Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCatalytic conversion network for lignocellulosic biomass valorization: a panoramic view
Shenyu
Wang†
a,
Aohua
Cheng†
a,
Fanhua
Liu
a,
Junjie
Zhang
a,
Tao
Xia
a,
Xiang
Zeng
a,
Wei
Fan
 *b and
Ying
Zhang
*b and
Ying
Zhang
 *a
*a
aCAS Key Laboratory of Urban Pollutant Conversion, Department of Chemistry, Anhui Province Key Laboratory for Biomass Clean Energy, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230026, China. E-mail: zhzhying@ustc.edu.cn
bGoessman Lab, 686 N Pleasant Street, Amherst, Massachusetts 01003, USA. E-mail: wfan@ecs.umass.edu
First published on 21st February 2023
Abstract
Efficient utilization of lignocellulosic biomass to substitute for fossil resources is an effective way to promote the sustainable development of current society. Numerous lignocellulose valorization routes for the production of value-added chemicals and fuels have been explored. Herein, we overview the catalytic reaction routes, reaction types and key steps involved in the selective preparation of various important products from lignocellulose. The information can facilitate the development of robust and selective catalytic systems to address the challenges in the major reaction steps. We present four catalytic conversion route maps starting from cellulose (including 5-hydroxylfurfural, HMF), hemicellulose and lignin, respectively. The reaction route for the important platform molecules of HMF and furfural, passing through critical intermediates to value-added chemicals and aviation fuels, is also highlighted. It provides a clear and concise panorama for people interested in this field and facilitates identifying the products or processes of interest with up-to-date research developments. We also put forward the current issues for the large-scale valorization of lignocellulose and the possible resolution strategies, focusing on the rational design of active and robust heterogeneous catalysts.
Keywords: Biomass; Lignocellulose valorization; Catalytic conversion network; Reaction routes; Renewable chemicals.
1 Introduction
Fossil fuel consumption contributes to significant greenhouse gas emissions, which are responsible for increasing severe climate issues, such as extreme heat, drought, and flooding, in recent years.1 It is crucial to explore sustainable alternatives to the current industrial production of chemicals and fuels.2 Biomass, the most abundant renewable organic carbon resource in nature, can help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels.3–6Lignocellulose, which is mainly composed of cellulose (30–50 wt%), hemicellulose (20–35 wt%), and lignin (15–30 wt%),7 is produced with an annual yield of about 180 billion tons worldwide.8 It is the most promising material among biomass resources due to its carbon neutrality, affordability, and ease of acquisition.3,5,8–13 The energy density of lignocellulose is however much lower than that of fossil fuels,14 which is because of the abundant oxygen-containing functional groups in the molecular structure of lignocellulose, such as hydroxyl, ether, aldehyde, ester, and so on.1,15 As a result, it is necessary to either deoxygenate lignocellulose to increase the energy density for fuel production or convert lignocellulose to chemicals with various functional groups for industrial applications. Starting with lignocellulose, a variety of routes for producing value-added chemicals have been created, and more than 200 different types of valuable substances have been generated.8 However, because of the intricate composition and structure of lignocellulose, even though (hemi)cellulose and lignin have been separated by pretreatment, complex reactions and pathways still interplay with each other in its downstream conversion, which put serious challenges in selectively producing the desired products.5,10,16
The valorization of lignocellulose to either chemicals or fuels is the subject of a tremendous amount of research papers, which have been comprehensively overviewed by numerous excellent reviewers with emphasis on reaction mechanism or catalyst performance for certain catalytic conversion reactions.1–3,5–8,10–15,17–20 Herein, based on a great quantity of reviews, we draw panoramic reaction network maps with critical steps for lignocellulosic biomass valorization. Following the maps, we introduce and discuss the conversions from cellulose to various valuable C2 to C6 chemicals, and reactions starting from or passing through the platform molecules of 5-hydroxylfurfural (HMF) and furfural to functional compounds and aviation fuels. We also describe the oxidative and reductive depolymerization of lignin and the following selective hydrodeoxygenation steps to various monomers. A number of valuable compounds in the lignocellulose valorization network are overviewed along with the reactions and active catalysts involved in their synthesis from lignocellulose or the platform molecules. At the end, we put forward and discuss the current issues for the catalytic valorization of lignocellulose on a large scale and the potential solutions, such as rational heterogeneous catalyst design.
2 Valorization of cellulose
2.1 Conversion network of cellulose
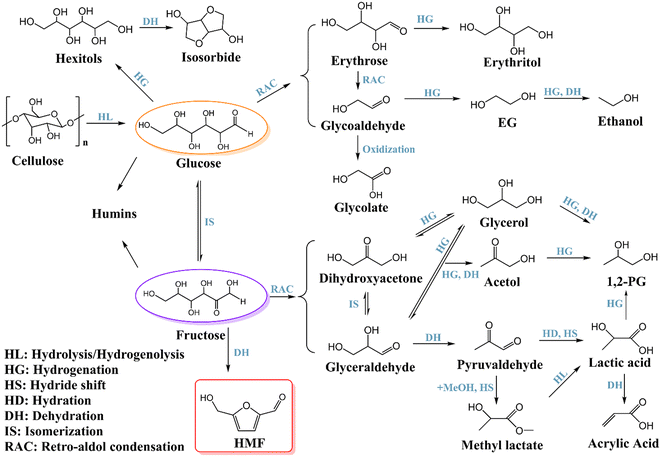
As the major component of lignocellulose, cellulose is a highly polymerized homopolymer with several polymorphs.21 It is composed of up to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 glucose units linked by β-glycosidic bonds.8 Cellulose and its derivatives can be transformed into a variety of useful compounds via different reactions such as hydrolysis, hydrogenolysis, hydrogenation, dehydration, oxidation, isomerization, retro-aldol condensation, and so on, which have emerged as the most promising research area in sustainable chemical and fuel production (Scheme 1).22,23 Due to the inherent heterogeneity and recalcitrance of lignocellulose, a pretreatment process is necessary before cellulose and hemicellulose are converted, which primarily includes treatment by acid, alkali, deep eutectic solvents, or the lignin-first strategy is undertaken.24–26
000 glucose units linked by β-glycosidic bonds.8 Cellulose and its derivatives can be transformed into a variety of useful compounds via different reactions such as hydrolysis, hydrogenolysis, hydrogenation, dehydration, oxidation, isomerization, retro-aldol condensation, and so on, which have emerged as the most promising research area in sustainable chemical and fuel production (Scheme 1).22,23 Due to the inherent heterogeneity and recalcitrance of lignocellulose, a pretreatment process is necessary before cellulose and hemicellulose are converted, which primarily includes treatment by acid, alkali, deep eutectic solvents, or the lignin-first strategy is undertaken.24–26
The hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose is the starting point for cellulose conversion,27,28 which is crucial to the entire selective conversion routes. Glucose is a basic feedstock for food production, pharmaceutics and other industrial sectors. It is also an important platform chemical for lignocellulose valorization. Through different catalytic pathways, glucose can be converted to various products as shown in Scheme 1.
First of all, glucose can be transformed into sorbitol by hydrogenation, a significant polyhydroxy sugar alcohol that is extensively used in the chemical, food, and medical industries. Different kinds of hydrogenation catalysts are effective for converting glucose to sorbitol, the most common of which are RANEY® nickel and Ru/AC.29 There are also a lot of examples of one-pot catalytic systems for producing sorbitol from cellulose, and the yields are considerably impacted by metal species involved in the catalysts, cellulose pretreatment or experimental parameters.30,31 Unfavorable side reactions may occur during this process, such as retro-aldol condensation, dehydration and condensation catalyzed by acidic or basic sites of the catalysts. To maintain an adequate balance of conversion and selectivity, the acidity and hydrogenation activity of the catalyst should be coordinated. Liu et al. developed a Ni/ZrP2 catalyst with moderate acidity and activity which could convert microcrystalline cellulose into 60.8% sorbitol after 5 hours under 5 MPa H2 at 200 °C.32 In particular, isosorbitol can be obtained by dehydration of sorbitol, which can be used as a novel solvent and the monomer for functional polymer materials.33 In particular, the reaction pathway requires more acidic sites than the synthesis of sorbitol because further dehydration is crucial for the one-pot synthesis of isosorbitol straight from cellulosic material.
Through controlled retro-aldol condensation, glucose is also able to produce erythrose and glycolaldehyde. Erythrose can be further hydrogenated to form erythritol or condensed to glycolaldehyde via retro-aldol reaction, which can be oxidized to glycolic acid or hydrogenated to ethylene glycol (EG). Ethylene glycol is the most basic diol and is widely employed in various industries as a synthetic polyester material, hygroscopic agent, plasticizer, surfactants, cosmetics, solvents, and antifreeze.34 Zhang's group first reported bio-ethylene glycol production via a highly efficient one-pot catalytic conversion process from cellulose in 2008.35 Since then, EG production from cellulose or glucose has been a hot and challenging process and has attracted great efforts from researchers.23 Hydrolysis and retro-aldol condensation are the key steps to produce EG from cellulose. While hydrogenation is necessary, it may lead to sorbitol and erythritol which cannot be further converted to EG; therefore, the hydrogenation activity of the catalysts needs to be tuned precisely. Other reactions involved in cellulose conversion should be suppressed. Among the metal catalysts including W, Mo, Cr, Sn, Pb, La, Ce, Y, V, Nb, Zn, Ti, and Zr, tungsten-based catalysts exhibit the highest catalytic selectivity.23
Further hydrogenation and dehydration of EG can form ethanol. Ethanol is recognized as the most widely used industrial raw material and can be mixed with gasoline to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.36 Although using glucose fermentation to prepare ethanol is currently widespread, it is both time- and energy-consuming and suffers a significant carbon loss.36 Chemical catalysis might be applied to remedy this issue. One-pot ethanol generation from cellulose or glucose necessitates a catalytic system with a higher acidity and stronger hydrogenation activity than ethylene glycol production, since further dehydration and hydrogenation steps are involved. Multi-functional H2WO4–Pt/ZrO2, Mo/Pt/WOx and Ru–WOx/HZSM-5 catalysts have been developed for the one-pot production of ethanol from cellulose and even biomass via the EG pathway and achieved promising results, although the economic feasibility for production of ethanol from the pathway needs to be further justified.37–39
In the reaction network, glucose can also be isomerized into fructose, which is an important biomass platform molecule. Similar to glucose, fructose can also be hydrogenated to generate hexitols.2 Through retro-aldol condensation, fructose can be converted to dihydroxyacetone (DHA) or glyceraldehyde (GLY) and then be further hydrogenated to acetol and 1,2-propylene glycol (1,2-PG).40 Acetol is a crucial intermediate for the preparation of medicines, acrolein, heterocyclic compounds, and additives for food and cosmetics. From cellulose to acetol, it undergoes tandem reactions including hydrolysis, isomerization, dehydration, and hydrogenation. As an intermediate, acetol can be facilely converted into 1,2-PG by hydrogenation. Therefore, it is of great significance to fine-tune the properties of the catalyst to achieve efficient conversion of cellulose to acetol. Basic catalysts can catalyze both isomerization of aldose to ketose and retro-aldol condensation. Therefore, Ni–Sn/SiO2 and Co–Sn/SiO2 catalysts with the desired Lewis acid sites (for hydrogenolysis of cellulose), strong basic sites (for isomerization of glucose to fructose and the following retro-aldol condensation to C3 intermediates), and weak hydrogenation sites (for partial hydrogenation) demonstrate synergistic catalytic activities and achieve up to 61.6% yield of acetol via one-pot conversion of cellulose.41,42
1,2-PG is a crucial commodity chemical utilized in the chemical industry (such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, fragrances, etc.).43 The transformation of cellulose to 1,2-PG includes more reaction steps in comparison to those for EG formation; a catalytic system with multifunctional active sites is required.44
Lactic acid has been extensively utilized in food, medicine, and cosmetics. It is a significant platform molecule that can be used to create degradable polymers and solvents.45 In 2010, Holm et al.46 made a significant advancement in the direct creation of methyl lactate from glucose over the Sn Lewis acid zeolite catalyst. This discovery paves the way for several studies on the chemical catalytic synthesis of lactic acid and lactic acid derivatives. From glucose to lactic acid, glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone derived from fructose via retro-aldol condensation undergo dehydration to acetone aldehyde and then 1,2-hydride shift to form the end product. This process calls for a catalyst with multifunctional active sites. A range of metal catalysts, including Sn, Pb, Y, Er, Al, and other elements, demonstrate good efficiency in the production of lactic acid/lactate.8,47 Additionally, strong bases (like NaOH and KOH) have received a lot of attention as homogeneous catalysts in the reaction because they can break the C–C bond in aqueous solution.
Acrylic acid, an important raw material, is used to synthesize adhesives, polishing agents, coatings, textiles and plastics. Using lignocellulosic biomass as feedstock, acrylic acid can be obtained by dehydration of lactic acid, which is an important way to synthesize the chemical from non-fossil products.45,48
2.2 Conversion network of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
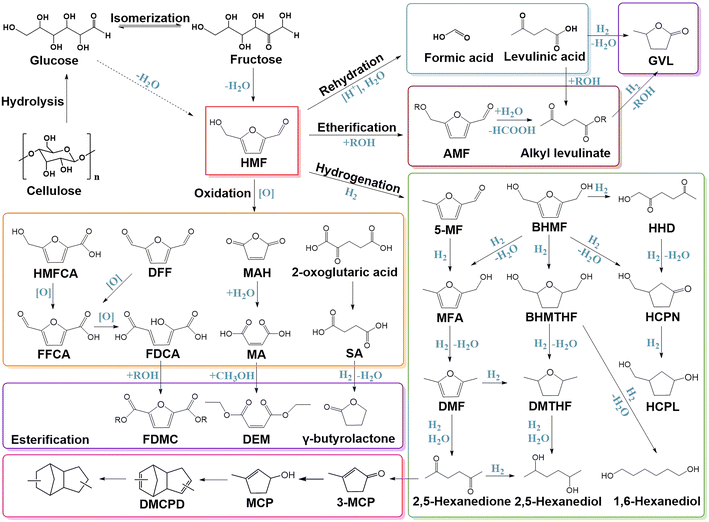
For the exploitation of lignocellulose, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) is one of the most significant and researched platform molecules, thanks to its ability to be converted into various value-added chemicals through multiple pathways (Scheme 2).49–52 HMF can be produced from both glucose and fructose by a dehydration process, but it is more common to use fructose as the starting material, since the enolization of the sugar molecules is the rate-determining step in the synthesis of HMF.48 In water, fructose forms a 5-membered ring, which is closer to the structure of HMF, while glucose is in the form of a 6-membered ring. Fructose has a higher enolization rate than glucose because of its unstable ring structure.53 As a result, fructose reacts considerably more quickly than glucose does to produce HMF, which can inhibit by-product formation. Isomerizing glucose to fructose first can also increase the selectivity of HMF.53 Additionally, many studies in recent years have concentrated on the direct production of HMF from cellulose in a one-pot process, but there are also lots of challenges like limited output, difficulty in product separation, and production of humins and by-products.8,54–56 Exploring a new catalyst system with high 5-HMF selectivity at low reaction temperature is an important research direction for glucose conversion to 5-HMF in the future.Levulinic acid (LA) is an essential platform chemical obtained from cellulose, which can be used to produce a number of high-value compounds, such as levulinic esters, γ-valerolactone (GVL), valeric acid and ester, butene, 5-nonanone, and methyltetrahydrofuran.57 Through the process of rehydration (involves several hydration, dehydration and C–C bond cleavage steps),58,59 HMF can be transformed into LA and formic acid. This process is usually carried out in acidic systems. In particular, H2SO4 and HCl are widely used acid catalysts in this process, and the acid-catalyzed conversion rate of HMF and the yield of LA are closely related to the H+ concentration. In addition, solid acid catalysts have also been developed as efficient heterogeneous catalysts for the synthesis of LA from HMF. For example, an Al-doped mesoporous niobium phosphate (Al–NbOPO4) solid acid catalyst can convert cellulose into levulinic acid in aqueous solution with a yield of 52.9%, in which HMF is the key intermediate.60 Strong acid strength and an appropriate B/L acid molar ratio of this catalyst are responsible for the high selectivity and yield of LA, and the authors found that the strong Lewis acid could improve the selectivity to LA in HMF conversion. Using a catalyst with the desired hydrogenation activity can transform LA directly into γ-valerolactone, which is another significant bioderived compound with several practical applications (such as solvent for biomass conversion and fuel additives). HMF can also react with alcohols to create HMF-derived ethers, which can then be further converted to alkyl levulinate.61,62 Alternatively, alkyl levulinate can also be produced by esterification of levulinic acid with alcohols. After that, alkyl levulinate can be further hydrogenated to produce γ-valerolactone. The catalytic conversion of LA using heterogeneous catalysts has been the subject of substantial research over the past ten years. Weng et al.63 overviewed the LA conversion to γ-valerolactone and its derivatives, including the choice of solvent, product distribution, catalytic stability, catalytic reactivity and strategies for improvement of this process.
Through hydrogenolysis or hydrogenation, HMF can be transformed into 5-methylfurfural (5-MF) or 2,5-bishydroxymethylfuran (BHMF). 5-MF continues to transform through the 5-MF → MFA → DMF process to realize the conversion of HMF to 2,5-dimethylfuran (DMF).64,65 BHMF can also be hydrodehydrated to MFA and then to DMF.66,67 DMF has a number of obvious benefits, including a high octane number, a reasonable boiling point for a liquid fuel, and a low solubility in water, which make it a viable liquid transportation biofuel component.68,69 Active sites efficient on both hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis can promote DMF production from HMF. For instance, Co/t-ZrO2 has a higher hydrogenation activity of carbonyl, while Co/m-ZrO2 has higher efficiency for the hydrogenolysis of the C–OH group.70 The Co catalyst supported on ZrO2 with both tetragonal and monoclinic phases achieves the highest yield of DMF (90.7%) under mild conditions. Different catalysts with a synergistic effect on C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O hydrogenation and C–OH hydrogenolysis also received satisfying results. Hydrolyzation of DMF can produce 2,5-hexadione. Cellulose can be selectively converted into 2,5-hexadione in the presence of HCl and Pd/C catalysts through the HMF intermediate with a high yield of 71.4% at 100 °C and 1 MPa H2.71 2,5-Hexanediol can be obtained by hydrogenation of 2,5-hexadione.
O hydrogenation and C–OH hydrogenolysis also received satisfying results. Hydrolyzation of DMF can produce 2,5-hexadione. Cellulose can be selectively converted into 2,5-hexadione in the presence of HCl and Pd/C catalysts through the HMF intermediate with a high yield of 71.4% at 100 °C and 1 MPa H2.71 2,5-Hexanediol can be obtained by hydrogenation of 2,5-hexadione.
BMHF can be converted to 2,5-bishydroxymethyltetrahydrofuran (BHMTHF) after the furan ring is saturated. According to the report of Fulignati et al.,72 commercial Ru/C catalysts can selectively hydrogenate HMF to 2,5-bishydroxymethylfuran (BHMF) under mild conditions (50 °C, 6 h, 30 bar H2) with a yield of more than 93 mol%, whereas under relatively harsh conditions (100 °C, 6 h, 50 bar H2), HMF can be selectively converted to BHMTHF in aqueous solution with a yield of more than 95 mol%. By selective catalytic transfer hydrogenation (CTH), which uses alcohols like 2-butanol as both hydrogen donor and solvent, HMF can also be converted into BHMF without H2.49,57,73 The transformation of HMF to BHMF is quite simple by using typical hydrogenation catalysts such as Cu, Co, and Ni. However, due to their special adsorption structure with the substrate and intermediate, only Ni-based catalysts among them can successfully hydrogenate the furan ring, resulting in the formation of BHMTHF.74 Hydrogenolysis of the two C–OH bonds of BHMTHF results in 2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran (DMTHF), while the cleavage of the C–O bond in the tetrahydrofuran ring followed by hydrogenolysis can produce 1,6-hexanediol (1,6-HDO) or 2,5-hexanediol. He et al.75 demonstrated that the Pt–WOx/TiO2 catalyst could convert BHMTHF to the high-value 1,6-HDO with a yield of up to 70% through a two-step process. The high activity and selectivity of Pt–WOx/TiO2 depend on the synergistic interaction between Pt and WOx. Xiao et al.76 reported that biomass-derived HMF could be directly and effectively converted into 1,6-HDO over Pd/SiO2 or Ir–ReOx/SiO2 catalysts; 57.8% yield of 1,6-HDO was obtained. DMTHF can also be obtained by hydrogenation of the furan ring of DMF.77,78
By opening the furan ring of BHMF, 1-hydroxyhexane-2,5-dione (HHD) can be produced. According to a study by Fujita et al.,79 nickel phosphide nanoparticles (Ni2P NPs) function as an effective heterogeneous catalyst for the conversion of HMF into HHD with a yield of up to 84%. The Ni species serve as the H2 activation sites, while P–OH species serve as the surface acid sites. Ni2P NPs combine their hydrogen-activating capacity and surface acidity, resulting in the excellent HHD selectivity. Hydrogenolysis of HHD and BHMF can produce 3-hydroxymethyl-cyclopentone (HCPN), which is regarded as a potential intermediate for the synthesis of high-value perfumes, insecticides, and polymers. As shown by Deng et al.,80 Pd supported on Lewis acid pyrochlore (Pd/Y2(Sn0.7Ce0.3)2O7−δ) can effectively convert HMF to HCPN, with the HCPN yield as high as 92.5%. According to Ramos et al.,81 the Cu–Al2O3 catalyst is effective in converting HMF to HCPN in the presence of H2 in aqueous solution, whereas Co–Al2O3 primarily transforms HMF to 3-hydroxymethylcyclopentanol (HCPL), with selectivity of 86% and 94%, respectively.
Oxidation is another important HMF valorization process. Common oxidants are O2 or H2O2. The oxidation of HMF to 2,5-furanedicarboxylic acid (FDCA) is the most studied route. The first step of this route is the oxidation of HMF to 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furan carboxylic acid (HMFCA) or 2,5-diformylfuran (DFF).50 HMFCA is an intermediate of the oxidation of HMF to FDCA, which is produced by the selective oxidation of the formyl group in HMF. Au is typically used in this step as the catalyst can synthesize HMFCA under alkaline circumstances.82 DFF, formed by the selective oxidation of HMF hydroxyl, can be obtained with a high selectivity on Co, Cu, MnO2, V2O5 and other catalysts.50,83,84 FDCA can be produced by both DFF and HMFCA oxidation via a 5-formyl-2-furan carboxylic acid (FFCA) intermediate. FDCA is an important precursor for the production of medicines and degradable polymers, e.g., polyethylene furanoate (PEF), to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET).48,84 With alcohols, FDCA can also be used to synthesize the corresponding esters, such as furan-2,5-dimethylcarboxylate (FDMC). FDMC is a viable replacement for FDCA in the polymer sector, and it can also be generated by direct oxidation of HMF. For example, ZIF-67 derived Co@C–N catalysts can realize oxidative esterification of HMF, yielding 95% FDMC.85 No DFF intermediate was found, demonstrating that the oxidative esterification of aldehyde preferentially proceeded on these catalysts. In a critical review, Xu et al.86 compared the mechanism and oxidation pathways of five noble metal catalysts (Au, Pt, Pd, Ru and Ag) on the HMF oxidation reaction in detail and discussed the effects of reaction conditions (such as temperature, pressure, time, etc.) on the catalytic performance of the metal catalysts. The challenges in the noble metal catalyst system (such as poor durability, high cost, etc.) and prospects for the development of HMF oxidation catalysts were also presented in the literature.
Maleic anhydride (MAH) and maleic acid (MA), important feedstocks for synthesizing unsaturated polyester resin, can also be obtained by oxidation of HMF.74,87 Usually, this process is carried out on vanadium-based catalysts. Li et al.88 achieved a MA yield of up to 79% from HMF on a simple vanadium oxide catalyst, and 50% overall yield of MA was achieved in one-pot two-step reactions from the conversion of fructose. Vanadium-oxo nanosheets (VONs) supported on graphene oxide (GO) catalyze HMF oxidation, with a 90.9% yield of maleic anhydride.89 In the presence of methanol, MA can synthesize diethylmaleate (DEM) through esterification reaction. DEM is a crucial chemical for the production of spices, insecticides, and polymers.90
HMF oxidation can produce valuable dicarboxylic acids like succinic acid (SA).87,91 For instance, Tirsoaga et al.92 reported that 92.7% SA selectivity with a HMF conversion of 78.6% can be obtained using a transition metal (Fe3O4) instead of a noble metal as catalyst. Subsequently, SA can be transformed into value-added chemicals like γ-butyrolactone (GBL) and 1,4-butanediol (BDO) through hydrogenation. Numerous studies have shown that GBL is the primary product when monometallic catalysts are used; however, the addition of secondary metal promoter can improve the selectivity of BDO and accelerate the conversion of SA.93
It is worth noting that from HMF, 3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one (3-MCP) via the 2,5-hexadione intermediate can be produced.71,94 After that, a few procedures can then be followed to prepare high-density aviation fuel RJ-4.95 The process begins with intramolecular condensation to produce 3-methylcyclopent-2-enone, which is subsequently reduced to enol. Dehydration and cycloaddition of MCP (3-methylcyclopent-2-en-1-ol) result in the production of DMCPD (methylcyclopentadiene dimers) at 25 °C, which can be further converted into RJ-4 fuel by hydrogenation with an overall yield of 74.4%.
3 Valorization of hemicellulose
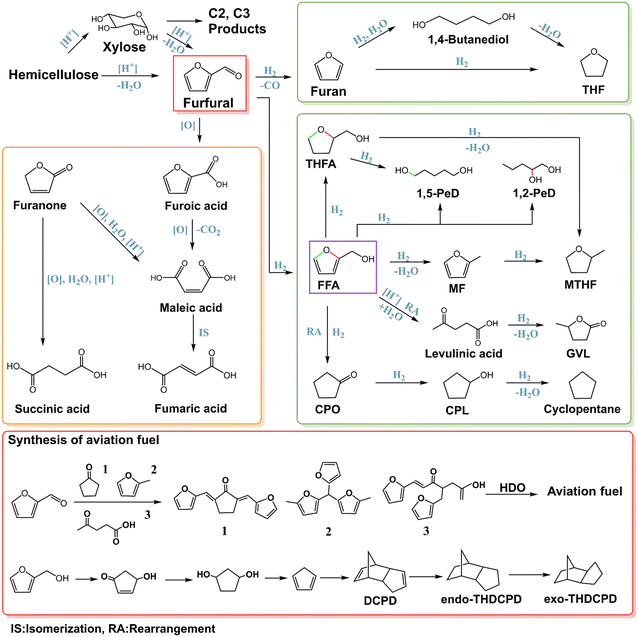
Hemicellulose is an amorphous polymer with about 200 C5 and C6 sugar units linked by β-glycosidic bonds and varies depending on the lignocellulose source.8 Similar to cellulose, hemicellulose can also be transformed into useful molecules.49,96 Acid hydrolysis of hemicellulose can provide a variety of sugars such as xylose and arabinose from the C5 units (e.g. xylan), which can then be further processed to create various compounds including xylitol, furfural, lactic acid, diols and ethanol.97–99 The C2 and C3 products can be formed from xylose via retro-aldol condensation and the following conversion is similar to that from C6 sugar described in the above section.Furfural is a crucial chemical used in the production of fuel additives and polyester monomers.100,101 Industrially, furfural is produced using lignocellulosic biomass with a high xylan content such as corn cobs and bagasse via aqueous H2SO4 hydrolysis and dehydration, with a global production of approximately 370![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 tons per year.8 Current strategies for improving furfural production focus on the development of environment-friendly catalytic systems.102 For example, a recent report reveals that 1,4-dioxane and Hβ zeolites can synergistically promote the selective conversion of xylose to furfural with a high yield of 93.6% at 140 °C.103 The high density of acid sites from Hβ in 1,4-dioxane solvent medium speeds up the transformation of xylose to furfural. 1,4-Dioxane solvent performed as a barrier to protect the acidic center and crystal structure of Hβ during the reactions, which can prevent furfural from polymerizing.
000 tons per year.8 Current strategies for improving furfural production focus on the development of environment-friendly catalytic systems.102 For example, a recent report reveals that 1,4-dioxane and Hβ zeolites can synergistically promote the selective conversion of xylose to furfural with a high yield of 93.6% at 140 °C.103 The high density of acid sites from Hβ in 1,4-dioxane solvent medium speeds up the transformation of xylose to furfural. 1,4-Dioxane solvent performed as a barrier to protect the acidic center and crystal structure of Hβ during the reactions, which can prevent furfural from polymerizing.
Due to its chemical and structural complexity, furfural can be converted directly or indirectly to more than 80 valuable compounds, mainly through reduction and oxidation.104 The paths for furfural transformation into major platform molecules are depicted in Scheme 3. Furfuryl alcohol (FFA) is a crucial monomer in the production of furan resins, which are widely utilized as casting/foundry resins, cements, adhesives, coating materials, and some fine chemical products, such as vitamin C, lysine, etc.105,106 The catalyst for the production of FFA from furfural should have a mild hydrogenation activity and low acidity in order to avoid the hydrogenation of the furan ring and the cleavage of C–O bonds. A copper-based catalyst is utilized for selective hydrogenation in the gas or liquid phase of furfural to produce FFA in industrial production.100,107 Catalytic transfer hydrogenation from a hydrogen donor to furfural is an efficient strategy for FFA preparation. Effective catalysts for catalytic transfer hydrogenation include solid acid–base catalysts (particularly Hf- and Zr-based catalysts) and transition metal catalysts (such as Pd, Pt, Ru, Ir, Au, Cu, Ni, etc.).108
Further hydrogenolysis of the side C–O bond of FFA can form 2-methylfuran (MF), which can be used as a biofuel and fuel additive and as a green solvent and feedstock for the production of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, perfume intermediates, etc. Catalysts with high C–OH and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O hydrogenolysis activity but low furan ring hydrogenation activity are suitable for 2-MF production.109–114 The furan ring saturation by catalysts with higher hydrogenation activity leads to 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (MTHF) formation.1 For example, Pd is a well-known metal with high hydrogenation activity. Bimetallic Cu–Pd catalysts display controlled catalytic activity toward the production of MF and MTHF in the presence of the hydrogen donor 2-propanol. MF (with lower Pd content) or MTHF (with higher Pd content) could be produced as the dominant product in a selective manner by adjusting the Pd ratios in the Cu–Pd catalyst.115
O hydrogenolysis activity but low furan ring hydrogenation activity are suitable for 2-MF production.109–114 The furan ring saturation by catalysts with higher hydrogenation activity leads to 2-methyltetrahydrofuran (MTHF) formation.1 For example, Pd is a well-known metal with high hydrogenation activity. Bimetallic Cu–Pd catalysts display controlled catalytic activity toward the production of MF and MTHF in the presence of the hydrogen donor 2-propanol. MF (with lower Pd content) or MTHF (with higher Pd content) could be produced as the dominant product in a selective manner by adjusting the Pd ratios in the Cu–Pd catalyst.115
Tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol (THFA) is a green solvent in the pharmaceutical industry. Supported Ni catalysts are used in industrial processes to produce THFA from FFA under mild reaction temperatures (50–100 °C). Transition-metal-based catalysts with good hydrogenation activity can be employed for catalytic hydrogenation of furfural to THFA.105 For instance, Li et al. achieved full conversion of furfural under mild conditions (40 °C, 1 MPa H2) with 100% selectivity for THFA over a palladium catalyst supported by hydroxyapatite.116 Hydrogenolysis of the side C–O bond can also produce MTHF from THFA.
pentanediols such as 1,2-pentanediol (1,2-PeD) and 1,5-pentanediol (1,5-PeD) are the desired monomers for polyesters, polyurethanes, polyamides, and intermediates for low-toxicity microbicides as well as potential fuels (or additives) and solvents. 1,2-PeD can be obtained by opening the furan ring of FFA at the C–O bond far from the side chain followed by hydrogenation.117–120 1,5-PeD can also be obtained from FFA by the cleavage of the C–O bond in the furan ring that is close to the side chain. However, due to side reactions, it is difficult to achieve satisfactory selectivity of 1,5-PeD directly from FF or FFA. Furan ring saturation followed by C–O bond cleavage can selectively produce 1,5-PeD. The active catalysts include Rh, Ir, Pt combined with the oxide of Re, Mo, V or W.121,122
Apart from HMF, levulinic acid (LA) can also be produced from furfural by selective hydrogenation of furfural to FFA and the hydrolysis of FFA over Brønsted acids.
Cyclopentanone (CPO) is another useful C5 molecule obtained from furfural. CPO can be used to manufacture fuels, medicines, fungicides, flavor and fragrance compounds and rubber chemicals.123 FFA undergoes protonation and rearrangement reactions over catalysts in water, leading to 2-cyclopentenone, and is transformed into CPO by hydrogenation. Water solvent and catalysts with the desired hydrogenation activity and desired acid–base properties are important for this process.100 Cu combined with other metals are the most investigated catalysts.124–126 Cu–Pd catalyst achieves 92% yield of CPO. Increasing the hydrogenation activity and H2 pressure and prolonging the reaction time can further convert CPO into CPL.127 Cyclopentane can be produced from CPL by hydrogenolysis.
Furan, the simplest five-membered heterocyclic compound containing oxygen, can be obtained by decarbonylation from furfural in both the gas and the liquid phases. Wang et al.128 used the catalyst Pd@S-1-OH and obtained 99.9% furan yield. The realization of high selectivity is attributed to the fact that zeolites can adsorb furfural and by-products but timely and effectively desorb furan. Apart from reductive conversion, furfural can also be oxidized to important compounds such as furoic acid, maleic acid (MAc), maleic anhydride (MA), succinic acid (SAc), furanones, and furoate esters. Zhu et al.101 reviewed the routes and catalysts for the oxidation of furfural to furoic acid or furanone and further synthesis of maleic acid, fumaric acid and succinic acid, in which catalysts with vanadium are frequently utilized.74 In particular, furoic acid generated from oxidation of the aldehyde group of furfural has several functions in the agrochemical, pharmaceutical, taste, and fragrance industries. The common method of oxidizing furfural is to use noble metals like Pd, Pt, Au, or Ag, which are supported on a wide range of metal oxides (Fe2O3, NiO, Co3O4, CuO, CeO2, TiO2, or Bi2O3, etc.) in an oxygen atmosphere.129 The formed furan from furfural can be further converted to tetrahydrofuran (THF) and 1,4-butanediol.130
In addition to obtaining the various value-added chemicals mentioned above, furfural can also be utilized to prepare jet fuels that are primarily made up of C8–C16 hydrocarbons. This approach will promote long-term development in the future by lowering air pollution and reducing carbon emissions in the environment and therefore has attracted extensive attention from the academic community.13 The most common way to synthesize aviation fuel in bioconversion starts from the condensation reaction of furfural with other organic molecules.131,132 The alkanes in the fuel range can be subsequently obtained by one or several steps of HDO/hydrogenation or other processes.133,134 The catalytic system consisting of well-dispersed Ru/HAP and acid zeolite HZSM-5 demonstrates excellent performance in HDO for nine oxygenated compounds which are obtained through the condensation of furfural with other lignocellulose derivatives under mild conditions. Incorporation of Pd to Ru/HAP can further increase the HDO activity. Besides, JP-10 is a high-density fuel that is extensively used for aircraft.135,136 Biobased JP-10 is successfully created by using furfuryl alcohol. First, furfuryl alcohol is rearranged to form 4-hydroxycyclopenta-2-enone followed by hydrogenation to 1,3-cyclopentanediol, dehydration to cyclopentadiene, and a Diels–Alder process to dicyclopentadiene (DCPD). Finally, endo-tetrahydrodicyclopentadiene (endo-THDCPD) is generated by hydrogenation and further isomerizes to exo-tetrahydrodicyclopentadiene (exo-THDCPD, JP-10).
4 Conversion network of lignin
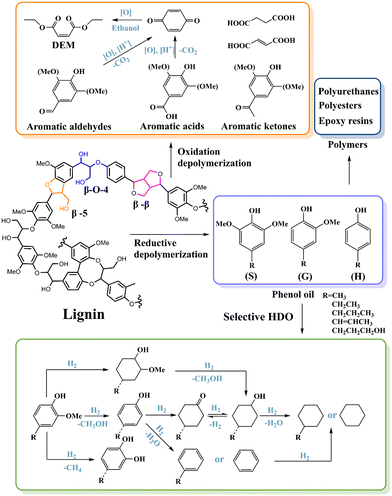
In parallel to cellulose and hemicellulose, lignin valorization has also been explored for fuel and chemical production. As the most abundant and sustainable aromatic resource in nature,12 lignin accounts for 15% to 30% of the mass content in most plants.7,137 Syringyl (S), p-hydroxyphenyl (H) and guaiacyl (G) account for most moieties in lignin,3 which are polymerized together by various C–O and C–C bonds, such as α-O-4, β-O-4, 4-O-5, β–β, and β-5 linkages.138 The inherent heterogeneity and recalcitrance of lignin are the major technical barriers for its conversion into value-added compounds. As a result, lignin has been treated as a waste or low-grade fuel for a long time. With the increase in demand for renewable chemicals and liquid fuels to replace their petroleum-derived counterparts, more and more efforts have been devoted to the research on lignin valorization. Several outstanding reviews have been published to comprehensively overview lignin depolymerization strategies and different catalytic systems for lignin upgrading.3,7,139–1434.1 Oxidative depolymerization
Oxidative depolymerization has been employed for a long time. During this process, the oxidative cleavage of inter-unit linkages of lignin and the oxidation of the side chains of the units produce unique aromatic compounds with polyfunctionalities, such as aromatic aldehydes and acids.8 In addition to aromatic products, quinones can be obtained by further oxidation of the side chain and aromatic ring, and then dicarboxylic acid can also be produced by subsequent ring cracking (Scheme 4).144 Various oxidants together with transition metal ion or polyoxometalate catalysts have been explored to obtain the above substances. The main factors affecting the product distribution during oxidative depolymerization are the reaction temperature, the reaction medium, oxidant, catalyst, reaction time and lignin composition. Higher temperature and alkalinity, stronger oxidizing agent and catalyst usually lead to deeper oxidation products.Vanillin (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde) is an important food flavor additive and ideal intermediate in the synthesis of fine chemicals and polymers. It can be produced on an industrial scale through partial oxidation of lignin. The global vanillin market reached 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 metric tons in 2015, 20% of which came from the valorization of lignin.145 Benzoquinones can be used as raw materials for the production of dyes and bioactive compounds, electrolytes in supercapacitors and redox flow batteries, and cathodes in solid-state batteries. They can be produced from lignin via aromatic aldehyde and acid intermediates. Using the cobalt–Schiff base complex as the catalyst, the yield of benzoquinone based on lignin is as high as 43%. Under the catalysis of polyoxymethylene ionic liquid [BSmim] and CuPW12O40, the oxidation of lignin can prepare diethyl maleate via a benzoquinone intermediate.146 More interestingly, this catalytic system can simultaneously convert the three components of lignocellulose into diethyl maleate with high productivity of 404.8 mg g−1 and selectivity of 72.7%.
000 metric tons in 2015, 20% of which came from the valorization of lignin.145 Benzoquinones can be used as raw materials for the production of dyes and bioactive compounds, electrolytes in supercapacitors and redox flow batteries, and cathodes in solid-state batteries. They can be produced from lignin via aromatic aldehyde and acid intermediates. Using the cobalt–Schiff base complex as the catalyst, the yield of benzoquinone based on lignin is as high as 43%. Under the catalysis of polyoxymethylene ionic liquid [BSmim] and CuPW12O40, the oxidation of lignin can prepare diethyl maleate via a benzoquinone intermediate.146 More interestingly, this catalytic system can simultaneously convert the three components of lignocellulose into diethyl maleate with high productivity of 404.8 mg g−1 and selectivity of 72.7%.
4.2 Reductive depolymerization
Reductive depolymerization is one of the most widely used and effective methods for generating lignin monomers in recent years. With H2 or a hydrogen donor (such as methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, and even lignin itself) as hydrogen source, lignin can be depolymerized into lower molecular weight phenolic compounds (phenol oil) over Ru-, Pt-, Pd-, Ni-, Rh-, Co- and Cu-based catalysts via hydrogenolysis, hydrocracking, hydrogenation, and hydrodeoxygenation (HDO).8 These fragmented phenolic compounds usually bear methoxy groups and other different O-containing functional groups, which cannot be utilized directly. Catalytic HDO is the most promising strategy to produce value-added monomers from lignin depolymerized phenol oil. Through selective HDO, precisely controlled reactions including hydrogenolysis, hydrogenation, dehydration, and direct deoxygenation, different lignin fragments can be further tailored into various value-added monomers (such as alkylphenol, phenol, cyclohexanone, cyclohexanol, cyclohexane, alkybenzene, benzene, etc.) (Scheme 4).143,147–151 The catalytic HDO of aromatic oxygenates typically follows two well-accepted reaction pathways: (1) ring hydrogenation and C–O bond breakage via hydrogenolysis and (2) straight deoxygenation via C–O bond cleavage, leaving the aromatic ring unchanged.149Alkylphenols can be produced from the S and G type compounds (methoxy phenols) in phenol oil through selective cleavage of the methoxy groups via hydrogenolysis without the hydrogenation of aromatic rings (Scheme 4). Phenol is a monomer for the production of polycarbonates and epoxide resins. It can also be synthesized from alkylphenols via dealkylation reaction over catalysts with the desired acidity and porosity.152 During the HDO conversion of methoxy phenols, if the catalysts possess higher hydrogenation activity, the aromatic ring is prone to saturation either before or after (alkyl)phenol formation, producing cyclohexanediols or via cyclohexanones to cyclohexanols, respectively. Cyclohexanols can be employed to produce pharmaceuticals, pesticides and cosmetics as well as used as fuel additives for diesels or synthetic diesels from gas-to-liquid (GTL) processes. Cyclohexanone is the precursor of caprolactam, the building block of nylon-6. It can be efficiently converted from phenol over Pd/C with a Lewis acid or Pd/HAP catalyst.153,154 Cyclohexanone can also be formed from dehydrogenation of cyclohexanol. When acidic sites exist, cyclohexanols will be further dehydrated and hydrogenated to form cyclohexane or alkylcyclohexane, as either fuel or solvent.155
To precisely tailor methoxy phenols to compounds in the abovementioned tandem conversion route, catalysts with controlled active sites are essential. For example, the CoNx@NC catalyst can convert eugenol to propylcyclohexanol with a yield of more than 99.9% at 200 °C and 2 MPa H2 through cracking the Caryl–OCH3 bond before hydrogenation of the aromatic ring.156 This reaction path requires lower activation energy than hydrogenating the aromatic ring before the cleavage of the Caryl–OCH3 bond. It is the main reason that cobalt-based catalysts can convert lignin-derived phenols to cyclohexanols under milder conditions than Ni, Pd and Ru catalysts. When HZSM-5 solid acid was added to the above reaction system, further dehydration and hydrogenation reactions occurred, leading to propylcyclohexane with a yield of 99.1%. To obtain the chemical intermediate, alkylphenols, aromatic ring hydrogenation must be suppressed. The incorporation of a small amount of Fe into CoNx@NC catalyst (Co1–Fe0.1@NC) significantly inhibited the further hydrogenation of the 4-propylphenol intermediate by weakening the adsorption capacity of the catalyst to 4-propylphenol, resulting in the selective preparation of 4-propylphenol from eugenol in 88.3% yield. Moreover, alkylphenols were successfully prepared from birch and corn stover by a lignin-first strategy.
The HDO reaction can straightly remove all of the oxygen-containing functional groups in lignin-derived phenols via C–O bond cleavage but leave the aromatic ring unchanged, which can finally produce arenes. The reaction conditions are critical for selective production of arenes. Higher temperature can promote HDO and low H2 pressures are favorable to decrease the ring hydrogenation. Applying hydrogen donor reagents such as methanol and formic acid instead of H2 is also effective for arene production. In addition, the design of the catalytic activity center is also essential. Metals with relatively strong oxophilicity, such as Ru, Re, Mo, W, Fe and Co, can lower the dissociation barrier of C–O bonds.148,157,158 Small-sized metal particles and acidic supports are favorable for C–O cleavage. Surface defects (such as oxygen vacancies) or coordinately unsaturated metal cation sites can effectively bind O atoms and activate C–O bonds.148 Tuning the electronic state of the active metal can help weaken the binding strength to the aromatic ring and thus suppress the ring hydrogenation. Moreover, the substrate adsorption mode can change the reaction path and affect the distribution of HDO products. The planar adsorption of lignin-derived phenols on the active site leads to the chemical adsorption of the benzene ring on the active site, which is beneficial to the ring hydrogenation. When the lignin-derived phenols are nonplanar adsorbed (vertical and tilted), the active site has chemical adsorption with the oxygen-containing functional groups instead of the benzene ring, which is conducive to C–O breaking and retaining the aromatic ring.159–161
Besides HDO, through demethylation, (alkyl)catechol, an important precursor in the pesticide, perfume, and pharmaceutical industries, can be obtained by the cleavage of the CarylO–CH3 bond.155,156 Usually, Brønsted acid sites tend to promote demethylation and increase the selectivity of (alkyl)catechol.
Among the various interunit linkages of lignin monomers, the C–C bond accounts for about 30% of all bridging bonds. The C–C bond has a higher dissociation energy (226–494 kJ mol−1) than the C–O bond (209–348 kJ mol−1), and the C–C bond is the most recalcitrant bond in lignin, which requires very harsh conditions to break.140,162,163 Therefore, the design of the catalytic activity center for breaking the C–C bond is the key to further improve the yield of lignin monomers and achieve the fullest valorization of lignin.164 Metal sulfides, such as CoS2 and FeS2, have a good catalytic effect on C–C bond dissociation, but metal sulfides have a limited structural stability, and sulfur loss will affect the subsequent process.165 Strong Brønsted acid sites can protonate the benzene ring, thus promoting the cleavage of the C–C bond.166
From the information above, we can know that lignin has been demonstrated to be a versatile starting material for the synthesis of many products. However, the inherent heterogeneity and recalcitrance of lignin inevitably lead to harsh reaction conditions and low single-platform chemical yield; the products typically comprise a variety of substances.3,16 Tremendous efforts have to be devoted to future studies in designing practical conversion processes and high-selectivity HDO catalysts. One-pot conversion is also a viable method for using lignin in industrial applications as compared to multi-step methods since it reduces the number of reactors and separation procedures. Cycloalkanes,167–169 aromatic hydrocarbons,166,170,171 and aromatic phenols172,173 have been successfully synthesized by lignin reduction in one pot using catalysts with varied hydrogenation properties.
In addition to synthetic hydrocarbon fuels and functional monomers, a variety of useful functional polymers can be synthesized from lignin as well such as polyurethanes,174,175 polyesters,176,177 epoxy resins,178,179etc. Recently, many great reviews of lignin synthetic polymers have been published.7,180,181 Through these cutting-edge studies, people can better understand and utilize the second-richest renewable polymer in the world. The effective use of these green and renewable synthesis methods will not only help reduce carbon dioxide emissions but also promote the sustainable development of the polymer industry.
5 Conclusions and perspectives
In conclusion, starting from cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, respectively, we draw a clear network for lignocellulosic biomass valorization in a panoramic view and summarize the reaction routes and reaction types involved in the preparation of various important chemicals from lignocellulosic biomass. In detail, hydrolysis of cellulose generates glucose, which can be isomerized to fructose. The two hexoses can also produce a variety of crucial C2, C3 and C4 chemicals through retro-aldol condensation together with other reactions. After dehydration, fructose is able to transform into HMF, an important platform molecule that can be employed to produce a number of high-value chemicals and fuels. Moreover, furfural is a key compound in the upgrading pathway of hemicellulose. It can be used to create a variety of C4–C5 chemicals and aviation fuels. Lignin is the only renewable feedstock in nature that comprises aromatic rings and it can be utilized to obtain essential aromatic or naphthenic chemicals that include aromatic aldehydes, aromatic ketones, aromatic acids, phenols, cycloalkanes, and other important chemicals by oxidative or reductive depolymerization.It is worth mentioning that the structure of hemicellulose/cellulose and lignin is different, which leads to the different chemistries and difficulties for their conversion. Both hemicellulose and cellulose are composed of sugar units linked by glycosidic bonds; the chemistry in them is similar. However, because hemicellulose is an amorphous polymer while cellulose is a crystalline polymer with several polymorphs, it usually requires harsher depolymerization conditions for cellulose than hemicellulose. Furfural derived from hemicellulose is the most mature and widely applied commodity chemical made from lignocellulosic biomass. Levulinic acid has been produced from furfural alcohol or directly from cellulose or hydrolysis in commercial scale. With technology progress, HMF and FDCA are being produced in semi-commercial facilities. Lignin is a complex and recalcitrant phenolic polymer randomly cross-linked by various C–C and C–O bonds. Controlled and complete depolarization of lignin is rather difficult. Except for vanillin which realizes commercialization due to its high value and high demand, the vast majority of the compounds converted from lignin are still in the laboratory scale. The technology readiness for chemicals and fuels from the lignocellulosic biomass conversion network has a great difference.
Currently, except for the few commercial and semi-commercial products (furfural, levulinic acid, vanillin, and HMF, FDCA) available from lignocellulose or its main components, most of the aforementioned research efforts are still at a laboratory scale. Going beyond the “proof-of-concept” stage to the “proof-of-value” stage is urgently required. The concept of an integrated biorefinery can only succeed if the costs of chemicals produced from lignocellulosic biomass are comparable or lower than those from fossil fuels. A set of metrics addressing resource efficiency (carbon footprint and waste production), catalyst performance (selectivity, activity and consumption) and product recovery (Table 1) proposed by Lange182 can serve as an initial guideline in evaluating what feedstock, chemistry and technology deserve further exploitation or in defining preliminary performance targets to unlock the industrial potential.
| Criteria | Minimum requirement | Ideal value | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| a These targets have been defined for commodity chemicals; they should be tightened for fuel. b Target selectivity (tprod per tfeed) > (feed price + CC) (US$ per tfeed)/product price (US$ per tprod). CC, conversion cost. c Distillation resistance Ω (°C−1) = 100 × ∑(fi/ΔTi), where fi is the weight fraction in the stream (wt/wt) and i represents the various components present in the stream; Ti is the temperature in °C. Prod, product; react, reactor; cat, catalyst. | |||
| C footprinta (tCO2 per tprod) | <6 | <4 | Defined from well-to-gate, including feed and utility |
| Waste productiona (twaste per tprod) | <5 | <1 | Defined as by-products, fuel and inorganic chemicals |
| Selectivity | Stoichiometry > target | Experimental > target | Target selectivity defined in footnoteb |
| Reactor productivity (tprod per m3react per h) | >0.1 | >0.5 | Determined by catalyst loading and intrinsic activity |
| Product concentration (wt%) | >3 | >10 | Determined by feed dilution and conversion per pass |
| Catalyst consumption (kgcat per tprod) | <1 | <0.1 | Determined by catalyst lifetime and intrinsic activity |
| Distillation resistance (°C−1) | <15 | <10 | Defined in footnotec |
For the C footprints defined in Table 1, a much lower value was expected for lignocellulosic feedstock than fossil resources.183 Nonetheless, poor feedstock efficiency and/or excessive energy and/or H2 requirements may offset the bio-feedstock advantage. Conversion processes with milder reaction conditions and fewer steps are highly desirable. If any of the three main components of lignocellulose cannot be rationally utilized, waste production during lignocellulose conversion could be relatively high. Therefore, it is crucial to develop efficient strategies to fractionate lignocellulose into separate components for further and full applications. Moreover, the transformation of lignocellulose to chemicals involves various reactions, including hydrolysis, hydrogenation, dehydration, decarbonylation, decarboxylation, rearrangement, condensation, etc. In most cases, several reactions occur simultaneously or sequentially. The side reactions are difficult to avoid, resulting in a significant number of by-products that are hard to separate, and thus, high waste production. For the same reason, the stoichiometry selectivity might be higher than the target one, but the experimental results could be lower than the limit for profit.
Achieving high selectivity often presents trade-offs with the metrics of reactor productivity, product concentration, and/or the distillation resistance shown in Table 1. In fact, studies that report good selectivity and yield in the catalysis literature frequently employ diluted feed (∼1 wt%) to reduce the unintended formation of humins and other side products. However, the low feed concentration limits productivity and raises production cost. Therefore, it is more important for scalable industrial production to employ a higher concentration and meanwhile achieve good selectivity and productivity. Additionally, besides distillation, more attention should be paid to the separation and purification of target products to put the process forward to practical applications. In fact, the development of highly stable, efficient, and cost-effective heterogeneous catalysts working under mild and eco-friendly conditions is essential to meet almost all of the metrics listed in Table 1 for the conversion of lignocellulose. Great challenges still remain in designing and developing industrially feasible heterogeneous catalysts for the conversion of lignocellulose into value-added chemicals and fuels:
(i) Successful synthesis of robust and easily regenerated catalysts
Most catalysts tend to deactivate in a short time when raw biomass-derived feedstocks were used due to the following facts: minerals and heteroatoms in biomass are prone to poison catalysts by irreversibly binding to the active sites. The catalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass usually involves high temperature and pressure and hence coke or tar will easily accumulate on the active sites via polymerization. Thermal processing of the catalysts is necessary to regenerate the active sites, but this may cause sintering. Besides, some acids used or generated in liquid-phase reactions are prone to dissolve and extract metal atoms out from the metal catalysts, particularly non-noble metal catalysts. The hot liquid water itself can make the porous structure of the catalyst collapse, which may impair the lifetime of the catalyst seriously. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop efficient and robust heterogeneous catalysts for the conversion of lignocellulose.
Several strategies may address these issues, including exploring advanced catalyst preparation methods to stabilize metal particles and supports by enhancing the strong metal–support interaction (SMSI), incorporating heteroatoms such as N, P, B or C into metallic catalysts or developing multi-functional supports that exhibit superior stability under hydrothermal conditions. For example, following these principles, the Co2PL/MnP-3 catalyst was developed with a strong metal phosphide and phosphate interaction (SMPSI).184 It combines the advantages of metal phosphide and phosphate support and possesses superior selective hydrogenation catalytic activities, excellent anti-acid and anti-oxidant capability, and remarkable stability. The SMPSI is universal and has great potential to be utilized to construct low-cost and robust non-noble metal catalysts for large-scale biomass valorization.
(ii) Precision design of multifunctional catalysts with high activity and selectivity
It is important to adjust the catalyst morphology and hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity to improve the accessibility of reactants and intermediates to the active sites. Various active sites with the desired adsorptive or catalytic capacities need to be precisely modulated to regulate the reaction intermediates going through the target pathway, rather than a bypass. Compared with single-metal catalysts, bi- or multi-metallic and heteroatom-anchoring catalysts have a unique synergistic effect, besides stability, which may also improve the activity and selectivity of catalysts. The main synergistic effect enables the generation of new reaction sites and promotes charge transfer. The active sites can be geometrically and electronically modified by the above effects and ultimately enhance their catalytic performance.
(iii) Thorough understanding of the reaction mechanism
Due to the intricate nature of the lignocellulose conversion process, it is essential to gain in-depth insight into the reaction mechanisms including identification of the key reaction intermediates, the rate-limiting step in the reaction pathway, the surface/interface reaction kinetics, active sites involved in the catalytic cycle, etc. Currently, a more fundamental understanding of the reaction process, active sites and structure–activity relationship of catalysts has been achieved via in situ or operando characterization studies of catalysts combined with quantum chemical or density functional theory calculations. This significantly promotes further optimization of the catalyst structure to obtain better catalytic performance.
Besides thermocatalytic conversion, photocatalysis and electrocatalysis have also been employed for lignocellulose transformation and demonstrated great potential for future application. Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven synthesis can also be employed to facilitate the screening of excellent catalysts and the development of efficient and economic pathways for the valorization of lignocellulosic biomass to value-added chemicals and liquid fuels. Hopefully in the near future, with the cooperation of scientists, engineers, economic appraisers, entrepreneurs and policymakers, some of these lignocellulose-derived substances can be produced on a massive scale to partially replace equivalent petrochemical counterparts.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFB1501502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22078311 and 51876200) and the Anhui Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (2108085J09).References
- J. C. Serrano-Ruiz, R. Luque and A. Sepulveda-Escribano, Transformations of biomass-derived platform molecules: From high added-value chemicals to fuels via aqueous-phase processing, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 5266–5281 RSC.
- X. Zhang, K. Wilson and A. F. Lee, Heterogeneously catalyzed hydrothermal processing of C5-C6 sugars, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 12328–12368 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Li, X. Zhao, A. Wang, G. W. Huber and T. Zhang, Catalytic transformation of lignin for the production of chemicals and fuels, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 11559–11624 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Gong, Y. Lin, C. Chen, M. Al-Mamun, H. S. Lu, G. Wang, H. Zhang and H. Zhao, Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube confined Co-Nx sites for selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived compounds, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, e1808341 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. M. Alonso, S. G. Wettstein and J. A. Dumesic, Bimetallic catalysts for upgrading of biomass to fuels and chemicals, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 8075–8098 RSC.
- H. Li, A. Bunrit, N. Li and F. Wang, Heteroatom-participated lignin cleavage to functionalized aromatics, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 3748–3763 RSC.
- B. M. Upton and A. M. Kasko, Strategies for the conversion of lignin to high-value polymeric materials: Review and perspective, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 2275–2306 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Deng, Y. Feng, J. Fu, H. Guo, Y. Guo, B. Han, Z. Jiang, L. Kong, C. Li, H. Liu, P. T. T. Nguyen, P. Ren, F. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, S. S. Wong, K. Yan, N. Yan, X. Yang, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhang, X. Zeng and H. Zhou, Catalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into chemicals and fuels, Green Energy Environ., 2023, 8, 10–114 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Ragauskas, C. K. Williams, B. H. Davison, G. Britovsek, J. Cairney, C. A. Eckert, W. J. Frederick, J. P. Hallett, D. J. Leak, C. L. Liotta, J. R. Mielenz, R. Murphy, R. Templer and T. Tschaplinski, The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials, Science, 2006, 311, 484–489 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Zhou, X. Xia, C. X. Lin, D. S. Tong and J. Beltramini, Catalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to fine chemicals and fuels, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 5588–5617 RSC.
- E. Calcio Gaudino, G. Cravotto, M. Manzoli and S. Tabasso, Sono- and mechanochemical technologies in the catalytic conversion of biomass, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 1785–1812 RSC.
- M. Wang and F. Wang, Catalytic scissoring of lignin into aryl monomers, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, e1901866 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. W. Huber, S. Iborra and A. Corma, Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: Chemistry, catalysts, and engineering, Chem. Rev., 2006, 106, 4044–4098 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Carpenter, T. L. Westover, S. Czernik and W. Jablonski, Biomass feedstocks for renewable fuel production: A review of the impacts of feedstock and pretreatment on the yield and product distribution of fast pyrolysis bio-oils and vapors, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 384–406 RSC.
- X. Chen, S. Song, H. Y. Li, G. Gozaydin and N. Yan, Expanding the boundary of biorefinery: Organonitrogen chemicals from biomass, Acc. Chem. Res., 2021, 54, 1711–1722 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Mei, H. Liu, X. Shen, Q. Meng, H. Liu, J. Xiang and B. Han, Selective utilization of the methoxy group in lignin to produce acetic acid, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 14868–14872 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Besson, P. Gallezot and C. Pinel, Conversion of biomass into chemicals over metal catalysts, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 1827–1870 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Mondelli, G. Gozaydin, N. Yan and J. Perez-Ramirez, Biomass valorisation over metal-based solid catalysts from nanoparticles to single atoms, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 3764–3782 RSC.
- L. Lin, X. Han, B. Han and S. Yang, Emerging heterogeneous catalysts for biomass conversion: Studies of the reaction mechanism, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 11270–11292 RSC.
- P. Sudarsanam, E. Peeters, E. V. Makshina, V. I. Parvulescu and B. F. Sels, Advances in porous and nanoscale catalysts for viable biomass conversion, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 2366–2421 RSC.
- C. E. Wyman, B. E. Dale, R. T. Elander, M. Holtzapple, M. R. Ladisch and Y. Y. Lee, Coordinated development of leading biomass pretreatment technologies, Bioresour. Technol., 2005, 96, 1959–1966 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. K. Rout, A. D. Nannaware, O. Prakash, A. Kalra and R. Rajasekharan, Synthesis of hydroxymethylfurfural from cellulose using green processes: A promising biochemical and biofuel feedstock, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2016, 142, 318–346 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zheng, J. Pang, R. Sun, A. Wang and T. Zhang, Selectivity control for cellulose to diols: Dancing on eggs, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 1939–1954 CrossRef CAS.
- M. M. Abu-Omar, K. Barta, G. T. Beckham, J. S. Luterbacher, J. Ralph, R. Rinaldi, Y. Román-Leshkov, J. S. M. Samec, B. F. Sels and F. Wang, Guidelines for performing lignin-first biorefining, Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14, 262–292 RSC.
- M. Taherzadeh, B. Parameswaran, K. Karimi, L. P. de Souza Vandenberghe and A. Kumar Patel, Recent advances on pretreatment of lignocellulosic and algal biomass, Bioresour. Technol., 2020, 316, 123957 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Zhai, F. Long, C.-y. Hse, F. Wang, T. F. Shupe, J. Jiang and J. Xu, Facile fractionation of bamboo wood toward biomass valorization by p-TsOH-Based methanolysis pretreatment, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 19213–19224 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-B. Huang and Y. Fu, Hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose by solid acid catalysts, Green Chem., 2013, 15, 1095–1111 RSC.
- L. Hu, L. Lin, Z. Wu, S. Zhou and S. Liu, Chemocatalytic hydrolysis of cellulose into glucose over solid acid catalysts, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 174–175, 225–243 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Xu, Z. Wang, J. Huang and Y. Jiang, Thermal catalytic conversion of biomass-derived glucose to fine chemicals, Energy Fuels, 2021, 35, 8602–8616 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Shrotri, H. Kobayashi and A. Fukuoka, Cellulose depolymerization over heterogeneous catalysts, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 761–768 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Fukuoka and P. L. Dhepe, Catalytic conversion of cellulose into sugar alcohols, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 5161–5163 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, X. Liu, N. Li, P. Ma and Y. Zhang, Direct synthesis of hexitols from microcrystalline cellulose and birch over zirconium(iv) phosphate supported nickel catalysts and the mechanism study, Green Chem., 2021, 23, 1353–1360 RSC.
- I. Bonnin, R. Mereau, T. Tassaing and K. De Oliveira Vigier, One-pot synthesis of isosorbide from cellulose or lignocellulosic biomass: a challenge?, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2020, 16, 1713–1721 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yue, Y. Zhao, X. Ma and J. Gong, Ethylene glycol: properties, synthesis, and applications, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 4218–4244 RSC.
- N. Ji, T. Zhang, M. Zheng, A. Wang, H. Wang, X. Wang and J. G. Chen, Direct catalytic conversion of cellulose into ethylene glycol using nickel-promoted tungsten carbide catalysts, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 8510–8513 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. F. Service, Cellulosic ethanol at last?, Science, 2014, 345, 1111 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Li, G. Xu, C. Wang, L. Ma, Y. Qiao, Y. Zhang and Y. Fu, One-pot chemocatalytic transformation of cellulose to ethanol over Ru-WOx/HZSM-5, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 2234–2239 RSC.
- M. Yang, H. Qi, F. Liu, Y. Ren, X. Pan, L. Zhang, X. Liu, H. Wang, J. Pang, M. Zheng, A. Wang and T. Zhang, One-Pot production of cellulosic ethanol via tandem catalysis over a multifunctional Mo/Pt/WOx catalyst, Joule, 2019, 3, 1937–1948 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Song, P. Wang, S. Li, W. Deng, Y. Li, Q. Zhang and Y. Wang, Direct conversion of cellulose into ethanol catalysed by a combination of tungstic acid and zirconia-supported Pt nanoparticles, Chem. Commun., 2019, 55, 4303–4306 RSC.
- K. Tomishige, M. Yabushita, J. Cao and Y. Nakagawa, Hydrodeoxygenation of potential platform chemicals derived from biomass to fuels and chemicals, Green Chem., 2022, 24, 5652–5690 RSC.
- X. Liu, X. Liu, G. Xu, Y. Zhang, C. Wang, Q. Lu and L. Ma, Highly efficient catalytic conversion of cellulose into acetol over Ni–Sn supported on nanosilica and the mechanism study, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 5647–5656 RSC.
- X. Liu, X. Liu, H. Wang, T. Xiao, Y. Zhang and L. Ma, A mechanism study on the efficient conversion of cellulose to acetol over Sn–Co catalysts with low Sn content, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 6579–6587 RSC.
- A. N. Ardila, M. A. Sánchez-Castillo, T. A. Zepeda, A. L. Villa and G. A. Fuentes, Glycerol hydrodeoxygenation to 1,2-propanediol catalyzed by CuPd/TiO2-Na, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 219, 658–671 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Dasari, P.-P. Kiatsimkul, W. R. Sutterlin and G. J. Suppes, Low-pressure hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propylene glycol, Appl. Catal., A, 2005, 281, 225–231 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Corma, S. Iborra and A. Velty, Chemical routes for the transformation of biomass into chemicals, Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 2411–2502 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. Holm, S. Saravanamurugan and E. Taarning, Conversion of sugars to lactic acid derivatives using heterogeneous zeotype catalysts, Science, 2010, 328, 602–605 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Maki-Arvela, I. L. Simakova, T. Salmi and D. Y. Murzin, Production of lactic acid/lactates from biomass and their catalytic transformations to commodities, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 1909–1971 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Iglesias, I. Martinez-Salazar, P. Maireles-Torres, D. Martin Alonso, R. Mariscal and M. Lopez Granados, Advances in catalytic routes for the production of carboxylic acids from biomass: A step forward for sustainable polymers, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 5704–5771 RSC.
- C. Xu, E. Paone, D. Rodriguez-Padron, R. Luque and F. Mauriello, Recent catalytic routes for the preparation and the upgrading of biomass derived furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 4273–4306 RSC.
- Z. Zhang and G. W. Huber, Catalytic oxidation of carbohydrates into organic acids and furan chemicals, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 1351–1390 RSC.
- T. Wang, M. W. Nolte and B. H. Shanks, Catalytic dehydration of C6 carbohydrates for the production of hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) as a versatile platform chemical, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 548–572 RSC.
- X. Kong, Y. Zhu, Z. Fang, J. A. Kozinski, I. S. Butler, L. Xu, H. Song and X. Wei, Catalytic conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to some value-added derivatives, Green Chem., 2018, 20, 3657–3682 RSC.
- A. A. Rosatella, S. P. Simeonov, R. F. M. Frade and C. A. M. Afonso, 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) as a building block platform: Biological properties, synthesis and synthetic applications, Green Chem., 2011, 13, 754–793 RSC.
- Y. Feng, M. Li, Z. Gao, X. Zhang, X. Zeng, Y. Sun, X. Tang, T. Lei and L. Lin, Development of betaine-based sustainable catalysts for green conversion of carbohydrates and biomass into 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, ChemSusChem, 2019, 12, 495–502 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Tang, L. Zhu, X. Fu, J. Dai, X. Guo and C. Hu, Insights into the kinetics and eeaction network of aluminum chloride-catalyzed conversion of glucose in NaCl–H2O/THF biphasic system, ACS Catal., 2016, 7, 256–266 CrossRef.
- L. Zhu, X. Fu, Y. Hu and C. Hu, Controlling the reaction networks for efficient conversion of glucose into 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 4812–4832 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Hou, X. Qi, M. Zhen, H. Qian, Y. Nie, C. Bai, S. Zhang, X. Bai and M. Ju, Biorefinery roadmap based on catalytic production and upgrading 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, Green Chem., 2021, 23, 119–231 RSC.
- J. Zhang and E. Weitz, An in situ NMR study of the mechanism for the catalytic conversion of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and then to levulinic acid using 13C labeled d-fructose, ACS Catal., 2012, 2, 1211–1218 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Girisuta, L. Janssen and H. J. Heeres, Kinetic study on the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of cellulose to levulinic acid, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2007, 46, 1696–1708 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Ding, J. Wang, J. Xi, X. Liu, G. Lu and Y. Wang, High-yield production of levulinic acid from cellulose and its upgrading to γ-valerolactone, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 3846–3853 RSC.
- C.-H. Kuo, A. S. Poyraz, L. Jin, Y. Meng, L. Pahalagedara, S.-Y. Chen, D. A. Kriz, C. Guild, A. Gudz and S. L. Suib, Heterogeneous acidic TiO2 nanoparticles for efficient conversion of biomass derived carbohydrates, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 785–791 RSC.
- D. Di Menno Di Bucchianico, Y. Wang, J.-C. Buvat, Y. Pan, V. Casson Moreno and S. Leveneur, Production of levulinic acid and alkyl levulinates: A process insight, Green Chem., 2022, 24, 614–646 RSC.
- R. Weng, Z. Yu, J. Xiong and X. Lu, Effects of water in the heterogeneous catalytic valorization of levulinic acid into γ-valerolactone and its derivatives, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 3013–3027 RSC.
- W. Han, M. Tang, J. Li, X. Li, J. Wang, L. Zhou, Y. Yang, Y. Wang and H. Ge, Selective hydrogenolysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-dimethylfuran catalyzed by ordered mesoporous alumina supported nickel-molybdenum sulfide catalysts, Appl. Catal., B, 2020, 268, 118748 CrossRef.
- Z. Zhang, S. Yao, C. Wang, M. Liu, F. Zhang, X. Hu, H. Chen, X. Gou, K. Chen, Y. Zhu, X. Lu, P. Ouyang and J. Fu, CuZnCoOx multifunctional catalyst for in situ hydrogenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with ethanol as hydrogen carrier, J. Catal., 2019, 373, 314–321 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Gan, Y. Liu, Q. He, H. Zhang, X. He and H. Ji, Facile synthesis of kilogram-scale Co-alloyed Pt single-atom catalysts via ball milling for hydrodeoxygenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 8, 8692–8699 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yang, H. Liu, S. Li, C. Chen, T. Wu, Q. Mei, Y. Wang, B. Chen, H. Liu and B. Han, Hydrogenolysis of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-Dimethylfuran under mild conditions without any additive, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 5711–5716 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, C. Zhu, D. Li, Q. Liu, J. Tan, C. Wang, C. Cai and L. Ma, Recent advances in catalytic conversion of biomass to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and 2, 5-dimethylfuran, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2019, 103, 227–247 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Hu, J. Xu, S. Zhou, A. He, X. Tang, L. Lin, J. Xu and Y. Zhao, Catalytic advances in the production and application of biomass-derived 2,5-dihydroxymethylfuran, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 2959–2980 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Xiao, X. Liu, G. Xu and Y. Zhang, Phase tuning of ZrO2 supported cobalt catalysts for hydrodeoxygenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-dimethylfuran under mild conditions, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 295, 120270 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, G. Li, Y. Hu, A. Wang, F. Lu, J.-J. Zou, Y. Cong, N. Li and T. Zhang, Integrated conversion of cellulose to high-density aviation fuel, Joule, 2019, 3, 1028–1036 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Fulignati, C. Antonetti, D. Licursi, M. Pieraccioni, E. Wilbers, H. J. Heeres and A. M. R. Galletti, Insight into the hydrogenation of pure and crude HMF to furan diols using Ru/C as catalyst, Appl. Catal., A, 2019, 578, 122–133 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Hu, X. Dai, N. Li, X. Tang and Y. Jiang, Highly selective hydrogenation of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)furan over an acid–base bifunctional hafnium-based coordination polymer catalyst, Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2019, 3, 1033–1041 RSC.
- Y. Feng, S. Long, X. Tang, Y. Sun, R. Luque, X. Zeng and L. Lin, Earth-abundant 3d-transition-metal catalysts for lignocellulosic biomass conversion, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50, 6042–6093 RSC.
- J. He, S. P. Burt, M. Ball, D. Zhao, I. Hermans, J. A. Dumesic and G. W. Huber, Synthesis of 1,6-hexanediol from cellulose derived tetrahydrofuran-dimethanol with Pt-WOx/TiO2 catalysts, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 1427–1439 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Xiao, M. Zheng, X. Li, J. Pang, R. Sun, H. Wang, X. Pang, A. Wang, X. Wang and T. Zhang, Synthesis of 1,6-hexanediol from HMF over double-layered catalysts of Pd/SiO2 + Ir-ReOx/SiO2 in a fixed-bed reactor, Green Chem., 2016, 18, 2175–2184 RSC.
- S. Chen, C. Ciotonea, K. De Oliveira Vigier, F. Jérôme, R. Wojcieszak, F. Dumeignil, E. Marceau and S. Royer, Hydroconversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-dimethylfuran and 2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran over non-promoted Ni/SBA-15, ChemCatChem, 2020, 12, 2050–2059 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Yang and A. Sen, One-step catalytic transformation of carbohydrates and cellulosic biomass to 2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran for liquid fuels, ChemSusChem, 2010, 3, 597–603 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Fujita, K. Nakajima, J. Yamasaki, T. Mizugaki, K. Jitsukawa and T. Mitsudome, Unique catalysis of nickel phosphide nanoparticles to promote the selective transformation of biofuranic aldehydes into diketones in water, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 4261–4267 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Deng, R. Gao, X. Li, J. Wang, Z. Zeng, J.-J. Zou and S. Deng, Hydrogenative ring-rearrangement of biobased furanic aldehydes to cyclopentanone compounds over Pd/pyrochlore by introducing oxygen vacancies, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 7355–7366 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Ramos, A. Grigoropoulos, N. Perret, M. Zanella, A. P. Katsoulidis, T. D. Manning, J. B. Claridge and M. J. Rosseinsky, Selective conversion of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to cyclopentanone derivatives over Cu-Al2O3 and Co-Al2O3 catalysts in water, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 1701–1713 RSC.
- S. E. Davis, B. N. Zope and R. J. Davis, On the mechanism of selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid over supported Pt and Au catalysts, Green Chem., 2012, 14, 143–147 RSC.
- J. Ma, Z. Du, J. Xu, Q. Chu and Y. Pang, Efficient aerobic oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 2,5-diformylfuran, and synthesis of a fluorescent material, ChemSusChem, 2011, 4, 51–54 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Sajid, X. Zhao and D. Liu, Production of 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA) from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF): Recent progress focusing on the chemical-catalytic routes, Green Chem., 2018, 20, 5427–5453 RSC.
- Y. Feng, W. Jia, G. Yan, X. Zeng, J. Sperry, B. Xu, Y. Sun, X. Tang, T. Lei and L. Lin, Insights into the active sites and catalytic mechanism of oxidative esterification of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by metal-organic frameworks-derived N-doped carbon, J. Catal., 2020, 381, 570–578 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Xu, X. Li, W. Hu, Z. Yu, H. Zhou, Y. Zhu, L. Lu and C. Si, Research progress of highly efficient noble metal catalysts for the oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, ChemSusChem, 2022, 15, e2022003 Search PubMed.
- P. L. Arias, J. A. Cecilia, I. Gandarias, J. Iglesias, M. L. Granados, R. Mariscal, G. Morales, R. Moreno-Tost and P. Maireles-Torres, Oxidation of lignocellulosic platform molecules to value-added chemicals using heterogeneous catalytic technologies, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2020, 10, 2721–2757 RSC.
- X. Li and Y. Zhang, The conversion of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF) to maleic anhydride with vanadium-based heterogeneous catalysts, Green Chem., 2016, 18, 643–647 RSC.
- G. Lv, S. Chen, H. Zhu, M. Li and Y. Yang, Determination of the crucial functional groups in graphene oxide for vanadium oxide nanosheet fabrication and its catalytic application in 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural oxidation, J. Cleaner Prod., 2018, 196, 32–41 CrossRef CAS.
- G. D. Yadav and M. B. Thathagar, Esterification of maleic acid with ethanol over cation-exchange resin catalysts, React. Funct. Polym., 2002, 52, 99–110 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ventura, D. Williamson, F. Lobefaro, M. D. Jones, D. Mattia, F. Nocito, M. Aresta and A. Dibenedetto, Sustainable synthesis of oxalic and succinic acid through aerobic oxidation of C6 polyols under mild conditions, ChemSusChem, 2018, 11, 1073–1081 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Tirsoaga, M. El Fergani, V. I. Parvulescu and S. M. Coman, Upgrade of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to dicarboxylic acids onto multifunctional-based Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic catalysts, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2018, 6, 14292–14301 CrossRef CAS.
- S. D. Le and S. Nishimura, Effect of support on the formation of CuPd alloy nanoparticles for the hydrogenation of succinic acid, Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 282, 119619 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Latifi, A. D. Marchese, M. C. W. Hulls, D. V. Soldatov and M. Schlaf, [Ru(triphos)(CH3CN)3](OTf)2 as a homogeneous catalyst for the hydrogenation of biomass derived 2,5-hexanedione and 2,5-dimethyl-furan in aqueous acidic medium, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 4666–4679 RSC.
- G. Nie, C. Shi, Y. Dai, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, C. Ma, Q. Liu, L. Pan, X. Zhang and J.-J. Zou, Producing methylcyclopentadiene dimer and trimer based high-performance jet fuels using 5-methyl furfural, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 7765–7768 RSC.
- F. Delbecq, Y. Wang, A. Muralidhara, K. El Ouardi, G. Marlair and C. Len, Hydrolysis of hemicellulose and derivatives-A Review of recent advances in the production of furfural, Front. Chem., 2018, 6, 146 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Maki-Arvela, T. Salmi, B. Holmbom, S. Willfor and D. Y. Murzin, Synthesis of sugars by hydrolysis of hemicelluloses- A review, Chem. Rev., 2011, 111, 5638–5666 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Delgado Arcaño, O. D. Valmaña García, D. Mandelli, W. A. Carvalho and L. A. Magalhães Pontes, Xylitol: A review on the progress and challenges of its production by chemical route, Catal. Today, 2020, 344, 2–14 CrossRef.
- J. Sun and H. Liu, Selective hydrogenolysis of biomass-derived xylitol to ethylene glycol and propylene glycol on supported Ru catalysts, Green Chem., 2011, 13, 135–142 RSC.
- X. Li, P. Jia and T. Wang, Furfural: A promising platform compound for sustainable production of C4 and C5 chemicals, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 7621–7640 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhu and G. Yin, Catalytic transformation of the furfural platform into bifunctionalized monomers for polymer synthesis, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 10058–10083 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Dutta, S. De, B. Saha and M. I. Alam, Advances in conversion of hemicellulosic biomass to furfural and upgrading to biofuels, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, 2, 2025–2036 RSC.
- W. Song, H. Liu, J. Zhang, Y. Sun and L. Peng, Understanding Hβ zeolite in 1,4-dioxane efficiently converts hemicellulose-related sugars to furfural, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 12833–12844 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Jaswal, P. P. Singh and T. Mondal, Furfural- A versatile, biomass-derived platform chemical for the production of renewable chemicals, Green Chem., 2022, 24, 510–551 RSC.
- Y. Wang, D. Zhao, D. Rodríguez-Padrón and C. Len, Recent advances in catalytic hydrogenation of furfural, Catalysts, 2019, 9, 796 CrossRef.
- Y. Nakagawa, M. Tamura and K. Tomishige, Catalytic reduction of biomass-derived furanic compounds with hydrogen, ACS Catal., 2013, 3, 2655–2668 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ma, G. Xu, H. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang and Y. Fu, Cobalt nanocluster supported on ZrREnOx for the selective hydrogenation of biomass derived aromatic aldehydes and ketones in water, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 1268–1277 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. An and J. Li, Recent advances in the catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol over heterogeneous catalysts, Green Chem., 2022, 24, 1780–1808 RSC.
- P. Panagiotopoulou and D. G. Vlachos, Liquid phase catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural over a Ru/C catalyst, Appl. Catal., A, 2014, 480, 17–24 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Panagiotopoulou, N. Martin and D. G. Vlachos, Liquid-phase catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural over homogeneous Lewis Acid-Ru/C catalysts, ChemSusChem, 2015, 8, 2046–2054 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Wang, C. Li, B. He, J. Qi and C. Liang, Highly stable and selective Ru/NiFe2O4 catalysts for transfer hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to 2-methylfuran, J. Energy Chem., 2017, 26, 799–807 CrossRef.
- H. Niu, J. Luo, C. Li, B. Wang and C. Liang, Transfer hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to 2-methylfuran over CuZnAl catalysts, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58, 6298–6308 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, P. Prinsen, K. S. Triantafyllidis, S. A. Karakoulia, A. Yepez, C. Len and R. Luque, Batch versus continuous flow performance of supported mono- and bimetallic nickel catalysts for catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural in isopropanol, ChemCatChem, 2018, 10, 3459–3468 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Grazia, D. Bonincontro, A. Lolli, T. Tabanelli, C. Lucarelli, S. Albonetti and F. Cavani, Exploiting H-transfer as a tool for the catalytic reduction of bio-based building blocks: The gas-phase production of 2-methylfurfural using a FeVO4 catalyst, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 4412–4422 RSC.
- X. Chang, A. F. Liu, B. Cai, J. Y. Luo, H. Pan and Y. B. Huang, Catalytic transfer hydrogenation of furfural to 2-methylfuran and 2-methyltetrahydrofuran over bimetallic copper-palladium catalysts, ChemSusChem, 2016, 9, 3330–3337 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Li, G. Xu, X. Liu, Y. Zhang and Y. Fu, Hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol over hydroxyapatite-supported Pd catalyst under mild conditions, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2017, 56, 8843–8849 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Zhang, Y. Zhu, G. Ding, H. Zheng and Y. Li, Selective conversion of furfuryl alcohol to 1,2-pentanediol over a Ru/MnOx catalyst in aqueous phase, Green Chem., 2012, 14, 3402–3409 RSC.
- R. Ma, X.-P. Wu, T. Tong, Z.-J. Shao, Y. Wang, X. Liu, Q. Xia and X.-Q. Gong, The critical role of water in the ring opening of furfural alcohol to 1,2-pentanediol, ACS Catal., 2016, 7, 333–337 CrossRef.
- P. P. Upare, Y. Kim, K.-R. Oh, S. J. Han, S. K. Kim, D.-Y. Hong, M. Lee, P. Manjunathan, D. W. Hwang and Y. K. Hwang, A bimetallic Ru3Sn7 nanoalloy on ZnO catalyst for selective conversion of biomass-derived furfural into 1,2-pentanediol, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2021, 9, 17242–17253 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Byun and J. Han, An integrated strategy for catalytic co-production of jet fuel range alkenes, tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol, and 1,2-pentanediol from lignocellulosic biomass, Green Chem., 2017, 19, 5214–5229 RSC.
- S. Koso, I. Furikado, A. Shimao, T. Miyazawa, K. Kunimori and K. Tomishige, Chemoselective hydrogenolysis of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol to 1,5-pentanediol, Chem. Commun., 2009, 2035–2037 RSC.
- S. Chen, R. Wojcieszak, F. Dumeignil, E. Marceau and S. Royer, How catalysts and experimental conditions determine the selective hydroconversion of furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 11023–11117 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Hronec, K. Fulajtárova, T. Liptaj, N. Prónayová and T. Soták, Bio-derived fuel additives from furfural and cyclopentanone, Fuel Process. Technol., 2015, 138, 564–569 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-L. Li, J. Deng, J. Shi, T. Pan, C.-G. Yu, H.-J. Xu and Y. Fu, Selective conversion of furfural to cyclopentanone or cyclopentanol using different preparation methods of Cu–Co catalysts, Green Chem., 2015, 17, 1038–1046 RSC.
- M. Hronec, K. Fulajtárová, I. Vávra, T. Soták, E. Dobročka and M. Mičušík, Carbon supported Pd-Cu catalysts for highly selective rearrangement of furfural to cyclopentanone, Appl. Catal., B, 2016, 181, 210–219 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, S. Sang, W. Zhu, L. Gao and G. Xiao, CuNi@C catalysts with high activity derived from metal-organic frameworks precursor for conversion of furfural to cyclopentanone, Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 299, 104–111 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-F. Ma, H. Wang, G.-Y. Xu, X.-H. Liu, Y. Zhang and Y. Fu, Selective conversion of furfural to cyclopentanol over cobalt catalysts in one step, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2017, 28, 1153–1158 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Wang, Z. Liu, L. Wang, X. Dong, J. Zhang, G. Wang, S. Han, X. Meng, A. Zheng and F.-S. Xiao, Importance of zeolite wettability for selective hydrogenation of furfural over Pd@Zeolite catalysts, ACS Catal., 2017, 8, 474–481 CrossRef.
- P. L. Arias, J. A. Cecilia, I. Gandarias, J. Iglesias, M. López Granados, R. Mariscal, G. Morales, R. Moreno-Tost and P. Maireles-Torres, Oxidation of lignocellulosic platform molecules to value-added chemicals using heterogeneous catalytic technologies, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2020, 10, 2721–2757 RSC.
- Y. Zhu, J. Yang, F. Mei, X. Li and C. Zhao, Bio-based 1,4-butanediol and tetrahydrofuran synthesis: Perspective, Green Chem., 2022, 24, 6450–6466 RSC.
- L. Faba, E. Diaz and S. Ordonez, One-pot aldol condensation and hydrodeoxygenation of biomass-derived carbonyl compounds for biodiesel synthesis, ChemSusChem, 2014, 7, 2816–2820 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. W. Huber, J. N. Chheda, C. J. Barrett and J. A. Dumesic, Production of liquid alkanes by aqueous-phase processing of biomass-derived carbohydrates, Science, 2005, 308, 1446–1450 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Li, F. Zhou, X. Liu, H. Ma, J. Deng, G. Xu and Y. Zhang, Hydrodeoxygenation of lignocellulose-derived oxygenates to diesel or jet fuel range alkanes under mild conditions, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2020, 10, 1151–1160 RSC.
- X. Li, X. Zeng and Y. Zhang, Efficient hydrodeoxygenation of lignocellulose derivative oxygenates to aviation fuel range alkanes using Pd-Ru/hydroxyapatite catalysts, Fuel Process. Technol., 2022, 232, 107263 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, L. Pan, L. Wang and J.-J. Zou, Review on synthesis and properties of high-energy-density liquid fuels: Hydrocarbons, nanofluids and energetic ionic liquids, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2018, 180, 95–125 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Li, B. Hou, A. Wang, X. Xin, Y. Cong, X. Wang, N. Li and T. Zhang, Making JP-10 superfuel affordable with a lignocellulosic platform compound, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 12154–12158 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. J. Ragauskas, G. T. Beckham, M. J. Biddy, R. Chandra, F. Chen, M. F. Davis, B. H. Davison, R. A. Dixon, P. Gilna, M. Keller, P. Langan, A. K. Naskar, J. N. Saddler, T. J. Tschaplinski, G. A. Tuskan and C. E. Wyman, Lignin valorization: Improving lignin processing in the biorefinery, Science, 2014, 344, 1246843 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Yue, F. Lu, R. Sun and J. Ralph, Synthesis and characterization of new 5-linked pinoresinol lignin models, Chemistry, 2012, 18, 16402–16410 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Schutyser, T. Renders, S. Van den Bosch, S. F. Koelewijn, G. T. Beckham and B. F. Sels, Chemicals from lignin: An interplay of lignocellulose fractionation, depolymerisation, and upgrading, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 852–908 RSC.
- C. P. Xu, R. A. D. Arancon, J. Labidi and R. Luque, Lignin depolymerisation strategies: Towards valuable chemicals and fuels, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 7485–7500 RSC.
- J. Zakzeski, P. C. A. Bruijnincx, A. L. Jongerius and B. M. Weckhuysen, The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 3552–3599 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, J. Song and B. Han, Catalytic transformation of lignocellulose into chemicals and fuel products in ionic liquids, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 6834–6880 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Wong, R. Y. Shu, J. G. Zhang, H. C. Liu and N. Yan, Downstream processing of lignin derived feedstock into end products, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 5510–5560 RSC.
- R. Ma, M. Guo and X. Zhang, Recent advances in oxidative valorization of lignin, Catal. Today, 2018, 302, 50–60 CrossRef CAS.
- V. K. Ponnusamy, D. D. Nguyen, J. Dharmaraja, S. Shobana, J. R. Banu, R. G. Saratale, S. W. Chang and G. Kumar, A review on lignin structure, pretreatments, fermentation reactions and biorefinery potential, Bioresour. Technol., 2019, 271, 462–472 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Cai, J. Long, Y. Li, L. Ye, B. Yin, L. J. France, J. Dong, L. Zheng, H. He, S. Liu, S. C. E. Tsang and X. Li, Selective production of diethyl maleate via oxidative cleavage of lignin aromatic unit, Chem, 2019, 5, 2365–2377 CAS.
- M. V. Bykova, D. Y. Ermakov, V. V. Kaichev, O. A. Bulavchenko, A. A. Saraev, M. Y. Lebedev and V. A. Yakovlev, Ni-based sol-gel catalysts as promising systems for crude bio-oil upgrading: Guaiacol hydrodeoxygenation study, Appl. Catal., B, 2012, 113–114, 296–307 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, M. Arai, Q. Wu, C. Zhang and F. Zhao, Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived phenolics- A review on the active sites of supported metal catalysts, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 8140–8168 RSC.
- J. Zhang, J. Sun and Y. Wang, Recent advances in the selective catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived oxygenates to arenes, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 1072–1098 RSC.
- H. Wang, J. Male and Y. Wang, Recent advances in hydrotreating of pyrolysis bio-oil and its oxygen-containing model compounds, ACS Catal., 2013, 3, 1047–1070 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Jing, L. Dong, Y. Guo, X. Liu and Y. Wang, Chemicals from lignin: A review of catalytic conversion involving hydrogen, ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 4181–4198 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liao, M. d'Halluin, E. Makshina, D. Verboekend and B. F. Sels, Shape selectivity vapor-phase conversion of lignin-derived 4-ethylphenol to phenol and ethylene over acidic aluminosilicates: Impact of acid properties and pore constraint, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 234, 117–129 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Z. Liu, T. Jiang, B. X. Han, S. G. Liang and Y. X. Zhou, Selective phenol hydrogenation to cyclohexanone over a dual supported Pd-Lewis acid catalyst, Science, 2009, 326, 1250–1252 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Xu, J. Guo, Y. Zhang, Y. Fu, J. Chen, L. Ma and Q. Guo, Selective hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone over Pd-HAP catalyst in aqueous media, ChemCatChem, 2015, 7, 2485–2492 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Liu, Q. Liu, A. Wang and T. Zhang, Direct catalytic hydrogenolysis of Kraft lignin to phenols in choline-derived ionic liquids, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2016, 4, 3850–3856 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, L. Xu, G. Xu, W. Jia, Y. Ma and Y. Zhang, Selective hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived phenols to cyclohexanols or cyclohexanes over magnetic CoNx@NC Catalysts under mild conditions, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 7611–7620 CrossRef CAS.
- K. P. Kepp, A quantitative scale of oxophilicity and thiophilicity, Inorg. Chem., 2016, 55, 9461–9470 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Robinson, J. E. Hensley and J. W. Medlin, Bifunctional catalysts for upgrading of biomass-derived oxygenates: A review, ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 5026–5043 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Shi, L. Arroyo-Ramírez and J. M. Vohs, The use of bimetallics to control the selectivity for the upgrading of lignin-derived oxygenates: Reaction of anisole on Pt and PtZn catalysts, J. Catal., 2016, 340, 219–226 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Tan, S. Rong, R. Zhao, H. Cui, N.-N. Zhang, Z.-N. Chen, Z. Li, W. Yi and F. Zhang, Targeted conversion of model phenolics in pyrolysis bio-oils to arenes via hydrodeoxygenation over MoOx/BaO@SBA-15 catalyst, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 438, 135577 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. S. Yun, C. E. Berdugo-Díaz and D. W. Flaherty, Advances in understanding the selective hydrogenolysis of biomass derivatives, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 11193–11232 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Rinaldi, R. Jastrzebski, M. T. Clough, J. Ralph, M. Kennema, P. C. Bruijnincx and B. M. Weckhuysen, Paving the way for lignin valorisation: Recent advances in bioengineering, biorefining and catalysis, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 8164–8215 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Yan, C. Zhao, P. J. Dyson, C. Wang, L. T. Liu and Y. Kou, Selective degradation of wood lignin over noble-metal catalysts in a two-step process, ChemSusChem, 2008, 1, 626–629 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, F. P. Bouxin, J. Fan, V. L. Budarin, C. Hu and J. H. Clark, Recent advances in the catalytic depolymerization of lignin towards phenolic chemicals: A review, ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 4296–4317 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Shuai, J. Sitison, S. Sadula, J. Ding, M. C. Thies and B. Saha, Selective C-C bond cleavage of methylene-linked lignin models and kraft lignin, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 6507–6512 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Dong, L. Lin, X. Han, X. Si, X. Liu, Y. Guo, F. Lu, S. Rudić, S. F. Parker, S. Yang and Y. Wang, Breaking the limit of lignin monomer production via cleavage of interunit carbon-carbon linkages, Chem, 2019, 5, 1521–1536 CAS.
- J. Kong, M. He, J. A. Lercher and C. Zhao, Direct production of naphthenes and paraffins from lignin, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 17580–17583 RSC.
- H. Wang, H. Ruan, M. Feng, Y. Qin, H. Job, L. Luo, C. Wang, M. H. Engelhard, E. Kuhn, X. Chen, M. P. Tucker and B. Yang, One-pot process for hydrodeoxygenation of lignin to alkanes using Ru-based bimetallic and bifunctional catalysts supported on zeolite Y, ChemSusChem, 2017, 10, 1846–1856 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Li, B. Zhang, X. Pan, J. Ji, Y. Ren, H. Wang, N. Ji, Q. Liu and C. Li, One-pot conversion of lignin into naphthenes catalyzed by a heterogeneous rhenium oxide-modified iridium compound, ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 4409–4419 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Shao, Q. Xia, L. Dong, X. Liu, X. Han, S. F. Parker, Y. Cheng, L. L. Daemen, A. J. Ramirez-Cuesta, S. Yang and Y. Wang, Selective production of arenes via direct lignin upgrading over a niobium-based catalyst, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 16104 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Meng, J. Yan, R. Wu, H. Liu, Y. Sun, N. Wu, J. Xiang, L. Zheng, J. Zhang and B. Han, Sustainable production of benzene from lignin, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 4534 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Li, L. Dong, D. Li, Y. Guo, X. Liu and Y. Wang, Hydrogen-free production of 4-alkylphenols from lignin via self-reforming-driven depolymerization and hydrogenolysis, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 15197–15206 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yan, Q. L. Meng, X. J. Shen, B. F. Chen, Y. Sun, J. F. Xiang, H. Z. Liu and B. X. Han, Selective valorization of lignin to phenol by direct transformation of C-s(p2)-C-sp3 and C-O bonds, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, 10 Search PubMed.
- M. Alinejad, C. Henry, S. Nikafshar, A. Gondaliya, S. Bagheri, N. Chen, S. K. Singh, D. B. Hodge and M. Nejad, Lignin-based polyurethanes: Opportunities for bio-based foams, elastomers, coatings and adhesives, Polymers, 2019, 11, 1202 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Chen, K. Gao, C. Peng, H. Xie, Z. K. Zhao and M. Bao, Preparation of lignin/glycerol-based bis(cyclic carbonate) for the synthesis of polyurethanes, Green Chem., 2015, 17, 4546–4551 RSC.
- S. Curia, A. Biundo, I. Fischer, V. Braunschmid, G. M. Gubitz and J. F. Stanzione, 3rd, Towards sustainable high-performance thermoplastics: Synthesis, characterization, and enzymatic hydrolysis of bisguaiacol-based polyesters, ChemSusChem, 2018, 11, 2529–2539 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Pang, J. Zhang, G. Wu, Y. Wang, H. Gao and J. Ma, Renewable polyesters derived from 10-undecenoic acid and vanillic acid with versatile properties, Polym. Chem., 2014, 5, 2843–2853 RSC.
- K. H. Nicastro, C. J. Kloxin and T. H. Epps, Potential lignin-derived alternatives to bisphenol A in diamine-hardened epoxy resins, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2018, 6, 14812–14819 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Zhao and M. M. Abu-Omar, Synthesis of renewable thermoset polymers through successive lignin modification using lignin-derived phenols, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017, 5, 5059–5066 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Sternberg, O. Sequerth and S. Pilla, Green chemistry design in polymers derived from lignin: Review and perspective, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2021, 113, 101344 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Fadlallah, P. S. Roy, G. Garnier, K. Saito and F. Allais, Are lignin-derived monomers and polymers truly sustainable? An in-depth green metrics calculations approach, Green Chem., 2021, 23, 1495–1535 RSC.
- J. P. Lange, Performance metrics for sustainable catalysis in industry, Nat. Catal., 2021, 4, 186–192 CrossRef CAS.
- J. G. G. Jonker, M. Junginger, J. Posada, C. S. Ioiart, A. P. C. Faaij and F. Hilst, Economic performance and GHG emission intensity of sugarcane- and eucalyptus-derived biofuels and biobased chemicals in Brazil, Biofuels, Bioprod. Biorefin., 2019, 13, 950–977 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Chen, X. Zeng, X. Li, Z. Lv, J. Li and Y. Zhang, Strong metal phosphide-phosphate support interaction for enhanced non-noble metal catalysis, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, e2106724 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © Institute of Process Engineering of CAS 2023 |