Inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ICP-TOFMS) with desolvating sample introduction and He collision gas for high-accuracy determination of Rh, Pd and Pt in automobile catalytic converters
Stanislav
Strekopytov
 ,
John
Entwisle
,
Sarah
Hill
,
John
Entwisle
,
Sarah
Hill
 and
Heidi
Goenaga-Infante
and
Heidi
Goenaga-Infante
 *
*
LGC National Measurement Laboratory, Queens Road, Teddington, Middlesex TW11 0LY, UK. E-mail: Heidi.Goenaga-Infante@lgcgroup.com
First published on 18th January 2024
Abstract
A novel and selective method has been developed for high-accuracy determination of Pd, Pt and Rh in complex autocatalyst matrices using isotope dilution (ID) analysis (for Pt and Pd) and internal standard (IS) matching (for Rh) with ICP-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ICP-TOFMS). By using a desolvating inlet interface and He collision gas, spectral interferences on selected isotopes (e.g., 105Pd, 195Pt, 196Pt) were successfully removed. Calibration is performed by exact-matching ID analysis for Pd (104Pd/105Pd) and Pt (196Pt/195Pt) and IS matching with 101Ru for monoisotopic 103Rh. Due to the quasi-simultaneous determination of all the isotopes of interest by ICP-TOFMS, isotope ratio precision was improved in comparison with that of sequential instrumentation, thus leading to reduced measurement uncertainties of <1% (k = 2), as required by autocatalyst manufacturers. This represents an approximately 2–3-fold improvement for Rh and Pd and 6-fold improvement for Pt in comparison to the uncertainties achieved using the same measurement strategy for sequential ICP-MS instrumentation. The method has been applied to the characterisation of a candidate CRM LGC3101 (unused automobile catalyst) containing high levels of Zr and Hf and validated by the analysis of similar matrix CRMs and by participation in an interlaboratory exercise.
Introduction
Palladium (Pd), platinum (Pt) and rhodium (Rh) are extensively employed in the production of automotive catalytic converters as active components used to control harmful emissions from exhaust fumes. In a catalytic converter, platinum group metals (PGM) are finely dispersed on a honeycomb-like structure of ceramic monolith made of either Al2O3 or cordierite (aluminosilicate) to create a large surface area. The monolith surface is coated with a layer of wash-coat that contains alumina (Al2O3), cerium oxide (CeO2) and zirconium oxide (ZrO2). The active substances which are metallic nanoparticles of PGEs are scattered on this wash-coat layer. For petrol-powered vehicles, both Pt and Pd are effective at oxidizing CO and hydrocarbons, and so the choice (or the ratio between them) is often made based on relative cost.1 Rhodium is generally used in addition to platinum and/or palladium in the three-way catalyst used for petrol vehicles as it must also be able to reduce NOx to nitrogen.2Catalytic converters are the main single PGM application at present, with automotive industry contributing 90%, 84% and 41% to the total gross demand for Rh, Pd and Pt, respectively.3 Recycling, including recycling of automobile catalytic converters, currently contributes 21–33% to the combined primary and secondary supply of these metals. The high economic value of platinum and associated PGMs continues to drive the development of accurate methods for their determination in new and used automobile catalytic converters. The expectation of the industry is high accuracy, which requires very low relative uncertainty (typically <1%, k = 2)4 of the reference values in quality control materials. Achieving such measurement uncertainty is challenging due to potential significant matrix interferences on isotopes of PGMs driving the need for matrix separation procedures prior to analysis which are tedious. Attractive alternatives are the use of collision/reaction ICP-MS or sector field/high resolution ICP-MS. Finding a trade-off between the required isotopic selectivity and a fit-for-purpose isotope ratio precision to achieve low measurement uncertainties by using isotope ratio techniques is still a challenge for PGMs in these complex matrices.
Automobile catalysts are challenging matrices requiring acid mixtures that contain hydrofluoric acid (HF) for complete acid decomposition.5,6 The major potential spectral interferences on the detection of Pd, Rh and Pt by ICP-MS originate from the elements present in the automobile catalyst matrix. They include molecular ions, mainly oxides (e.g.90Zr16O+ and 178, 179, 180Hf16O+), isobaric ions (e.g.104Ru+, 106Cd+ and 198Hg+) and, sometimes, doubly-charged ions, in particular, 206, 208Pb++ in used catalyst contaminated through the use of leaded fuel.7,8 Separation of many oxide interferences on PGM isotopes including 90Zr16O+ on 106Pd requires a resolution well over 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000, which is difficult to achieve with available instrumentation. The concentration of Zr (and associated Hf) in modern catalytic converters is significantly higher (e.g., 3–4 wt%)9,10 than in the NIST SRM 2556 and 2557 (ca. 300 mg kg−1). The SRM 2556 and 2557 were prepared before leaded petrol was completely banned in the USA in 1995,11 therefore, they also contain high levels of Pb (0.6–1.4 wt%) due to contamination from leaded fuel. High levels of Zr in modern automobile catalysts limits the applicability of SRM 2556 and SRM 2557 as matrix-matched QC samples and requires the analytical method described by Beary and Paulsen5 to be modified by using the 104Pd/105Pd ratio to avoid 90Zr16O+ interference at 106Pd.12 Although HfO+ interferences on Pt isotopes could, in principle, be resolved using the highest resolution setting of the high-resolution (HR)-ICP-MS instrumentation,7 except at very high Hf
000, which is difficult to achieve with available instrumentation. The concentration of Zr (and associated Hf) in modern catalytic converters is significantly higher (e.g., 3–4 wt%)9,10 than in the NIST SRM 2556 and 2557 (ca. 300 mg kg−1). The SRM 2556 and 2557 were prepared before leaded petrol was completely banned in the USA in 1995,11 therefore, they also contain high levels of Pb (0.6–1.4 wt%) due to contamination from leaded fuel. High levels of Zr in modern automobile catalysts limits the applicability of SRM 2556 and SRM 2557 as matrix-matched QC samples and requires the analytical method described by Beary and Paulsen5 to be modified by using the 104Pd/105Pd ratio to avoid 90Zr16O+ interference at 106Pd.12 Although HfO+ interferences on Pt isotopes could, in principle, be resolved using the highest resolution setting of the high-resolution (HR)-ICP-MS instrumentation,7 except at very high Hf![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Pt ratios, the sensitivity is strongly decreased at high resolution and this could cause detriment of the isotope ratio precision.13 Reducing the level of oxide formation through the use of desolvating sample introduction interfaces has been shown to eliminate polyatomic interferences on Rh and Pt isotopes in ICP-MS analysis of environmental samples.14,15 Determination of Pd proved to be more challenging, but introduction of ICP tandem mass spectrometers (ICP-MS/MS) allowed significant progress to be made by using NH3 reaction mode, eliminating the need for tedious matrix separation.16,17
Pt ratios, the sensitivity is strongly decreased at high resolution and this could cause detriment of the isotope ratio precision.13 Reducing the level of oxide formation through the use of desolvating sample introduction interfaces has been shown to eliminate polyatomic interferences on Rh and Pt isotopes in ICP-MS analysis of environmental samples.14,15 Determination of Pd proved to be more challenging, but introduction of ICP tandem mass spectrometers (ICP-MS/MS) allowed significant progress to be made by using NH3 reaction mode, eliminating the need for tedious matrix separation.16,17
Relatively low measurement uncertainty (<1%, k = 2) was achieved for Rh, Pd and Pt in two certified reference materials (CRM) of used automobile catalyst (NIST SRM 2556 and NIST SRM 2557), by using isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry (ID-ICP-QMS) for Pd and Pt and by ICP-QMS for Rh.5 Platinum in a representative test material IMEP-11 (used car exhaust catalyst) was also characterised by IDMS.18,19 Three more used automobile catalyst CRMs were characterised primarily with ICP-OES providing concentrations of Pd, Pt and Rh with similarly low uncertainty.20–22 The matrix in a used catalyst is very different from that in an unused catalyst as the former may contain contaminants deriving from fuel, oil and their additives such as carbon (e.g., 2–4 wt%),21,23 sulphur, lead, manganese, phosphorus and so on.24 Industry ideally requires both types of CRMs to check that the analytical methods used are equally applicable to both types of material.9–25 To our knowledge, only one CRM of unused automobile catalyst has ever been produced (ERM EB503a)26 and it is not currently commercially available. High accuracy determination of Pd and Pt in this material was conducted by an ID-multi-collector (MC)-ICP-MS.4,26 Although ID-ICP-QMS was used to determine certificate values for Pd and Pt in NIST automobile catalyst CRMs,5 direct comparison of ID-MC-ICP-MS and ID-ICP-QMS did show that the former can achieve lower relative uncertainty of Pt and Pd values when using a similar number of replicates.4 Lower uncertainty was also achieved for Rh mass fraction in ERM-EB503a by standard addition with 115In as an IS using MC-ICP-MS comparing with HR-ICP-MS (ur = 0.9% and 2.1%, respectively, without dry mass correction).27
Improvements in the design of ICP-TOFMS over the years and further research on IR measurement with this technique have demonstrated its potential to reach a precision comparable to that achieved by magnetic sector MC-ICP-MS.28 ICP-TOFMS, at sufficiently high signal intensities and for a moderate acquisition time, yields a typical isotope ratio precision of <0.05% RSD.29–32 MC-ICP-MS still provides better precision on isotope ratios (RSD between 0.010% and 0.005%) than an ICP-TOFMS, but the TOF is better suited to multi-elemental analyses performed without matrix separation. Large number of isotope ratios can be determined simultaneously because ICP-TOFMS, unlike MC-ICP-MS and ICP-QMS, is not limited by the number of detectors available but always records a full elemental mass spectrum.
Improvements made to ICP-TOFMS instrumentation in the 2010s led to further applications of ID-ICP-TOFMS, including areas requiring higher sensitivity such as single particle (sp) analysis for Pt in tissue sections by an on-line ID LA-ICP-TOFMS,33 Pt in nanoparticles by on-line isotope ID ICP-TOFMS34 and monomethylmercury in a sediment CRM by species-specific isotope dilution (SSID) gas chromatography (GC)-ICP-TOFMS.35 So far, the vast majority of published ID-ICP-TOFMS applications were specifically developed for transient signal analysis. The potential of ID-ICP-TOFMS as a tool for high-precision elemental analysis such as the characterisation of certified reference materials (CRM) is still underutilised. Apart from a simultaneous determination of Cd, Hg and Pb in an acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resin CRM by ID-ICP-TOFMS, 36 no such work, to the authors' knowledge, has been published yet.
The aim of this study is to develop methodology that enables accurate quantification of Pt, Rh and Pd in unused automobile catalyst of high complexity with a relative expanded measurement uncertainty (k = 2) below 1%. By using ICP-TOFMS, methodology was developed for the simultaneous determination of Pt and Pd by IDMS and of Rh by exact matching internal standardisation. The use of He collision gas combined with desolvating sample introduction was investigated to achieve the required isotopic selectivity in presence of significant matrix interferences. The accuracy of the developed method was assessed by analysis of similar matrix CRMs and by participation in an interlaboratory comparison. Application to the characterisation of a candidate CRM LGC3101 (unused automobile catalyst) containing high levels of Zr and Hf was undertaken.
Materials and methods
Sample preparation
The sample (candidate reference material LGC3101) is a mixture of unused automobile catalysts supplied and prepared by a commercial manufacturer. The material has been ground to <40 μm particle size and homogenized.Approximately 0.2 g of sample was accurately weighed into fluoropolymer microwave digestion vessels followed by the addition of appropriate quantities of either 105Pd spike (CK Gas Products Ltd, UK) or 196Pt spike (Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA) (Table 1) and Ru internal standard (Romil Ltd, UK) to give isotope blend ratios within the recommended range in order to maintain reasonable signal intensities for both analyte and spike isotopes:37 about 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2.5 for signal intensity for 104Pd/105Pd and close to the ideal 1
2.5 for signal intensity for 104Pd/105Pd and close to the ideal 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio for both 195Pt/196Pt and 103Rh/101Ru.
1 ratio for both 195Pt/196Pt and 103Rh/101Ru.
| 105Pd spike | 196Pt spike | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Isotope | Isotopic enrichment (atom%) | Isotope | Isotopic enrichment (atom%) |
| 102Pd | <0.03 | 190Pt | <0.01 |
| 104Pd | 0.16 | 192Pt | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| 105Pd | 98.4 ± 0.1 | 194Pt | 1.45 ± 0.01 |
| 106Pd | 1.24 | 195Pt | 3.55 ± 0.01 |
| 108Pd | 0.15 | 196Pt | 94.57 ± 0.01 |
| 110Pd | 0.05 | 198Pt | 0.42 ± 0.01 |
A solution blend in 1% (v/w) HCl with both 105Pd/106Pd and 195Pt/196Pt close to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, containing 5–50 μg kg−1 Pd and Pt, 0.4–4 μg kg−1 Rh and 2.5–25 μg kg−1 Ru was separately prepared for method development including estimation of IR uncertainty and comparison between ICP-TOFMS and ICP-QMS.
1, containing 5–50 μg kg−1 Pd and Pt, 0.4–4 μg kg−1 Rh and 2.5–25 μg kg−1 Ru was separately prepared for method development including estimation of IR uncertainty and comparison between ICP-TOFMS and ICP-QMS.
For the determination of Pd, three microwave batches, each containing 3 blends of the automobile catalyst sample, together with QCs, matrix certified reference materials (CRMs), standards and procedural blanks were prepared and measured on three separate days. A similar procedure was used for the determination of Rh and Pt. Samples for Pd determination were prepared separately from those for Rh and Pt determination due to the isobaric interference from 104Ru on 104Pd. Nitric acid (4 mL), hydrochloric acid (2 mL) and hydrofluoric acid (2 mL) were added to each vessel and sealed before being placed in the microwave system (Ethos UP, Milestone S.r.l., Italy). The program applied included ramping to 140 °C (10 min), then to 190 °C (10 min), and holding at 190 °C (50 min). Immediately after cooling, the digests were quantitatively transferred to 50 mL polypropylene tubes using 1% (v/w) HCl and made up to 50 g. Further dilutions were performed in 1% HCl.
Independently sourced calibration standards of Pd, Rh (ROMIL Ltd, Cambridge, UK) and Pt (VHG, LGC Standards, Teddington, UK) were used as a confirmatory QC standard. Matrix CRMs (used auto catalyst, monolith NIST SRM2557 and unused automobile catalyst ERM-EB503a) and a QC sample were used to confirm accuracy of the analytical procedure. Additionally, an aliquot of the LGC3101 sample was spiked with a known amount of the calibration standard prior to digestion to determine recovery.
Instrumentation
An Apex Q desolvating introduction system equipped with a PFA-50 (50 μL min−1) fluoropolymer nebulizer (Elemental Scientific Inc., Omaha, Nebraska, USA) was used to reduce oxide formation.The ICP-TOFMS instrument used in the study was and icpTOF2R (Tofwerk AG, Thun, Switzerland). In order to avoid discrete noise components caused by rotation of the peristaltic pump, self-aspiration mode was used for sample introduction. During method development the instrument was tuned and optimized daily for optimal sensitivity and precision. Notch filters were used to reduce the intensity of 40Ar+ as well as of the isotopes of Zr and Pb present at relatively high levels in the matrix of either LGC3101 or QC samples. Typical instrumental parameters are detailed in Table 2. Helium collision gas was used to remove matrix induced polyatomic interferences, particularly on 195Pt+ and 196Pt+, caused by 179Hf16O+ and 180Hf16O+, respectively. For the method development comparison, standard sample introduction was used that consisted of a glass concentric nebulizer (MicroMist, Glass Expansion), peristaltic pump rotating at 40 rpm and a quartz cyclonic spray chamber cooled to 2 °C.
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| RF power | 1550 W |
| Plasma gas | 14 L min−1 |
| Auxiliary gas | 0.8 L min−1 |
| Carrier gas | 0.65–0.71 L min−1 (optimised daily) |
| Cell gas (He) | 3.0 mL min−1 |
| Notch filter | 40Ar, 90Zr, 208Pb |
| Isotope ratios | 103Rh/101Ru, 104Pd/105Pd, 195Pt/196Pt |
| Time resolution | 0.1518 s |
| 140CeO+/140Ce+ | ≤0.17% |
| 90ZrO+/90Zr+ | ≤0.05% |
| 179HfO+/179Hf+ | ≤0.3% |
| 138Ba++/138Ba+ | <2% |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) |
|
| Apex Q settings | |
| Spray chamber temperature | 100 °C |
| Condenser temperature | 2 °C |
| Additional gas (Ar) | 0.46–0.49 L min−1 (optimised daily) |
For comparison, ICP-QMS analysis was performed using the Agilent 8800 ICP-MS/MS (Agilent Technologies, Cheshire, UK) equipped with an Apex Q desolvating introduction system. The instrument was tuned and optimised daily for optimal sensitivity and precision. Typical instrumental parameters are detailed in Table 3.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| RF power | 1540 W |
| Plasma gas | 15 L min−1 |
| Auxiliary gas | 0.9 L min−1 |
| Carrier gas | 0.89 L min−1 |
| Cell gas (He) | 6 mL min−1 |
| Isotope ratios | 103Rh/101Ru, 106Pd/105Pd, 195Pt/196Pt |
| Sweeps per replicate | 300 |
| Dwell time | 0.2 s |
| 140CeO+/140Ce+ | ≤0.06% |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) |
|
| Apex Q settings | |
| Spray chamber temperature | 100 °C |
| Condenser temperature | 2 °C |
| Additional gas (Ar) | 0.37 L min−1 |
Data acquisition and processing
Details of IDMS procedure for Pd and Pt and the calibration for Rh, both employing the exact matching standard-sample bracketing (SSB) technique, are described by Simpson et al.4 The only difference with the procedure described here is that, in this study, 104Pd/105Pd ratio was used to obtain final values in the automobile catalyst samples to avoid significant interference from 90Zr16O+ and 92Zr16O+ on 106Pd and 108Pd, respectively.Three independently digested replicates of the automobile catalyst sample were measured within each analytical run. Mass bias within the run was corrected using a solution of known isotopic composition analysed before and after the measurement of an isotopic blend (SSB approach).38
After allowing ca. 180 s for sample uptake and signal stabilisation, mass-spectra for each instrumental replicate (30.36 s, 10 replicates per sample) were recorded at 151.8 ms intervals, creating 200 datapoints per replicate (3300 waveforms, 20 bus, 10 writes, 10 runs). Each instrumental replicate was recorded as a separate data file.
Data processing was performed using the data analysis packages Tofware (version 3.2.0) and Iolite (version 3.71), both running in the Igor Pro (Wavemetrics, OR, USA) environment. Tofware was used to model and subtract the baseline intensities that elevate the total signal on each m/z channel. Following mass calibration, baseline subtraction and peak integration of isotopes from every TOFMS spectrum, the integrated signal time traces for all m/z channels were exported as comma-separated value (csv) files compatible with Iolite. Iolite was used to calculate average intensities in each instrumental replicate, using a “baseline subtract” data reduction scheme, with no rejection of outliers. Further data reduction was performed using Microsoft Excel.
Dry mass correction
Mass loss due to heating was determined for each batch at the time of preparation. Duplicate 2 g portions were taken and subjected to the following temperature programme using a muffle furnace: (1) ramping temperature to 105 °C over 5 minutes (15 °C min−1) and holding for 30 minutes; (2) ramping to 500 °C over 20 minutes (20 °C min−1) and holding for 30 minutes. Samples were allowed to be cooled in a desiccator before weighing. Average loss of weight on drying at 500 °C was found to be 2.80 ± 0.18 (1sd, n = 6) wt%.Results and discussion
Reduction of molecular interferences
The selectivity of the ICP-TOFMS instrumentation with a standard sample introduction system can be improved through reduction of the level of molecular interferences by using He as a collision gas in the CRC. A He flow of 2 mL min−1, while leading to a reduced level of oxide interferences from 2.3% CeO+/Ce+ to approximately 1% CeO+/Ce+, has shown to have little effect on the sensitivity of Pt isotopes. However, the signal intensity of Pd isotopes decreased by 2.5-fold (Table 4). Increase of He flow beyond 3 mL min−1 was found to have a detrimental effect on lighter elements such as Pd and was not considered in this study due to counting statistics potentially becoming a limiting factor.| Standard sample introduction | Apex Q | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No gas | 2 mL min−1 He | No gas | 3 mL min−1 He | |
| Nebuliser gas flow, Ar, L min−1 | 1.07 | 1.07 | 0.65 | 0.65 |
| Additional gas, Ar, L min−1 | — | — | 0.48 | 0.48 |
| 106Pd, 1 μg kg−1, ions s−1 | 5400 | 2100 | 5100 | 800 |
| 196Pt, 1 μg kg−1, ions s−1 | 8100 | 6700 | 7800 | 5000 |
| CeO+/Ce+ | 2.3% | 1% | 0.35% | 0.17% |
A desolvating nebuliser was found to reduce the oxide interferences more dramatically than He collision gas alone, from 2.3% CeO+/Ce+ to approximately 0.35% CeO+/Ce+, while potentially leading to increased sensitivity and, therefore, to better counting statistics than the standard system. By using a desolvating nebuliser in combination with 3 mL min−1 He in the CRC, an even lower level of oxide interferences (e.g., ≤0.17% CeO+/Ce+) was achieved.
Dependence of isotope ratio precision on the acquisition time
Mass-spectrometric detection is subject to fundamental noise, which can never be totally eliminated, and, therefore, ultimately limits the precision that can be achieved. Due to a quasi-simultaneous nature of TOF detection, correlated noise caused by instabilities associated with the ICP ion source e.g. variations in plasma parameters, nebulisation efficiency or peristaltic pump have less significant effect on the isotope ratio precision in comparison with sequential ICP-MS.39 Ratioing of simultaneously measured intensities on two channels, where a strong correlation exists between them, has been shown effective in cancellation of these types of noise.40 The contribution made by ion source to noise can be assumed to be negligible for isotope ratio measurements made using appropriate data acquisition parameters such as time resolution.41Time resolution in the ICP-TOFMS analysis is determined by the number of waveforms (mass spectra from individual extractions into the time-of-flight tube) integrated into a single segment of data. For continuous sample introduction, the time resolution of 250–300 ms seems to maximise the average-spectrum dynamic range.30,42 Slightly shorter measurement intervals (100–200 ms) have typically been applied when the isotope ratio was measured such as in ID-ICP-TOFMS.30,35 While further optimisation of the time resolution for ID-ICP-TOFMS is outside of the scope of the current study, a value of 150 ms has been found optimum for continuous liquid analysis43 and it was, therefore, used throughout this study.
The precision of an isotope ratio measurement is at least limited by the statistics of the ion counting, described by the Poisson probability distribution, in which uncertainty is proportional to the square root of the total counts measured. Uncertainty of the measured isotope abundance ratio, r, contributed by counting statistics only, in the case of simultaneous detection, can be expressed as:39
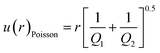 | (1) |
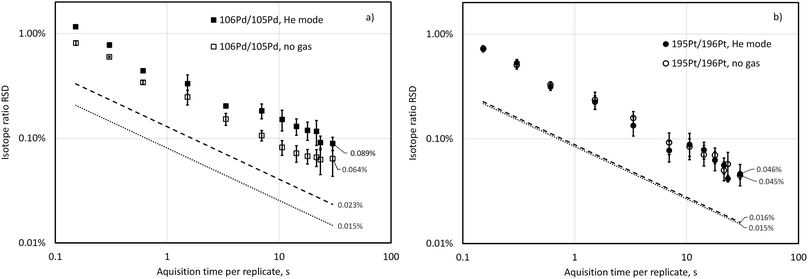
Fig. 1 shows isotope-ratio precision attained for 106Pd/105Pd and 195Pt/196Pt isotopic pairs when analysing a blend containing about 50 ng g−1 Pd and Pt with both 106Pd/105Pd and 195Pt/196Pt close to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. These data were acquired at a spectral averaging time (time resolution) of 150 ms and isotope signals were summed across relevant time windows in data post-processing to achieve respective integration periods. Isotope-ratio precision roughly follows Poisson limits calculated according to eqn (1). with a possible exception of 106Pd/105Pd in He mode, for which the difference between Poisson-predicted and experimentally obtained RSD is statistically increasing with increasing acquisition time (at p = 0.05, n = 12). At an integration time of 30 s with no gas in the cell, isotope-ratio precisions of 0.064% and 0.045% RSD were attained for 106Pd/105Pd and 195Pt/196Pt, respectively, while the RSD predicted by counting statists only decrease at this integration time to 0.015% for both isotope pairs. Platinum isotope ratio precision is not affected by the presence of a collision gas He at 2 mL min−1 because the count rate for Pt isotopes is not affected, while the Pd signal is suppressed, and this is reflected in a slightly larger IR precision (0.089% RSD). Hendriks et al.30 studied the precision of the ICP-TOFMS determination of Eu and Ag isotope ratios up to 300 s integration time and found similar behaviour and RSD as well as some IR drift at integration times over 100 s. For previous generations of ICP-TOFMS instrumentation with both axial and orthogonal geometry, it was observed that increasing the acquisition time per replicate to values of more than 30–50 s resulted in a slightly deteriorated isotope ratio precision.29,32 For our purposes, increasing integration time over 30 s was not practicable due to a necessity to minimise the total run time of an exact matching standard-sample sequence of the ID-ICP-TOFMS batch.
1. These data were acquired at a spectral averaging time (time resolution) of 150 ms and isotope signals were summed across relevant time windows in data post-processing to achieve respective integration periods. Isotope-ratio precision roughly follows Poisson limits calculated according to eqn (1). with a possible exception of 106Pd/105Pd in He mode, for which the difference between Poisson-predicted and experimentally obtained RSD is statistically increasing with increasing acquisition time (at p = 0.05, n = 12). At an integration time of 30 s with no gas in the cell, isotope-ratio precisions of 0.064% and 0.045% RSD were attained for 106Pd/105Pd and 195Pt/196Pt, respectively, while the RSD predicted by counting statists only decrease at this integration time to 0.015% for both isotope pairs. Platinum isotope ratio precision is not affected by the presence of a collision gas He at 2 mL min−1 because the count rate for Pt isotopes is not affected, while the Pd signal is suppressed, and this is reflected in a slightly larger IR precision (0.089% RSD). Hendriks et al.30 studied the precision of the ICP-TOFMS determination of Eu and Ag isotope ratios up to 300 s integration time and found similar behaviour and RSD as well as some IR drift at integration times over 100 s. For previous generations of ICP-TOFMS instrumentation with both axial and orthogonal geometry, it was observed that increasing the acquisition time per replicate to values of more than 30–50 s resulted in a slightly deteriorated isotope ratio precision.29,32 For our purposes, increasing integration time over 30 s was not practicable due to a necessity to minimise the total run time of an exact matching standard-sample sequence of the ID-ICP-TOFMS batch.
Dependence of isotope ratio precision on the sample introduction system and collision gas
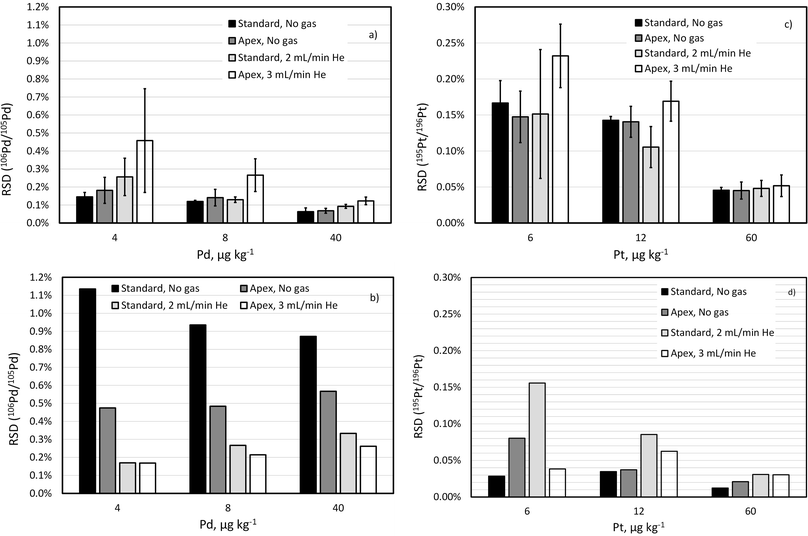
A fit-for-purpose selectivity for the isotopes of interest is necessary for unbiased analysis of complex matrices. While removing most of solvent (e.g., H2O and HCl) in a desolvating nebulisation system greatly reduces the level of oxide interferences, using a collision gas can reduce the interference level even further (e.g., by 2-fold). Because this approach pushes up the limit determined by counting statistics, especially for lighter isotopes, it is necessary to check how it affects the repeatability of isotope ratio measurements.Isotope ratio (106Pd/105Pd and 195Pt/196Pt) repeatability has been compared for a standard sample introduction system and a desolvating nebuliser with and without addition of He collision gas in the CRC. Comparison is made based on two parameters: (1) RSD of 10 consecutive replicates (internal precision), which is used in the calculation of the IR uncertainty in the ID-ICP-MS method;4 (2) RSD of 3 non-consecutive measurements of the same sample approximately 1 h apart, or external precision,44 which reflects the within-day repeatability of the IR measurements (Fig. 2).
While improvement of the IR precision using a desolvating nebuliser in self-aspiration mode has been observed when compared to standard sample introduction using a peristaltic pump for sequential ICP-MS such as ICP-QMS,45 it is not clear whether the same effect can be achieved for ICP-TOFMS measurements.
As shown in Fig. 2, the internal precision of isotope ratios for Pt isotopes is not only much better than for Pd isotopes but also seems to be more robust and less dependent on the sample introduction system or collision gas. This is due to the sensitivity being less depended on the ICP-MS parameters, for example, much less suppressed by the collision gas than that of the Pd isotopes.
To compare external precision (Fig. 2b and d) with internal precision (Fig. 2a and c), a difference in counting time per replicate measurement (300 s versus 30 s) needs to be considered. According to eqn (1), external precision RSD is expected to be approximately 3.2 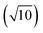 times lower. This seems to be indeed the case for Pt isotopes, at least at higher concentrations, leading, for a solution containing 50 ng g−1 Pt, to external precision RSD (195Pt/196Pt, n = 3) = 0.012–0.031%.
times lower. This seems to be indeed the case for Pt isotopes, at least at higher concentrations, leading, for a solution containing 50 ng g−1 Pt, to external precision RSD (195Pt/196Pt, n = 3) = 0.012–0.031%.
The external precision of 106Pd/105Pd ratio, on the other hand, seems to be much larger than the internal precision, reflecting the drift of the isotope ratio over several hours. Importantly the ICP-MS parameters seem to significantly affect the magnitude of the IR drift. Smaller drift of 106Pd/105Pd ratio when using a desolvating nebuliser and even smaller drift when using He as collision gas have been observed.
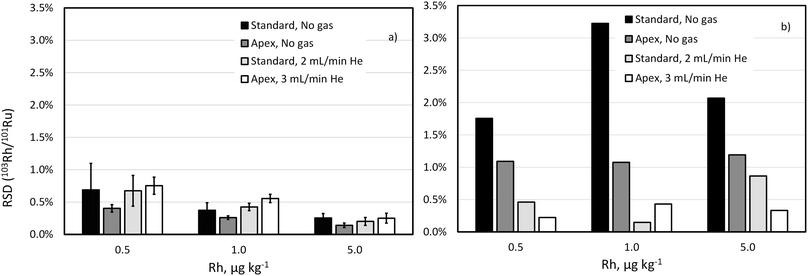
Drift of the 103Rh/101Ru ratio, which is even more significant with the standard sample introduction and unpressurized cell, was also largely reduced by using He as collision gas (Fig. 3). Note that the concentration of Rh in this experiment is much lower than that of Pd and Pt reflecting lower content this element in commercial automobile catalytic converters.
These experiments support the choice of high-selectivity setup (desolvating nebuliser in combination with He collision gas) in the ID-ICP-TOFMS determination of Pd and in the IS matching ICP-TOFMS determination of Rh.
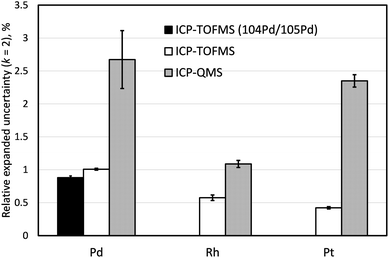
Comparison of measurement uncertainties obtained by ICP-TOFMS and ICP-QMS
Three independently prepared samples of LGC3101 were analysed within the same analytical batch both by ICP-TOFMS and ICP-QMS to compare the achievable measurement estimated uncertainties according to Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (GUM)46 (Fig. 4). Successful investigation into mitigating interferences using the capability of the Agilent 8800 ICP-MS/MS instrument to form ammonia reaction products were performed for Pd and Pt but uncertainties significantly larger than the target 1% were achieved. Similar configuration of the sample introduction system and He as a collision gas were kept on both instruments for consistency (Tables 2 and 3). Because for the determination of Pd the 106Pd/105Pd isotope ratio was used in the ID-ICP-QMS method, the same ratio was used for the ID-ICP-TOFMS analysis in this experiment, even though for the final analysis by ID-ICP-TOFMS the 104Pd/105Pd was used to avoid the 90Zr16O+ interference. The measurement uncertainty of ID-ICP-TOFMS determination of Pd based on the 104Pd/105Pd ratio is also shown in Fig. 4.When using quadrupole mass spectrometry, expanded relative uncertainties for both Pd and Pt (2.7% and 2.3%, respectively) are significantly above the typical level of uncertainty expected from the IDMS measurement (Ur = 1%, k = 2), while ID-ICP-TOFMS achieves much lower uncertainties, 1.0% and 0.4%, respectively. Monoisotopic Rh is present at much lower concentrations in the automobile catalyst sample comparing to Pd and Pt. Both QMS- and TOFMS-based methods using exact matching with 101Ru as an IS provided high-precision values for this element (Ur = 1.1% and 0.6%, respectively; k = 2).
Potential sources of bias caused by the matrix of automobile catalyst
Semi-quantitative ICP-QMS analysis of LGC3101 has been performed in order to understand possible ICP-MS interferences caused by the elements present in the sample matrix. Out of the elements that can cause significant spectral interferences on Rh, Pd and Pt, only Zr, Hf and W were found to be present at high levels (100s to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000s mg kg−1). Hafnium is commonly associated with Zr, which is present at the level of 10
000s mg kg−1). Hafnium is commonly associated with Zr, which is present at the level of 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000s mg kg−1 in modern catalytic converters. Relatively high level of tungsten (100s mg kg−1) in LGC3101 seems to be less usual for catalytic converters, but the only relevant interference that could be caused by this element (180W16O on 196Pt) is deemed to be negligible due to the very low abundance of 180W (0.12%).
000s mg kg−1 in modern catalytic converters. Relatively high level of tungsten (100s mg kg−1) in LGC3101 seems to be less usual for catalytic converters, but the only relevant interference that could be caused by this element (180W16O on 196Pt) is deemed to be negligible due to the very low abundance of 180W (0.12%).
Rhodium is monoisotopic (103Rh), but potentially significant spectral interferences (87Sr16O+, 63Cu40Ar+, 66Zn37Cl+, 68Zn35Cl+ and 206Pb++) are not likely to be an issue in the matrix of LGC3101. Potential interferences on 101Ru, which is used as an IS for Rh determination, (84Sr16OH+, 61Ni40Ar+ and 64Zn37Cl+)47 do not seem to be significant in the matrix of the catalytic converters.
Considering a very high content of Zr in LGC3101, 104Pd as the reference isotope and 105Pd as the spike isotope were chosen in this work as these are the only Pd isotopes free from ZrO+ interferences. Isobaric interference of 104Ru+ must be considered for 104Pd, but semi-quantitative analysis indicated a very high Pd![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru ratio (>2000) rendering this interference negligible. Ruthenium, although initially tested as a catalyst in automotive industry,48 is not currently expected to be a component of commercial automotive catalysts.49 None of the other possible interferences (88Sr16O+, 64Zn40Ar+ and 208Pb++ on 104Pd, and 89Y16O+, 68Zn37Cl+ and 88Sr16OH+ on 105Pd)7,14 are significant in the matrix of LGC3101. Argide interferences are not easily formed and would require considerable amounts of Cu, Ni or Zn in the samples to affect the determination of Rh, Ru or Pd.4 Doubly charged interferences from 206, 208Pb++ must, nevertheless, be considered in the determination of 103Rh and 104Pd by ICP-QMS in the matrices containing very high level of lead such as used automobile catalyst samples NIST SRM 2556 and 2557. The mass resolution of icpTOF2R is, however, sufficient to resolve these interferences (m/Δm required is ca. 1250).14 The use of leaded petrol stopped in high-income countries by 2002 and globally in July 2021 when service stations in Algeria stopped providing it,50 so the probability of high level of Pb found in used catalytic converters is now low and decreasing.
Ru ratio (>2000) rendering this interference negligible. Ruthenium, although initially tested as a catalyst in automotive industry,48 is not currently expected to be a component of commercial automotive catalysts.49 None of the other possible interferences (88Sr16O+, 64Zn40Ar+ and 208Pb++ on 104Pd, and 89Y16O+, 68Zn37Cl+ and 88Sr16OH+ on 105Pd)7,14 are significant in the matrix of LGC3101. Argide interferences are not easily formed and would require considerable amounts of Cu, Ni or Zn in the samples to affect the determination of Rh, Ru or Pd.4 Doubly charged interferences from 206, 208Pb++ must, nevertheless, be considered in the determination of 103Rh and 104Pd by ICP-QMS in the matrices containing very high level of lead such as used automobile catalyst samples NIST SRM 2556 and 2557. The mass resolution of icpTOF2R is, however, sufficient to resolve these interferences (m/Δm required is ca. 1250).14 The use of leaded petrol stopped in high-income countries by 2002 and globally in July 2021 when service stations in Algeria stopped providing it,50 so the probability of high level of Pb found in used catalytic converters is now low and decreasing.
For 195, 196Pt the only significant interferences are 179, 180Hf16O+. These cannot be resolved by using current ICP-TOFMS instrumentation and need to be minimized by other means. Desolvating sample introduction systems have been shown to significantly reduce the level of HfO+ and, therefore, to minimise interferences on 195Pt and 196Pt.15,51 A solution containing 60 μg kg−1 Hf was analysed in each batch to confirm the level of interferences of HfO+ on Pt isotopes. Because 179, 180HfO+/179, 180Hf+ was kept <0.3%, the contribution of 179, 180HfO+ interference to the 195, 196Pt+ signal at the level of Hf present in the LGC3101 sample extract was estimated as <0.03% and deemed insignificant comparing to other sources of analytical bias.
Mass fractions of Rh, Pd and Pt in automobile catalyst materials
Isotope dilution ICP-TOFMS analysis under the conditions chosen for best selectivity as well as for best isotope ratio precision (with a desolvating nebuliser and He collision gas) is expected to provide data with low analytical bias, usually caused by spectral interferences. Another important source of bias is sample preparation, e.g., incomplete acid digestion. Simpson et al.4 showed that, even in cases where a small fraction of ceramics constitution the catalytic converter is not fully dissolved, it is unlikely to cause a detectable bias in the Rh, Pd and Pt concentration due to these elements being efficiently leached out of the solid matrix into solution. Analysis of both used and unused automobile catalyst CRMs (NIST SRM2557 and ERM-EB503a) that were extracted simultaneously using the same acid mixture as the LGC3101 sample showed recoveries of 96–100% (Table 5). The mass fractions of all three elements of interest (Rh, Pd and Pt) in the candidate CRM LGC3101 have been determined with relative combined expanded uncertainties Ur ≤ 1.0%. Equally low uncertainties (Ur ≤ 1.2%) are associated with the measurements of Rh and Pt mass fractions in both NIST SRM2557 and ERM-EB503a and of Pd in ERM-EB503a. The mass fraction of Pd in NIST SRM2557, which is much lower than that in the other two materials analysed in this study, was determined with larger uncertainty.| Sample | Rh | Pd | Pt | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w, mg kg−1 | U, mg kg−1 | U r, % | Reference value ± U (k = 2), mg kg−1 | w, mg kg−1 | U, mg kg−1 | U r, % | Reference value ± U (k = 2), mg kg−1 | w, mg kg−1 | U, mg kg−1 | U r, % | Reference value ± U (k = 2), mg kg−1 | |
| a Beary and Paulsen (1995),5 uncertainties recalculated to k = 2. b Hearn et al. (2008),9 Hauswaldt et al. (2012).27 c European Reference Materials (2008).26 | ||||||||||||
| LGC3101 | 203.2 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2875 | 28 | 1.0 | 1878 | 14 | 0.8 | |||
| NIST SRM2557 | 133.1 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 135.1 ± 1.5a | 234.1 | 7.6 | 3.3 | 233.2 ± 1.5a | 1123 | 8 | 0.7 | 1131 ± 9a |
| ERM-EB503a | 232.9 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 234.0 ± 4.2b | 2675 | 26 | 1.0 | 2780 ± 80c | 1841 | 18 | 1.0 | 1880 ± 30c |
Assessment of the developed methodology by participation in an interlaboratory comparison study
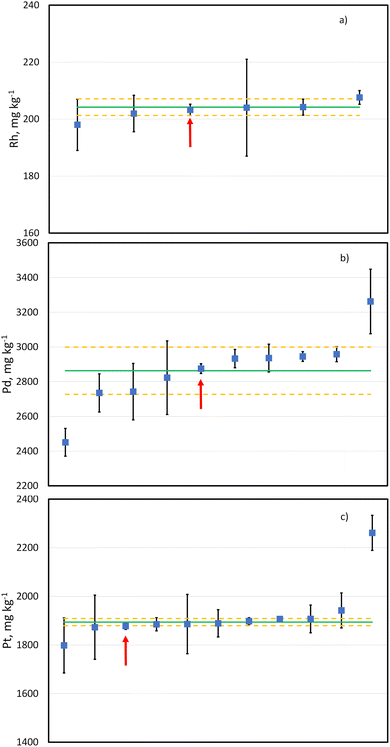
The candidate reference material LGC3101 has also been used as the sample in the international interlaboratory comparison study CCQM K160 (Platinum Group Elements in Automotive Catalyst).52 Results for this study have been produced by participating national metrology and designated institutes. More institutions submitted results for Pt and Pd (11 and 10, respectively) than for Rh (6). However, there deemed to be enough data to produce provisional comparison reference values for all three elements. Anonymised submitted results with their uncertainties as well as provisional consensus values are shown in Fig. 5. For all the three elements the results provided with the method described in this paper are well within the uncertainty of the provisional comparison reference values and they all have an associated relative expanded uncertainty (k = 2) lower than 1%. This demonstrates the accuracy of the developed methodology for the determination of Pt, Rh and Pd in an automobile catalyst with the required measurement uncertainty by PGMs manufacturers.Conclusions
Isotope dilution ICP-TOFMS determination of Pd and Pt and exact matching internal standard determination of Rh in complex autocatalyst matrices at concentration levels of ca. 3000, 2000 and 200 mg kg−1, respectively, was achieved with an expanded combined uncertainty (k = 2) lower than 1%. This was possible due to improved isotope ratio precision by ICP-TOFMS combined with use of a desolvating nebuliser and He collision gas, the latter being used for reduction of matrix-induced interferences on the target PGM isotopes. The developed methodology was validated by analysis of two CRMs with a similar matrix and by participation in the international interlaboratory comparison study CCQM K160 (Platinum Group Elements in Automotive Catalyst) in which the LGC values agreed well with the comparison reference values and their associated measurement uncertainty.Author contributions
S. Strekopytov: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, validation, visualization, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing. J. Entwisle: methodology, investigation, validation, writing – review & editing. S. Hill: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing – review & editing. H. Goenaga Infante: conceptualisation, methodology, resources, supervision, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The work described in this paper was funded in part by the UK Government's Department for Science, Innovation and Technology (DSIT) through the UK National Measurement System Chemical and Biological Metrology Programme. Reference Material Production Team, LGC is acknowledged for the preparation of the automotive catalyst sample LGC3101 and Christian Ward-Deitrich is thanked for data checking.References
- M. Omrani, M. Goriaux, Y. Liu, S. Martinet, L. Jean-Soro and V. Ruban, Platinum group elements study in automobile catalysts and exhaust gas samples, Environ. Pollut., 2020, 257, 113477 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Golunski, Why use platinum in catalytic converters?, Platinum Met. Rev., 2007, 51(3), 162 CrossRef CAS.
- P. L. C. Johnson Matthey, PGM Market Report May 2023, 2023 Search PubMed.
- L. Simpson, R. Hearn, S. Merson and T. Catterick, The development of a high accuracy method for the analysis of Pd, Pt and Rh in auto catalysts using a multi-collector ICP-MS, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2004, 19, 1244–1251 RSC.
- E. S. Beary and P. J. Paulsen, Development of high-accuracy ICP mass spectrometric procedures for the quantification of Pt, Pd, Rh, and Pb in used auto catalysts, Anal. Chem., 1995, 67, 3193–3201 CrossRef CAS.
- J. A. Brown, F. W. Kunz and R. K. Belitz, Characterization of automotive catalysts using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: Sample preparation, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1991, 6, 393–395 RSC.
- S. Rauch, M. Motelica-Heino, G. M. Morrison and O. F. X. Donard, Critical assessment of platinum group element determination in road and urban river sediments using ultrasonic nebulisation and high resolution ICP-MS, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2000, 15, 329–334 RSC.
- L. Bencs, K. Ravindra and R. V. Grieken, Methods for the determination of platinum group elements originating from the abrasion of automotive catalytic converters, Spectrochim. Acta, Part B, 2003, 58, 1723–1755 CrossRef.
- R. Hearn, C. S. J. Wolff-Briche and M. Sargent, CCQM-P63: Platinum Group Elements in an Automotive Catalyst, LGC/VAM/2006/028, 2008 Search PubMed.
- FLUXANA GmbH & Co. KG, Certified Reference Materials Used Auto Catalyst FLX-CRM 132, FLX-CRM 133, Certificate of Analysis, 2016 Search PubMed.
- A. Coad, G. Biggi and E. Giuliani, Asbestos, Leaded Petrol, and Other Aberrations: Comparing Countries' Regulatory Responses to Disapproved Products and Technologies, JRC Working Papers on Corporate R&D and Innovation No 08/2019, European Commission, 2019 Search PubMed.
- F. M. Pennebaker and M. B. Denton, High-precision, simultaneous analysis of Pt, Pd, and Rh in catalytic converter samples by Carius tube dissolution and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy with charge-injection device detection, Appl. Spectrosc., 2001, 55, 504–509 CrossRef CAS.
- J. A. Rodríguez-Castrillón, M. Moldovan and J. Ignacio García Alonso, Internal correction of hafnium oxide spectral interferences and mass bias in the determination of platinum in environmental samples using isotope dilution analysis, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2009, 394, 351–362 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Köllensperger, S. Hann and G. Stingeder, Determination of Rh, Pd and Pt in environmental silica containing matrices: Capabilities and limitations of ICP-SFMS, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2000, 15, 1553–1557 RSC.
- C. Fragniére, M. Haldimann, A. Eastgate and U. Krähenbühl, A direct ultratrace determination of platinum in environmental, food and biological samples by ICP-SFMS using a desolvation system, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2005, 20, 626–630 RSC.
- N. Sugiyama and Y. Shikamori, Removal of spectral interferences on noble metal elements using MS/MS reaction cell mode of a triple quadrupole ICP-MS, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2015, 30, 2481–2487 RSC.
- T. Suoranta, S. N. H. Bokhari, T. Meisel, M. Niemelä and P. Perämäki, Elimination of Interferences in the determination of palladium, platinum and rhodium mass fractions in moss samples using ICP-MS/MS, Geostand. Geoanal. Res., 2016, 40, 559–569 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Held, L. Van Nevel, E. Poulsen and P. D. P. Taylor, IMEP-11: Metals in car exhaust catalyst, Report to Participants, GE/R/IM/1/99, EUR 18735 EN, 1999 Search PubMed.
- L. Van Nevel, I. Papadakis and P. Taylor, International Measurement Evaluation Programme (IMEP); prospects at the start of the 21st century, CITAC (Co-operation on International Traceability in Analytical Chemistry) News, 2000, February 2000, 8 Search PubMed.
- S. Recknagel and M. Michaelis, Certification of the mass fractions of Pt, Pd and Rh in a used car catalyst reference material, Accredit. Qual. Assur., 2009, 14, 277–280 CrossRef CAS.
- Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM), ERM-EB504a Platinum group elements in used automobile catalyst, Certificate of analysis, 2016 Search PubMed.
- Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM), BAM-M504b Used automobile catalyst, Certificate of analysis, 2022 Search PubMed.
- M. Senila, O. Cadar, L. Senila, S. Böringer, K. Seaudeau-Pirouley, A. Ruiu and P. Lacroix-Desmazeset, Performance parameters of inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry techniques for Pd and Pt determination in automotive catalysts, Materials, 2020, 13, 5136 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Payette, The determination of platinum, palladium and rhodium in autocatalyst. An exploration of sample preparation techniques for the rapid sequential multi-elemental ICP-MS analysis, MSc thesis, Laurentian University, Sudbury, Ontario, Canada, 1997.
- J. Faber and K. Brodzik, Influence of preparation and analysis methods on determination of Rh, Pd and Pt content in automotive catalysts samples, IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2018, 421, 042018 Search PubMed.
- European Reference Materials, ERM-EB503a Platinum Group Elements in Unused Automobile Catalyst, Certificate of Analysis, 2008 Search PubMed.
- A. L. Hauswaldt, O. Rienitz, R. Jährling, N. Fischer, D. Schiel, G. Labarraque and B. Magnusson, Uncertainty of standard addition experiments: A novel approach to include the uncertainty associated with the standard in the model equation, Accredit. Qual. Assur., 2012, 17, 129–138 CrossRef.
- K. G. Heumann, S. M. Gallus, G. Radlinger and J. Vogl, Precision and accuracy in isotope ratio measurements by plasma source mass spectrometry, Anal. At. Spectrom., 1998, 13, 1001–1008 RSC.
- F. Vanhaecke, L. Moens, R. Dams, L. Allen and S. Georgitis, Evaluation of the isotope ratio performance of an axial time-of-flight ICP mass spectrometer, Anal. Chem., 1999, 71, 3297–3303 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Hendriks, A. Gundlach-Graham, B. Hattendorf and D. Günther, Characterization of a new ICP-TOFMS instrument with continuous and discrete introduction of solutions, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2017, 32, 548–561 RSC.
- S. Willie, Z. Mester and R. E. Sturgeon, Isotope ratio precision with transient sample introduction using ICP orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight mass spectrometer, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2005, 20, 1358–1364 RSC.
- R. E. Sturgeon, J. W. H. Lam and A. Saint, Analytical characteristics of a commercial ICP orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight mass spectrometer (ICP-TOFMS), J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2000, 15, 607–616 RSC.
- O. B. Bauer, O. Hachmöller, O. Borovinskaya, M. Sperling, H.-J. Schurek, G. Ciarimboli and U. Karst, LA-ICP-TOF-MS for rapid, all-elemental and quantitative bioimaging, isotopic analysis and the investigation of plasma processes, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2019, 34, 694–701 RSC.
- M. von der Au, S. Faßbender, M. I. Chronakis, J. Vogl and B. Meermann, Size determination of nanoparticles by ICP-ToF-MS using isotope dilution in microdroplets, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2022, 37, 1203–1207 RSC.
- S. Faßbender, M. von der Au, M. Koenig, J. Pelzer, C. Piechotta, J. Vogl and B. Meermann, Species-specific isotope dilution analysis of monomethylmercury in sediment using GC/ICP-ToF-MS and comparison with ICP-Q-MS and ICP-SF-MS, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2021, 413, 5279–5289 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Ohata and H. Hagino, Examination on simultaneous multi-element isotope ratio measurement by inductively coupled plasma time of flight mass spectrometry, Int. J. Mass Spectrom., 2018, 430, 31–36 CrossRef CAS.
- R. L. Watters Jr, K. R. Eberhardt, E. S. Beary and J. D. Fassett, Protocol for isotope dilution using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) for the determination of inorganic elements, Metrologia, 1997, 34, 87–96 CrossRef.
- Y.-C. Yip, J. C.-W. Lam and W.-F. Tong, Commonly used methodologies for inorganic analysis in international key comparisons, Trends Anal. Chem., 2009, 28, 214–236 CrossRef CAS.
- D. C. Baxter, I. Rodushkin and E. Engström, Isotope abundance ratio measurements by inductively coupled plasma-sector field mass spectrometry, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2012, 27, 1355–1381 RSC.
- J.-M. Mermet and J. C. Ivaldi, Real-time internal standardization for inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry using a custom segmented-array charge coupled device detector, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1993, 8, 795–801 RSC.
- I. S. Begley and B. L. Sharp, Characterisation and correction of instrumental bias in inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry for accurate measurement of lead isotope ratios, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1997, 12, 395–402 RSC.
- F. Burgay, T. Erhardt, D. D. Lunga, C. M. Jensen, A. Spolaor, P. Vallelonga, H. Fischer and C. Barbante, Fe2+ in ice cores as a new potential proxy to detect past volcanic eruptions, Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 654, 1110–1117 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Theiner, A. Schoeberl, S. Neumayer and G. Koellensperger, FI-ICP-TOFMS for high-throughput and low volume multi-element analysis in environmental and biological matrices, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2019, 34, 1272–1278 RSC.
- D. R. Bandura and S. D. Tanner, Effect of collisional damping in the dynamic reaction cell on the precision of isotope ratio easurements, At. Spectrosc., 1999, 20(2), 69–72 CAS.
- P. K. Appelblad, I. Rodushkin and D. C. Baxter, Sources of uncertainty in isotope ratio measurements by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Anal. Chem., 2001, 73, 2911–2919 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- JCGM 100:2008 GUM 1995 with Minor Corrections. Evaluation of Measurement Data—Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement, JCGM, 2008 Search PubMed.
- R. R. Barefoot, Determination of the precious metals in geological materials by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 1998, 13, 1077–1084 RSC.
- M. Shelef and H. S. Gandhi, The reduction of nitric oxide in automobile emissions: Stabilisation of catalysts containing ruthenium, Platinum Met. Rev., 1974, 18(1), 2–14 CAS.
- M. Müller and K. G. Heumann, Isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry in connection with a chromatographic separation for ultra trace determinations of platinum group elements (Pt, Pd, Ru, Ir) in environmental samples, Fresenius. J. Anal. Chem., 2000, 368, 109–115 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Rukikaire, Era of leaded petrol over, eliminating a major threat to human and planetary health, United Nations Environment Programme, 30 August 2021, https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/press-release/era-leaded-petrol-over-eliminating-major-threat-human-and-planetary, Retrieved 23/11/2023 Search PubMed.
- P. Gabrielli, A. Varga, C. Barbante, C. Boutron, G. Cozzi, V. Gaspari, F. Planchon, W. Cairns, S. Hong, C. Ferrari and G. Capodaglio, Determination of Ir and Pt down to the sub-femtogram per gram level in polar ice by ICP-SFMS using preconcentration and a desolvation system, J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2004, 19, 831–837 RSC.
- J. Entwisle, C. Ward-Deitrich, S. Strekopytov, A. Abukashabeh, S. Hill and H. Goenaga-Infante, The Use of ICP-MS/MS to Overcome Interferences for the Determination of Technology Critical Elements Relevant to the Urban Mine and Recycling Industry, European Winter Conference on Plasma Spectrochemistry, Ljubljana, Slovenia, January 29th – February 3rd, Book of Abstracts, 2023, p. 119 Search PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |