Themed collection Materials for biosurfaces

Front cover

Inside front cover

Materials for biosurfaces
Guest editors Christian Ohm, M. Elizabeth Welch and Christopher K. Ober introduce this Journal of Materials Chemistry themed issue on Materials for biosurfaces.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19343-19347
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM90126A
Biomimetic functionalization of porous substrates: towards model systems for cellular membranes
Herein we present applications for arrays of nano- to micrometre sized pores in membrane research and as biosensors.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19348-19356
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31737K
Switchable adhesion by chemical functionality and topography
This feature article discusses recent advances of “smart” adhesives with reversibly switchable adhesion properties controlled by chemical modification or surface topography.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19390-19401
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31747H
Cell and cell sheet recovery from pNIPAm coatings; motivation and history to present day approaches
A comprehensive review highlighting the major developments of thermoresponsive cell platforms in regenerative culture.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19376-19389
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31748F
Utilizing click chemistry to design functional interfaces through post-polymerization modification
Post-polymerization modification using click chemistry is highlighted in this feature article as an effective method to add complex functionality to a polymeric interface.
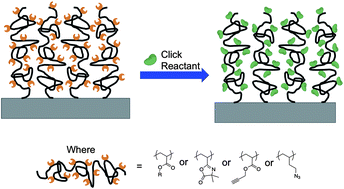
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19357-19365
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31708G
Biomimetic 3D self-assembling biomicroconstructs by spontaneous deformation of thin polymer films
The manuscript overviews recent advance in the development and application of wrinkling, creasing and folding polymer films in biotechnology.
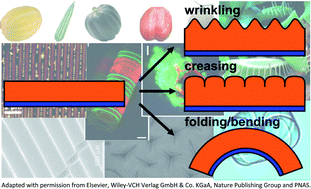
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19366-19375
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31643A
Photocrosslinkable dextran hydrogel films as substrates for osteoblast and endothelial cell growth
Functional hydrogel films on solid supports are versatile materials with large potential for cell growth and tissue engineering.
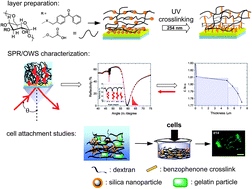
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19590-19604
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM34006B
It takes walls and knights to defend a castle – synthesis of surface coatings from antimicrobial and antibiofouling polymers
A novel bifunctional material consisting of a poly(oxonorbornene)-based antibiofouling poly(zwitterion) grafted onto a surface-immobilized poly(oxonorbornene)-based antimicrobial polymer network is presented.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19579-19589
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31695A
Reversible swelling of chitosan and quaternary ammonium modified chitosan brush layers: effects of pH and counter anion size and functionality
We describe the swelling behaviour of chitosan and quaternary ammonium modified chitosan brush layers depending on degree of substitution of quaternary ammonium salts, pH, and counter-anion type using a quartz-crystal microbalance with dissipation.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19605-19616
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM34316A
A covalently modified hydrogel blend of hyaluronan–methyl cellulose with peptides and growth factors influences neural stem/progenitor cell fate
Conjugation of platelet-derived growth factor-A and a cell-adhesive peptide to an injectable hydrogel increases neural stem cell differentiation into oligodendrocytes, for ultimate application in cell delivery.
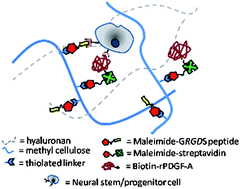
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19402-19411
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM33680D
The protein resistance of silicones prepared with a PEO-silane amphiphile
Silicone coatings with improved resistance to plasma proteins were prepared by incorporating a PEO-silane amphiphile: α-(EtO)3Si-(CH2)2-oligodimethylsiloxane13-block-poly(ethylene oxide)8-OCH3.
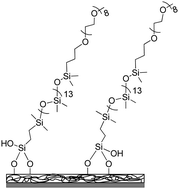
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19540-19546
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32322B
Electrospinning of in situ crosslinked collagen nanofibers
A simple one-step approach to electrospin Type I collagen in the presence of the chemical crosslinking agents 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl-aminopropyl)-1-carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) has been developed to generate water-insoluble collagen nanofiber scaffolds without the need for post-crosslinking.
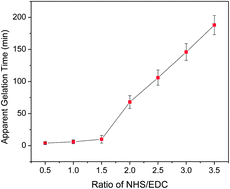
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19412-19417
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31618H
Osteoconductive surfaces generated from peptide functionalized poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl phosphate) brushes
Natural bone extracellular matrix mimetic surface coatings were prepared by surface-initiated atom transfer radical copolymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl phosphate and subsequent peptide post-modification.
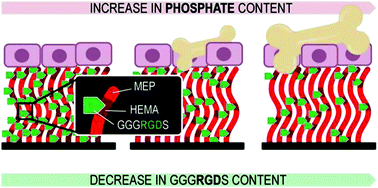
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19570-19578
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31568H
Dynamically cell separating thermo-functional biointerfaces with densely packed polymer brushes
Thermo-responsive polymer brush grafted glass surfaces with various brush lengths were prepared through surface-initiated ATRP as cell separating intelligent biointerfaces. A precisely designed PIPAAm brush is able to separate cells by the utilization of different detachment properties of cells from the surfaces.
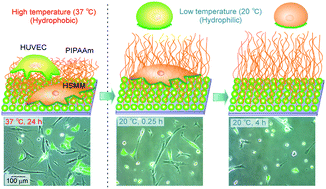
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19514-19522
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31797D
Crosslink density of a biomimetic poly(HEMA)-based hydrogel influences growth and proliferation of attachment dependent RMS 13 cells
Attachment dependent RMS 13 human muscle fibroblasts demonstrate adaptive attachment dependence on the bound water content within poly(HEMA) hydrogels.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19529-19539
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32516K
Biomimetic supported lipid bilayers with high cholesterol content formed by α-helical peptide -induced vesicle fusion
We present a technique to create complex, high cholesterol-containing supported lipid bilayers using α-helical peptide-induced vesicle fusion.
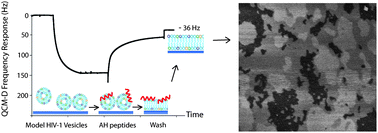
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19506-19513
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32016A
Influence of surface charge and protein intermediary layer on the formation of biomimetic calcium phosphate on silica nanoparticles
Formation of biomimetic calcium phosphate nano-composite through protein mediated manipulation of substrate charge characteristics.

J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19562-19569
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31733H
Dendritic polyglycerolamine as a functional antifouling coating of gold surfaces
Coating gold substrates with PG-amino monolayers is a useful strategy for producing surfaces with defined (bio)specific bindings as well as protein repellant properties.
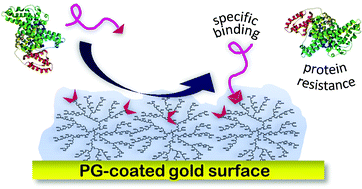
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19488-19497
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32486E
Combinatorial screening of chemically defined human mesenchymal stem cell culture substrates
SAM array technology was used to investigate the effects of multiple, distinct peptides and peptide combinations on human mesenchymal stem cell behavior.
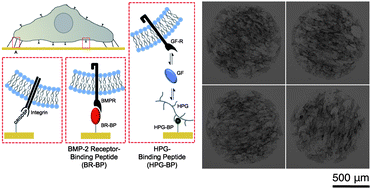
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19474-19481
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32242K
Thiol -ene “click” networks from amphiphilic fluoropolymers: full synthesis and characterization of a benchmark anti-biofouling surface
Photo-initiated, thiol-ene crosslinking has been employed to generate nanoscopically complex, heterogeneous surfaces that resist protein adsorption.
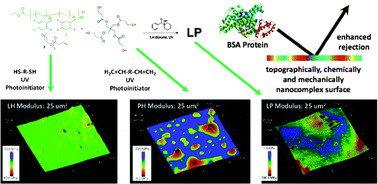
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19462-19473
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32005C
Protein -resistant polymer surfaces
Neutral, water-swollen polymer coatings effectively repel proteins through ‘entropic shielding’ which makes them excellent candidates as non-fouling materials.
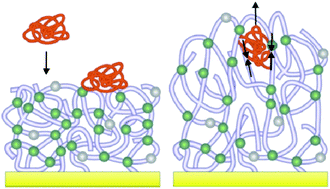
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19547-19561
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM30820G
Electrochemically stimulated release of lysozyme from an alginate matrix cross-linked with iron cations
An electrochemically generated alginate matrix cross-linked with Fe3+ cations was used to entrap lysozyme and then release it upon application of an electrochemical signal.
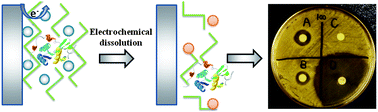
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19523-19528
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32008H
PEDOT:TOS with PEG: a biofunctional surface with improved electronic characteristics
Devices based on conducting polymers offer great promise for interfacing with cells.
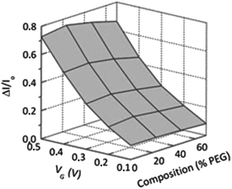
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19498-19505
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32188B
pH-responsive branched peptide amphiphile hydrogel designed for applications in regenerative medicine with potential as injectable tissue scaffolds
Tailoring properties of peptide amphiphile assemblies for therapeutic applications through molecular design.
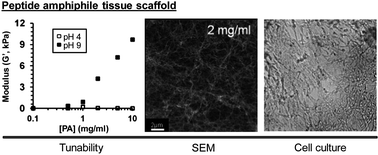
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19447-19454
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31745A
Antimicrobial efficacy and optimized cell adhesion from defined plasma polymerised multilayer structures involving zinc acetylacetonate and allylamine
A multilayer structure comprising of a zinc burst release system and a cytocompatible plasma polymer top-coating is discussed with the concept of developing antimicrobial, yet biocompatible coatings suitable for use on implants and medical devices.
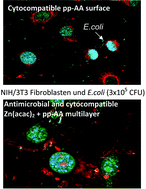
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19455-19461
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM30344B
Biocompatible stimuli-responsive hydrogel porous membranes via phase separation of a polyvinyl alcohol and Na-alginate intermolecular complex
Stimuli-responsive porous hydrogel thin films fabricated from sodium alginate and polyvinyl alcohol via a spinodal decomposition mechanism in a low immiscibility limit.
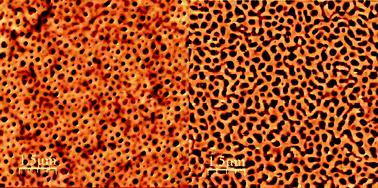
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19482-19487
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31778H
Photoreactive elastin-like proteins for use as versatile bioactive materials and surface coatings
A cell-adhesive elastin-like protein biomaterial enables photocrosslinking into stable coatings, films, and scaffolds across the nanometre to millimetre length scales.
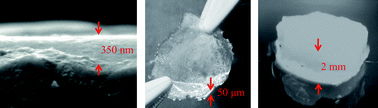
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19429-19437
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31768K
GAGs-thiolated chitosan assemblies for chronic wounds treatment: control of enzyme activity and cell attachment
Surface active multilayered coatings comprising thiolated chitosan and glycosaminoglycans inhibit enzymes related to chronic inflammation and display tuneable fibroblast attachment.
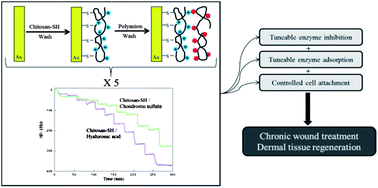
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19438-19446
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM31051A
Bacterial adherence on self-assembled films of brush polymers bearing zwitterionic sulfobetaine moieties
The adherences of bacteria on self-assembled films of sulfobetaine-containing brush polymers were quantitatively investigated in aspects of surface characteristics and thermodynamics.
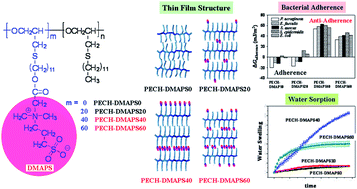
J. Mater. Chem., 2012,22, 19418-19428
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM15912K
About this collection
Journal of Materials Chemistry presents a themed issue on ‘Materials for biosurfaces’ with guest editors Christian Ohm, M. Elizabeth Welch and Christopher K. Ober.