Themed collection Journal of Materials Chemistry B Emerging Investigators

Journal of Materials Chemistry B profiles: Contributors to the Emerging Investigators 2017 issue
Journal of Materials Chemistry B profiles: Contributors to the Emerging Investigators issue.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4259-4265
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB90077E
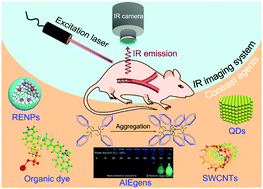
Advancements in infrared imaging platforms: complementary imaging systems and contrast agents
Recent advancements in the design of complementary infrared (IR) fluorescence imaging systems and IR-emitting contrast agents are highlighted. The ability to maximize the full performance of any IR imaging platform relies on the thorough understanding of the requirements of the imaging system and physical characteristics of the complementary contrast agents.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4266-4275
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00123A
Interactions of organic nanoparticles with proteins in physiological conditions
The efficacy of nanoparticles in biomedical applications is strongly influenced by their ability to bind proteins onto their surface. The analysis of organic nanoparticles interacting with proteins in physiological conditions may help in the successful design of next generation nanoparticles with improved biodistributions and therapeutic performances.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4393-4405
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00146K
Nanoscale silicon for subcellular biointerfaces
Semiconductor nanomaterials are emerging as a class of materials that can push the fundamental limits of current biomedical devices and possibly revolutionize healthcare.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4276-4289
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00151G
Optical nanoprobes for biomedical applications: shining a light on upconverting and near-infrared emitting nanoparticles for imaging, thermal sensing, and photodynamic therapy
Shining a light on spectrally converting lanthanide (Ln3+)-doped nanoparticles: progress, trends, and challenges in Ln3+-nanoprobes for near-infrared bioimaging, nanothermometry, and photodynamic therapy.
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4365-4392
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00403F
Cultured cell-derived decellularized matrices: a review towards the next decade
Summary of recent progress in cell-derived decellularized matrices preparation and application, with perspectives towards the next decade.
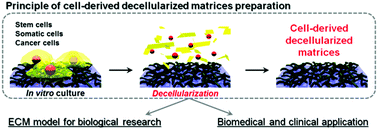
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4322-4331
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00074J
Peptides for tumor-specific drug targeting: state of the art and beyond
This review outlines the most recent advances in peptide-mediated tumor-targeting and gives insight into the direction of the field.
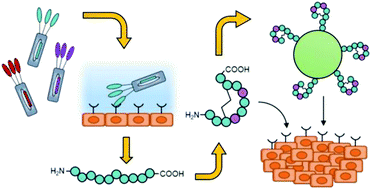
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4348-4364
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00318H
Activatable probes for diagnosis and biomarker detection by MRI
This review describes the strategies employed and the mechanisms behind both 1H and 19F-MRI based activatable probes for diagnosis and biomarker detection.
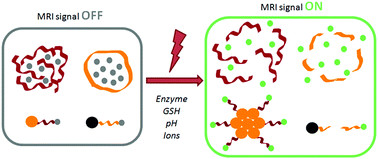
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4332-4347
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00093F
Thermo-responsive polymers and their application as smart biomaterials
This review summarises smart thermo-responsive polymeric materials with reversible and ‘on–off’ remotely switchable properties for a wide range of biomedical and biomaterials applications.
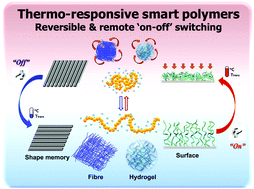
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4307-4321
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00157F
Physical principles of graphene cellular interactions: computational and theoretical accounts
Clarifying the physical principles of graphene cellular interactions is critical for the wider application of graphene-based nanomaterials in nanomedicine. This review highlights the advances in computational and theoretical accounts for this emerging field.
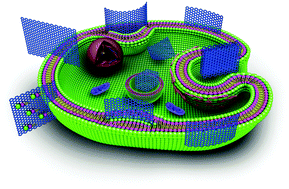
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4290-4306
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03310E
Biocompatible pH-responsive nanoparticles with a core-anchored multilayer shell of triblock copolymers for enhanced cancer therapy
pH-Responsive drug nanocarriers were made via facile self-assembly, showing excellent stability in bio-media (50% PBS/FBS) and enhanced drug efficacy towards cancer cells.
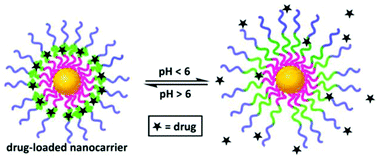
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4421-4425
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00654C
Single-molecule study of the synergistic effects of positive charges and Dopa for wet adhesion
Using AFM based single-molecule force spectroscopy, we studied the synergy between Dopa and lysine for wet adhesion on titania (TiO2) and mica surfaces.
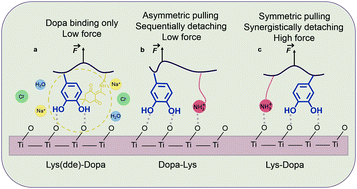
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4416-4420
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00131B
Janus nanoparticles for T cell activation: clustering ligands to enhance stimulation
Janus nanoparticles displaying clustered ligands enhance T cell activation by increasing the local surface density of ligand stimuli.
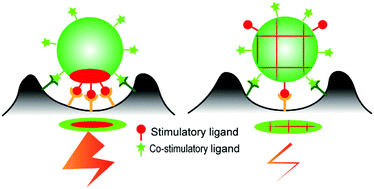
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4410-4415
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00150A
Near-infrared absorbing amphiphilic semiconducting polymers for photoacoustic imaging
Near-infrared (NIR) absorbing amphiphilic semiconducting polymers with absorption maximum at 804 nm were designed and synthesized. This polymer can spontaneously self-assemble into homogeneous water-soluble nanoparticles in aqueous solution and efficiently convert photon energy into heat, allowing for photoacoustic imaging of tumor in living mice.
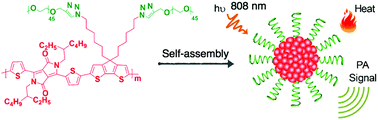
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4406-4409
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03393H
Covalently-controlled drug delivery via therapeutic methacrylic tissue adhesives
Therapeutic methacrylic (TMA) monomers lend local, covalently-controlled release of therapeutics, tunable mechanical properties, and increased cytocompatibility to cyanoacrylate medical adhesives.
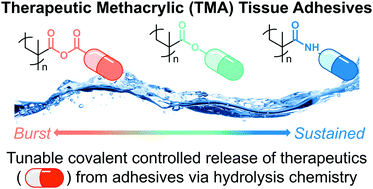
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 7743-7755
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB01151B
The effect of hyperbranched poly(acrylic acid)s on the morphology and size of precipitated nanoscale (fluor)hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite and fluorhydroxyapatite (F)HA nanoparticles were synthesised in the presence of branched poly(acrylic acid)s and compared to those synthesised in the presence of linear PAA.

J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 6027-6033
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00144D
ZnO nanoparticles as an antimicrobial tissue adhesive for skin wound closure
A solution of zinc oxide nanoparticles was explored as an antimicrobial tissue adhesive for skin wound closure.
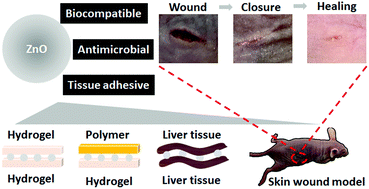
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4535-4541
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00664K
New design of hydrogels with tuned electro-osmosis: a potential model system to understand electro-kinetic transport in biological tissues
A series of charged polymer gels with precisely controlled magnitude and direction of electro-osmotic flow was prepared and opens up the possibility for understanding the contribution of electro-osmosis to transport phenomenon in native biological tissues.
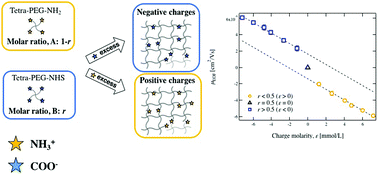
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4526-4534
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00064B
Crystallization and sintering of borosilicate bioactive glasses for application in tissue engineering
Typical silicate bioactive glasses are known to crystallize readily during the processing of porous scaffolds. New borosilicate bioactive glass can be sintered without significant sign of crystallization.
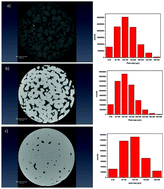
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4514-4525
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00106A
Electrochemical deposition of dopamine–hyaluronic acid conjugates for anti-biofouling bioelectrodes
Electrochemical deposition of dopamine-hyaluronic acid conjugates onto electrode surfaces can lead to preserved electrochemical activities and anti-biofouling properties of the electrodes.
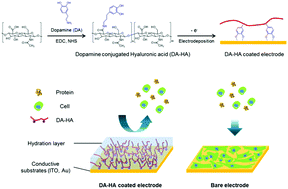
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4507-4513
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00028F
Drawing in poly(ε-caprolactone) fibers: tuning mechanics, fiber dimensions and surface-modification density
This work describes the complex interplay between mechanical manipulation of coextruded fibers and the resulting photochemical yield of surface modification.
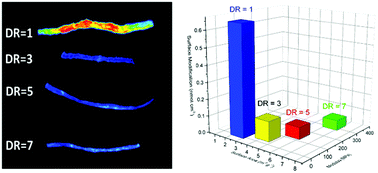
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4499-4506
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00096K
Photomediated oxime ligation as a bioorthogonal tool for spatiotemporally-controlled hydrogel formation and modification
Biocompatible, synthetic hydrogels were formed and modified by photomediated oxime ligation with full spatiotemporal control.
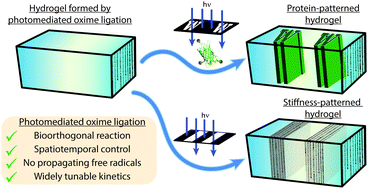
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4435-4442
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03400D
Tunable delayed controlled release profile from layered polymeric microparticles
Solvent evaporation parameters and ethanol content during PLGA/PLLA microparticle (MP) fabrication affect protein distribution and MP structure, thereby altering the protein release profiles.
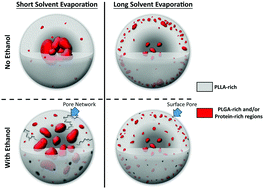
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4487-4498
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00138J
A comparison study to investigate the effect of the drug-loading site on its delivery efficacy using double hydrophilic block copolymer-based prodrugs
Two types of thermo-sensitive DHBCs-based micelle prodrugs with drug tethered to the hydrophilic shell or encapsulated with the hydrophobic core was fabricated, and compared further for their drug delivery efficacy.
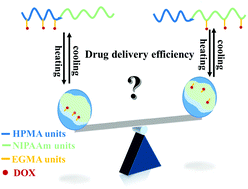
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4443-4454
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00261K
Understanding the functional properties of bio-inorganic nanoflowers as biocatalysts by deciphering the metal-binding sites of enzymes
The biomineralisation of metal phosphates is a promising approach to develop more efficient nanobiocatalysts; elucidating which protein regions most likely participate in the mineral formation will guide the fabrication of more efficient biocatalysts based on metal-phosphate nanoflowers.
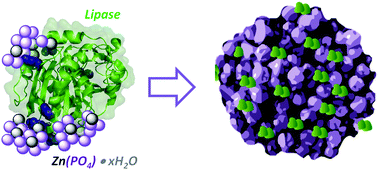
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4478-4486
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03295H
Hydrazone-modulated peptides for efficient gene transfection
The synthetic potential of dynamic bond formation is introduced for the delivery of plasmid DNA by modulated amphiphilic peptides. The synthetic advantage of these dynamic bonds allowed the identification of improved reagents (better efficiency and lower toxicity) for plasmid transfection assays in human HeLa cells.
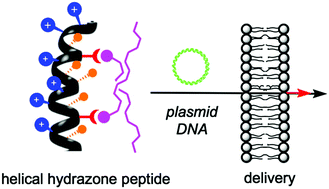
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4426-4434
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00179G
One-pot synthesis of redox-triggered biodegradable hybrid nanocapsules with a disulfide-bridged silsesquioxane framework for promising drug delivery
Redox-triggered biodegradable hybrid nanocapsules with the disulfide-bridged silsesquioxane framework were developed for promising drug delivery.
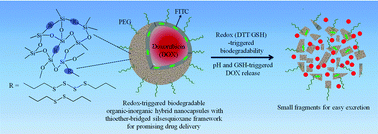
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4455-4469
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03368G
GSH-triggered size increase of porphyrin-containing nanosystems for enhanced retention and photodynamic activity
We demonstrate the rational design of a size changeable nanosystem triggered by intracellular GSH for enhanced retention and photodynamic activity.
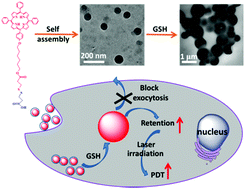
J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017,5, 4470-4477
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00063D
About this collection
Journal of Materials Chemistry B is proud to present this themed issue highlighting 2017’s rising stars of materials chemistry research. This issue gathers the very best work from materials chemists in the early stages of their independent career.
Each contributor was recommended by experts in their fields as carrying out work with the potential to influence future directions in materials chemistry. Congratulations to all of those who feature on their important work so far in the field of materials for biology and medicine.