Optical property control of π-electronic systems bearing Lewis pairs by ion coordination†
Takahiro
Yanbe
,
Kei
Mizuguchi
,
Ryohei
Yamakado
 * and
Shuji
Okada
* and
Shuji
Okada

Department of Organic Materials Science, Graduate School of Organic Materials Science, Yamagata University, Yonezawa 992-8510, Japan. E-mail: yamakado@yz.yamagata-u.ac.jp
First published on 25th August 2020
Abstract
π-Electronic systems bearing Lewis pairs were synthesized and their optical responses to added ions were investigated. The tuning of the optical properties was demonstrated by the addition of various ion pairs, and these behaviours were elucidated by theoretical calculations.
The development of donor–π–acceptor (D–π–A) molecules, in which an electron-rich donor and an electron-poor acceptor are linked by π-conjugated moieties to enable intramolecular charge transfer (ICT), has attracted much attention because these compounds find various applications, including in fluorescent materials,1 dye-sensitized solar cells,2 and second-order nonlinear optics.3 The optical properties of D–π–A molecules with a large dipole moment can be controlled by the solvent polarity. However, the effective control of these properties in the solid state remains unexplored. In order to modify the optical properties of D–π–A molecules by changing their surroundings in the solid state, thermally stable components such as ion pairs are required. Anion and cation receptors are sensitive to ions and form complexes with such species.4,5 Hence, π-electronic systems containing both cation and anion receptors would display multi-responsive properties to ion pairs. However, such ion-pair receptors have been rarely studied.6
As ion pair receptors, we focused on Lewis pairs (LPs). The potential use of boron compounds, a Lewis acid, to detect anions such as F− and CN− has been reported.7 Although π-electronic systems bearing Lewis pairs have been reported, their ion-binding behaviour has not been studied.8 In order to use a Lewis pair to prevent the formation of a complex through coordination bonds, it is necessary to introduce bulky substituents. Combinations of Lewis bases (such as trimesitylphosphine) and acids (such as tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane) bearing bulky substituents are called frustrated Lewis pairs (FLPs). FLPs are used as organic catalysts because of their unique arrangement of Lewis acid and base that enables the activation of relatively inert small molecules such as dihydrogen.9 Recently, FLPs were employed for fabricating self-healing10 and CO2-responsive materials.11 There are also a few reports on ion-pair coordination by FLPs.12 Inspired by the properties of FLPs, we hypothesised that the electronic structure of π-electronic systems containing a Lewis pair with bulky substituents can be controlled by adding ion pairs even in the solid state (Fig. 1a), resulting in control over various optical properties using a single π-conjugated molecule. In this study, we investigated the interaction between LPs and ion pairs and revealed the optoelectronic properties of LP-containing π-electronic systems in the presence of different ion pairs.
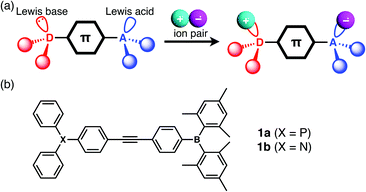 | ||
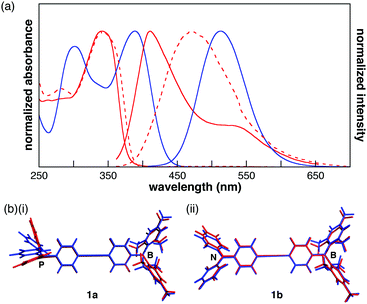
| Fig. 1 (a) Schematic illustration of the complex formation between a LP-containing π-electronic system and ion pair, and (c) the chemical structures of 1a and 1b. | ||
The designed LP-containing diphenylacetylenes (1a, b, Fig. 1b) combine one of two kinds of Lewis base, phosphine or amine, and one Lewis acid, borane, and were prepared in high yields by Sonogashira coupling of (4-iodophenyl)dimesitylborane with 4-ethynyl-N,N-diphenylaniline or (4-ethynylphenyl)diphenylphosphine, respectively, in a diisopropylamine/toluene mixture in the presence of CuI and Pd(PPh3)4. Compounds 1a and 1b were characterised by NMR, UV-vis spectroscopy, and ESI-MS analyses. The broad 11B NMR signals of 1a and 1b at approximately 73 ppm (CH2Cl2) were typical of trigonal-planar boron centres. The 31P NMR signal of 1a at −4.45 ppm was comparable to that of PPh3 (−4.50 ppm, CH2Cl2).
In the UV-vis spectra of 1a and 1b (10−5 M in CH2Cl2), the absorption maxima were observed at 342 and 388 nm, respectively (Fig. 2a). The lowest-energy absorption band, which was assigned to the ICT transition by time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) calculations at the B3LYP/6-311+G(d,p)//B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) (PCM = CH2Cl2) level of theory,13 was red-shifted by the replacement of the donor moiety from phosphine to amine. Although 1b showed a structureless fluorescence spectrum with a peak at 513 nm, 1a exhibited a fluorescence maximum at 411 nm with a shoulder at 530 nm (Fig. 2a). The lowest-energy fluorescence band of 1a derived from ICT was red-shifted from that of 1b, indicating that 1a undergoes a larger conformational change in its excited state than 1b. TD-DFT calculations were performed using the optimized structures in the first excited (S1) state to elucidate the fluorescence spectra. In the optimized structure of 1a, a large conformational change from the ground state (S0) to the S1 state was observed around the phosphine moiety, while the conformation around the borane changed only slightly (Fig. 2b(i)). The HOMO of 1a in the S1 state is localized on the phosphorus atom and the two terminal phenyl rings, whereas in the S0 state it is localized on the phosphorus atom and diphenylacetylene moiety (Fig. S8, ESI†). As such, the higher HOMO level of 1a in the S1 state corresponds to the emission in the long wavelength region. In contrast, the optimized structures of 1b around the nitrogen and borane atoms differ only slightly between the S0 and S1 states (Fig. 2b(ii)). Therefore, the HOMO–LUMO energy gap of 1b in the S1 state was larger than that of 1a. Additionally, the absorption maxima of 1a and 1b were not influenced by the solvent, whereas the peaks of the fluorescence spectra red-shifted with the increase in the solvent's dielectric constant (Fig. S4, ESI†). These results suggest a large polarization in the excited states. In the film, the absorption and fluorescence bands of 1a were observed at 340 and 469 nm, respectively (Fig. 2a). The similarity between the absorption spectra of the film and the CH2Cl2 solution indicated that the aggregation of the π-electronic systems was inhibited by the bulky substituents on the boron and phosphorus atoms. On the other hand, in the fluorescence spectrum of 1a in the film state, the fluorescence band at 411 nm accompanied by a shoulder band was changed to a broad structureless spectrum, which may indicate that the conformational change in the S1 state was restricted in the film.
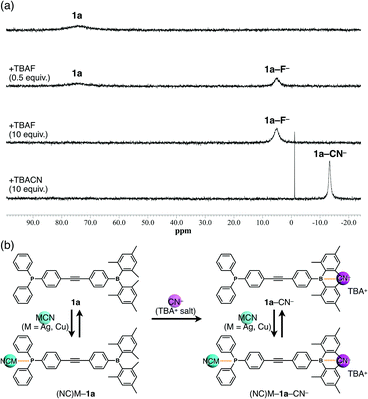
The ion-binding properties of 1a in solution were investigated by 11B and 31P NMR spectroscopy. The 11B NMR signal of 1a at approximately 73 ppm decreased and a new peak corresponding to 1a–F− appeared at 5.04 ppm upon addition of F− as a TBA salt in CH2Cl2 (Fig. 3a). Similarly, the peaks at −0.53 and −13.38 ppm were observed upon addition of AcO− and CN−, respectively (Fig. 3a and Fig. S12–S14, ESI†). Thus, the bindings of F−, AcO−, and CN− to the boron centre were demonstrated. Moreover, the sharp high-field-shifted signal of 1a–CN− may suggest strong anion binding and restricted pyramidal conformation of a boron centre by the large anion. However, no boron–anion complexes were obtained by the addition of Cl− and Br−, although tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane gives an anion complex with Cl− and Br− (Fig. S11, ESI†). These results indicated that the anion-binding ability is increased by electron-withdrawing groups such as pentafluorophenyl substituents on the boron atom and decreased by bulky and electron-donating groups such as mesityl substituents. Next, complex formation with MCN (M = Ag or Cu) was investigated (Fig. 3b). As AgCN and CuCN are insoluble in CH2Cl2, the samples were prepared by heating mixtures of 1a and 1 equiv. of AgCN or CuCN in CH2Cl2 to complete dissolution.14 The 31P NMR signals of (NC)Ag–1a and (NC)Cu–1a at 9.62 and –3.59 ppm, respectively, differed from that of 1a (−5.05 ppm). In contrast, the 11B NMR spectra remained unchanged. These results indicated that CN− did not act as a free anion, which would undergo complexation with borane, because of the high binding ability of Ag+ or Cu+. Therefore, a further 1 equiv. of CN− was added as TBACN (Fig. 3b), upon which a new 11B NMR signal at −13.27 ppm was observed in both the (NC)Ag–1a and (NC)Cu–1a samples, indicating the coexistence of free borane and B–CN− complexes. Moreover, new signals appeared in the 31P NMR spectra between those of the free and coordinated phosphines.‡ Hence, anion-free species (free 1a) and mono-, and dicoordinated species ((NC)M–1a or 1a–CN−, and (NC)M–1a–CN−, respectively) coexisted in solution as shown.
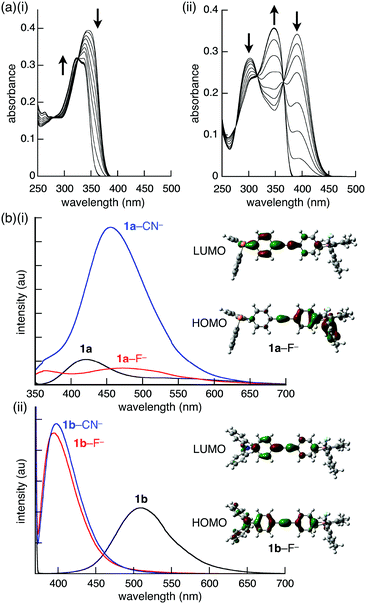
The effect of ion-binding in the π-electronic systems was revealed by the UV-vis absorption and fluorescence spectral changes of 1a and 1b. Upon addition of F− as a TBA+ salt, the absorption maxima of 1a and 1b (λ = 342 and 388 nm, respectively) decreased in intensity and shifted to 324 and 348 nm, respectively (Fig. 4a). Similar blue-shifts were also observed upon addition of CN− and AcO− as TBA+ salts, suggesting that the corresponding π → pπ(B) CT transition was quenched by the anion-binding, in which the empty boron p-orbital was filled by the electrons of the anions. The fluorescence spectra of 1a and 1b upon the addition of 3 equiv. of anions in CH2Cl2, were also measured. Interestingly, although 1b provided similar spectra by the addition of F− and CN−, 1a provided different spectra depending on the anion complexes (Fig. 4b). In the presence of F−, the fluorescence at 411 nm with a shoulder at 530 nm of 1a disappeared, and a new weak and broad fluorescence band at 483 nm appeared. In contrast, fluorescence of higher intensity was observed at 461 nm in the presence of CN−. The quantum yields for 1a, 1a–F−, and 1a–CN− were 6, 27, and 18%, respectively. The spectral changes upon anion addition can be explained by the TD-DFT calculations. In 1a–F− and 1a–CN−, the absorption band at the long wavelength region corresponds to the ICT from the phenyl attached to the borane–anion complex to the phenyl substituted with the phosphine, whereas that of 1a stemmed from the ICT in the opposite direction (from the phenylphosphine toward the phenylborane, Fig. 4b(i)). Therefore, the borane–anion complex behaves as a donor. In addition, the electron density of the anion affects the HOMO level, especially in the S1 state, clarifying the difference between the fluorescence spectra of 1a–F− and 1a–CN−. Moreover, the larger oscillator strength of 1a–CN− (f = 1.260) than of 1a (f = 0.106) and 1a–F− (f = 0.791) was consistent with the experimental fluorescence intensity. However, the HOMO of 1b, 1b–F−, and 1b–CN− is localized on the aniline moiety, whereas the LUMO is localized on the ethynyl moiety (Fig. 4b(ii)). Consequently, the anion complexes of 1b provided similar fluorescence spectra regardless of the anions.
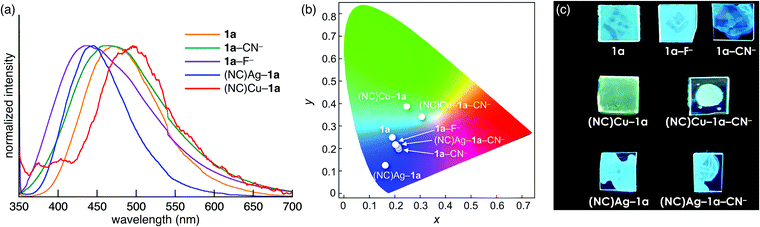
The control over the optical properties of 1a by the addition of ion pairs was demonstrated in film samples. Spin-coated films of 1a, 1a–F−, 1a–CN−, (NC)Ag–1a, (NC)Cu–1a, (NC)Ag–1a–CN−, and (NC)Cu–1a–CN− were prepared from the CH2Cl2 solutions of 1a and its mixtures with 1 equiv. of one or two ion pairs. In the presence of anions, the fluorescence was blue-shifted from that of 1a (λ = 469, 431, and 461 nm for 1a, 1a–F−, and 1a–CN−, respectively), and 1a–F− and 1a–CN− films exhibited different colours than the corresponding solutions (Fig. 5a). Furthermore, the addition of AgCN (λ = 445) and CuCN (λ = 496) induced blue- and red-shifts, respectively (Fig. 5a). The fluorescence colours of (NC)Ag–1a and (NC)Cu–1a further changed upon addition of CN− as a TBA+ salt as a result of coordination of 1a by both MCN (M = Ag or Cu) and CN− in the film. The emission colour coordinates of the film samples on the Commission Internationale de L’Eclairage (CIE) 1931 chromaticity diagram are shown in Fig. 5b. The colours with the CIE coordinates (0.186, 0.255), (0.202, 0.224), (0.212, 0.203), (0.158, 0.130), (0.243, 0.389), (0.197, 0.218), and (0.299, 0.346) were displayed by 1a, 1a–F−, 1a–CN−, (NC)Ag–1a, (NC)Cu–1a, (NC)Ag–1a–CN−, and (NC)Cu–1a–CN−, respectively. Thus, LP-containing 1a is a potential on-demand fluorescent material in the presence of various ion pairs (Fig. 5c).
In summary, LP-containing diphenylacetylenes were synthesized by coupling reactions. The anion-binding properties and the formation of boron–anion complexes were revealed by 11B NMR and UV-vis absorption spectra. High binding constants with F− and CN− were obtained. Based on the solution behaviour and the results of the theoretical studies, the electron density provided by coordination with anions led to changes in the energy of the HOMO at the S1 state, resulting in the fluorescence spectral changes depending on the nature of the anion. Similarly, the phosphorus–metal interaction upon complexation with AgCN and CuCN was observed by 31P NMR spectroscopy. The addition of further CN− as a TBA+ salt provided the dual complexes. Based on this behaviour, the optical properties of the film samples were controlled by the addition of various ion pairs, and fluorescence colour changes from blue to green were achieved by the combination of one π-electronic system with various ion pairs. Thus, the optical properties of LP-containing diphenylacetylenes in the solid state were controlled by the guest ion pairs. Other ion-pairing combinations for a wider range of spectral changes and different amounts of guest ion pairs are currently under investigation within the development of novel on-demand fluorescent materials.
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI for Early-Career Scientists (JP19K15616), Research Foundation for the Electrotechnology of Chubu, The Iwatani Naoji Foundation and Yashima Environment Technology Foundation. Theoretical calculations were performed using Research Centre for Computational Science, Okazaki, Japan. We thank Prof. Akito Masuhara, Dr Takayuki Chiba and Ms Hinako Ebe, Yamagata University, for various measurements.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Notes and references
- Z. M. Hudson and S. Wang, Acc. Chem. Res., 2009, 42, 1584–1596 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) Y. Wu and W. Zhu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 2039–2058 RSC; (b) F. Wurthner, Acc. Chem. Res., 2016, 49, 868–876 CrossRef.
- (a) T. Verbiest, S. Houbrechts, M. Kauranen, K. Clays and A. Persoons, J. Mater. Chem., 1997, 7, 2175–2189 RSC; (b) L. Beverina and G. A. Pagani, Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47, 319–329 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. L. Sessler, P. A. Gale and W.-S. Cho, Anion Receptor Chemistry, RSC Publishing, Cambridge, UK, 2006 Search PubMed; (b) Heterocyclic Chemistry, ed. P. A. Gale and W. Dehaen, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2010, vol. 24, pp. 1–370 Search PubMed; (c) N. Busschaert, C. Caltagirone, W. Van Rossom and P. A. Gale, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 8038–8155 CrossRef CAS.
- G. W. Gokel, Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry, ed. J.-M. Lehn, J. L. Atwood, J. E. D. Davies, D. D. MacNicol and F. Vögtle, Pergamon, Oxford, UK, 1996, vol. 1 Search PubMed.
- Y. H. Lee, N. V. Nghia, M. J. Go, J. Lee, S. U. Lee and M. H. Lee, Organometallics, 2014, 33, 753–762 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhao, L. A. Leamer and F. P. Gabbai, Dalton Trans., 2013, 42, 8164–8178 RSC.
- A. Fukazawa, H. Yamada and S. Yamaguchi, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 5582–5585 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) G. C. Welch and D. W. Stephan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 1880–1881 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. C. Neu, E. Y. Ouyang, S. J. Geier, X. Zhao, A. Ramos and D. W. Stephan, Dalton Trans., 2010, 39, 4285–4294 RSC; (c) A. J. Marwitz, J. L. Dutton, L. G. Mercier and W. E. Piers, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 10026–10029 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. Lindqvist, K. Axenov, M. Nieger, M. Raisanen, M. Leskela and T. Repo, Chem. – Eur. J., 2013, 19, 10412–10418 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) M. Wang, F. Nudelman, R. R. Matthes and M. P. Shaver, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 14232–14236 CrossRef CAS; (b) U. Yolsal, M. Wang, J. R. Royer and M. P. Shaver, Macromolecules, 2019, 52, 3417–3425 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. Chen, R. Liu and Q. Yan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 9336–9340 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. Liu, X. Liu, K. Ouyang and Q. Yan, ACS Macro Lett., 2019, 8, 200–204 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) C. Appelt, J. C. Slootweg, K. Lammertsma and W. Uhl, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 5911–5914 CrossRef CAS; (b) W. Uhl, M. Lange, A. Hepp and M. Layh, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 2018, 644, 1469–1479 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Frisch, et al., Gaussian 16 (Revision A.03), Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016 Search PubMed.
- Y. Y. Lin, S. W. Lai, C. M. Che, W. F. Fu, Z. Y. Zhou and N. Zhu, Inorg. Chem., 2005, 44, 1511–1524 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Synthetic procedures, optical properties, theoretical calculations and ion-binding properties. See DOI: 10.1039/d0cc04442c |
| ‡ Although the free borane and its CN− complex were distinguishable by the 11B NMR, the free and coordinated phosphines were indistinguishable by 31P NMR because of the different time scales of the measurements and the dynamic equilibria. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |