Themed collection Artificial Water Channels

List of participants
Poster list
Artificial water channels: inspiration, progress, and challenges
Developing bioinspired artificial water channels may lead to the next-generation filtration membranes with ultra-high pore density and exclusive water permeability.

Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 415-427
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00132D
Imidazole derivatives as artificial water channel building-blocks: structural design influence on water permeability
A series of mono- and di-ureidoethylimidazole derivatives were tested as self-assembled supramolecular channels for water transport across a vesicle bilayer. Structural modifications of the selected compounds were related to permeability variation.
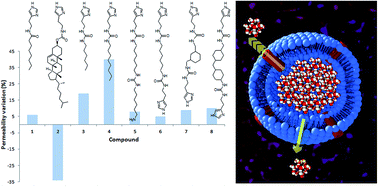
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 113-124
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00024G
Unique selectivity trends of highly permeable PAP[5] water channel membranes
In this paper, two unique selectivity trends of ML-PAP[5] membranes are discussed from the perspectives of channel geometry, ion exclusion, and linear molecule transport.
![Graphical abstract: Unique selectivity trends of highly permeable PAP[5] water channel membranes](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C8FD00043C&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2018)
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 193-204
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00043C
From channel proteins to industrial biomimetic membrane technology
Here we discuss how highly selective aquaporin proteins can be used to enhance the performance of the classical thin film composite membrane, and how this can be used in relevant membrane elements and module form factors.
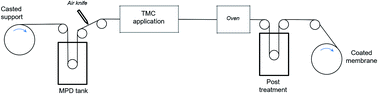
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 287-301
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00061A
Carboxyl-functionalized nanochannels based on block copolymer hierarchical structures
Hierarchical isotropic porous structures with spherical micrometer-sized cavities, interconnected by hexagonally ordered nanochannels, were prepared based on the phase separation of polystyrene-b-poly(t-butyl acrylate) block copolymers, following a nucleation and growth mechanism.
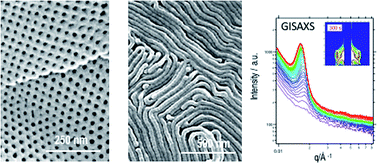
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 303-314
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00015H
G4-quartet hydrogels from 5′-hydrazino-guanosine for the non-covalent and covalent remediation of contaminants from water
HG 2·KCl hydrogel assemblies non-covalently bind anionic dyes and covalently bind an aldehyde in water.
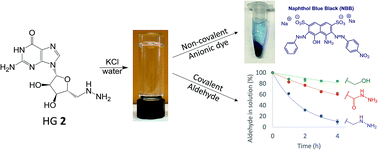
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 97-112
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00038G
Single-file transport of water through membrane channels
After a short introduction into the single-file transport theory, we analyze experiments in which the unitary water permeability, pf, of water channel proteins (aquaporins, AQPs), potassium channels (KcsA), and antibiotics (gramicidin-A derivatives) has been obtained. A short outline of the underlying methods is also provided.
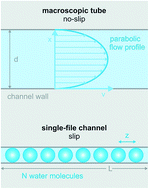
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 9-33
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00122G
Water permeation across artificial I-quartet membrane channels: from structure to disorder
Investigation of water dynamics during permeation events through I-quartet membrane channels in ordered and disordered systems.

Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 125-148
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00046H
Driven water/ion transport through narrow nanopores: a molecular dynamics perspective
Atomistic Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations provide numerous insights into the process whereby water is driven through a narrow nanopore (diameter on the order of a few water molecules) by application of hydrostatic pressure.
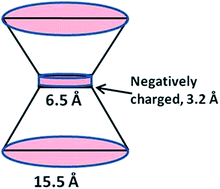
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 249-257
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00073E
Protein–protein interactions in AQP regulation – biophysical characterization of AQP0–CaM and AQP2–LIP5 complex formation
Biophysical characterization of interactions between full-length aquaporins and regulatory proteins provides new insights into binding mechanisms.
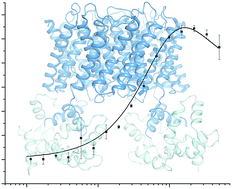
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 35-54
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00065D
Impact of PEG additives and pore rim functionalization on water transport through sub-1 nm carbon nanotube porins
In the past, sub-1 nm diameter carbon nanotube porins embedded in a lipid membrane matrix demonstrated extremely high water permeabilities and strong ion selectivities. In this work, we explore additional factors that influence transport in these channels.
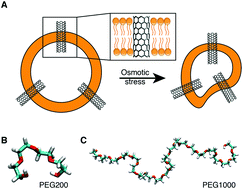
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 359-369
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00068A
Parameterization and atomistic simulations of biomimetic membranes
We have developed CHARMM force-field compatible parameters and conducted all-atom explicit-solvent MD simulations of biomimetic membranes composed of block copolymers of poly(butadiene), poly(isoprene), and poly(ethylene oxide).
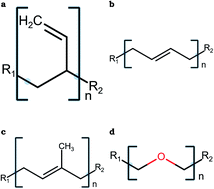
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 161-178
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00047F
Water and hydrophobic gates in ion channels and nanopores
Simulations of water behaviour have been used to probe hydrophobic gates in BEST1 and TMEM175, which can reveal important design principles for the engineering of gates in novel biomimetic nanopores.
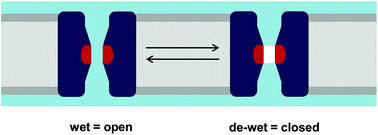
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 231-247
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00013A
Electric field mediated separation of water–ethanol mixtures in carbon-nanotubes integrated in nanoporous graphene membranes
The tunable separation of water–ethanol mixtures inside CNTs by varying the electric field orientation angle θ.
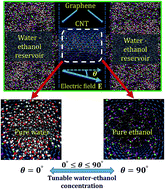
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 259-271
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00027A
Molecular dynamics simulations of carbon nanotube porins in lipid bilayers
Carbon nanotube porins embedded in lipid membranes are studied by molecular dynamics simulations.
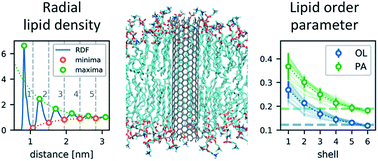
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 341-358
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00011E
2D graphene oxide channel for water transport
Proper crosslinking and reduction can effectively prevent graphene oxide from swelling, thus enabling the precise control of interlayer spacing.
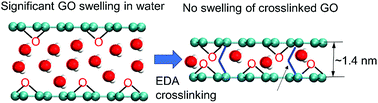
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 329-340
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00026C
Hyperpolarised NMR to follow water proton transport through membrane channels via exchange with biomolecules
Using hyperpolarised NMR attains sufficient sensitivity to detect water proton uptake in biomolecules following the crossing of membrane channels.
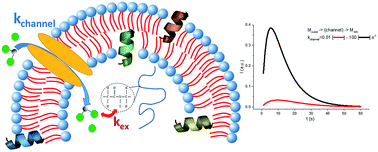
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 67-82
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00021B
Positively charged residues at the channel mouth boost single-file water flow
Positively charged residues in the vicinity of the channel entrance or exit accelerate single-file water flow.
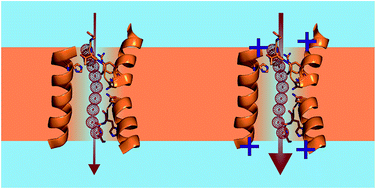
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 55-65
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00050F
Selectivity and polarization in water channel membranes: lessons learned from polymeric membranes and CNTs
The aspects of ion exclusion and concentration polarization are highlighted as critical for achieving high selectivity in an artificial water channel.
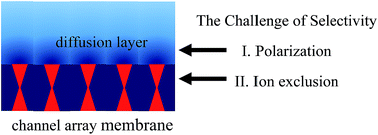
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 371-388
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00054A
Localization of transmembrane multiblock amphiphilic molecules in phase-separated vesicles
Multiblock-amphiphiles preferentially distribute in the Ld phase and encourage delocalization of cholesterol in both the Ld and Lo phases.
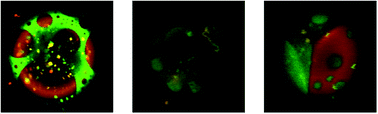
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 315-328
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00022K
A synthetic channel that efficiently inserts into mammalian cell membranes and destroys cancer cells
A tubular molecule with terminal positively charged amino groups that displays a strong ability to insert into the membrane of mammalian cells.

Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 149-159
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00009C
Creating cross-linked lamellar block copolymer supporting layers for biomimetic membranes
In this study, we propose a strategy for incorporation of artificial channels that mimic biological channels into stable polymeric membranes.
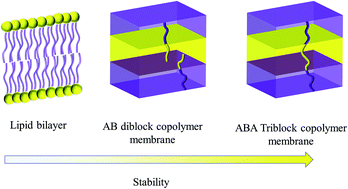
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 179-191
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD00044A
Biomimetic water channels: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 205-229
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90020E
The modelling and enhancement of water hydrodynamics: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 273-285
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90021C
Structure and function of natural proteins for water transport: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 83-95
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90019A
Applications to water transport systems: general discussion
Faraday Discuss., 2018,209, 389-414
https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FD90022A
About this collection
We are delighted to share with you a selection of the papers which will be presented at our Faraday Discussion on Artificial Water Channelstaking place in Glasgow, UK in June 2018. More information about the event may be found here: http://rsc.li/water-channels. Additional articles will be added to the collection as they are published. The final versions of all the articles presented and a record of the live discussions will be published after the event.
The development of synthetic biomimetic artificial water-channels and pores is key for a better understanding of the natural function of protein channels. It is hoped to offer new strategies to generate highly selective, advanced materials for water purification systems. While synthetic chemists have produced sophisticated architectures able to confine water clusters, most water channel based work is being conducted with natural protein channels as selectivity components, embedded in the diverse arrays of bio-assisted artificial systems. Such systems combine natural proteins that present high water conductance states under natural conditions with artificial lipidic or polymeric matrices. Experimental results have demonstrated that natural biomolecules can be used as bio-assisted building blocks for the construction of highly selective water transport through artificial channels. A next step is the design and construction of simpler compounds that maintain the high conduction activity obtained with natural compounds, leading to fully synthetic artificial biomimetic channels. Such studies aim to use constitutional artificial desalination membranes for highly selective water transport.
Moving to simpler water-channel systems offers a chance to better understand mechanistic and structural behaviours and to uncover novel interactive water channels that might parallel those in biomolecular systems.