Ti3C2 MXene-anchored photoelectrochemical detection of exosomes by in situ fabrication of CdS nanoparticles with enzyme-assisted hybridization chain reaction†
Abstract
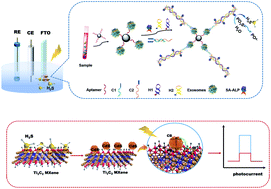
Exosomes that carry large amounts of tumor-specific molecular information have been identified as a potential non-invasive biomarker for early warning of cancer. In this work, we reported an enzyme-assisted photoelectrochemical (PEC) biosensor for quantification of exosomes based on the in situ synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene/CdS composites with magnetic separation technology and hybridization chain reaction (HCR). First, exosomes were specifically bound between aptamer-labeled magnetic beads (CD63-MBs) and a cholesterol-labeled DNA anchor. The properly designed anchor ends acted as a trigger to enrich the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) through HCR. It catalyzed more sodium thiophosphate to generate the sulfideion (S2−), which combined with Cd2+ for in situ fabrication of CdS on Ti3C2 MXene resulting in elevated photocurrent. The Ti3C2 MXene-anchored PEC method was realized for the quantitative detection of exosomes, which exhibited the dynamic working range from 7.3 × 105 particles per mL to 3.285 × 108 particles per mL with a limit of detection of 7.875 × 104 particles per mL. The strategy showed acceptable stability, high sensitivity, rapid response and excellent selectivity. Furthermore, we believe that the PEC biosensor has huge potential as a routine bioassay method for the precise quantification of exosomes from breast cancer in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...