Impact of sp2 carbon material species on Pt nanoparticle-based electrocatalysts produced by one-pot pyrolysis methods with ionic liquids†
Abstract
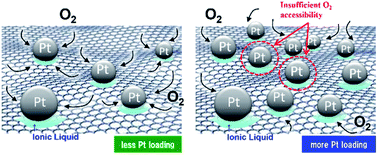
Pt-nanoparticle-supported graphene nanoplatelets (Pt/GNPs) and multiwalled carbon nanotube composite (Pt/MWCNTs) electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) can be prepared using a one-pot method through the pyrolytic decomposition of the platinum precursor, platinum(II) bis(acetylacetonate) (Pt(acac)2) in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide ([C4mim][Tf2N]) or N,N,N-trimethyl-N-propylammonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide ([N1,1,1,3][Tf2N]) ionic liquids (ILs) with the target sp2 carbon support. In this one-pot pyrolysis method, which does not require any reagents to reduce Pt metal precursors or stabilize Pt nanoparticles, Pt nanoparticles are readily immobilized onto the sp2 surface by a thin IL layer formed at the interface, which can work as a binder. We used three types of sp2 carbon materials with different geometric shapes (graphene nanoplatelets with <3 (GNPs-3) and 18–24 layers (GNPs-20) and multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)) to investigate Pt nanoparticle formation and anchoring. All the electrocatalysts, especially Pt/MWCNTs, showed higher durability than the commercial catalyst owing to the combined effect of the IL binder and sp2 carbon materials. Our findings strongly suggest that the original carbon surface properties are also an important factor for creating high-performance ORR electrocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...