A study of the electrochemical behavior at low temperature of the Li3V2(PO4)3 cathode material for Li-ion batteries
Abstract
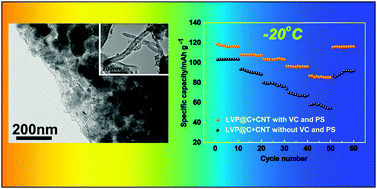
In this paper, glucose and carbon nanotube (CNT) modified Li3V2(PO4)3 have been synthesised via a carbon thermal reduction method. The structure of Li3V2(PO4)3 has been confirmed by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and scanning and transmission electron microscopy. The CNT modified Li3V2(PO4)3 materials, combined with the synthesized electrolyte, overcome the limitations of the low temperature performance of Li-ion batteries. The synthesized electrolyte is made up of 1.2 M LiPF6 dissolved in EC : DMC : EMC (1 : 1 : 1 in volume) with vinylene carbonate (VC) and propylene sulfite (PS) as the additive agents. The electrochemical behaviors of the cells have been evaluated by electrochemical tests over the temperature range from 25 to −20 °C. The specific capacities are 116.2, 108.2, 103.7, 96.3, and 86.1 mA h g−1 at 0.5C, 1C, 2C, 5C, and 10C, respectively, between 3.0 and 4.3 V at −20 °C. After 300 cycles, the capacity retention still reached 97% even at −20 °C. The excellent rate capability and low temperature performance are attributed to the synergistic effect between the CNTs and the synthesized low temperature electrolyte.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...