lepró, D. S. Galvao, C. S. Haines, N. Y. Yuan, S. G. Yin, D. W. Lee, R. Wang, H. Y. Wang, W. Lv, C. Dong, R. C. Zhang, M. J. Chen and Q. Yin, Science, 2015, 349, 400 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Voorthuyzen, A. P. Bergveld and A. J. Sprenkels, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 1989, 2, 267 CrossRef.
- T. Someya, T. Sekitani and S. Iba, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, 27, 9966 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. B. Chang, V. Liu and V. Subramanian, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 1, 79 Search PubMed.
- C. Metzger, E. Fleisch and J. Meyer, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 1, 41 Search PubMed.
- C. H. Mastrangelo, X. Zhang and W. C. Tang, J. Microelectromech. Syst., 1996, 2, 98 CrossRef.
- I. Lee and H. J. Sung, Exp. Fluids, 1999, 1, 27 CrossRef.
- A. V. Shirinov and W. K. Schomburg, Sens. Actuators, A, 2008, 1, 48 CrossRef.
- M. Hussain, Y. H. Choa and K. Niihara, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2001, 6, 525 CrossRef.
- T. Yamada, Y. Hayamizu and Y. Yamamoto, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2011, 5, 296 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. G. King, A. J. Baragwanath and M. C. Rosamond, Procedia Chem., 2009, 1, 568 CrossRef.
- L. Zhao, F. Qiang and S. W. Dai, Nanoscale, 2019, 21, 10229 RSC.
- A. D. Smith, F. Niklaus, A. Paussa, S. Schröder, A. C. Fischer, M. Sterner, S. Wagner, S. Vaziri, F. Forsberg, M. D. Stling and M. C. Lemme, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 9879 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Zhang, C. Wang, H. Wang, M. Jian, X. Hao and Y. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1604795 CrossRef.
- Y. Yue, N. Liu, W. Liu, M. Li, Y. Ma, C. Luo, S. Wang, J. Rao, X. Hu, J. Su, Z. Zhang, Q. Huang and Y. Gao, Nano Energy, 2018, 50, 79 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Pang, X. Song, Z. X. Xu, Y. Liu, L. Zhong, Y. Peng, J. Wang, J. Zhou, F. Meng, J. Wang and C. Gao, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eabd4045 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Gagliardi, M. Salza, S. Avino, P. Ferraro and P. De Natale, Science, 2010, 330, 1081 CrossRef CAS.
- H. B. Yao, J. Ge and C. F. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 6692 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wu, Y. Han and X. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 6246 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Mahmood, Z. Yuan and J. Schmidt, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2016, 60, 317 CrossRef CAS.
- S. C. B. Mannsfeld, B. C. Tee and K. R. M. Stoltenberg, Nat. Mater., 2010, 10, 859 CrossRef.
- H. Wang, R. Zhou and D. Li, ACS Nano, 2021, 6, 9690 CrossRef.
- S. Y. Hong, J. H. Oh and H. Park, NPG Asia Mater., 2017, 11, 448 CrossRef.
- S. Sukhwinder, D. Jyotirmoy, K. Suresh, S. Utpal and S. Sandeep, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2022, 3, 3913 Search PubMed.
- D. Fan, Z. Ge, C. Chenpu, J. Shu, T. Hao, T. Liang and M. Ming, ACS Appl. Electron. Mater., 2021, 2, 761 Search PubMed.
- L. Meng, J. Dai and S. Rong, Appl. Biochem., 2021, 6, 1192 Search PubMed.
- C. Wu, X. Huang, X. Wu, R. Qian and P. Jiang, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 5658 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Chen, W. Ren and L. Gao, Nat. Mater., 2011, 6, 424 CrossRef.
- Y. Z. Yu, J. Chen, C. Z. Xie, R. Guo, Z. Liu and Z. Zheng, Adv. Mater., 2013, 5, 810 CrossRef.
- Y. M. Choi, S. Y. Cho, D. Jang, H. J. Koh, J. Choi, C. H. Kim and H. T. Jung, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1808319 CrossRef.
- J. Zhang, T. Zhou and J. Zhao, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2015, 11, 41644 Search PubMed.
- M. Pruvost, W. J. Smit and C. Monteux, npj Flex. Electron., 2019, 1, 1 Search PubMed.
- Y. Ma, N. Liu and L. Li, Nat. Commun., 2017, 1, 1 Search PubMed.
- X. P. Li, Y. Li and X. Li, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 542, 54 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Bandar, R. M. Weissing, M. Wilhelm, Y. Demidov, J. Auer, S. Ghazanfari and H. Maleki, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 29, 34996 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Zhu, J. Liu and T. Guo, ACS Nano, 2021, 1, 1465 CrossRef.
- S. Zhang, H. Liu and S. Yang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 10922 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Zhao, F. Qiang and S. W. Dai, Nanoscale, 2019, 21, 10229 RSC.
- H. Guo, Y. J. Tan and G. Chen, Nat. Commun., 2020, 1, 1 Search PubMed.
- B. M. Upton and A. M. Kasko, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 2275 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Laurichesse and L. Avérous, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2014, 7, 1266 CrossRef.
- N. Mahmood, Z. Yuan and J. Schmidt, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2016, 60, 317 CrossRef.
- S. Wang, W. Liu and D. Yang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2018, 1, 496 Search PubMed.
- H. W. H. G. Engels and A. R. Pirkl, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 36, 9422 CrossRef.
- X. Ma, C. Zhang, P. Gnanasekar, P. Xiao, Q. Luo, S. Q. Li, D. D. Qin, T. Chen, J. Chen, J. Zhu and N. Yan, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 415, 128956 CrossRef.
- S. Abdulla, T. L. Mathew and B. Pullithadathil, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, 221, 1523 CrossRef.
- A. Abodurexiti, C. Yang and X. Maimaitiyiming, Macromol. Mater. Eng., 2020, 7, 2000181 CrossRef.
- H. Park, J. W. Kim, S. Y. Hong, G. Lee, D. S. Kim, J. H. Oh, S. W. Jin, Y. R. Jeong, S. Y. Oh, J. Y. Yun and J. S. Ha, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 33, 1707013 CrossRef.
- Z. Sang, K. Ke and I. Manas-Zloczower, Small, 2019, 45, 1903487 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Cheng, B. Wang, Y. S. Tan, Y. J. Yin and C. X. Wang, Macromol. Mater. Eng., 2021, 5, 2000772 CrossRef.
- Y. Fei, F. Chen and W. Fang, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2021, 38, 13103 RSC.
- X. Wang, H. Li and T. Wang, RSC Adv., 2022, 22, 14190 RSC.
- C. S. Boland, U. Khan and M. Binions, Nanoscale, 2018, 11, 5366 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ma00960a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |