Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleAza-bicyclodiene based photoswitches for molecular solar thermal energy storage†
Akanksha Ashok
Sangolkar
,
Rama Krishna
Kadiyam
and
Ravinder
Pawar
 *
*
Laboratory of Advanced Computation and Theory for Materials and Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, National Institute of Technology Warangal (NITW), Warangal, Telangana-506004, India. E-mail: ravinder_pawar@nitw.ac.in
First published on 28th November 2023
Abstract
Harnessing and storage of solar radiations employing molecular photoswitches are certainly of intense research interest en route to alleviate the increasing energy demand. The present report aims to scrutinize the effect of N-Substitution on the photoswitching behaviour of bicyclodienes with different bridge lengths for molecular solar thermal energy storage (MOST) application. The result reveals that the bicyclodiene attains stability with an increase in bridge length due to a decreasing ring strain, while the photoproduct acquires strain and becomes destabilized. Consequently, as the bridge length increases, the storage energy is enhanced while the back reaction barrier decreases. The photoswitching properties can be greatly altered based on the position of N in aza-bicyclodiene. Aza-bicyclodiene photoswitches are isobaric with the parent systems and do not reduce the energy storage density, unlike the bulky electron releasing and withdrawing substituents. N-substitution at the bridgehead position enhances the thermal back reaction barrier without compromising the storage energy in long-bridged switches. Further, N-substitution is effective at shifting (bathochromic) the excitation wavelength to the longer wavelength region of the spectrum. Therefore, N-substitution in long-bridge bicyclodiene photoswitches could be beneficial to improve the thermochemical as well as photophysical properties for MOST application.
1. Introduction
Fossil fuels, like natural gas, crude oil, and coal—although they are exhaustible energy resources—are currently the chief contributors to meet the energy demand.1,2 The natural reserves of these energy resources, however, are rapidly exhausting, but nevertheless the requirement for energy is always perpetual.2,3 The worldwide need for energy is further likely to increase by at least two-fold in the future.2,4 Therefore, the search for an inexhaustible energy resource to sustainably meet the increasing energy crises is an ongoing and focussed area of research.1,2,5The solar radiations emitted by the Sun are the fundamental, inexhaustible and ultimate energy resource responsible for the existence of life on the Earth.3,6 Living organisms containing chlorophyll pigments are capable of harvesting the solar energy and convert it into chemical energy via photosynthesis.6,7 This biological phenomenon has inspired researchers to develop modern technologies, like solar cells, photocatalytic devices, energy dense fuels, molecular solar thermal energy storage devices, etc., that can utilize energy from solar radiation.5,8–13 The intermittent and uneven geographical distribution of solar radiation has triggered the development of technological devices that not only aid the harnessing but also facilitate the long-term storage of solar energy.2,5,14
A light-responsive molecule that can undergo photoinduced excitation to produce a metastable isomer and revert back to the parent isomer when triggered is known as a molecular photoswitch.15 Photoswitching couples have a potential to mimic this biological phenomenon and possess the ability to harness solar energy and store it in the chemical bonds as a metastable photoisomer.5,16–20 This stored chemical energy can be converted back into the thermal energy via activation of the metastable photoproduct when desired.5,21 The photoswitching molecules can serve as a means to harvest, store, and release energy, and thus promise to meet the energy crisis in a sustainable manner.5,21 The devices that employ photoswitches for the harvesting and storage of solar energy are called molecular solar thermal energy storage (MOST) systems or solar thermal fuels (STF).5,16–19,22,23
The pioneering work on abiotic light harvesting molecular photoswitching systems were reported by Yoshida (1985) and Bren et al. (1991), and previously summarized by Dubonosov et al. (2002).24–26 Thereafter, the field was thoroughly investigated and significantly uplifted by Moth-Poulsen and co-workers with their several experimental and theoretical studies. These investigations have inspired the scientific research community to further inspect the chemical photoswitches for MOST applications.5,17–19,21,22,27–35 Hitherto, a variety of molecular photoswitches, including the tetracarbonyl-fulvalene-diruthenium complexes, anthracenes, norbornadiene/quadricyclane (NBD/QC), dihydroazulene/vinylheptafulvene, azobenzenes, etc., are known.5,21,29,32,33,36–55 Among all, the NBD/QC couple, which involves the [2+2]-cycloaddition of bridged bicyclodiene molecule to give a strained metastable photoadduct is extensively investigated for MOST applications due to its high energy storage density.5,22,31,41,54–56 However, the low thermal back-reaction barrier and optical absorption in the UV region hinders its practical applicability as an effective MOST systems.16–18En route to make NBD/QC couple relevant for the practical real-life application, research has also been conducted to tune their thermochemical and photophysical properties via different substitutions.5,14,21,26,57 Despite of enormous efforts, a photoswitching couple with all the desired properties for practical MOST applications has not been achieved yet.5,14 This is because incorporating all the essential features in a single photochromic couple for their practical MOST application is extremely challenging.5,21,24
Recently, the Moth-Poulsen and Mikkelsen groups demonstrated that an increase by one methylene (–CH2–) bridging unit in the NBD/QC system results in a bicyclooctadiene/tetracyclooctane (BOD/TCO) couple with an enhanced storage energy.17,18 Thereafter, a high-throughput screening of nearly half a million photoswitches carried out to analyse the MOST applications reveals that the best properties were mostly exhibited by the systems with longer bridges.58 Further increases in bridge length of the bicyclic diene improves the storage energy but compromises the thermal back reaction (TBR) barrier.16 This is attributed to ring strain, however the strain energy has not been quantitatively assessed, which is certainly crucial for rational designing of the photoswitching systems in the future. More recently, the influence of N-substitution on the properties of a BOD/TCO photoswitch has been reported, however there is no clue for the effect of N-substitution with the different bridge lengths.59
In the present investigation, ring strain in various bicyclic diene photoswitching systems with different bridge lengths were quantified. Further, the impacts of ring strain on the thermochemical properties are discussed to assist future MOST system designing and engineering. The prominent objective is to forecast the influence of the position of aza-substitution on the thermochemical and photophysical properties of various bicyclic diene photoswitching systems with different bridge lengths.
2. Computational details
The geometries of all the reactants, transition states (TS) and products were fully optimized employing the M06-2X functional and 6-311++G** Pople-style basis set without any geometrical or symmetrical constraints. Previous benchmarking studies of both the NBD/QC and BOD/TCO photoswitching couples suggest that the geometry and thermochemical properties are better predicted with the M062X/6-311++G** level of theory.17,55 Therefore, the same method was employed for the computation of the studied bicyclodiene photoswitches. The nature of the critical point structures was characterized as local minima by the harmonic frequency calculations. The time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) calculations were performed to shed light on the photophysical properties of the photoswitching systems. The vertical excitation energies for first fifteen singlet electronic excited states were calculated with the TD-M06-2X/6-311++G** method. The ring strain energy (SE) which is calculated as the difference between the energy of the molecule with the sum of the energy of the group equivalents in the molecule. SE is calculated at the M06-2X/6-31+G(2df,p) level of theory, as illustrated in a recent report.60 All these calculations were performed using the Gaussian16 suite program.61The harnessed solar energy that can be stored as chemical energy in a metastable photoproduct is the storage energy (ΔGstr) of the photoswitching couple. The storage energy is calculated as the difference between the Gibbs free energy of the metastable photoisomer and the parent molecule using the following equation:
| ΔGstr = Gphotoproduct − Gparent | (1) |
| ΔGstr = ΔEstr − ΔGthermal | (2) |
The thermal back reaction barrier (ΔGTBR) is the amount of activation energy required for back conversion of the metastable photoproduct into the parent isomer. It can be calculated as:
| ΔGTBR = GTS − Gphotoproduct | (3) |
The transition state involves the formation of singlet biradicals during the thermal ring-opening of the metastable cycloadduct.22 Owing to the multireference character of the transition state, the DFT functionals are inappropriate to predict the structure and often overestimates the thermal back reaction (TBR) barrier.22 Previous benchmarking studies have revealed that the PBE functional is better to predict the transition state geometry while its energy can be determined with the multiconfigurational complete active space (CAS) calculations.22 Therefore, in this investigation, the geometry of the transition state interconnecting the parent molecule and corresponding photoproduct was determined with PBE via climbing image nudged elastic band (CI-NEB) calculations implemented in the Quantum Espresso package.62 Thereafter, the electronic energy of the transition state and photoproduct was determined with the (8,8)-CASPT2/6-311++G** method, analogous to that in the previous report.16 Therefore, the computational methods employed for the calculations of the studied systems are appropriate as required for the bicyclic diene based photoswitches.
Here, the ΔETBR was calculated as the difference in the electronic energy of the biradical TS (ETS) and photoproduct (Ephotoproduct) using the following equation:
| ΔETBR = Ephotoproduct − ETS | (4) |
The parent bicyclic dienes with different bridge lengths and their corresponding N-substituted photoswitches considered in this investigation, along with their abbreviations used throughout the text, are schematically presented in Scheme 1. Herein, a total of 42 photochromic couples were analysed for their properties relevant for MOST applications. More accurate electronic energies of 84 molecules were estimated with single point energy calculations at the DLPNO-CCSD(T)/Def2TZVP level. In addition, the electronic energy of 84 molecules were calculated using the complete active space method (8,8)-CASPT2/6-311++G** for an appropriate consideration of their multireference character.
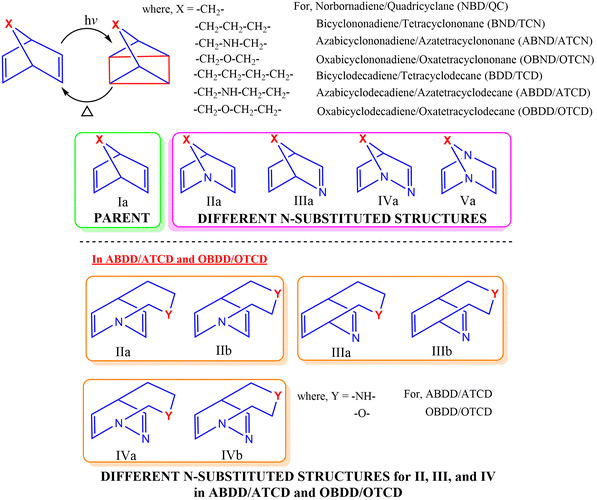 | ||
| Scheme 1 Schematic representation of the various parents and N-substituted bicyclodiene based photoswitching systems considered for the study. | ||
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Ring strain energy (SE) analysis
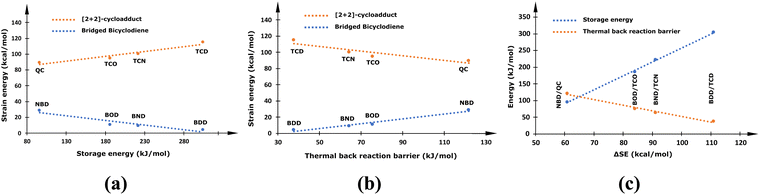
Recent studies have suggested that increasing the methylene (–CH2–) bridging units in a prototypical NBD/QC couple enhances the storage energy of the resulting bridged bicyclodiene photoswitching systems.16,18 This is achieved due to the alteration of molecular ring strain in the bicyclic diene and corresponding [2+2]-photoadduct. The molecular ring strain is measured by the strain energy (SE) and governs the stability of cyclic molecule, and thus modifies the thermochemical properties of the photoswitches. Even though molecular strain is a useful entity for the rational designing of strained bridged bicyclodiene-based photoswitches, it has not been quantitatively assessed yet. Therefore, in the present investigation, ring SEs in the bridged bicyclic dienes and their respective photoisomers were estimated. Moreover, the variation in the thermochemical properties with the ring SEs were analysed and the resulting data is systematically presented in Fig. 1. The calculated energy values are provided in S1 of the ESI† (Table S1).The calculated ring strain energy decreases from 28.95 to 4.28 kcal mol−1 with the progressive increase of –CH2– units in the bridge (NBD to BDD) and the resulting bicyclic diene attains a high stability. However, the ring SE in the metastable [2+2]-cycloadduct obtained upon photoconversion increases from 89.75 to 115.19 kcal mol−1 with bridge length (QC to TCD), thereby drastically increasing the instability of the photoproduct. Consequently, the difference in SE between the parent bicyclodiene and the corresponding cycloadduct (ΔSE) becomes larger (60.79 to 110.91 kcal mol−1) as the bridge length increases. Therefore, the storage energy is remarkably improved from the NDB/QC (96.06 kJ mol−1) to the BDD/TCD (304.39 kJ mol−1) photoswitching system. The enhanced instability induced due to ring strain in the metastable photoisomer upsurges its propensity to revert back to the parent molecule. Therefore, the barrier to a thermal back reaction decreases from 121.77 to 37.63 kJ mol−1 with the increase in –CH2– bridging units (QC to TCD). Overall, the ring strain energy of the photoisomers is crucial to modulate the thermochemical properties of the MOST applications, as can be clearly seen in Fig. 1. The increase in bridge length, although it enhances the storage energy, remarkably affects the storage time due to the enhanced ring strain in the metastable photoisomer. Therefore, a larger ΔSE between two photoisomers can improve the thermochemical properties, provided that the ring strain in the metastable product does not increase significantly.
3.2 Thermochemical properties
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ε = 2) at ∼267 nm in acetonitrile solvent, which is also closer to the excitation wavelength computed in the gaseous phase.65 This ensures the reliability of the obtained outcomes.
ε = 2) at ∼267 nm in acetonitrile solvent, which is also closer to the excitation wavelength computed in the gaseous phase.65 This ensures the reliability of the obtained outcomes.
| System | Storage energy (kJ mol−1) | λ reactant (nm) | λ product (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated | Reported16 | Calculated | Reported16 | Calculated | Reported16 | |
| NBD/QC | 96.06 | 96.30 | 214.42 | 213.65 | 184.63 | 190.74 |
| BND/TCN | 222.00 | 223.00 | 206.69 | 206.67 | 199.61 | 208.46 |
| ABND/ATCN | 220.32 | 220.50 | 242.09 | 250.44 | 207.27 | 223.07 |
| OBND/OTCN | 213.25 | 213.70 | 213.22 | 216.45 | 193.35 | 204.87 |
| BDD/TCD | 304.39 | 305.80 | 207.52 | 207.66 | 202.19 | 210.97 |
| ABDD/ATCD | 299.99 | 302.60 | 223.66 | 239.98 | 208.76 | 219.63 |
| OBDD/OTCD | 290.76 | 292.40 | 204.14 | 211.98 | 198.98 | 209.74 |
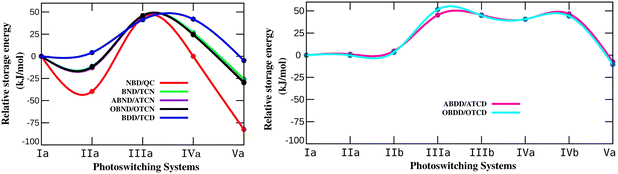
En route to unravel the impact of N-substitution, ΔGstr was estimated for the various N-substituted systems of different bicyclodiene photoswitches. The variation in ΔGstr for different N-substitutions in the studied bicyclodiene systems with different bridge lengths is shown in Fig. 2. Herein, the ΔGstr of parent molecular photoswitching systems was considered as zero and the energies for different aza-substituted systems were accounted relative to their parent photoswitches. The calculated ΔGstr values are provided in S2 of the ESI† (Tables S2–S8).
It has been observed that the presence of N at the bridgehead position (IIa-NBD/QC) decreases the storage energy to 56.47 kJ mol−1 when compared with that of the parent NBD/QC (96.06 kJ mol−1) (Table S2 of the ESI†). The calculated storage energy for IIa-NBD/QC is in accordance with the previously reported value of 53.81 kJ mol−1 (12.86 kcal mol−1) for the same system calculated with the B3LYP/6-311++G* level.66 The storage energy is significantly reduced to 13.48 kJ mol−1 in the Va-NBD/QC photoswitch, where both the bridgehead C atoms are replaced by N. Notably, the substitution of N at the unsaturated C of a bicyclodiene (IIIa-NBD/QC) significantly increases the storage energy up to 139.77 kJ mol−1. This value is also in agreement with the earlier reported value of 135.90 kJ mol−1 (32.48 kcal mol−1) for N-substitution at the unsaturated position in the NBD.66 The storage energy of IVa-NBD/QC is 96.02 kJ mol−1 which is close to the parent NBD/QC system. This infers that the effect on ΔGstr is only marginal if the bridgehead and closest unsaturated C of bicyclodiene are replaced by N. The observed trend of variation in storage energy with position of N in bicyclodiene-based photoswitches with different bridge lengths resembles that of the NBD/QC system and the recently reported BOD/TCO system.59 This indicates that the position of N is crucial for modulating the storage energy in bicyclodiene-based photoswitches with different bridge lengths. Notably, the presence of N in the unsaturated position improves the storage energy, whereas replacing the bridgehead C with N may degrade the energy storage properties in the studied bicyclodiene based photoswitches.
Although the trend in ΔGstr depends on the position of N, the extent of variation for the studied bicyclic dienes differs considerably with the bridge length. The reductions in ΔGstr for the bridgehead N-substituted IIa- and Va-NBD/QC systems are 39.59 and 82.58 kJ mol−1, respectively. A recently reported BOD/TCO couple displayed a decrease in ΔGstr of 19.42 and 39.12 kJ mol−1 for the same bridgehead N-substituted systems.59 However, the reductions in ΔGstr in the BND/TCN, ABND/ATCN, and OBND/OTCN photoswitches are only 11.24 to 12.90 kJ mol−1 for the IIa and 25.71 to 29.88 kJ mol−1 for the Va systems. ΔGstr is decreased by only 0.23 kJ mol−1 for the IIa-OBDD/OTCD couple. Interestingly, the ΔGstr is even enhanced by 1.09 to 4.62 kJ mol−1 in the IIa-BDD/TCD and IIa-ABDD/ATCD systems due to the presence of N at the bridgehead position. But, upon replacement of both bridgehead C atoms with N, 4.76 to 10.39 kJ mol−1 decreases in ΔGstr of the Va-BDD/TCD, Va-ABDD/ATCD, Va-ABDD/ATCD systems are observed. The presence of a heteroatom (N or O) on the bridge has a comparatively minor effect on ΔGstr of the bridged bicyclodiene-based photoswitches. These observations led to the inference that the reduction in ΔGstr with N-substitution at the bridgehead position is more drastic for the NBD/QC system with short bridge lengths. Noteworthy, the decreasing effect in ΔGstr becomes less prominent after elongation of the bridge with –CH2– units. Therefore, the N-substitution at the bridgehead position provides better storage properties in bicyclodiene photoswitches with longer bridges.
It can be noted that the storage energy increases significantly when an unsaturated C is replaced with N in the studied bicyclodiene-based photoswitching systems. The enhancement in ΔGstr is almost constant and ranges from 41.26 to 51.59 kJ mol−1 (Fig. 2) for the studied switches. This clearly suggest that, contrary to N-substitution at the bridgehead position, the increase in ΔGstr of the photoswitching system due to unsaturated N in the bicyclic diene does not depend on the bridge length. Therefore, N-substitution at the unsaturated position of the bicyclodiene would be beneficial to improve the storage energy of all the studied bridged bicyclic diene switches.
Furthermore, there is no significant variation in ΔGstr after replacement of the bridgehead and unsaturated C with N (IVa-NBD/QC) when compared with that of the parent NBD/QC system. According to a recent report, ΔGstr in the BOD/TCO couple increases by 14.34 kJ mol−1 with N substitution at the bridgehead and unsaturated position. The increase in ΔGstr is 24.41 to 26.51 kJ mol−1 for the IVa-BND/TCN, IVa-ABND/ATCN, and IVa-OBND/OTCN systems and 40.59 to 46.66 kJ mol−1 for the IVa-BDD/TCD, IVa-/IVb-ABDD/ATCD, and IVa-/IVb-OBDD/OTCD systems. This clearly indicates that substituting the bridgehead and unsaturated C with N tends to increase ΔGstr with increasing bridge length of the bicyclodiene-based photoswitches. Therefore, the photoswitching systems with longer bridge lengths are better for improving storage energy due to N-substitution at the bridgehead and unsaturated position.
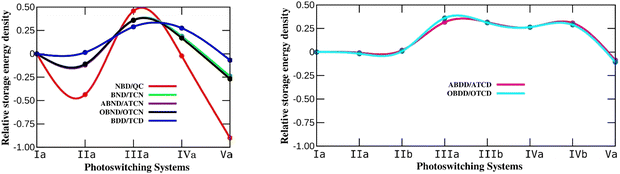
Since molecular photoswitching systems must have a low molecular weight, energy storage density is a more useful quantity to predict the properties of MOST systems. Therefore, energy storage density is calculated for all the studied systems and the values are tabulated in S2 of the ESI† (Tables S2–S8). The variation in energy storage density of N-substituted chemical photoswitches relative to the parent systems is depicted in Fig. 3. It is apparent from the figure that the energy storage density in aza-bicyclodiene based photoswitches depends on the position of N. The trend observed for the variation in energy storage density for the different N-substituted systems is similar to that of storage energy. Since aza-bicyclodiene photoswitches are isobaric with their parent system, the energy density is not affected due to the mass of N. The properties of photoswitching systems are usually tuned by substituting electron donating and withdrawing groups, which reduces the energy storage density.58 In aza-bicyclodiene switches, N may internally involve a push–pull mechanism and the properties can be tuned without reducing the energy storage density due to the mass of N, and thus is advantageous over bulky group substituents.59
During the thermal back conversion of the photoproduct to bicyclodiene, dissociation of the two bonds occurs through an asynchronous mechanism.22 Initially, a bond is cleaved, leading to the formation of singlet biradicals in the transition state (TS).22 Owing to the multireference character of TS, the DFT functionals are inappropriate for predicting the TS and they overestimate the energy barrier.22 Multiconfigurational methods, like CASSCF, are rather more suitable for an accurate prediction of the energy barrier.22 As multiconfigurational calculations are computationally expensive, they cannot be routinely employed for simulations.16,22 A previous benchmark study demonstrated that the electronic energy calculated by CASSCF methods for TS geometries obtained using the PBE functional determine ΔETBR close to the experimental values at a cheaper computational cost.22 Therefore, in the present investigation, the geometry of transition states is obtained through climbing image nudged elastic band (CI-NEB) calculations using the PBE functional. Subsequently, the electronic energy of the transition states and photoproducts were computed with a single point energy calculation at the (8,8)-CASPT2/6-311++G** level of theory.
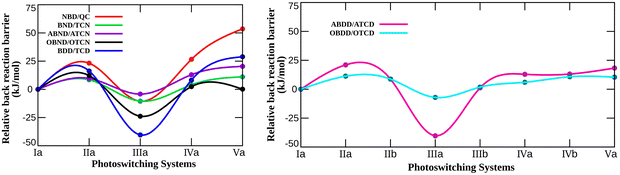
It is apparent from the figure that the energy barrier for the thermal back conversion reaction significantly alters due to N-Substitution. Consistent with the storage energy, the observed trend for the thermal back reaction barrier in the aza-substituted photoswitches depends solely on the position of the N atom. As can be seen from the figure, the barrier height increases by 23.17 kJ mol−1 when N is substituted at the bridgehead position (IIa-NBD/QC) in the NBD/QC photoswitching pair. If both the bridgehead positions are replaced with N atoms (Va-NBD/QC), a substantial increment (53.62 kJ mol−1) in the energy barrier is noticed. In contrast, if the unsaturated C is replaced with N (IIIa-NBD/QC), the ΔETBR decreases by 10.52 kJ mol−1. Moreover, the barrier increases by 26.56 kJ mol−1 when the bridgehead and nearest unsaturated C atoms are replaced with N (IVa-NBD/QC). This clearly indicates that the presence of N in the bridgehead position enhances the energy barrier for the thermal back conversion reaction. Further, substitution of N in the unsaturated position lowers the energy barrier relative to that of the parent photoswitching system. The trend observed for ΔETBR in various N-substituted NBD/QC systems is opposite to that of ΔGstr (Fig. 3 and 4). This simply means that when the thermal back reaction barrier for N-substitution in the short-bridged NBD/QC photoswitches is increased, then the storage energy is adversely affected and vice versa.
The variation in ΔETBR with N-substitution in the photoswitches of different bridge length relative to that of their parent system follows the same trend as that of the aza-NBD/QC pair. Therefore, ΔETBR also increases with the presence of N at the bridgehead position in the photoswitching systems with a longer bridge length. The calculated increase in the energy barriers of the thermal back reaction in the IIa-BDD/TCD and Va-BDD/TCD systems relative to that of their parent BDD/TCD pair are 16.28 and 28.88 kJ mol−1, respectively. As mentioned earlier, the reducing effect of ΔGstr with bridgehead N-substitution becomes less prominent as the bridge length increases in bicyclodiene-based switches. Therefore, the N-substitution at the bridgehead position of the long-bridge photoswitching systems can uplift the barrier height (ΔETBR) without compromising the storage energy.
The overall analysis of thermochemical properties explicitly advocates that the presence of heteroatoms on the bridge have a minimal impact on the photoswitching properties, whereas replacement of the bridgehead or unsaturated C of bicyclodiene by N has a significant effect. Close analysis of the storage energy suggests that the substitution of N at one of the unsaturated C atoms in bicyclodiene remarkably improves the storage energy of the photoswitching system. The storage energy decreases when N is present at the bridgehead position in the short-bridge bicyclodiene photoswitch (NBD/QC pair). Interestingly, the decrease in storage energy becomes less prominent as the bridge length increases. Moreover, the barrier height for thermal back isomerization increases in bridgehead N-substituted systems. Thus, N-substitution at the bridgehead position of the long-bridge bicyclodiene photoswitch (aza-BDD/TCD) exhibits better thermochemical properties than those of the parent BDD/TCD pair. Therefore, it is interesting to mention that in the case of long-bridge photoswitches, the lifespan of the metastable photoproduct can be enhanced without adversely affecting the amount of energy harnessed from solar radiation.
The short-bridged NBD/QC has the least storage energy (96.06 kJ mol−1) and highest TBR barrier (121.76 kJ mol−1). Contrarily, the long bridged BDD/TCD couple displays the largest storage energy (304.39 kJ mol−1) with the least thermal barrier (37.63 kJ mol−1). This clearly infers that an increase in bridge length enhances storage energy of the bicyclic diene photoswitches and compromises the TBR barrier, which is in accordance with the previous report.16 Owing to the large storage energy of the long bridged BDD/TCD couple, it could be considered as a better system to further investigate in the future, as it provides a large scope for tuning the photoswitching properties. Therefore, any structural modifications in the long bridged bicyclic dienes that enhance the thermal barrier for isomerization are desirable for engineering the MOST system.
Outcomes of this work reveal that the impact of N-substitution in these bicyclic dienes depends upon the position of N and size of the bridge. N-substitution at one of the unsaturated positions in diene (III) increases the storage energy by 41.94–51.60 kJ mol−1 at the expense of the TBR barrier. The N-substitution at the bridgehead position (II and III) enhances the barrier for thermal isomerization at the cost of storage energy in the case of short bridged photoswitches. In contrast to this, N-substitution at the bridgehead position enhances the barrier for thermal isomerization without compromising the storage energy in the case of long bridged photoswitches.
Overall, the impact of N-substitution at bridgehead position in the long bridged Va-BDD/TCD couple is the enhancement of TBR by 28.88 kJ mol−1 without significantly reducing the energy storage density relative to that of the Ia-BDD/TCD pair. Therefore, the N-substitution assists tuning the properties of the studied bridged bicyclic diene photoswitches and may guide the future designing of photoswitches for practical MOST applications. Despite the highest increment in TBR, the absolute TBR barrier of IIa- and Va-BDD/TCD systems remains lower than that desired for long-time energy storage devices due to the low intrinsic barrier in the Ia-BDD/TCD system. The results suggest that N-substitution at the bridgehead position could be one of the approaches that will considerably enhance the thermal barrier, while further substitutions must be carried out to make it relevant for practical MOST applications.
Furthermore, the substitution of N at the bridgehead and closest unsaturated position (IV) increases the TBR barrier and storage energy. Therefore, the molecules with these N-substitutions display the best photoswitching properties among the studied switches for MOST applications. The intrinsic TBR barrier of the short-bridged NBD/QC system is larger, and N-substitutions enhance the TBR barrier to 148.33 kJ mol−1 without compromising the storage energy. Thus, among the studied photochromic couples, IVa-NBD/QC could be considered as the best system for energy storage applications.
3.3 Photophysical properties
Absorption of solar radiation by the molecule is one of the pre-requisites to serve as a photoswitching system for MOST applications. Therefore, critical analysis of the photophysical properties of the photoswitching couple is important. The photophysical properties of the studied photochromic couples were calculated and the optical absorption spectra of the parent BDD/TCD, ABDD/ATCD, their various N-substituted bicyclodienes and corresponding photoproducts are depicted in Fig. 5. The optical spectra of other studied systems are provided in S3 of the ESI† (Fig. S1). The spectral data, including the molar absorption coefficient, first important excitation wavelength and oscillatory strength (surpassing 0.01), are tabulated in S3 of ESI† (Tables S9–S15).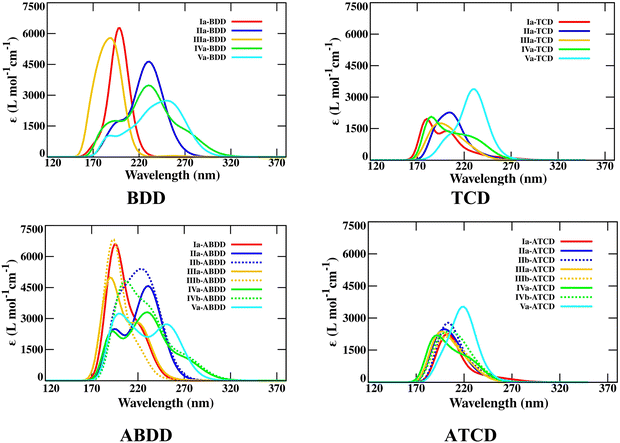 | ||
| Fig. 5 Optical absorption spectra of the parent and N-substituted BDD/TCD and ABDD/ATCD photoswitching systems. | ||
The calculated first excitation wavelengths for NBD, BND, and BDD are 214.42, 206.69, and 207.52 nm, respectively, which is in close agreement with the recently reported values of 213.65, 206.67, and 207.66 nm.16 The photophysical properties are greatly influenced by the substitution of N in these bicyclodienes. Further, the optical absorption spectra (optical properties) vary with the position of N in bicyclodiene molecules similar to that of thermochemical properties. It is noteworthy that the presence of N at the bridgehead position considerably red-shifts the first important excitation wavelength of bicyclodienes. The red-shift in the excitation wavelength becomes more prominent when both bridgehead C atoms are replaced with N. It has been noticed that the replacement of unsaturated C with N in bicyclodienes shows a slight hypsochromic shift in the first important excitation wavelength. This demonstrates that the position of N plays a crucial role in modulating the photophysical properties of bicyclodiene-based photoswitching systems, analogous with the thermochemical properties.
Upon substitution of both the bridgehead C atoms with N, bathochromic shifts of 58.67 and 51.63 nm are noticed in the first excitation wavelengths of Va-BND and Va-BDD, respectively, when compared with those of their parent molecules. The first optical excitation wavelength of Va-BDD is 271.66 nm which is longer than the first excitation wavelength of the most studied NBD (213.65 nm), recently reported bicyclooctadiene (196.44 nm), and unsubstituted bicyclodiene molecules with different bridge lengths.16
En route to probe the delocalization of electrons in aza-bicyclodiene based photoswitches, natural bond orbital (NBO) analyses have been performed for the bicyclic diene and photoproducts. It has been observed that the lone pair of bridgehead N (Nlp) involves the delocalization with π*-bonding orbitals in the bicyclic diene. The stabilization energy for the Nlp → π* charge transfer is 1.21, 3.25, and 15.13 kcal mol−1 in the IIa-NBD, IIa-BND, and IIa-BDD molecules, respectively. This infers that the extent of stabilization achieved due to Nlp → π* electron delocalization increases with the length of the bridge. Likewise, the extent of stabilization achieved due to the Nlp → σ* charge transfer in the photoproduct increases from 4.88 kcal mol−1 in IIa-QC to 14.33 kcal mol−1 in IIa-TCD. This suggests that the lone pair on N may involve an internal push–pull mechanism and assist to modulate the properties of the photoswitches. The stabilization achieved due to the delocalization of Nlp to π*-bonding orbitals in bridgehead N-substituted (II) bicyclic diene photoswitches of different bridge lengths is shown in Fig. 6. In contrast to the bridgehead N, the lone pair on unsaturated N does not facilitate delocalization with the π*-bonding orbitals.
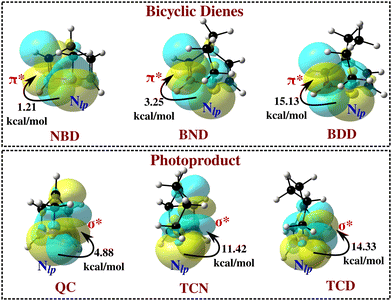 | ||
| Fig. 6 The stabilization achieved due to delocalization of Nlp in bridgehead N-substituted bicyclic diene photoswitches with different bridge lengths. | ||
The relationship of the molecular structure, particularly the position of N with the thermochemical and photophysical properties is systematically summarized in a concise manner in Fig. 7. The results reveal that the substitution of N at the bridgehead position (II) increases the TBR barrier and the first important wavelength of excitation at the cost of the storage energy. The effect is found to be more pronounced if both the bridgehead positions are substituted with N (V). In contrast, the presence of N at the unsaturated position (III) improves the storage energy while the TBR barrier and wavelength of absorption is observed to decrease. Further, the substitution of N at the bridgehead and the closest unsaturated position (IV) mostly increases all three parameters in the studied bridged bicyclic diene photoswitches.
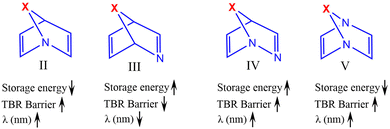 | ||
| Fig. 7 Systematic summary of the relationships of the molecular structure, particularly the position of N with the thermochemical and photophysical properties. | ||
4. Conclusion
The decreasing ring strain energy (28.95 to 4.28 kcal mol−1) stabilizes the bicyclodiene, whereas increasing ring SE (89.75 to 115.19 kcal mol−1) destabilizes the metastable photoproduct with progressive increase in bridge length of the bicyclodiene-based photoswitches. Therefore, the storage energy is improved while the barrier for the thermal back reaction is reduced with an increase in –CH2– units in the bridge. The photoswitching properties of the bridged bicyclodiene-based photoswitches can be significantly altered with the N-substitution and are governed by the position of N. The thermochemical properties elucidate that the replacement of unsaturated C in bicyclodiene with N increases the storage energy but decreases the thermal back reaction barrier. The presence of N at the bridgehead position in the NBD/QC increases the barrier for thermal isomerization at the cost of storage energy. The decrease in storage energy due to N-substitution at the bridgehead position becomes less prominent with an increase in bridge length. Therefore, it is worth mentioning that the thermal back reaction barrier of the bridgehead N-substituted BDD/TCD photoswitch can be uplifted by 28.88 kJ mol−1 without compromising storage energy. Furthermore, the replacement of bridgehead C with N remarkably red-shifts the first important excitation wavelength. Therefore, N-substitution significantly improves the thermochemical and photophysical properties, particularly of the long-bridged bicyclic diene switches. Moreover, the substitution of N at the bridgehead and the closest unsaturated position improves the storage energy, TBR barrier and first excitation wavelength of the studied photoswitching pairs, making them more relevant for MOST applications. The outcomes exclusively emphasize that the N-substitution can greatly modulate the photoswitching properties and will, indeed, be beneficial for future designing of a novel photochromic couple for practical MOST applications.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
We are sincerely thankful to the DST-SERB (EEQ/2023/000424, ECR/2018/002346 and EEQ/2019/000656) for providing the financial support for this work. We are grateful to the Director, National Institute of Technology Warangal (NITW), Warangal, for providing all the facilities required for this work. AAS wishes to thank SERB for the JRF and SERB and the Ministry of Education (MoE), India, for the SRF, and RKK wishes to thank the MoE, India, for the SRF.References
- P. J. Megía, A. J. Vizcaíno, J. A. Calles and A. Carrero, Hydrogen Production Technologies: From Fossil Fuels toward Renewable Sources. A Mini Review, Energy Fuels, 2021, 35, 16403–16415 CrossRef.
- N. S. Lewis and D. G. Nocera, Powering the planet: Chemical challenges in solar energy utilization, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006, 103, 15729–15735 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Ngô and J. B. Natowitz, Our Energy Future, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2016, pp. 1–25 Search PubMed.
- M. Grätzel, Powering the planet, Nature, 2000, 403, 363 CrossRef.
- J. Orrego-Hernández, A. Dreos and K. Moth-Poulsen, Engineering of Norbornadiene/Quadricyclane Photoswitches for Molecular Solar Thermal Energy Storage Applications, Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53, 1478–1487 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. S. Amthor, From sunlight to phytomass: on the potential efficiency of converting solar radiation to phyto-energy, New Phytol., 2010, 188, 939–959 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Collini, Light-Harvesting: The Never-Ending Lesson of Nature, ACS Cent. Sci., 2022, 8, 306–308 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. D. Scholes, G. R. Fleming, A. Olaya-Castro and R. van Grondelle, Lessons from nature about solar light harvesting, Nat. Chem., 2011, 3, 763–774 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Su and L. Vayssieres, A Place in the Sun for Artificial Photosynthesis?, ACS Energy Lett., 2016, 1, 121–135 CrossRef CAS.
- D. K. Dogutan and D. G. Nocera, Artificial Photosynthesis at Efficiencies Greatly Exceeding That of Natural Photosynthesis, Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52, 3143–3148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Gao, K. Huang, C. Long, Y. Ding, J. Chang, D. Zhang, L. Etgar, M. Liu, J. Zhang and J. Yang, Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells: From Materials and Device Architectures to Applications, ACS Energy Lett., 2022, 7, 1412–1445 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Melchionna and P. Fornasiero, Updates on the Roadmap for Photocatalysis, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 5493–5501 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Romano, G. D’Angelo, S. Perathoner and G. Centi, Current density in solar fuel technologies, Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14, 5760–5787 RSC.
- Z. Wang, H. Hölzel and K. Moth-Poulsen, Status and challenges for molecular solar thermal energy storage system based devices, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51, 7313–7326 RSC.
- M.-M. Russew and S. Hecht, Photoswitches: From Molecules to Materials, Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 3348–3360 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Hillers-Bendtsen, P. G. Iuel Lunøe Dünweber, L. H. Olsen and K. V. Mikkelsen, Prospects of Improving Molecular Solar Energy Storage of the Norbornadiene/Quadricyclane System through Bridgehead Modifications, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2022, 126, 2670–2676 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Hillers-Bendtsen, M. Quant, K. Moth-Poulsen and K. V. Mikkelsen, Investigation of the Structural and Thermochemical Properties of [2.2.2]-Bicyclooctadiene Photoswitches, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2021, 125, 10330–10339 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Quant, A. E. Hillers-Bendtsen, S. Ghasemi, M. Erdelyi, Z. Wang, L. M. Muhammad, N. Kann, K. V. Mikkelsen and K. Moth-Poulsen, Synthesis, characterization and computational evaluation of bicyclooctadienes towards molecular solar thermal energy storage, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 834–841 RSC.
- A. Lennartson, A. Roffey and K. Moth-Poulsen, Designing photoswitches for molecular solar thermal energy storage, Tetrahedron Lett., 2015, 56, 1457–1465 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Morikawa, Y. Yamanaka and N. Kimizuka, Liquid Bisazobenzenes as Molecular Solar Thermal Fuel with Enhanced Energy Density, Chem. Lett., 2022, 51, 402–406 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Wang, P. Erhart, T. Li, Z.-Y. Zhang, D. Sampedro, Z. Hu, H. A. Wegner, O. Brummel, J. Libuda, M. B. Nielsen and K. Moth-Poulsen, Storing energy with molecular photoisomers, Joule, 2021, 5, 3116–3136 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Kuisma, A. M. Lundin, K. Moth-Poulsen, P. Hyldgaard and P. Erhart, Comparative Ab-Initio Study of Substituted Norbornadiene-Quadricyclane Compounds for Solar Thermal Storage, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, 3635–3645 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. N. Cho, D. Zhitomirsky, G. G. D. Han, Y. Liu and J. C. Grossman, Molecularly Engineered Azobenzene Derivatives for High Energy Density Solid-State Solar Thermal Fuels, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 8679–8687 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Yoshida, New molecular energy storage systems, J. Photochem., 1985, 29, 27–40 CrossRef CAS.
- V. A. Bren’, A. D. Dubonosov, V. I. Minkin and V. A. Chernoivanov, Norbornadiene–quadricyclane—an effective molecular system for the storage of solar energy, Russ. Chem. Rev., 1991, 60, 451 CrossRef.
- A. D. Dubonosov, V. A. Bren and V. A. Chernoivanov, Norbornadiene–quadricyclane as an abiotic system for the storage of solar energy, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2002, 71, 917 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Bertram, F. Waidhas, M. Jevric, L. Fromm, C. Schuschke, M. Kastenmeier, A. Görling, K. Moth-Poulsen, O. Brummel and J. Libuda, Norbornadiene photoswitches anchored to well-defined oxide surfaces: From ultrahigh vacuum into the liquid and the electrochemical environment, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, 044708 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Börjesson, A. Lennartson and K. Moth-Poulsen, Efficiency Limit of Molecular Solar Thermal Energy Collecting Devices, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2013, 1, 585–590 CrossRef.
- K. Börjesson, A. Lennartson and K. Moth-Poulsen, Fluorinated fulvalene ruthenium compound for molecular solar thermal applications, J. Fluorine Chem., 2014, 161, 24–28 CrossRef.
- U. Jacovella, E. Carrascosa, J. T. Buntine, N. Ree, K. V. Mikkelsen, M. Jevric, K. Moth-Poulsen and E. J. Bieske, Photo- and Collision-Induced Isomerization of a Charge-Tagged Norbornadiene–Quadricyclane System, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11, 6045–6050 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Waidhas, M. Jevric, M. Bosch, T. Yang, E. Franz, Z. Liu, J. Bachmann, K. Moth-Poulsen, O. Brummel and J. Libuda, Electrochemically controlled energy release from a norbornadiene-based solar thermal fuel: increasing the reversibility to 99.8% using HOPG as the electrode material, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 15658–15664 RSC.
- Z. Wang, H. Hölzel and K. Moth-Poulsen, Status and challenges for molecular solar thermal energy storage system based devices, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51, 7313–7326 RSC.
- Z. Wang, H. Moïse, M. Cacciarini, M. B. Nielsen, M. Morikawa, N. Kimizuka and K. Moth-Poulsen, Liquid-Based Multijunction Molecular Solar Thermal Energy Collection Device, Adv. Sci., 2021, 8, 2103060 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wang, Z. Wu, Z. Hu, J. Orrego-Hernández, E. Mu, Z.-Y. Zhang, M. Jevric, Y. Liu, X. Fu, F. Wang, T. Li and K. Moth-Poulsen, Chip-scale solar thermal electrical power generation, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci., 2022, 3, 100789 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Kjaersgaard, H. Hölzel, K. Moth-Poulsen and M. B. Nielsen, Photolytic Studies of Norbornadiene Derivatives under High-Intensity Light Conditions, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2022, 126, 6849–6857 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Hillers-Bendtsen, M. H. Hansen and K. V. Mikkelsen, The influence of nanoparticles on the excitation energies of the photochromic dihydroazulene/vinylheptafulvene system, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21, 6689–6698 RSC.
- A. E. Hillers-Bendtsen, M. B. Johansen and K. V. Mikkelsen, Promoting the thermal back reaction of vinylheptafulvene to dihydroazulene by physisorbtion on nanoparticles, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021, 23, 12889–12899 RSC.
- S. Helmy, F. A. Leibfarth, S. Oh, J. E. Poelma, C. J. Hawker and J. Read de Alaniz, Photoswitching Using Visible Light: A New Class of Organic Photochromic Molecules, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 8169–8172 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Crespi, N. A. Simeth and B. König, Heteroaryl azo dyes as molecular photoswitches, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2019, 3, 133–146 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Bolle, C. Menet, M. Puget, H. Serier-Brault, S. Katao, V. Guerchais, F. Boucher, T. Kawai, J. Boixel and R. Dessapt, Enhanced reversible solid-state photoswitching of a cationic dithienylethene assembled with a polyoxometalate unit, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2021, 9, 13072–13076 RSC.
- R. Eschenbacher, T. Xu, E. Franz, R. Löw, T. Moje, L. Fromm, A. Görling, O. Brummel, R. Herges and J. Libuda, Triggering the energy release in molecular solar thermal systems: Norbornadiene-functionalized trioxatriangulen on Au(111), Nano Energy, 2022, 95, 107007 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Li, L. Sun, L. Ji and H. Chao, Ruthenium(II) complexes with dppz: from molecular photoswitch to biological applications, Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 13261–13276 RSC.
- R. Boese, J. K. Cammack, A. J. Matzger, K. Pflug, W. B. Tolman, K. P. C. Vollhardt and T. W. Weidman, Photochemistry of (Fulvalene)tetracarbonyldiruthenium and Its Derivatives: Efficient Light Energy Storage Devices, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 6757–6773 CrossRef CAS.
- A. A. Beharry and G. A. Woolley, Azobenzene photoswitches for biomolecules, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 4422–4437 RSC.
- M. W. H. Hoorens, M. Medved’, A. D. Laurent, M. Di Donato, S. Fanetti, L. Slappendel, M. Hilbers, B. L. Feringa, W. Jan Buma and W. Szymanski, Iminothioindoxyl as a molecular photoswitch with 100 nm band separation in the visible range, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 2390 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. L. Greenfield, M. A. Gerkman, R. S. L. Gibson, G. G. D. Han and M. J. Fuchter, Efficient Electrocatalytic Switching of Azoheteroarenes in the Condensed Phases, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 15250–15257 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Zhao, Y. Li, J. Bai, J. Mu, L. Chen, N. Zhang, J. Han, F. Liu and S. Yan, Preparation of flexible photo-responsive film based on novel photo-liquefiable azobenzene derivative for solar thermal fuel application, Dyes Pigm., 2022, 202, 110277 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Cacciarini, M. Jevric, J. Elm, A. U. Petersen, K. V. Mikkelsen and M. B. Nielsen, Fine-tuning the lifetimes and energy storage capacities of meta-stable vinylheptafulvenes via substitution at the vinyl position, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 49003–49010 RSC.
- M. D. Kilde, P. G. Arroyo, A. S. Gertsen, K. V. Mikkelsen and M. B. Nielsen, Molecular solar thermal systems – control of light harvesting and energy storage by protonation/deprotonation, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 6356–6364 RSC.
- A. Mengots, A. Erbs Hillers-Bendtsen, S. Doria, F. Ørsted Kjeldal, N. Machholdt Høyer, A. Ugleholdt Petersen, K. V. Mikkelsen, M. Di Donato, M. Cacciarini and M. Brøndsted Nielsen, Dihydroazulene-Azobenzene-Dihydroazulene Triad Photoswitches, Chem. – Eur. J., 2021, 27, 12437–12446 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. H. Cardenuto, H. M. Cezar, K. V. Mikkelsen, S. P. A. Sauer, K. Coutinho and S. Canuto, A QM/MM study of the conformation stability and electronic structure of the photochromic switches derivatives of DHA/VHF in acetonitrile solution, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2021, 251, 119434 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Asato, C. J. Martin, T. Nakashima, J. P. Calupitan, G. Rapenne and T. Kawai, Energy Storage upon Photochromic 6-π Photocyclization and Efficient On-Demand Heat Release with Oxidation Stimuli, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 11391–11398 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Jones, T. E. Reinhardt and W. R. Bergmark, Photon energy storage in organic materials—The case of linked anthracenes, Sol. Energy, 1978, 20, 241–248 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Lorenz, F. Wullschläger, A. Rüter, B. Meyer and A. Hirsch, Tunable Photoswitching in Norbornadiene (NBD)/Quadricyclane (QC) – Fullerene Hybrids, Chem. – Eur. J., 2021, 27, 14501–14507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Ree and K. V. Mikkelsen, Benchmark study on the optical and thermochemical properties of the norbornadiene-quadricyclane photoswitch, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2021, 779, 138665 CrossRef CAS.
- A. E. Hillers-Bendtsen, F. Ø. Kjeldal, N. M. Høyer and K. V. Mikkelsen, Optimization of the thermochemical properties of the norbornadiene/quadricyclane photochromic couple for solar energy storage using nanoparticles, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2022, 24, 5506–5521 RSC.
- R. Szabo, K. N. Le and T. Kowalczyk, Multifactor theoretical modeling of solar thermal fuels built on azobenzene and norbornadiene scaffolds, Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2021, 5, 2335–2346 RSC.
- A. E. Hillers-Bendtsen, J. L. Elholm, O. B. Obel, H. Hölzel, K. Moth-Poulsen and K. V. Mikkelsen, Searching the Chemical Space of Bicyclic Dienes for Molecular Solar Thermal Energy Storage Candidates, Angew. Chem., 2023, e202309543 CAS.
- A. A. Sangolkar, M. Faizan, K. R. Krishna and R. Pawar, Aza-bicyclooctadiene/tetracyclooctane couples as promising photoswitches for molecular solar thermal energy storage applications, Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2023, 8, 853–865 RSC.
- P. R. Rablen, A Procedure for Computing Hydrocarbon Strain Energies Using Computational Group Equivalents, with Application to 66 Molecules, Chemistry, 2020, 2, 347–360 CrossRef.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, X. Li, M. Caricato, A. V. Marenich, J. Bloino, B. G. Janesko, R. Gomperts, B. Mennucci, H. P. Hratchian, J. V. Ortiz, A. F. Izmaylov, J. L. Sonnenberg, D. Williams-Young, F. Ding, F. Lipparini, F. Egidi, J. Goings, B. Peng, A. Petrone, T. Henderson, D. Ranasinghe, V. G. Zakrzewski, J. Gao, N. Rega, G. Zheng, W. Liang, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, K. Throssell, J. A. Montgomery Jr., J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. J. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. N. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, T. A. Keith, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. P. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, J. M. Millam, M. Klene, C. Adamo, R. Cammi, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, O. Farkas, J. B. Foresman and D. J. Fox, Gaussian 16, Revision C.01, 2016 Search PubMed.
- P. Giannozzi, O. Baseggio, P. Bonfà, D. Brunato, R. Car, I. Carnimeo, C. Cavazzoni, S. de Gironcoli, P. Delugas, F. Ferrari Ruffino, A. Ferretti, N. Marzari, I. Timrov, A. Urru and S. Baroni, Quantum ESPRESSO toward the exascale, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, 154105 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Neese, Software update: the ORCA program system, version 4.0, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci., 2018, 8, e1327 Search PubMed.
- X. An and Y. Xie, Enthalpy of isomerization of quadricyclane to norbornadiene, Thermochim. Acta, 1993, 220, 17–25 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Gray, A. Lennartson, P. Ratanalert, K. Börjesson and K. Moth-Poulsen, Diaryl-substituted norbornadienes with red-shifted absorption for molecular solar thermal energy storage, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 5330–5332 RSC.
- E. Vessally, Maximizing the Solar Energy Storage of the Norbornadiene-Quadricyclane System: Mono-Heteroatom Effect by DFT Calculations, Phosphorus, Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem., 2009, 184, 2307–2313 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: The calculated storage energies, energy storage densities, and thermal back reaction barriers of all the studied systems, optical absorption spectra of the reactants and photoproducts of the considered photoswitching couples, spectral data including the molar absorption coefficient, first important absorption wavelength (surpassing 0.01) and corresponding oscillatory strength for the bicyclodiene and photoisomer. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ya00455d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |